前k 条最短路径算法
戴维编译
一、算法说明
Deletion Algorithm 删除算法的核心是通过在有向图中已有的最短路径上删
除某条弧,并寻找替换的弧来寻找下一条可选的最短路径。删除算法实际上是通
过在有向图中增加附加节点和相应的弧来实现的。算法描述如下:
1. 利用 Dijkstra 算法求得有向图 (N,A) 中以开始节点 s 为根的最短路径树(注
意,这里的最短路径树并不是最小生成树,因为 Dijkstra 算法并不保证能生
成最小生成树),标记从开始节点 s 到结束节点 t 之间的最短路径
为 pk , k=1 。
2. 如果 k 小于要求的最短路径的最大数目 K,并且仍然有候选路径存在, 令当
前路径 p=pk ,转 3。否则,程序结束。
3. 找出当前路径 p 中从第一个节点开始的入度大于 1 的第一个节点,记为 nh 。
如果 nh 的扩展节点 n’ h 不在节点集 N 中,则转 4 ,否则找出路径 p 中 nh 后
面所有节点中,其对应的扩展节点不在 N 中的第一个节点,记为 ni ,转 5 。
4.为节点 nh 构建一个扩展节点 n’ h ,并把其添加到集合 N 中,同时从图 (N,A) 中
所有 nh 的前驱节点 连接一条到 n’ h 的弧,弧对应的权重不变,添加这些弧
到弧集 A 中,但 nh 在 p 中的前一个节点 nh-1 除外。计算从开始节
点 s 到 n’ h 的最短路径,并记 ni = nh+1 。
5. 对于 p 中从 ni 开始的所有后续节点,不妨记为 nj ,依次执行如下操作:
5.1 添加 nj 的扩展节点 n’ j 到节点集合 N 中。
5.2 除了路径 p 中 nj 的前一个节点 nj-1 外,分别连接一条从 nj 前驱节点到其
扩展节点 n’ j 的弧,弧上的权值保持不变,并把这些弧添加到弧集 A 中。另
外,如果 p 中 nj 的前一个节点 nj-1 具有扩展节点 n’ j-1 的话,也需要连接一条
从 n’ j-1 到 n’ j 的弧,权值和弧 (nj-1 , nj ) 的权值相等。
5.3 计算从开始节点 s 到 n’ j 的最短路径。
6. 更新当前最短路径树,求得从开始节点 s 到结束节点的当前扩展节点 t(k)’ 之
间的最短路径为第 k 条最短路径,令 k=k+1 ,转 2 继续。
在上述步骤 4 、5 、6 中均需要计算从开始节点到当前扩展节点的最短路径,
因为程序开始时便生成了以开始节点为根的最短路径树,那么只要在扩充节点
时,记录下每个新节点相对于开始节点的最短路径中其前一个节点编号以及从开
�
始节点到当前节点的最短路径长度,就可以很容易求得任意时刻有向图中从开始
节点到结束节点(或其扩充节点)之间的最短路径。
扩展节点 :上一条最短路径上的节点可能会在求取下一条最短路径的过程中进行扩
展 ,也就是在上次节点集合的基础上增加相应的新节点,这些新的节点均称为扩展节点,
其会继承被扩展结点的邻接边关系(具体请参见上述步骤 4,5)。一个扩展节点仍然可能
会在求取下一条最短路径的时候进行扩展,表现在示例图中就是在一个节点标记后面加一撇
表示是在原始节点上扩展,加两撇表示是在上次扩展节点上再扩展,依次类推。
前驱节点 :就是最短路径中某个节点的前一个节点。
二、算法示例
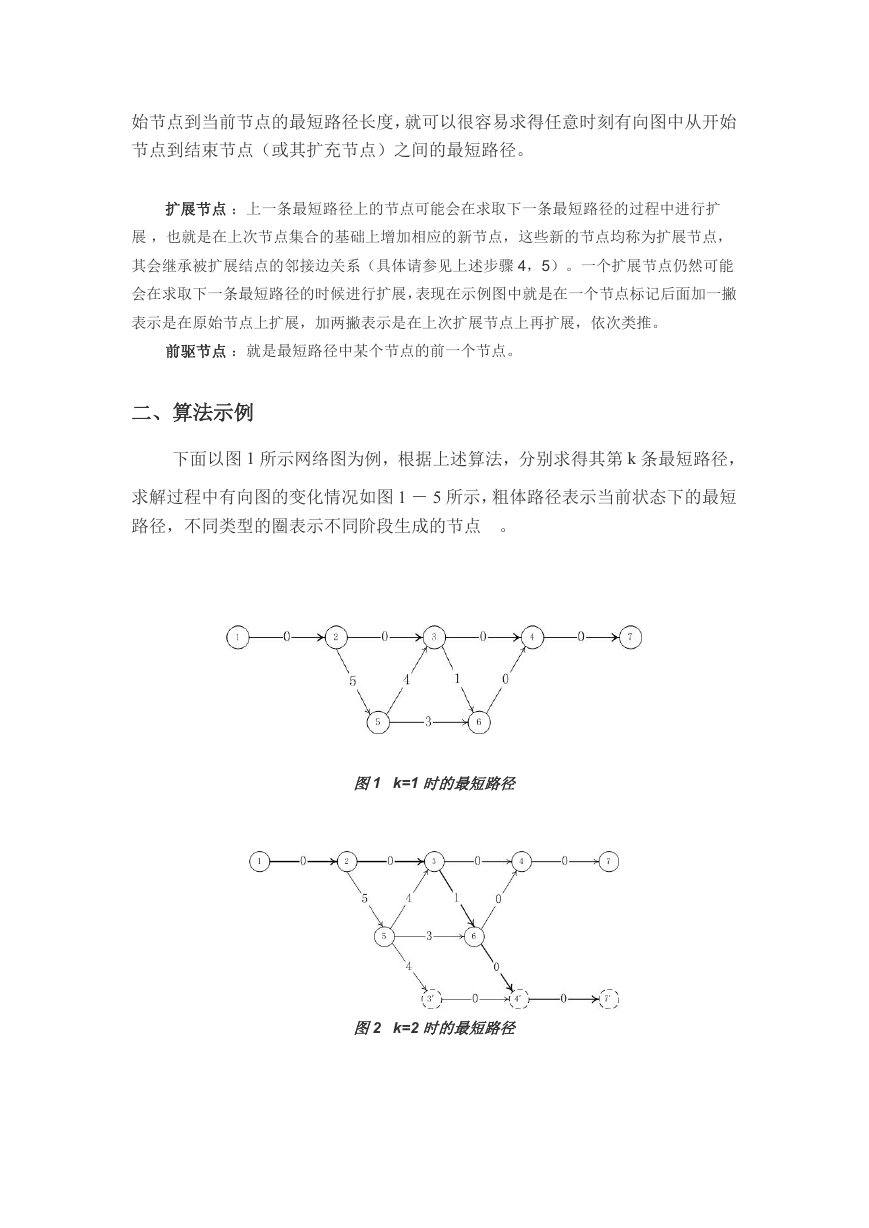
下面以图 1 所示网络图为例,根据上述算法,分别求得其第 k 条最短路径,
求解过程中有向图的变化情况如图 1 - 5 所示,粗体路径表示当前状态下的最短
路径,不同类型的圈表示不同阶段生成的节点 。
图1 k=1 时的最短路径
图2 k=2 时的最短路径
�
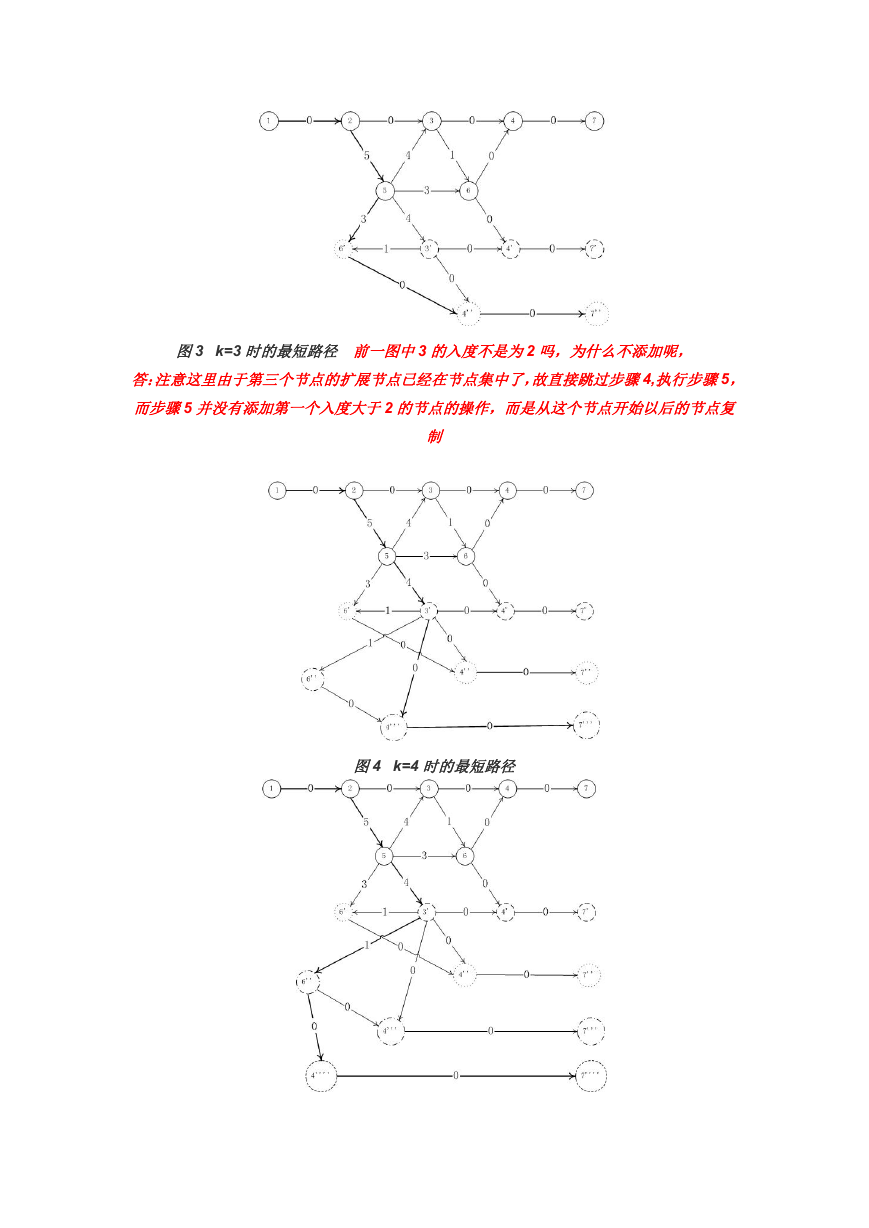
图3 k=3 时的最短路径 前一图中3 的入度不是为2 吗,为什么不添加呢,
答:注意这里由于第三个节点的扩展节点已经在节点集中了,故直接跳过步骤4,执行步骤5,
而步骤5 并没有添加第一个入度大于2 的节点的操作,而是从这个节点开始以后的节点复
制
图4 k=4 时的最短路径
�
图5 k=5 时的最短路径
/*
*/
Graph library Demo.
David D. 2006
#include "Graph.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace Mido::Utility;
const int N = 7;
const double dag[N][N] = {
{-1, 0,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},
{-1,-1, 0,-1, 5,-1,-1},
{-1,-1,-1, 0,-1, 1,-1},
{-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1, 0},
{-1,-1, 4,-1,-1, 3,-1},
{-1,-1,-1, 0,-1,-1,-1},
{-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1}};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
double** array = new double*[N];
for(int i=0;i
_array[i].resize(_size);
for(int j=0;j<_size;j++)
_array[i][j] = array[i][j];
{
}
}
Graph::Graph(const double **array, unsigned N) : _N(N), _size(N)
{
}
_array.resize(_size);
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
{
}
_array[i].resize(_size);
for(int j=0;j<_size;j++)
_array[i][j] = array[i][j];
//this->Output(); // for debug
Graph::~Graph()
{
}
void Graph::Restart(const dag_t& array)
{
}
_array.clear();
_N = _size = array.size();
_array.resize(_size);
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
{
}
_array[i].resize(_size);
for(int j=0;j<_size;j++)
_array[i][j] = array[i][j];
//this->Output(); // for debug
void Graph::Restart(const double** array,unsigned N)
{
_array.clear();
�
_N = _size = N;
_array.resize(_size);
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
_array[i].resize(_size);
for(int j=0;j<_size;j++)
_array[i][j] = array[i][j];
{
}
}
double Graph::Dijkstra( path_t& path )
{
}
int* paths = new int[_size];
double min = dijkstra(paths);
if(min < 0) { delete[] paths; return -1;}
// parse the shortest path
int i = _size - 1;
while(i>=0)
{
}
path.push(i);
i=paths[i];
// push the start node
path.push(0);
delete[] paths;
return min;
double Graph::Dijkstra( unsigned start , unsigned end , path_t& path )
{
if(end == start || start >= _size) return -1;
int* paths = new int[_size];
double min = dijkstra(paths,start,end);
if(min < 0) { delete[] paths; return -1;}
// parse the shortest path
if(end > _size-1) end = _size - 1;
int i = end;
while(i>=0)
{
path.push(i);
�
i=paths[i];
}
// push the start node
if(_array[start][path.top()]>=0)
path.push(start);
else
{ delete[] paths; return -1;}
delete[] paths;
return min;
}
void Graph::Output(ostream& out)
{
}
/*
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
{
}
S
T
out.width(2);
out << std::right << i << " ";
for(int j=0;j<_size;j++)
{
}
out.width(10); //out.precision(8);
out << std::right <<_array[i][j] <<" ";
out << endl;
-- START node.
-- END node
Path[]
-- Path[i]=j indicates the previous node of node i is j. Path[i]=-1 indicates
node i
has not previous node, e.g. START node. It could be expanded dynamically.
Dist[]
-- store the lengths of the shortest pathes from START node to END node. It could
be
START
expanded dynamically.Dist[i]=INFINITY indicates there is not a path from
node to node i.
Prime[] -- Prime[i] indicates node Prime[i] is the prime node of node i. Prime[i]=-1
indicates
the node i has not prime node.
Base[]
-- In opposition to Prime[i], node Base[i] is the original node of node i, that
is to say,
node i is the prime node of node Base[i].
�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc