Symmetry Operations and Space Groups
Crystal Symmetry
32 point groups of crystals compatible with 7 crystal systems
crystallographers use Hermann-Mauguin symmetry symbols
Carl Hermann
Charles-Victor Mauguin
German
1898 - 1961
French
1878 - 1958
Symmetry Elements
Center of Symmetry: 1
there are 5 types in point symmetry
1. center of symmetry (or inversion)
2. rotation (or proper) axis
3. mirror
4. rotation–inversion axis
5. identity
: point
: line
: plane
: line
: no element
1
n
m
n
1
a point in the molecule through which if another point on the
molecule is taken, will meet an identical point on the molecule
an equal distance away
1
Center of Symmetry: 1
Rotation Axis: n
all points (x, y, z)
(–x, –y, –z) if 1 is placed at the origin
y
1
z
+ (x, y, z)
x
(–x, –y, –z)
–
n is an integer which gives the degrees of rotation:
2
n
or
360o
n
n is the number of times molecule is rotated,
at an identical appearance,
each time stopping
before returning to the starting point
2
3
4
6
n is the foldness of the rotation axis
only 2, 3, 4, and 6-fold axes allowed in crystal symmetry
9/18/2013
1
�
9/18/2013
Rotation Axis: 4
360o
4
= 90o
Mirror: m
plane within the molecule that, when acting as a mirror, reflects
the molecule into itself
90o
180o
270o
360o
4
Rotation-Inversion n
Representation of Symmetry
rotation followed by inversion
this is a different definition than Schoenflies system
Arthur Moritz Schönflies – German 1891
rotation followed by reflection
point symmetry often represented symbolically in the form of
points on a circle (projection of a sphere)
a point above plane is a filled circle:
a point below plane is an open circle:
two points directly on top of each other:
starting with one point, find other points generated by symmetry
32 point groups compatible with 7 crystal systems
Triclinic
1
1
(Ci)
1
(C1)
highest symmetry in each crystal system is called:
Laue Group
(Schoenflies symbol)
have center of symmetry
Monoclinic
2
2
m
(Cs)
(C2)
(C2h)
monoclinic convention: symmetry located wrt b axis
2/m
2: 2-fold axis along b
m: mirror perpendicular to b
2/m: 2-fold axis along b, perpendicular to a mirror
2
�
Monoclinic
Orthorhombic
2
m
2/m
2
(C2v)
mm2
xyz
3 symbols refer to:
222
(D2)
mmm
(D2h)
axes along a, b, or c
mirrors perpendicular to a, b, or c
Rhombohedral (Trigonal)
Tetragonal
3
(C3)
2
3
(S6)
3m
(C3v)
4
(C4)
4
(S4)
4/m
(C4h)
32
(D3)
3m
(D3d)
4mm
(C4v)
42m
(D2d)
422
(D4)
4/mmm
(D4h)
3
32
3
3m
3m
Tetragonal
Hexagonal
4
4
4mm
42m
4/m
422
6
(C6)
6
(C3h)
6/m
(C6h)
6mm
(C6v)
6m2
(D3h)
622
(D6)
4/mmm
6/mmm
(D6h)
9/18/2013
3
�
9/18/2013
Hexagonal
Cubic
6
6
6mm
6m2
6/m
622
6/mmm
Lattices
14 Bravais lattices have Laue symmetry
Lattices
14 Bravais lattices have Laue symmetry
all have a center of symmetry
center of symmetry very important in crystallography:
centrosymmetric or noncentrosymmetric
23
(T)
m3
(Th)
43m
(Td)
432
(O)
m3m
(Oh)
23
432
m3
m3m
43m
14 Bravais Lattices
triclinic
monoclinic
P1
P2/m
C2/m
orthorhombic
Pmmm
Cmmm
Immm
Fmmm
rhombohedral
tetragonal
R3m
P4/mmm
I4/mmm
hexagonal
cubic
P6/mmm
Pm3m
Im3m
Fm3m
Translational Symmetry
in repeating lattices, two additional symmetry elements
translational elements
1. screw axis
rotation and translation:
nr
rotation by 360o/n;
followed by translation of r/n along that axis (a, b or c)
2-fold screw axis most common: 21
2. glide plane
reflection and translation:
a, b, c, n or d
reflection across plane;
followed by translation of 1/2 (usually) unit cell parallel to
plane along a, b, c, face diagonal (n), or body diagonal (d)
4
�
,
c
b
a
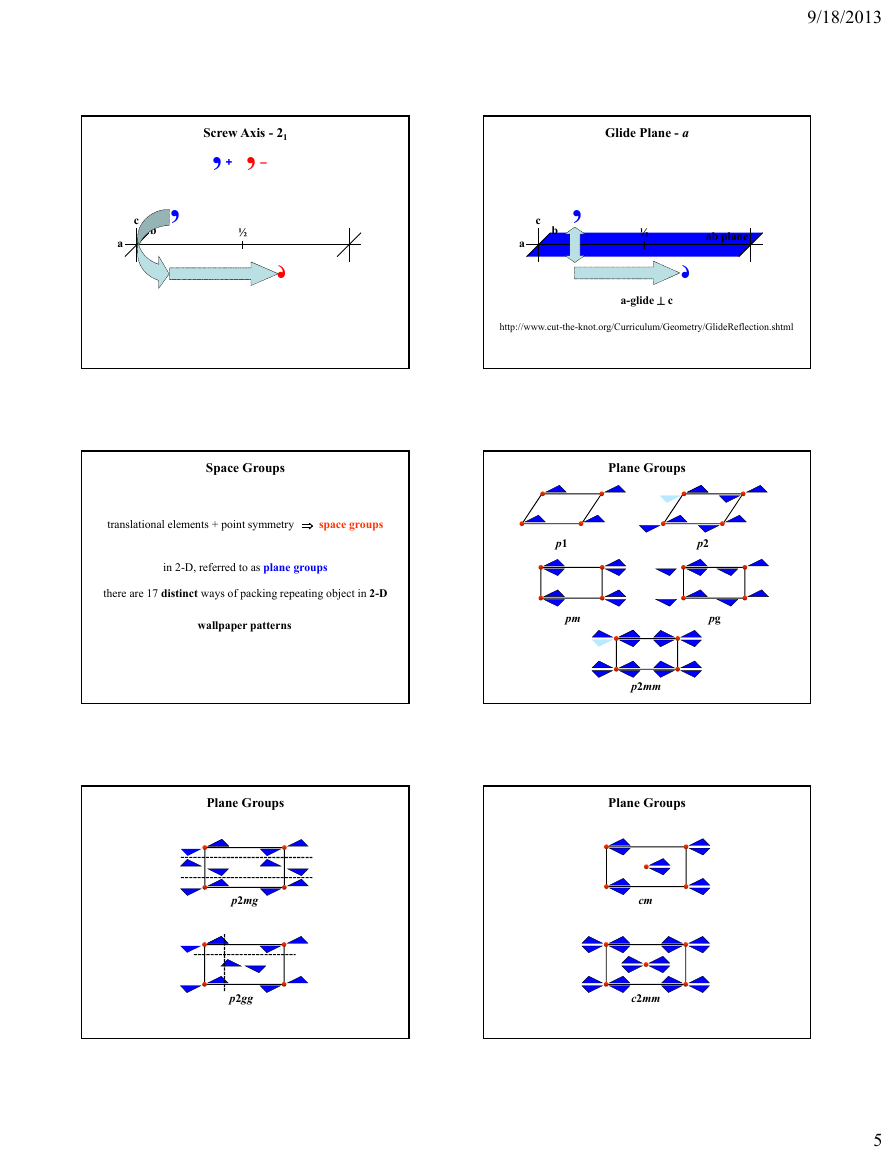
Screw Axis - 21
, + , –
½
‛
,
c
b
a
Glide Plane - a
ab plane
½
‛
a-glide c
http://www.cut-the-knot.org/Curriculum/Geometry/GlideReflection.shtml
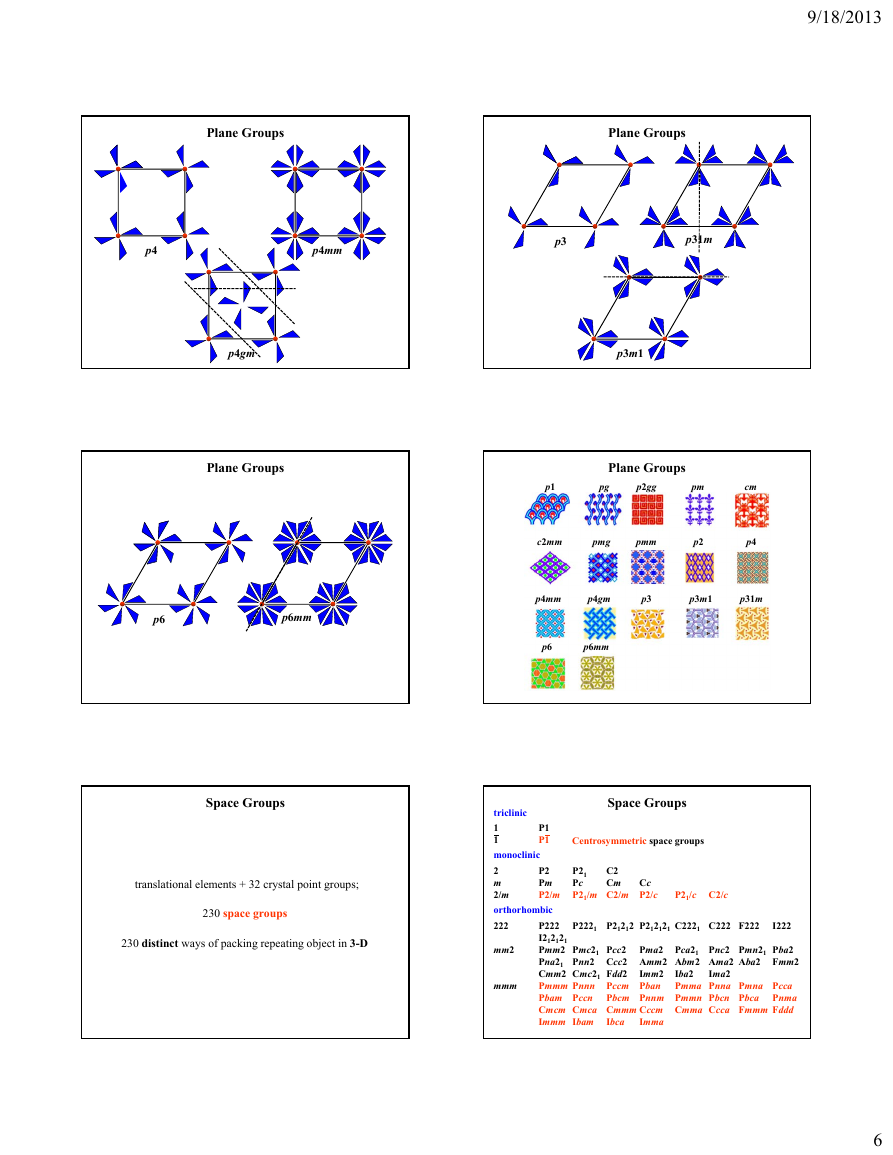
Space Groups
Plane Groups
translational elements + point symmetry space groups
in 2-D, referred to as plane groups
there are 17 distinct ways of packing repeating object in 2-D
wallpaper patterns
p1
pm
p2
pg
p2mm
Plane Groups
Plane Groups
p2mg
p2gg
cm
c2mm
9/18/2013
5
�
Plane Groups
Plane Groups
p4
p4mm
p3
p31m
p4gm
p3m1
Plane Groups
p6
p6mm
Plane Groups
p1
pg
p2gg
pm
cm
c2mm
pmg
pmm
p2
p4
p4mm
p4gm
p3
p3m1
p31m
p6
p6mm
Space Groups
translational elements + 32 crystal point groups;
230 space groups
230 distinct ways of packing repeating object in 3-D
Space Groups
Centrosymmetric space groups
P21
Pc
P2
Pm
Cc
P2/m P21/m C2/m P2/c
C2
Cm
P21/c C2/c
P1
P1
triclinic
1
1
monoclinic
2
m
2/m
orthorhombic
222
mm2
mmm
I222
P2221 P21212 P212121 C2221 C222 F222
P222
I212121
Pmm2 Pmc21 Pcc2
Pma2 Pca21 Pnc2 Pmn21 Pba2
Pna21 Pnn2 Ccc2 Amm2 Abm2 Ama2 Aba2 Fmm2
Cmm2 Cmc21 Fdd2
Imm2
Iba2
Pmmm Pnnn Pccm Pban
Pmma Pnna Pmna Pcca
Pbam Pccn
Pnma
Cmcm Cmca Cmmm Cccm Cmma Ccca Fmmm Fddd
Immm Ibam Ibca
Pbcm Pnnm Pmmn Pbcn Pbca
Imma
Ima2
9/18/2013
6
�
Space Groups
P42
P43
I4
I41
I4/m
P4222
I41/a
P42212
tetragonal
4
4
4/m
422
4mm
42m
P4
P4
P4/m
P422
P4322
P4mm
P42mc
P42m
P42b
P41
I4
P42/m
P4212
P43212
P4bm
P42bc
P42c
P4n2
P4/n
P4122
I422
P42cm
I4mm
P421m
I4m2
P42/n
P41212
I4122
P42nm
I4cm
P421c
I4c2
4/mmm P4/mmm P4/mcc P4/nbm P4/nnc
P4cc
I41md
P4m2
I42m
P4/mbm P4/mnc
P42/nnm
P4/nmm P4/nnc
P42/mbc P42/mnm P42/nmc P42/ncm I4/mmm I4/mcm
I41/amd
P42/mmc P42/mcm P42/nbc
P4nc
I41cd
P4c2
I42d
I41/acd
Space Groups
P32
P3
P3
P312
P3m1
P31m
trigonal/rhombohedral
P31
3
R3
3
P3112
32
P321
P31m P3c1
3m
3m
P31c
P3m1
hexagonal
6
6
6/m
622
6mm
P61
P65
P6
P6
P6/m
P622
P6mm
P62m
P6m2
P63/m
P6122
P6cc
P62c
P6c2
6m2
6/mmm P6/mmm P6/mcc P63/mcm P63/mmc
P62m
P62c
R3
P3121
P31c
P3c1
P3212
R3m
R3m
P3221 R32
R3c
R3c
P62
P64
P63
P6522
P6222
P63cm P63mc
P6422
6m2
P6322
P6m2 P6c2
cubic
23
m3
432
43m
m3m
Space Groups
Symmetry
P23
Pm3
P432
P4132
P43m
Pm3m
Fd3m
F23
Pn3
P4232
I4132
F43m
Pn3n
Fd3c
I23
Fm3
F432
I43m
Pm3n
Im3m
P213
Fd3
F4132
P43n
Pn3m
Ia3d
I213
Im3
I432
F43c
Fm3m
Pa3
P4332
I43d
Fm3c
7 crystal systems:
point symmetry of external lattice
14 Bravais lattices: translational symmetry of lattice points
32 point groups:
point symmetry of external crystal
230 space groups:
translational symmetry inside crystal
molecules
Space Groups
Cambridge Structural Database (CSD)
all compounds crystallize in one or more of these space groups
usually possible to find P1, but always try to find the
highest possible symmetry.
structures observed in all 230 space groups
~95% of all structures: monoclinic, triclinic, orthorhombic
~83% of all structures: P21/c, P1, P212121, C2/c, P21, Pbca
http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/
592938 structures
40000
35000
30000
25000
20000
15000
10000
5000
s
e
r
u
t
c
u
r
t
S
f
o
r
e
b
m
u
N
0
1965
1975
1985
Year
1995
2005
9/18/2013
7
�
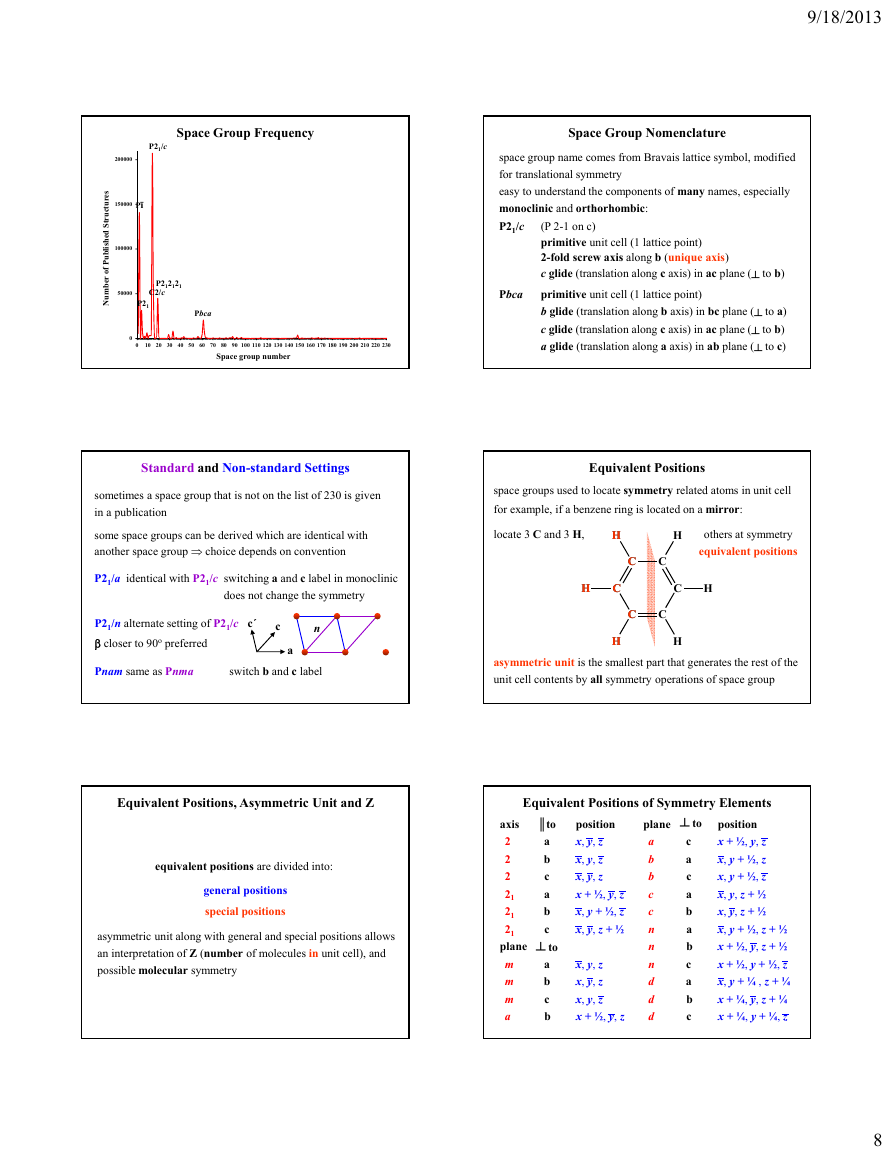
Space Group Frequency
Space Group Nomenclature
P21/c
200000
150000
Pī
100000
s
e
r
u
t
c
u
r
t
S
d
e
h
s
i
l
b
u
P
f
o
r
e
b
m
u
N
space group name comes from Bravais lattice symbol, modified
for translational symmetry
easy to understand the components of many names, especially
monoclinic and orthorhombic:
P21/c
(P 2-1 on c)
primitive unit cell (1 lattice point)
2-fold screw axis along b (unique axis)
c glide (translation along c axis) in ac plane (┴ to b)
primitive unit cell (1 lattice point)
b glide (translation along b axis) in bc plane (┴ to a)
c glide (translation along c axis) in ac plane (┴ to b)
a glide (translation along a axis) in ab plane (┴ to c)
P212121
C2/c
50000
P21
Pbca
0
0
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230
Space group number
Pbca
Standard and Non-standard Settings
Equivalent Positions
sometimes a space group that is not on the list of 230 is given
in a publication
some space groups can be derived which are identical with
another space group choice depends on convention
P21/a identical with P21/c switching a and c label in monoclinic
does not change the symmetry
P21/n alternate setting of P21/c
closer to 90o preferred
c΄
c
n
a
Pnam same as Pnma
switch b and c label
space groups used to locate symmetry related atoms in unit cell
for example, if a benzene ring is located on a mirror:
locate 3 C and 3 H,
H
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
H
others at symmetry
equivalent positions
C
H
H
H
H
asymmetric unit is the smallest part that generates the rest of the
unit cell contents by all symmetry operations of space group
Equivalent Positions, Asymmetric Unit and Z
Equivalent Positions of Symmetry Elements
equivalent positions are divided into:
general positions
special positions
asymmetric unit along with general and special positions allows
an interpretation of Z (number of molecules in unit cell), and
possible molecular symmetry
axis
2
2
2
21
21
21
plane
m
m
m
a
║to
a
b
c
a
b
c
┴ to
a
b
c
b
position
x, y, z
x, y, z
x, y, z
x + ½, y, z
x, y + ½, z
x, y, z + ½
x, y, z
x, y, z
x, y, z
x + ½, y, z
plane ┴ to
a
b
b
c
c
n
n
n
d
d
d
c
a
c
a
b
a
b
c
a
b
c
position
x + ½, y, z
x, y + ½, z
x, y + ½, z
x, y, z + ½
x, y, z + ½
x, y + ½, z + ½
x + ½, y, z + ½
x + ½, y + ½, z
x, y + ¼ , z + ¼
x + ¼, y, z + ¼
x + ¼, y + ¼, z
9/18/2013
8
�








 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc