GWR4.09 User Manual
GWR4
Windows Application for Geographically
Weighted Regression Modelling
Tomoki Nakaya
Update 24 March 2016
Update 12 March 2014
Updated 20 Nov 2012
Updated 7 May 2012
3 June 2009
GWR 4 Development Team
Tomoki Nakaya (Department of Geography, Ritsumeikan University),
Martin Charlton, Chris Brunsdon, Paul Lewis (National Centre of
Geocomputation, National University of Ireland),
Jing Yao (School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow),
A Stewart Fotheringham (School of Geographical Sciences &
Urban Planning, Arizona State University)
�
1
Contents
1.
Introduction ................................................................................................ 2
What is GWR4? .................................................................................................. 2
New features compared to GWR3.x ................................................................... 3
Notes for use of GWR4 ....................................................................................... 4
2.
Installation / Uninstallation ....................................................................... 4
3. Starting the program, Exiting the program, and Tab design ...................... 5
Five steps in GWR calibration ........................................................................... 6
4. Step 1: The Data Tab .................................................................................. 7
Data preparation ................................................................................................ 7
Operations in the data tab page ........................................................................ 9
5. Step 2: The Model Tab .............................................................................. 10
Basic operations: using an example of Gaussian GWR .................................. 11
Semiparametric GWR ...................................................................................... 13
Extensions of GWR: GWGLM .......................................................................... 15
Geographically weighted Poisson regression (GWPR) ................................ 15
Geographically weighted logistic regression (GWLR) ................................. 16
Modelling Options ............................................................................................ 18
Standardisation ............................................................................................ 18
Geographical variability test ........................................................................ 18
LtoG / GtoL variable selection. ..................................................................... 21
6. Step 3: The Kernel Tab ............................................................................. 22
Possible fixed and adaptive kernel functions for geographical weighting ...... 23
Bandwidth selection routines .......................................................................... 24
Selection criteria .............................................................................................. 26
7. Step 4: The Output Tab ............................................................................ 27
Session Control File ......................................................................................... 27
Common output files ........................................................................................ 28
The “Prediction at non-regression points” option ............................................ 28
8. Step 5: The Execute Tab ........................................................................... 29
The Execute button .......................................................................................... 29
Fields in a listwise output ............................................................................... 31
Handling a session and batch mode (optional) ................................................ 32
Example output ................................................................................................ 33
9. References ................................................................................................ 39
�
2
1. Introduction
What is GWR4?
GWR4 is a new release of a Microsoft Windows-based application software for
calibrating geographically weighted regression (GWR) models, which can be used
to explore geographically varying relationships between dependent/response
variables and independent/explanatory variables. A GWR model can be considered
a type of regression model with geographically varying parameters. A conventional
GWR is described by the equation
,
where
,
, and
are, respectively, dependent variable, kth independent
variable, and the Gaussian error at location i; (
) is the x-y coordinate of the ith
location; and coefficients
are varying conditionals on the location. Such
modelling is likely to attain higher performance than traditional regression models,
and reading the coefficients can lead to a new interpretation of the phenomena
under study. An important extension of GWR is its semiparametric formation by
mixing globally fixed and geographically varying coefficients.
.
Local terms
Global terms
where
is the lth independent variable with a fixed coefficient
. Such a model
may reduce the model complexities and enhance its predictable performance. Using
the framework of geographically weighted generalised linear modelling (GWGLM),
logistic and Poisson regression models with geographically varying coefficients are
also popular for binary or count data modelling. GWR4 enables the fitting of such
GWR and GWGLM models with their semiparametric formations, associated
statistical tests, and model selections by user-defined data and model settings.
kiikiikixvuy,),(iyikx,iiivu,),(iikvukilillikiikizxvuy,,),(ilz,l�
3
Main features
(1) Semiparametric GWR
As noted above, a most remarkable feature of this release is the function to fit
semiparametric GWR models, which allow you to mix globally fixed terms and
locally varying terms of explanatory variables simultaneously. The function
can be applied to popular types of generalized linear modelling including
Gaussian, Poisson, and logistic regressions. Using the semiparametric
modelling scheme, a new statistical test of geographical variability on
geographically varying coefficients is enabled. It is also possible to use variable
selection routines by which variables are automatically selected as either fixed
or varying terms by recursive model comparisons.
(2) Interface
A tabbed interface has been introduced to enable modelling sessions to
intuitively proceed in a step-by-step manner. Datasets and geographically
listwise results can be viewed in separate spreadsheet-like windows. Several
popular file types can be used as input data files (space, comma, tab separated
text, and dbase IV formats). In addition, Areal key field can be integrated into
the output of GWR modelling, enabling you to join your output CSV file to a
GIS attribute table via the key field for mapping the result in a GIS
environment. GWR4 can be also used by a batch mode without the Windows
interface.
(3) Requirements
GWR4 runs on Windows Vista, Windows 7, 8 and 10 environments with
the .NET Framework 4. The maximum size of data is dependent on your local
machine environment. GWR4 dynamically allocates memory for large matrices
(n by n, where n is the number of regression points) even for conventional GWR
models. Thus using a PC having relatively large memory size (equal to or larger
than 4GB) for running GWR4 is recommended. If the PC has multi-core
processors, GWR4 automatically uses multi-threading routines to speed-up the
computation.
�
4
Notes for use of GWR4
(i)
(ii)
GWR4 is copyrighted by the GWR4 development team.
GWR4 can be freely distributed and used for academic and non-profit
purposes. The developers of GWR4 are not responsible for any
difficulties that users of the software may encounter.
(iii) When any results using GWR4 are published, the author(s) should
clearly state that GWR4 was used. Recommended citations for the
theoretical backgrounds of GWR4 modelling may be found in the
References in this manual.
2. Installation / Uninstallation
< How to install GWR4 >
Download the GWR4 installer, GWR4_setup.exe,
GWR4_setup.exe
and then double-click the icon.
< .NET Framework and Visual C++ 2012/2015 Redistributable Package>
GWR4 works only in Microsoft Windows environments that have the .NET
Framework 4 and Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Package installed. If
your PC does not have them installed, a message will pop up suggesting that
you download the .Net Framework 4 Client Profile and the redistributable
package from a Microsoft website, and automatically start setting up them if
your PC is connected to the Internet. If your PC is off-line, obtain the stand
alone installers of the .Net Framework Client Profile and the redistributable
package which are available from from the Microsoft website download centre.
< When the installer starts … >
Follow the instructions to select the GWR4 installation folder and users. If the
installation is successful, a shortcut to the program will appear on your desktop
and in the GWR4 program group. You may access the program by clicking this
shortcut.
< To uninstall >
To uninstall GWR4 from your local environment, you may use “uninstall
GWR4” menu in the GWR4 program group. Alternatively, you can use the
“Uninstall Programs” utility in the Control Panel group in Windows
environments.
�
5
3. Starting the program, Exiting the program, and Tab design
< Starting the program >
To start the program, double click the GWR4 shortcut icon on the
desktop,
or select it from the GWR4 program
group.
< Tab design >
Ensure that there are five tabs labelled Step 1 to Step 5. Click a tab label to
move to the corresponding tab page. The first tab page when the program starts
is “Step 1: Data>”.
Tab labels
< Exiting the program >
Figure 3.1: GWR4 startup screen
To exit the program, select “Quit(Q)” on the File menu
(alternatively, you can press the Alt and “F” keys
simultaneously and then press the “Q” key), or you
can click the close button in the top-right corner of the
window.
�
6
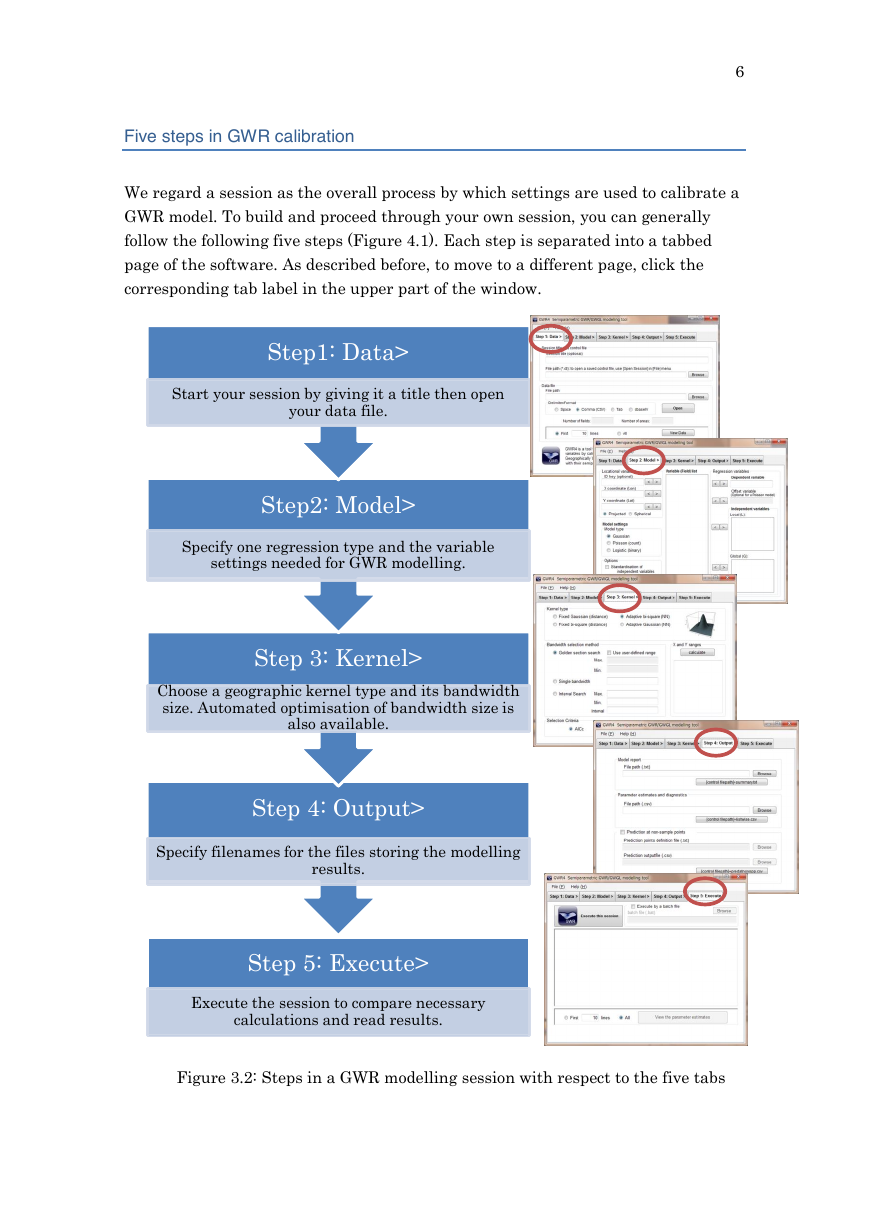
Five steps in GWR calibration
We regard a session as the overall process by which settings are used to calibrate a
GWR model. To build and proceed through your own session, you can generally
follow the following five steps (Figure 4.1). Each step is separated into a tabbed
page of the software. As described before, to move to a different page, click the
corresponding tab label in the upper part of the window.
Step1: Data>
Start your session by giving it a title then open
your data file.
Step2: Model>
Specify one regression type and the variable
settings needed for GWR modelling.
Step 3: Kernel>
Choose a geographic kernel type and its bandwidth
size. Automated optimisation of bandwidth size is
also available.
Step 4: Output>
Specify filenames for the files storing the modelling
results.
Step 5: Execute>
Execute the session to compare necessary
calculations and read results.
Figure 3.2: Steps in a GWR modelling session with respect to the five tabs
�
7
4. Step 1: The Data Tab
Data preparation
< What fields do I have to prepare in my dataset? >
To calibrate a GWR model, you must prepare a tabular dataset that contains fields
of dependent and independent variables, and x-y coordinates. Every variable
should consist of numeric values, except for Areal key, as an identifier of
observation. Areal key is treated as a string field in GWR4.
< Coordinates >
Both projected and latitude/longitude (lat/lon) decimal degrees coordinates can be
used as x-y coordinates in GWR4. However, projected coordinates are superior to
decimal degrees in terms of computing time.
< Possible data formats >
GWR4 can open data files in text format delimited by space, comma, or tab; as well
as files in dbase IV format (*.dbf). The most popular type is CSV (a text format that
uses the comma delimiter).
< dbase IV files >
Since the shapefile spatial data format—a common GIS file format from ESRI
Inc.—uses dbase IV as an attribute database linking with geographic objects, the
function to read dbase file provides an easy way to use such a GIS data file in
GWR4. However, there is one caveat for this function:
In the case of dbase IV, the length of the filename must not exceed 8 characters,
due to the restriction on database connection used in this software. Some examples
of readable and unreadable filenames are shown below:
Readable filenames: tokyom.dbf, tokyodat.dbf
Unreadable filenames: dublindata.dbf, irelandmortality.dbf
< Field names >
In the case of text formats, the first line (row) of the data file must be the list of
field names. (A dbase IV file automatically has the field name lists.)
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc