R. Haettel, M. Kavasoglu, A. Daneryd and C. Ploetner, ABB, 2014-09-18
Prediction of Transformer Core Noise
Multiphysics Approach
�
Presentation Outline
Introduction and Background
Transformer Acoustics
Model development for Core Noise
Electromagnetic Model
Magnetostriction Implementation
Mechanical and Acoustic Models
Model Validation
Conclusion
© ABB Group
Month DD, Year
| Slide 2
�
Product and System Examples
© ABB Group
November 18, 2014 | Slide 3
�
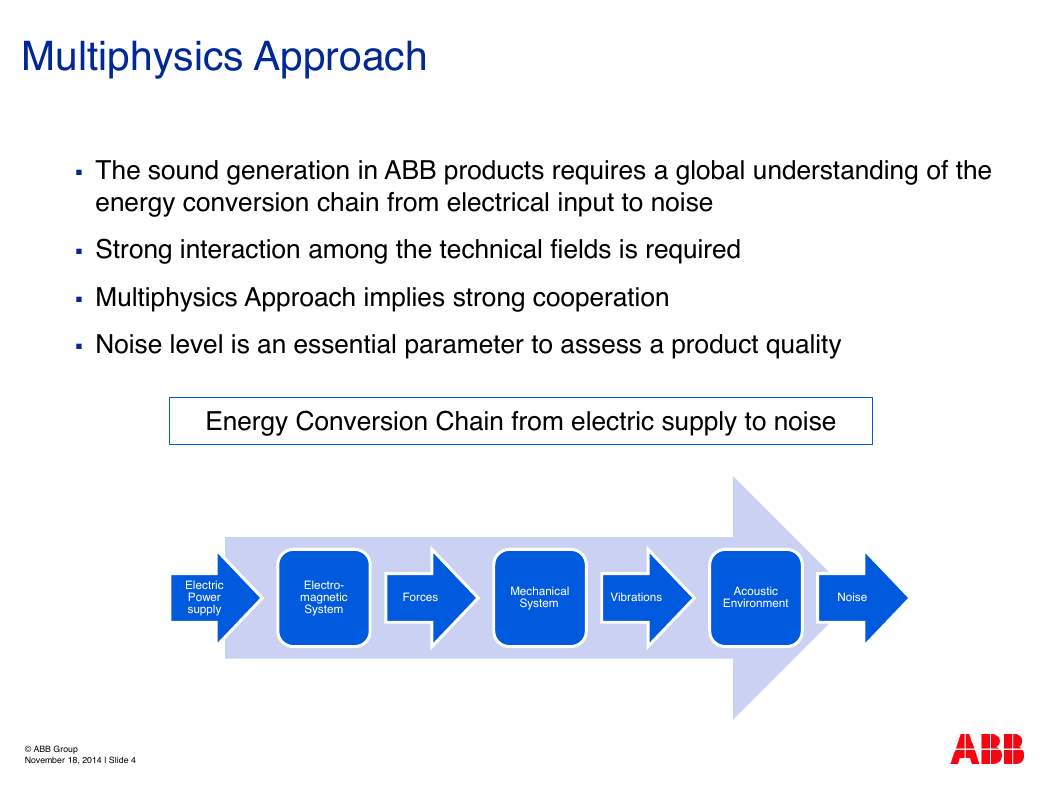
Multiphysics Approach
The sound generation in ABB products requires a global understanding of the
energy conversion chain from electrical input to noise
Strong interaction among the technical fields is required
Multiphysics Approach implies strong cooperation
Noise level is an essential parameter to assess a product quality
Energy Conversion Chain from electric supply to noise
Electric
Power
supply
Electro-
magnetic
System
Forces
Mechanical
System
Vibrations
Acoustic
Environment
Noise
© ABB Group
November 18, 2014 | Slide 4
�
Project Drivers
Costs for noise issues such as orders lost, costly modifications and overkill margins in
design
Significant advances by major competitors in noise mitigation
Increased focus on environmental issues (customer requirements)
Product development: Tools to investigate the impact of present and future requirements
and design
© ABB
Month DD, YYYY | Slide 5
�
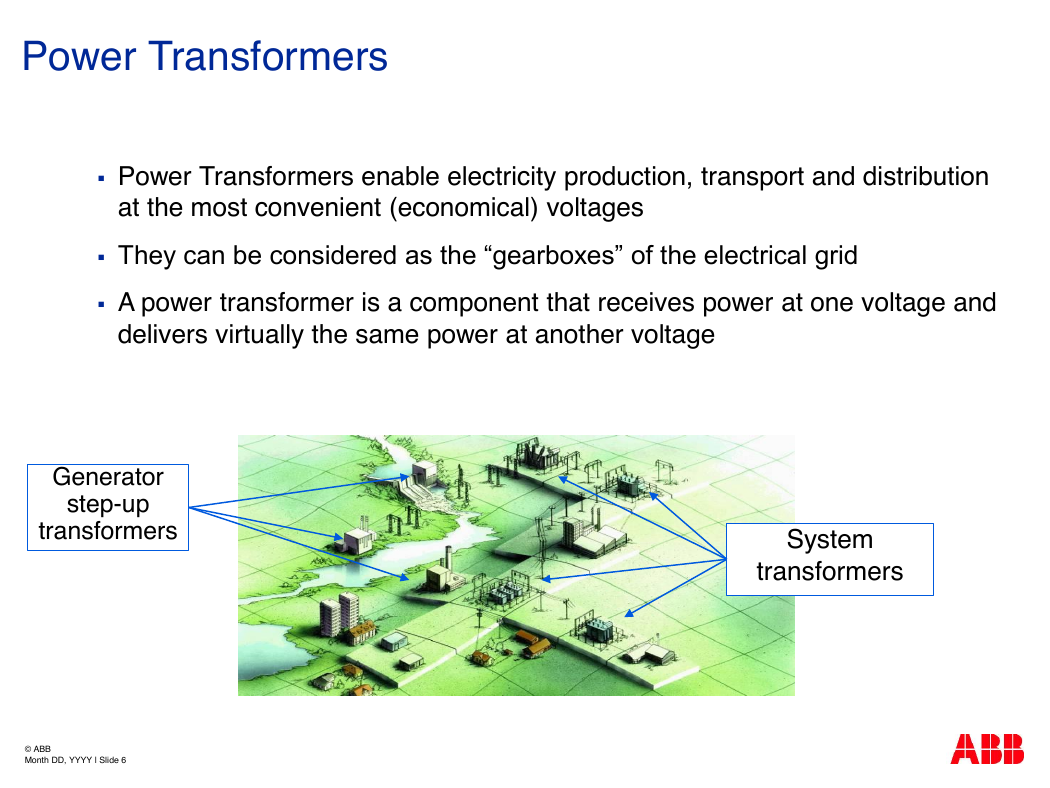
Power Transformers
Power Transformers enable electricity production, transport and distribution
at the most convenient (economical) voltages
They can be considered as the “gearboxes” of the electrical grid
A power transformer is a component that receives power at one voltage and
delivers virtually the same power at another voltage
Generator
step-up
transformers
© ABB
Month DD, YYYY | Slide 6
System
transformers
�
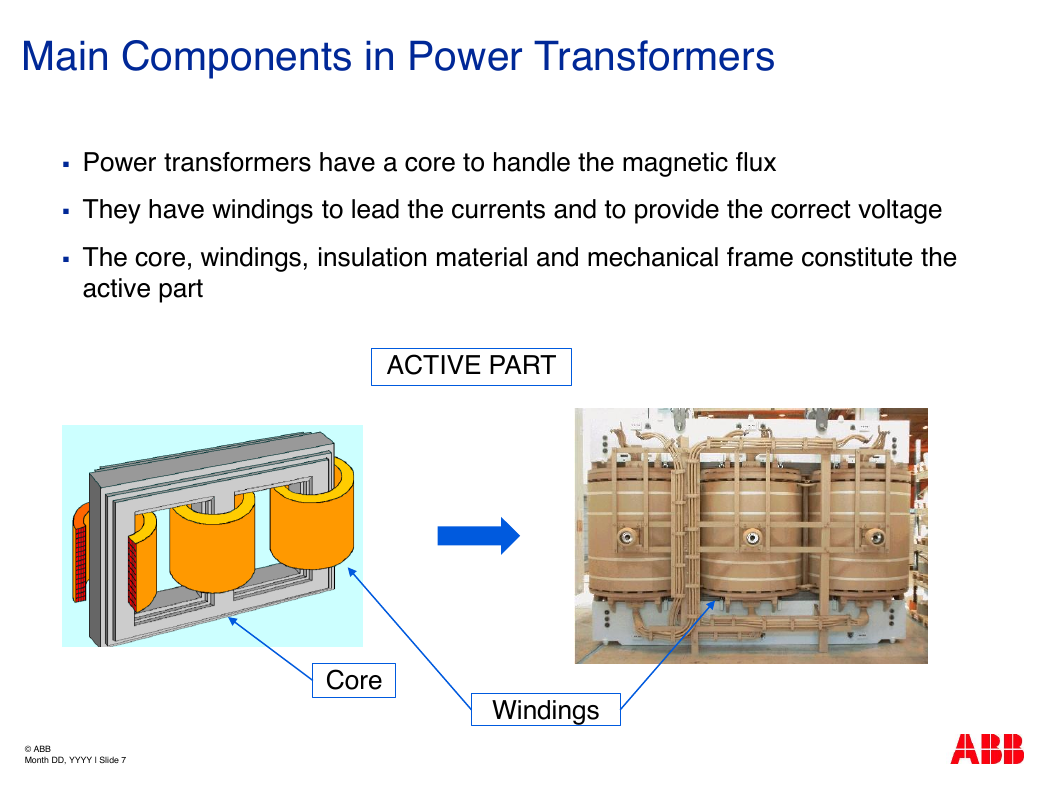
Main Components in Power Transformers
Power transformers have a core to handle the magnetic flux
They have windings to lead the currents and to provide the correct voltage
The core, windings, insulation material and mechanical frame constitute the
active part
ACTIVE PART
Core
Windings
© ABB
Month DD, YYYY | Slide 7
�
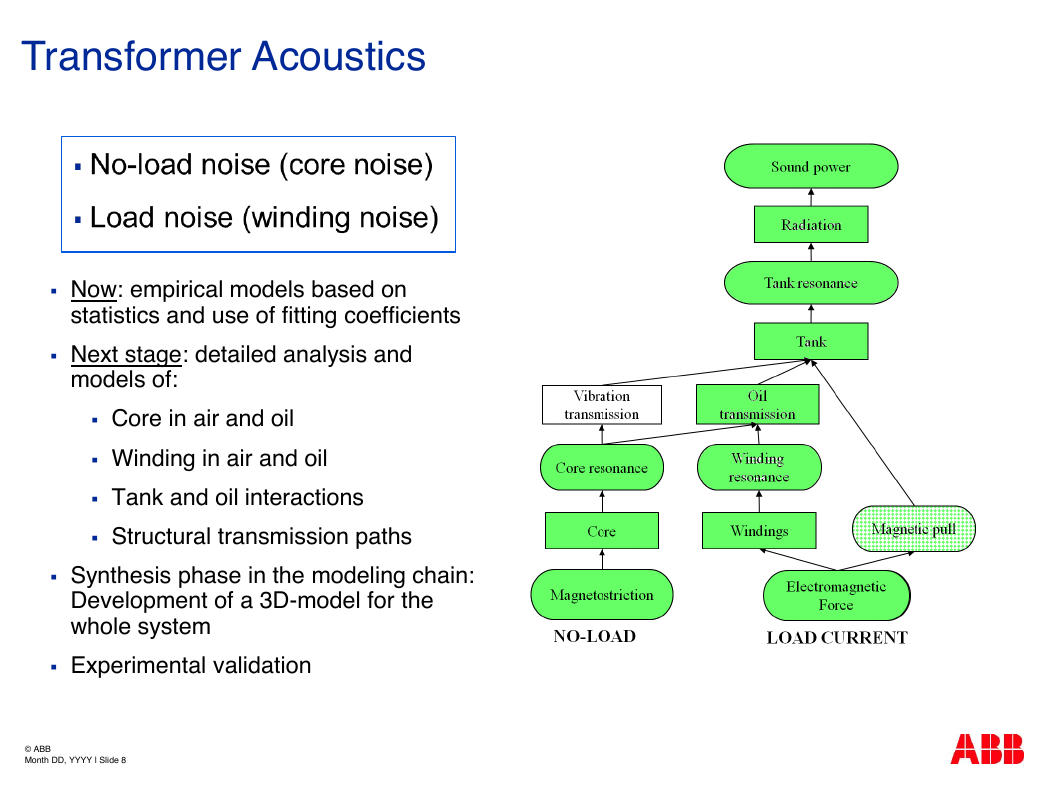
Transformer Acoustics
Now: empirical models based on
statistics and use of fitting coefficients
Next stage: detailed analysis and
models of:
Core in air and oil
Winding in air and oil
Tank and oil interactions
Structural transmission paths
Synthesis phase in the modeling chain:
Development of a 3D-model for the
whole system
Experimental validation
© ABB
Month DD, YYYY | Slide 8
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc