ZedBoard
(Zynq™ Evaluation and Development)
Hardware User’s Guide
Version 2.2
27 January 2014
�
Table of Contents
1
2
2.3
1.1
2.2.1
2.2.2
2.2.3
INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................................. 2
ZYNQ BANK PIN ASSIGNMENTS ...................................................................................................... 4
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................ 5
2.1
ALL PROGRAMMABLE SOC ............................................................................................................. 5
2.2 MEMORY ......................................................................................................................................... 5
DDR3 ...................................................................................................................................... 5
SPI Flash ................................................................................................................................ 7
SD Card Interface ..................................................................................................................10
USB ...............................................................................................................................................11
USB OTG ...............................................................................................................................11
USB-to-UART Bridge ............................................................................................................11
USB-JTAG .............................................................................................................................12
USB circuit protection ...........................................................................................................13
DISPLAY AND AUDIO ......................................................................................................................13
HDMI Output .........................................................................................................................13
VGA Connector......................................................................................................................16
I2S Audio Codec ....................................................................................................................17
OLED .....................................................................................................................................18
CLOCK SOURCES .............................................................................................................................18
RESET SOURCES .............................................................................................................................18
2.3.1
2.3.2
2.3.3
2.3.4
2.4.1
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.4.4
2.5
2.6
2.4
2.7
2.8
2.9
2.10.1
2.9.1
2.9.2
2.9.3
2.7.1
2.7.2
2.7.3
2.6.1
2.6.2
2.6.3
Power‐on Reset (PS_POR_B) ................................................................................................18
Program Push Button Switch .................................................................................................19
Processor Subsystem Reset ....................................................................................................19
USER I/O ........................................................................................................................................19
User Push Buttons .................................................................................................................19
User DIP Switches .................................................................................................................19
User LEDs .............................................................................................................................20
10/100/1000 ETHERNET PHY ........................................................................................................20
EXPANSION HEADERS ....................................................................................................................21
LPC FMC Connector .............................................................................................................21
Digilent Pmod™ Compatible Headers (2x6).........................................................................22
Agile Mixed Signaling (AMS) Connector, J2 .........................................................................23
2.10 CONFIGURATION MODES ................................................................................................................26
JTAG ......................................................................................................................................27
2.11 POWER ...........................................................................................................................................28
2.11.1
Primary Power Input .............................................................................................................28
2.11.2 On/Off Switch ........................................................................................................................28
2.11.3
Regulators ..............................................................................................................................28
Sequencing .............................................................................................................................29
2.11.4
Power Good LED ..................................................................................................................30
2.11.5
Power Estimation ..................................................................................................................30
2.11.6
2.11.7
Testing ...................................................................................................................................31
2.11.8
Probes ....................................................................................................................................31
ZYNQ-7000 AP SOC BANKS .............................................................................................................32
ZYNQ-7000 AP SOC BANK VOLTAGES ..........................................................................................33
4
JUMPER SETTINGS ............................................................................................................................34
5 MECHANICAL ....................................................................................................................................36
6 REVISION HISTORY ..........................................................................................................................37
3.1
3
1
27-Jan-2014
�
Introduction
1
The ZedBoard is an evaluation and development board based on the Xilinx ZynqTM-7000 All
Programmable SoC (AP SoC). Combining a dual Corex-A9 Processing System (PS) with 85,000
Series-7 Programmable Logic (PL) cells, the Zynq-7000 AP SoC can be targeted for broad use in
many applications. The ZedBoard’s robust mix of on-board peripherals and expansion
capabilities make it an ideal platform for both novice and experienced designers. The features
provided by the ZedBoard consist of:
• Xilinx® XC7Z020-1CLG484C Zynq-7000 AP SoC
o Primary configuration = QSPI Flash
o Auxiliary configuration options
Cascaded JTAG
SD Card
• Memory
•
Interfaces
o 512 MB DDR3 (128M x 32)
o 256 Mb QSPI Flash
o USB-JTAG Programming using Digilent SMT1-equivalent circuit
Accesses PL JTAG
PS JTAG pins connected through PS Pmod
• On-board Oscillators
• Display/Audio
o 10/100/1G Ethernet
o USB OTG 2.0
o SD Card
o USB 2.0 FS USB-UART bridge
o Five Digilent Pmod™ compatible headers (2x6) (1 PS, 4 PL)
o One LPC FMC
o One AMS Header
o Two Reset Buttons (1 PS, 1 PL)
o Seven Push Buttons (2 PS, 5 PL)
o Eight dip/slide switches (PL)
o Nine User LEDs (1 PS, 8 PL)
o DONE LED (PL)
o 33.333 MHz (PS)
o 100 MHz (PL)
o HDMI Output
o VGA (12-bit Color)
o 128x32 OLED Display
o Audio Line-in, Line-out, headphone, microphone
o On/Off Switch
o 12V @ 5A AC/DC regulator
o
o License voucher for ChipScope™ Pro locked to XC7Z020
ISE® WebPACK Design Software
• Power
• Software
2
27-Jan-2014
�
Flash
QSPI
Pmod
Gbit
Enet
USB
OTG
SD
USB
UART
1 LED,
2 buttons
PHY
PHY
USB
Cont
7
8
14
12
8
2
3
QSPI
ENET/
MDIO
USBOTG
SD
)
I
O
M
(
O
/
I
d
e
x
e
p
l
i
t
l
USBUART
u
M
PS_GPIO
512Mbyte
DDR3 (x32)
DDR3
71
DDR
)
S
P
(
m
e
Reset
33Mhz
Clk
1
1
PS_RST
PS_CLK
i
t
s
y
S
g
n
s
s
e
c
o
r
P
PMOD
FMC
GPIO
I2S/ACD
HDMI
VGA
OLED
DONE
PROG
)
L
P
i
(
c
g
o
L
l
e
b
a
m
m
a
r
g
o
r
P
GPIO/VP/VN
JTAG
GCLK
32
82
21
8
27
10
5
1
1
8
4
1
Pmods
FMC-LPC
GPIO (8 LEDs,
8 slide switches,
5 pushbuttons)
HdPhn Out
Line Out
Line In
MIC In
Type A
HDMI Out
VGA (12-
bit color)
I2S Audio
Codec
HDMI
transmitter
128x32 OLED
Display
DONE LED
PROG
XADC
Primary JTAG
100Mhz
USB
Cont
Clk
ZYNQ XC7Z020-CLG484
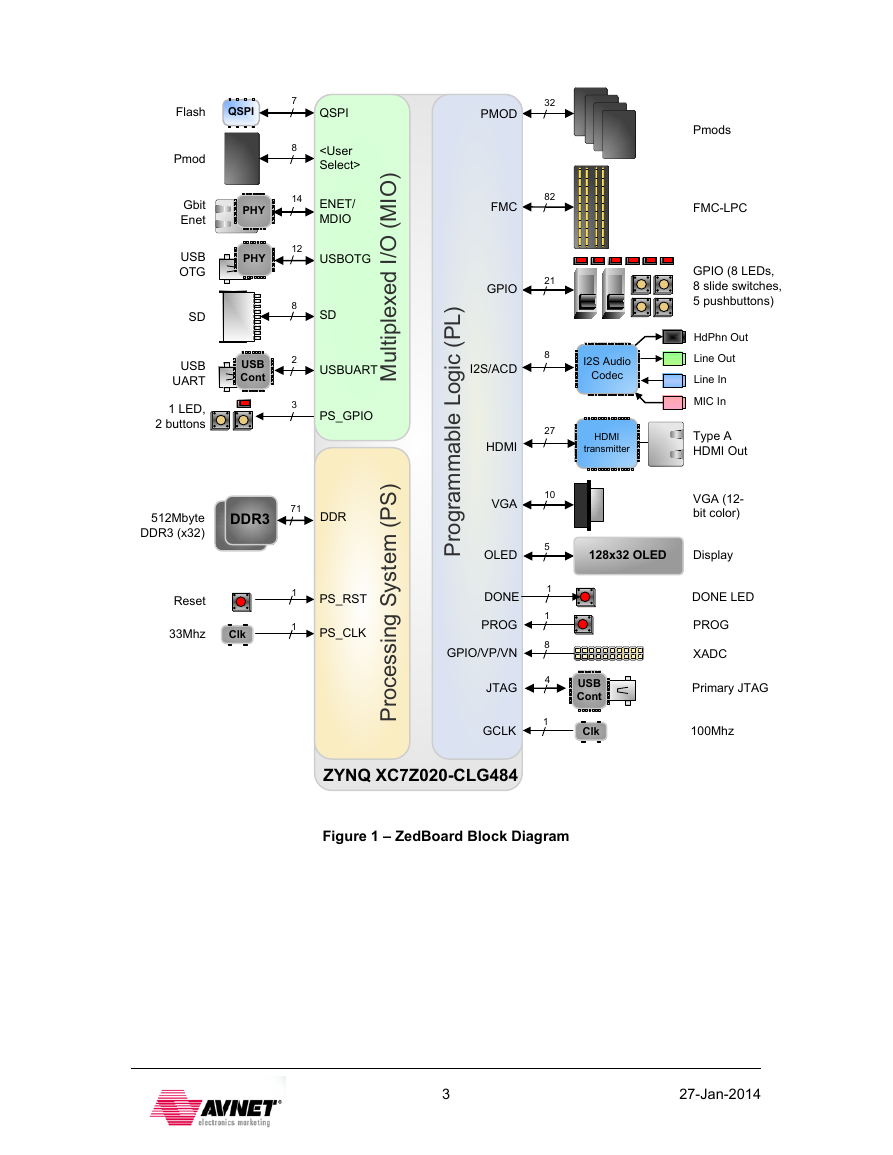
Figure 1 – ZedBoard Block Diagram
3
27-Jan-2014
�
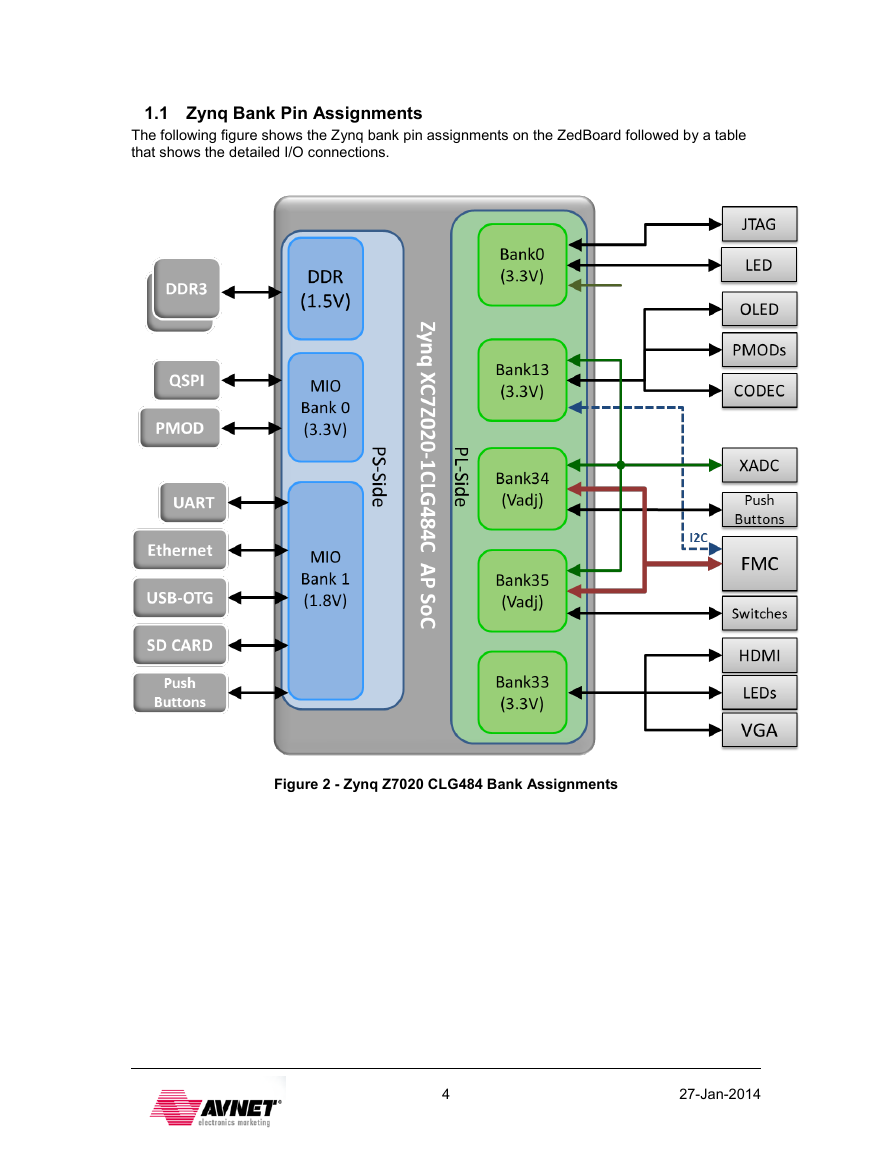
1.1 Zynq Bank Pin Assignments
The following figure shows the Zynq bank pin assignments on the ZedBoard followed by a table
that shows the detailed I/O connections.
Figure 2 - Zynq Z7020 CLG484 Bank Assignments
4
27-Jan-2014
�
2 Functional Description
2.1 All Programmable SoC
The ZedBoard features a Xilinx Zynq XC7Z020-1CLG484 All Programmable SoC (AP SoC).
Initial ZedBoards were marked ‘Rev C’ and shipped with Engineering Sample "CES" grade
silicon. Later ‘Rev D’ shipments switched to production "C" grade silicon once those became
available. The Zynq-7000 AP SoC part markings indicate the silicon grade.
2.2 Memory
Zynq contains a hardened PS memory interface unit. The memory interface unit includes a
dynamic memory controller and static memory interface modules.
2.2.1 DDR3
The ZedBoard includes two Micron DDR3 128 Megabit x 16 memory components creating a 32-
bit interface, totaling 512 MB.
Earlier ZedBoards used Micron MT41J128M16HA-15E:D, but
As of August 2012, this device has been marked by Micron for end-of-life. There are several
options that Micron offers for a replacement. ZedBoard will likely migrate to the
MT41K128M16JT-125 device, although this is pending validation. The DDR3 is connected to the
hard memory controller in the Processor Subsystem (PS) as outlined in the Zynq datasheet.
The multi-protocol DDR memory controller is configured for 32-bit wide accesses to a 512 MB
address space. The PS incorporates both the DDR controller and the associated PHY, including
its own set of dedicated I/Os. DDR3 memory interface speeds up to 533MHz (1066Mbs) are
supported.
The DDR3 uses 1.5V SSTL-compatible inputs. DDR3 Termination is utilized on the ZedBoard.
The Zynq-7000 AP SoC and DDR3 have been placed close together keeping traces short and
matched.
DDR3 on the PS was routed with 50 ohm targeted trace impedance for single-ended signals, and
DCI resistors (VRP/VRN) as well as differential clocks set to 80 ohms. Each DDR3 chip needs its
own 240-ohm pull-down on ZQ. The Xilinx Zynq-7000 All Programmable SoC PCB Design and
Pin Planning Guide (UG933) recommends using 40 ohm trace impedance for DDR3 single-ended
signals, so designers looking to duplicate the ZedBoard design may want consider this in their
own board design. See the appropriate ZedBoard Errata document for more details.
DDR-VDDQ is set to 1.5V to support the DDR3 devices selected. DDR-VTT is the termination
voltage which is ½ DDR-VDDQ. DDR-VREF is a separate buffered output that is equal to ½
nominal DDR-VDDQ. The DDR-VREF is isolated to provide a cleaner reference for the DDR
level transitions.
5
27-Jan-2014
�
Signal Name
DDR_CK_P
DDR_CK_N
DDR_CKE
DDR_CS_B
DDR_RAS_B
DDR_CAS_B
DDR_WE_B
DDR_BA[2:0]
DDR_A[14:0]
DDR_ODT
DDR_RESET_B
DDR_DQ[31:0]
DDR_DM[3:0]
DDR_DQS_P[3:0]
DDR_DQS_N[3:0]
DDR_VRP
DDR_VRN
Description
Differential clock
output
Differential clock
output
Clock enable
Chip select
RAS row address
select
RAS column address
select
Write enable
Bank address
Address
Output dynamic
termination
Reset
I/O Data
Data mask
I/O Differential data
strobe
I/O Differential data
strobe
I/O Used to calibrate
input termination
I/O Used to calibrate
input termination
I/O Reference
voltage
Zynq pin
N4
N5
V3
P6
R5
P3
R4
PS_DDR_BA[2:0]
PS_DDR_A[14:0]
P5
F3
DDR3 pin
J7
K7
K9
L2
J3
K3
L3
BA[2:0]
A[14:0]
K1
T2
PS_DDR_[31:0]
PS_DDR_DM[3:0]
DDR3_DQ pins
LDM/UDM x2
PS_DDR_DQS_P[3:0]
UDQS/LDQS
PS_DDR_DQS_N[3:0]
UDQS#/LDQS#
N7
M7
N/A
N/A
The PCB design guidelines outlined in Zynq datasheet must be followed for trace matching, etc.
Table 1 - DDR3 Connections
H1
H7, P7
DDR_VREF[1:0]
For best DDR3 performance, DRAM training is enabled for write leveling, read gate, and read
data eye options in the PS Configuration Tool in Xilinx Platform Studio (XPS) or the IP Editor in
Vivado. Two entries allow for DQS to Clock Delay and Board Delay information to be specified for
each of the four byte lanes. The tools will calculate these board training details based upon
specific trace lengths for certain DDR3 signals.
The PCB lengths are contained in the ZedBoard PCB trace length reports. The DQS to CLK
Delay and Board Delay values are calculated specific to the ZedBoard memory interface PCB
design. The Xilinx tools allow for up to 4 memory devices to be configured for DDR3 4x8 flyby
topology. Note that ZedBoard is configured for DDR3 2x16 flyby routing topology. The first two
clock trace midpoint values (CLK0 and CLK1) are used to represent the Micron device electrically
furthest from the 7Z020 (IC25) and the second two clock trace midpoint values (CLK2 and CLK3)
are used to represent the Micron device electrically closest to the 7Z020 (IC26). The worksheet
calculation results are shown in the following table.
6
27-Jan-2014
�
Pin Group Length
(mm)
Length
(mils)
Table 2 - DDR3 Worksheet Calculations
Package
Length
(mils)
Total
Length
(mils)
Propagation
Delay
(ps/inch)
Total
Delay
(ns)
DQS to
CLK
Delay
(ns)
Board
Delay
(ns)
0.410
0.411
0.341
0.358
0.025
0.028
-0.009
-0.061
160
160
160
160
160
160
160
160
160
160
160
160
470
470
470
470
504
495
520
835
465
480
550
780
0.427
0.427
0.336
0.336
0.402
0.399
0.345
0.398
0.393
0.396
0.346
0.380
2195.9
2195.9
1631.1
1631.1
2008.0
1998.8
1637.6
1649.4
1993.3
1996.4
1609.9
1597.8
2665.9
2665.9
2101.1
2101.1
2512.0
2493.8
2157.6
2484.4
2458.3
2476.4
2159.9
2377.8
55.77
CLK0
55.77
CLK1
41.43
CLK2
41.43
CLK3
51.00
DQS0
50.77
DQS1
41.59
DQS2
41.90
DQS3
50.63
DQ[7:0]
50.71
DQ[15:8]
DQ[23:16] 40.89
DQ[31:24] 40.58
The DQS to CLK Delay fields in the PS7 DDR Configuration window should be populated using
the corresponding values from the previous table.
The configuration fields of the tool may not allow you to input a negative delay value, this is a
known problem with the 14.1 tools and scheduled for correction in the 14.2 tools release. In the
case of DQS2 and DQS3 fields for DQS to CLK Delay, simply enter a value of zero rather than
the negative delay values. This is an acceptable workaround since the calculated values are
relatively close to zero and the values provided in these fields are used as initial values for the
read/write training for DDR3. Keep in mind for LPDDR2 there is no write leveling, and for DDR2
there is no training whatsoever. In these memory use cases, the accuracy of the trace length info
is more important. This is covered in further detail in section 10.6.8 of the Xilinx Zynq TRM,
UG585.
Figure 3 - DQS to Clock Delay Settings
The Board Delay fields in the PS7 DDR Configuration window should be populated using the
corresponding values from the table above.
Figure 4 - DDR3 Board Delay Settings
2.2.2 SPI Flash
The ZedBoard features a 4-bit SPI (quad-SPI) serial NOR flash. The Spansion S25FL256S is
used on this board. The Multi-I/O SPI Flash memory is used to provide non-volatile code, and
data storage. It can be used to initialize the PS subsystem as well as configure the PL
subsystem (bitstream). Spansion provides Spansion Flash File System (FFS) for use after
booting the Zynq-7000 AP SoC.
7
27-Jan-2014
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc