§5.4 Radon 变换
5.4.4 Matlab 中的实现[4]
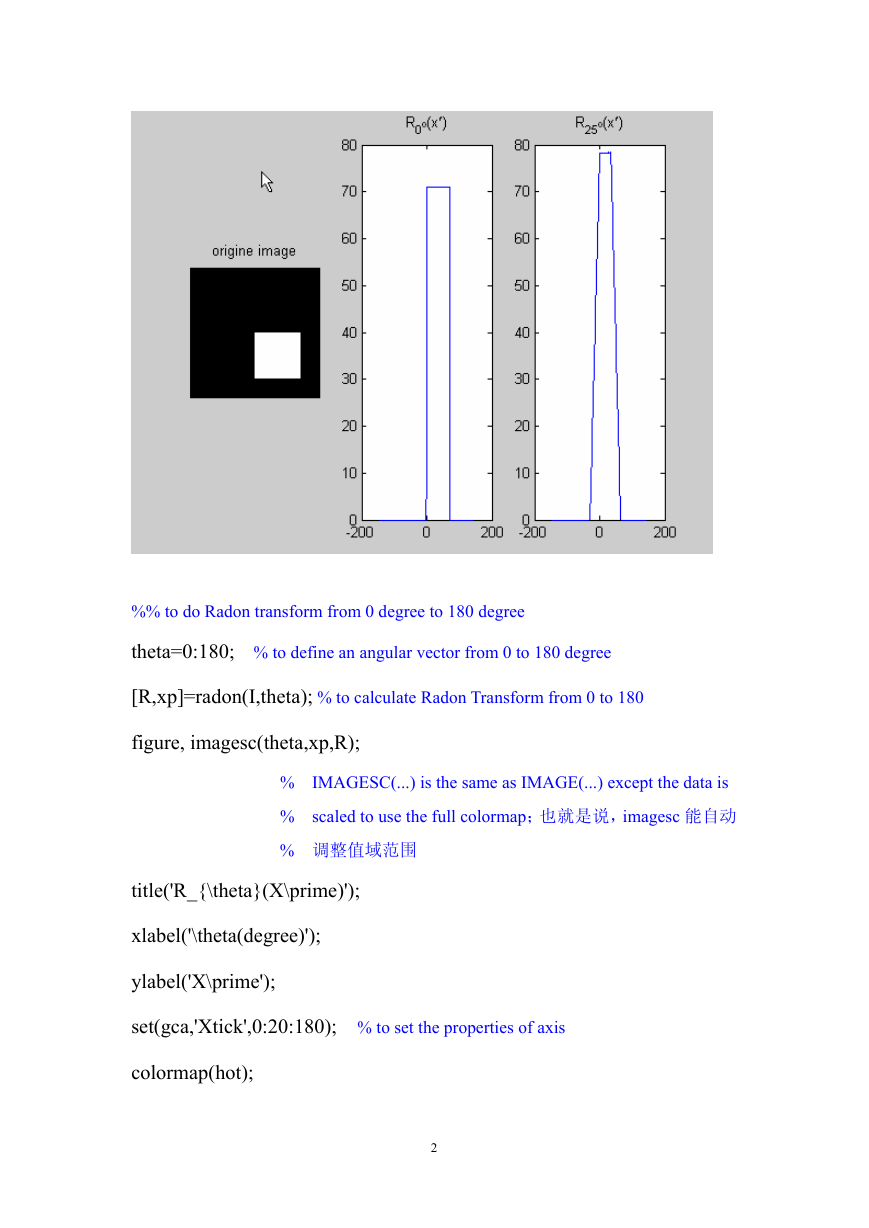
例、对一个正方形黑框进行 Radon 变换。
I=zeros(200,200);
I(100:170,100:170)=1; % to produce a square black frame
Figure,imshow(I);
title('origine image');
%% to do Radon transform of 0 and 25 degree
[R,xp]=radon(I,[0 25]); % to calculate the Radon transform of the black frame,
% R shows the Radon transform values for theta angles:
% 0 and 25 degree;
% xp 矢量表示沿 ˆx′ 轴相应的坐标值
subplot(1,3,2),plot(xp,R(:,1));
title('R(0^o)(x\prime)');
subplot(1,3,3),plot(xp,R(:,2));
title('R(25^o)(x\prime)');
1
�
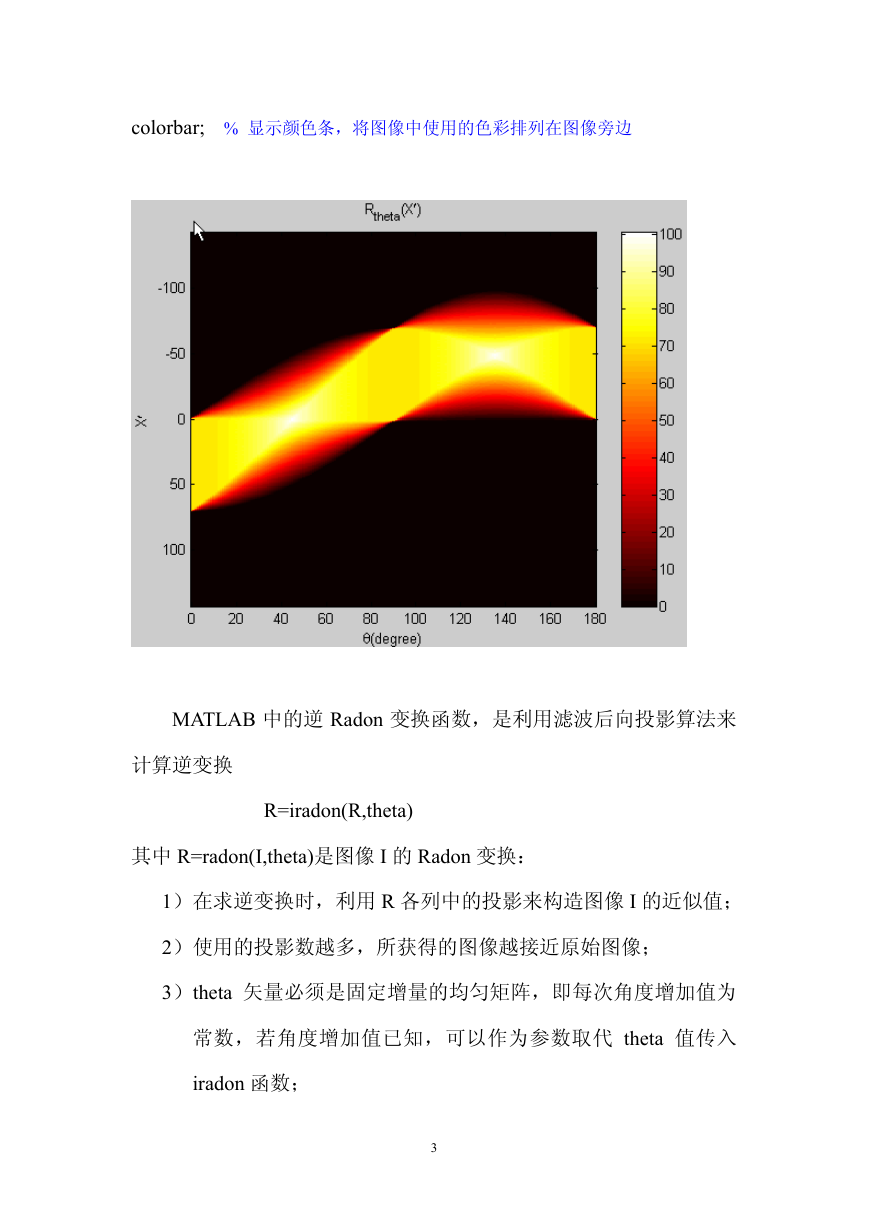
%% to do Radon transform from 0 degree to 180 degree
theta=0:180; % to define an angular vector from 0 to 180 degree
[R,xp]=radon(I,theta); % to calculate Radon Transform from 0 to 180
figure, imagesc(theta,xp,R);
% IMAGESC(...) is the same as IMAGE(...) except the data is
% scaled to use the full colormap;也就是说,imagesc 能自动
% 调整值域范围
title('R_{\theta}(X\prime)');
xlabel('\theta(degree)');
ylabel('X\prime');
set(gca,'Xtick',0:20:180); % to set the properties of axis
colormap(hot);
2
�
colorbar; % 显示颜色条,将图像中使用的色彩排列在图像旁边
MATLAB 中的逆 Radon 变换函数,是利用滤波后向投影算法来
计算逆变换
R=iradon(R,theta)
其中 R=radon(I,theta)是图像 I 的 Radon 变换:
1)在求逆变换时,利用 R 各列中的投影来构造图像 I 的近似值;
2)使用的投影数越多,所获得的图像越接近原始图像;
3)theta 矢量必须是固定增量的均匀矩阵,即每次角度增加值为
常数,若角度增加值已知,可以作为参数取代 theta 值传入
iradon 函数;
3
�
4)投影值含有噪声时,可以通过加窗消去高频噪声:
IR=iradon(R,theta,'Shepp-Logan');
% 采用 Shepp-Logan 窗做滤波: The Shepp-Logan filter multiplies
% the Ram-Lak filter by a sinc function.
IR=iradon(R,theta,' Cosine');
% 采用 Cosine 窗做滤波:The cosine filter multiplies the Ram-Lak
% filter by a cosine function.
IR=iradon(R,theta, 'Hamming');
% 采用 Hamming 窗做滤波:The Hamming filter multiplies the
% Ram-Lak filter by a Hamming window.
IR=iradon(R,theta,0.90);
% iradon允许指定归一化频率 D,高于 D 的滤波器响应为零,整
% 个滤波器压缩在[0,D]的范围内。假若系统不含高频信息而存在
% 高频噪声时可用来完全拟制噪声,又不会影响图像重建。
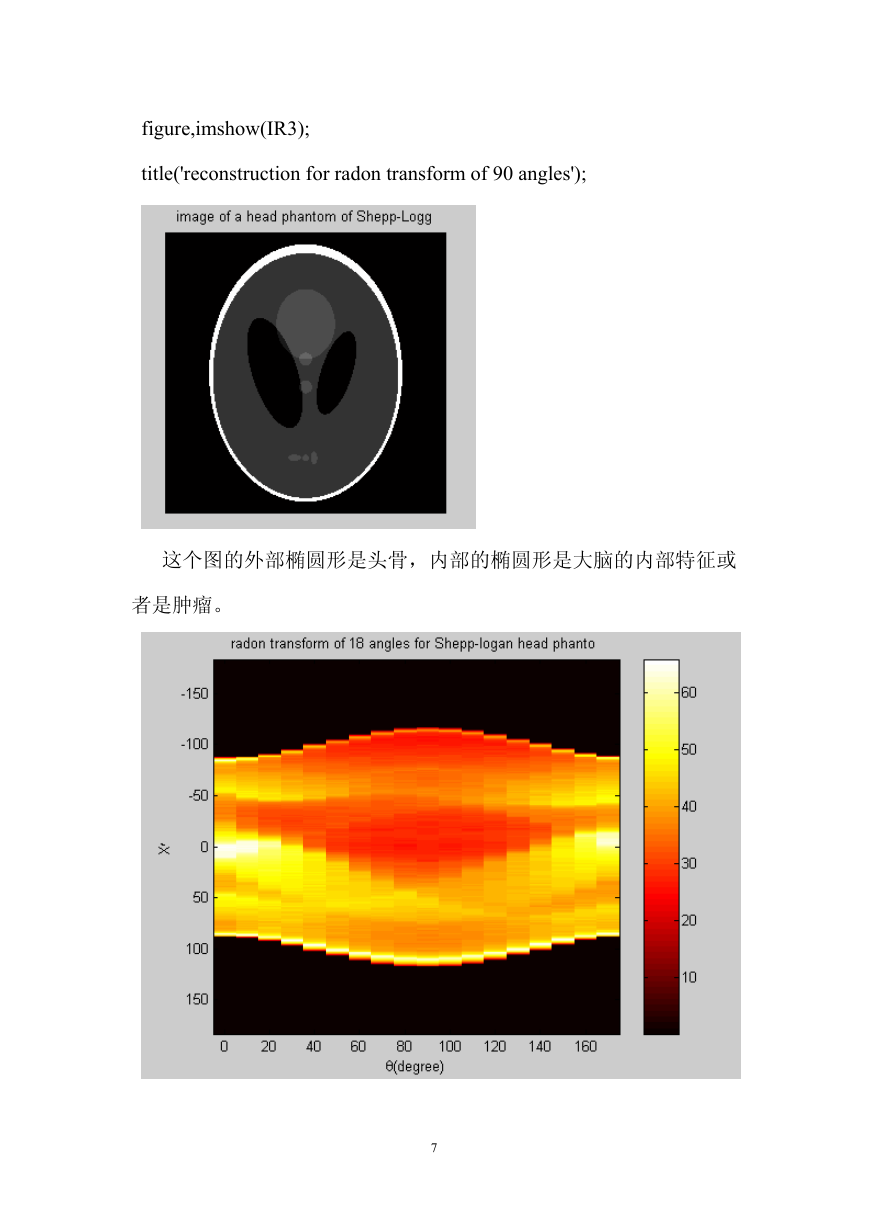
例、从一个简单图像的投影重建图像
在 Matlab 图像处理工具箱中的 Phantom 函数,可以产生 Shepp
-Logan 的大脑图,该图作为一个测试图,可反映人大脑的许多性质。
P=phantom(256);
% P = PHANTOM(DEF,N) generates an image of a head phantom that can
% be used to test the numerical accuracy of RADON and IRADON or other
% 2-D reconstruction algorithms. P is a grayscale intensity image that
% consists of one large ellipse (representing the brain) containing
% several smaller ellipses (representing features in the brain).
figure,imshow(P);
title('image of a head phantom of Shepp-Logg');
4
�
theta1=0:10:170;
[R1,xp]=radon(P,theta1);
% to calculate radon transform of R1 which includes 18 angles
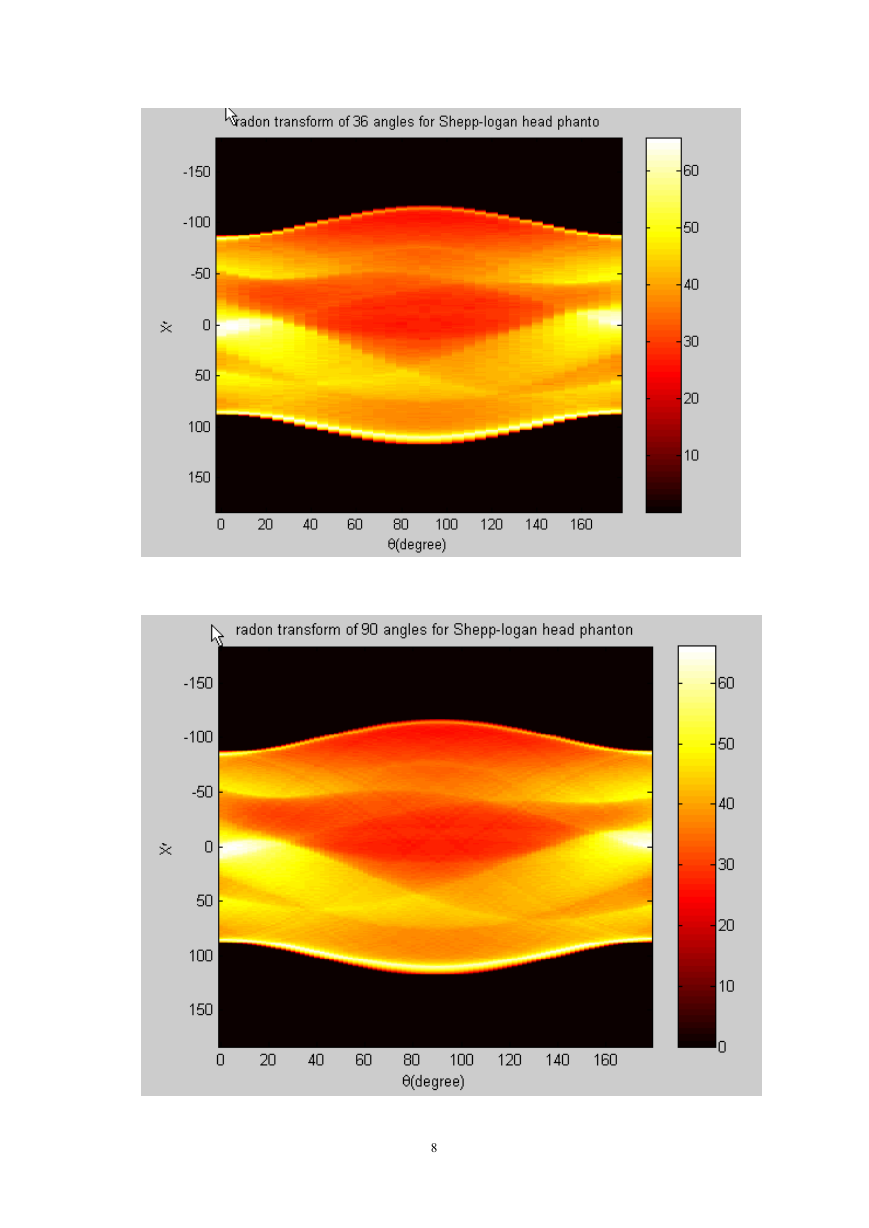
theta2=0:5:175;
[R2,xp]=radon(P,theta2);
% to calculate radon transform of R2 which includes 36 angles
theta3=0:2:178;
[R3,xp]=radon(P,theta3);
% to calculate radon transform of R3 which includes 90 angles
figure,imagesc(theta1,xp,R1);
% IMAGESC(...) is the same as IMAGE(...) except the data is
% scaled to use the full
colormap.title('R_{theta}(X\prime)');
title('radon transform of 18 angles for Shepp-logan head phanto ');
xlabel('\theta(degree)');
ylabel('X\prime');
set(gca,'Xtick',0:20:180); % to set the properties of axis
colormap(hot);
colorbar;
figure, imagesc(theta2,xp,R2);
5
�
title('radon transform of 36 angles for Shepp-logan head phanto');
xlabel('\theta(degree)');
ylabel('X\prime');
set(gca,'Xtick',0:20:180); % to set the properties of axis
colormap(hot);
colorbar;
figure, imagesc(theta3,xp,R3);
title('radon transform of 90 angles for Shepp-logan head phanton');
xlabel('\theta(degree)');
ylabel('X\prime');
set(gca,'Xtick',0:20:180); % to set the properties of axis
colormap(hot);
colorbar;
IR1=iradon(R1,theta1,0.85); % 指定归一化频率为 0。85
figure,imshow(IR1);
title('reconstruction for radon transform of 18 angles');
IR2=iradon(R2,theta2,0.85);
figure,imshow(IR2);
title('reconstruction for radon transform of 36 angles');
IR3=iradon(R3,theta3,0.85);
6
�
figure,imshow(IR3);
title('reconstruction for radon transform of 90 angles');
这个图的外部椭圆形是头骨,内部的椭圆形是大脑的内部特征或
者是肿瘤。
7
�
8
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc