《程序设计艺术与方法》课程实验报告
实验名称
姓
名
实验日期
实验一 STL 的熟悉与使用
系院专业
班
级
指导教师
学
成
号
绩
一、实验目的和要求
1.掌握 C++中 STL 的容器类的使用;
2.掌握 C++中 STL 的算法类的使用.
二、实验预习内容
1.预习 ICPC 讲义,大致了解 STL 的相关内容。
2.了解 STL 中一些类 vector list 类的使用方法
3.了解泛型算法的使用
三、实验项目摘要
(1) 练习 vector 和 list 的使用。
定义一个空的 vector,元素类型为 int,生成 10 个随机数插入到 vector 中,用迭代
器遍历 vector 并输出其中的元素值。在 vector 头部插入一个随机数,用迭代器遍历 vector
并输出其中的元素值。用泛型算法 find 查找某个随机数,如果找到便输出,否则将此数
插入 vector 尾部。用泛型算法 sort 将 vector 排序,用迭代器遍历 vector 并输出其中的元
素值。删除 vector 尾部的元素,用迭代器遍历 vector 并输出其中的元素值。将 vector 清
空。
定义一个 list,并重复上述实验,并注意观察结果。
(2) 练习泛型算法的使用。
定义一个 vector,元素类型为 int,插入 10 个随机数,使用 sort 按升序排序,输出
每个元素的值,再按降叙排序,输出每个元素的值。练习用 find 查找元素。用 min 和
max 找出容器中的最小元素个最大元素,并输出。
�
四、实验结果与分析
(1)练习 vector 和 list 的使用。
vector:
源代码:
#include
#include //动态数组
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
vector a;
vector::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a.push_back(rand() % 100);
}
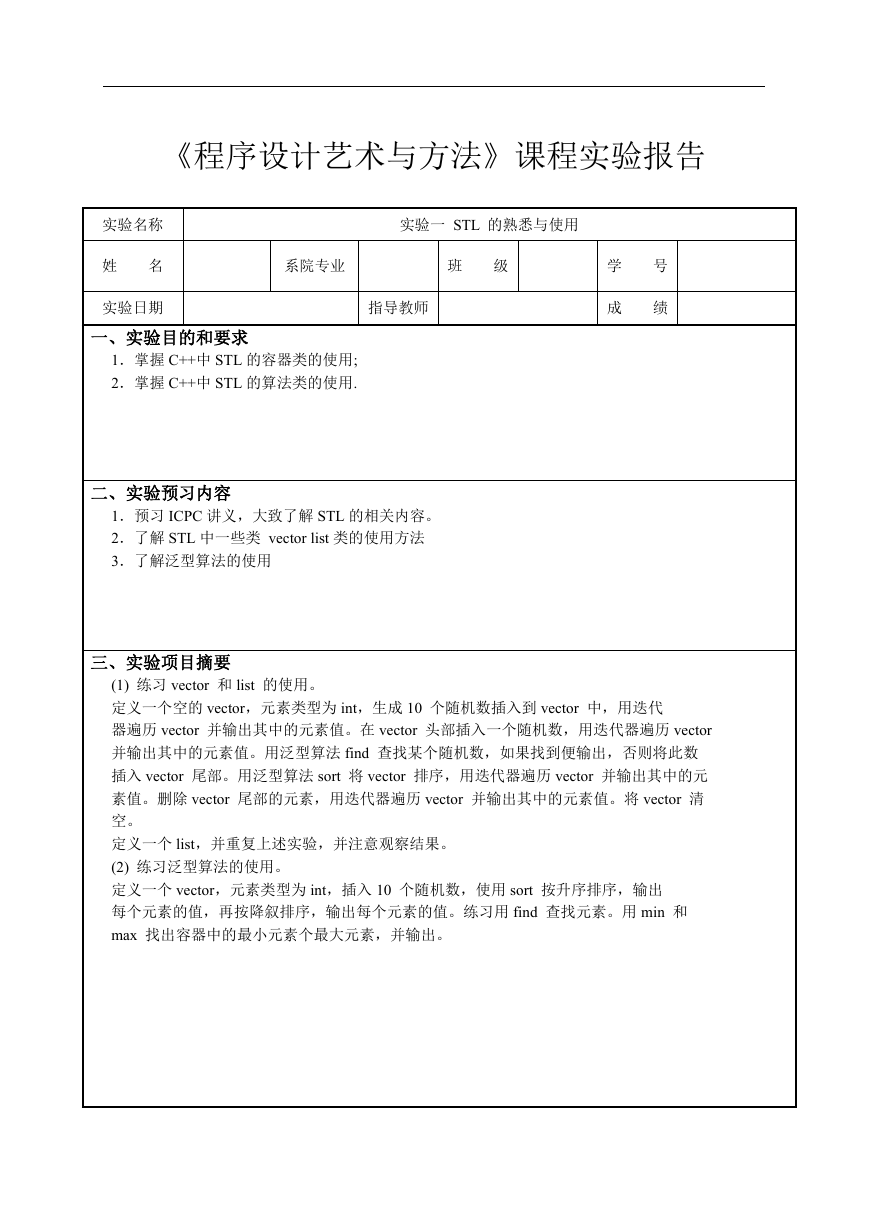
cout << "已随机插入数组 a 中十个数:";
//输出数组a 中的元素
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
//迭代器输出
}
cout << endl << "在数组 a 的头部插入一个随机数:";
int num_insert = rand() % 100;
cout << num_insert << endl;
it = a.begin();
a.insert(it, num_insert); //插入该100 以内的随机数;
cout << "插入后容器内的元素为:";
for (it=a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
int num_seek = rand() % 100;
cout << endl << "查找随机数:" << num_seek;
it = find(a.begin(), a.end(), num_seek);
if (it != a.end())
cout << endl << "已查找到" << num_seek;
else {
cout << endl << "未查找到" << num_seek << ",将其插入 vector 尾端";
a.push_back(num_seek);
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
�cout << endl << "泛型算法 sort 排序:";
//输出排序后的数组a 中的元素
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
it = a.end() - 1;
cout << endl << "删除 vector 其尾端值" << *it;
a.pop_back();
cout << endl << "删除后其容器内的元素为:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
a.clear();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
截图:
List
源代码:
#include
#include//带头节点的双向循环链表
#include
#include
using namespace std;
�
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //创建时间随机种子
list a;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a.push_back(rand() % 100);
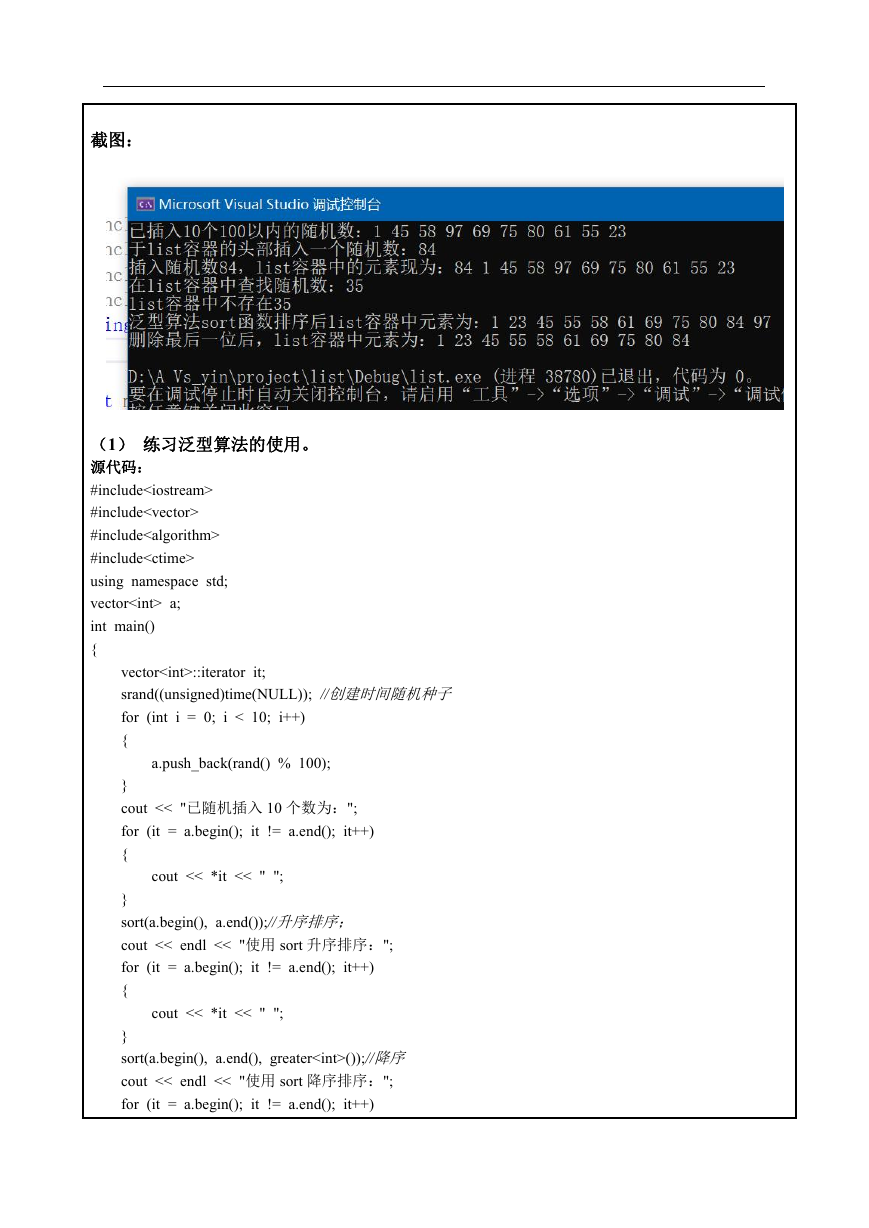
cout << "已插入 10 个 100 以内的随机数:";
list::iterator it;
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
int num_insert = rand() % 100;
cout << endl << "在 list 容器的头部插入一个随机数:" << num_insert << endl;
a.push_front(num_insert);
cout << "插入随机数" << num_insert << ",list 容器中的元素现为:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
int num_seek = rand() % 100;
cout << endl << "在 list 容器中查找随机数:" << num_seek << endl;
it = find(a.begin(), a.end(), num_seek);
if (it != a.end())
{
cout << "list 容器中存在" << num_seek << ",插入该随机值。" << endl;
a.push_back(num_seek);
}
else
cout << "list 容器中不存在" << num_seek << endl;
a.sort();
cout << "泛型算法 sort 函数排序后 list 容器中元素为:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
a.pop_back();
cout << "删除最后一位后,list 容器中元素为:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
a.clear();
return 0;
}
�
截图:
(1) 练习泛型算法的使用。
源代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
vector a;
int main()
{
vector::iterator it;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //创建时间随机种子
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a.push_back(rand() % 100);
}
cout << "已随机插入 10 个数为:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());//升序排序;
cout << endl << "使用 sort 升序排序:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), greater());//降序
cout << endl << "使用 sort 降序排序:";
for (it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++)
�{
cout << *it << " ";
}
int num_seek = rand() % 100;
//判断是否存在随机值
it = find(a.begin(), a.end(), num_seek);
cout << endl<< "查找随机数:" << num_seek;
if (it!=a.end())
cout << ",找到该随机数" << num_seek;
else
cout << ",容器中不存在该随机数" << endl;
cout << "容器中最小值为;" << *min_element(a.begin(), a.end());
cout << "容器中最大值为;" << *max_element(a.begin(), a.end());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
截图:
�
《程序设计艺术与方法》课程实验报告
实验名称
实验二 搜索算法的实现
姓
名
系院专业
班
级
学
号
实验日期
指导教师
成
绩
一、实验目的和要求
1.掌握宽度优先搜索算法。
2.掌握深度优先搜索算法。
二、实验预习内容
1.预习 ICPC 讲义中的搜索的内容
2. 了解什么是深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索。
三、实验项目摘要
1. 将书上的走迷宫代码上机运行并检验结果,并注意体会搜索的思想。
2.八皇后问题:在一个国际象棋棋盘上放八个皇后,使得任何两个皇后之间不相互攻击,求出所有的
布棋方法。上机运行并检验结果。
3. 骑士游历问题:在国际棋盘上使一个骑士遍历所有的格子一遍且仅一遍,对于任意给定的顶点,
输出一条符合上述要求的路径。
4.倒水问题:给定 2 个没有刻度容器,对于任意给定的容积,求出如何只用两个瓶装出 L 升
的水,如果可以,输出步骤,如果不可以,请输出 No Solution。
四、实验结果与分析(源程序及相关说明)
1. 八皇后问题
1.1 思路分析:
设立数组 a[n],数组下标对应棋盘的行;数组存储的值为列;数组的每个下标(列)对应相应的
行;
递归遍历所有的棋盘点,通过棋子是否在对角线或同一列判断是否能落子;
递归的同时输出满足条件的方法;
1.2 解题详情
eightQueen()函数判断是否能落子
当 queenCount == n 时,print()函数输出此种情况下落子情况。
1.3 源代码:
#include
�
#include
#include //UNICODE工程-wide-character,用于双字节字符串
using namespace std;
#define n 8//皇后的个数
int a[n] = { 0 };
int total = 0;
//判断此列是否能满足条件
bool is_play(int row) {
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
if ((abs(i - row) == abs(a[i] - a[row])) || (a[i] == a[row]))//在对角线或者同一列
return false;
return true;
}
void print() {//打印各种解决放置方式
cout << "第" << total << "种方法,列位置为:";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void eightQueen(int queenCount) {
if (queenCount == n) {
total++;
print();
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a[queenCount] = i;
if (is_play(queenCount))
eightQueen(queenCount + 1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cout << "
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << i<<" ";
行数:" ;
cout << endl;
eightQueen(0);
return 0;
}
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc