Project acronym:
Project title:
Project reference:
Programme:
EVITA
E-safety vehicle intrusion protected applications
224275
Seventh Research Framework Programme (2007–2013) of the
European Community
ICT-2007.6.2: ICT for cooperative systems
Collaborative project
1 July 2008
42 months
Objective:
Contract type:
Start date of project:
Duration:
Deliverable D1.2.5.2:
Presentation Slides from the
Final EVITA Workshop on
Security of Automotive On-Board Networks
Editor:
Dissemination level:
Deliverable type:
Date:
Workshop venue:
Public
Other
23 November 2011
Honda Academy, Erlensee, Germany
Olaf Henniger (Fraunhofer Institute SIT)
�
Abstract
Car-to-car communication heralds a new era of traffic safety and intelligent traffic manage-
ment, but at the same time also entails new threats. To provide a secure basis for car-to-car
communication, the European research project EVITA designed, verified, and prototyped
security building blocks for automotive on-board networks. The security building blocks are
deployed inside lab cars demonstrating various applications that require security measures. As
the project draws to a close, the EVITA consortium held a Workshop on Security of Auto-
motive On-Board Networks in order to present major results of the project to the public. The
workshop took place at the Honda Academy in Erlensee, Germany, on the day before the Car
2 Car Forum 2011 of the Car 2 Car Communication Consortium. All interested parties were
invited to attend the Final EVITA Workshop.
ii
�
Contents
Hans Brandl (Infineon Technologies AG)
Keynote address: Trusted computing for mobile and embedded systems .......... 1
Yves Roudier (EURECOM)
Motivation, objectives, and approach of the EVITA project ............................ 15
Marko Wolf (escrypt GmbH)
Secure on-board architecture specification ..................................................... 19
Hendrik Schweppe (EURECOM)
Secure on-board protocols ............................................................................... 28
Hervé Seudié (Robert Bosch GmbH)
Integration into AUTOSAR ............................................................................... 37
Benjamin Weyl (BMW Group Research and Technology)
EVITA prototype and demonstrator overview .................................................. 43
Jos Dumortier (K.U. Leuven)
Legal requirements on automotive on-board networks .................................... 52
Frank Kargl (University of Twente)
Uptake of EVITA results in the PRESERVE project ......................................... 56
iii
�
iv
�
Workshop
"Security of Automotive On-Board Networks“
Trusted Computing in
Mobile and Embedded
Systems
23. November 2011
Hans.brandl@infineon.com
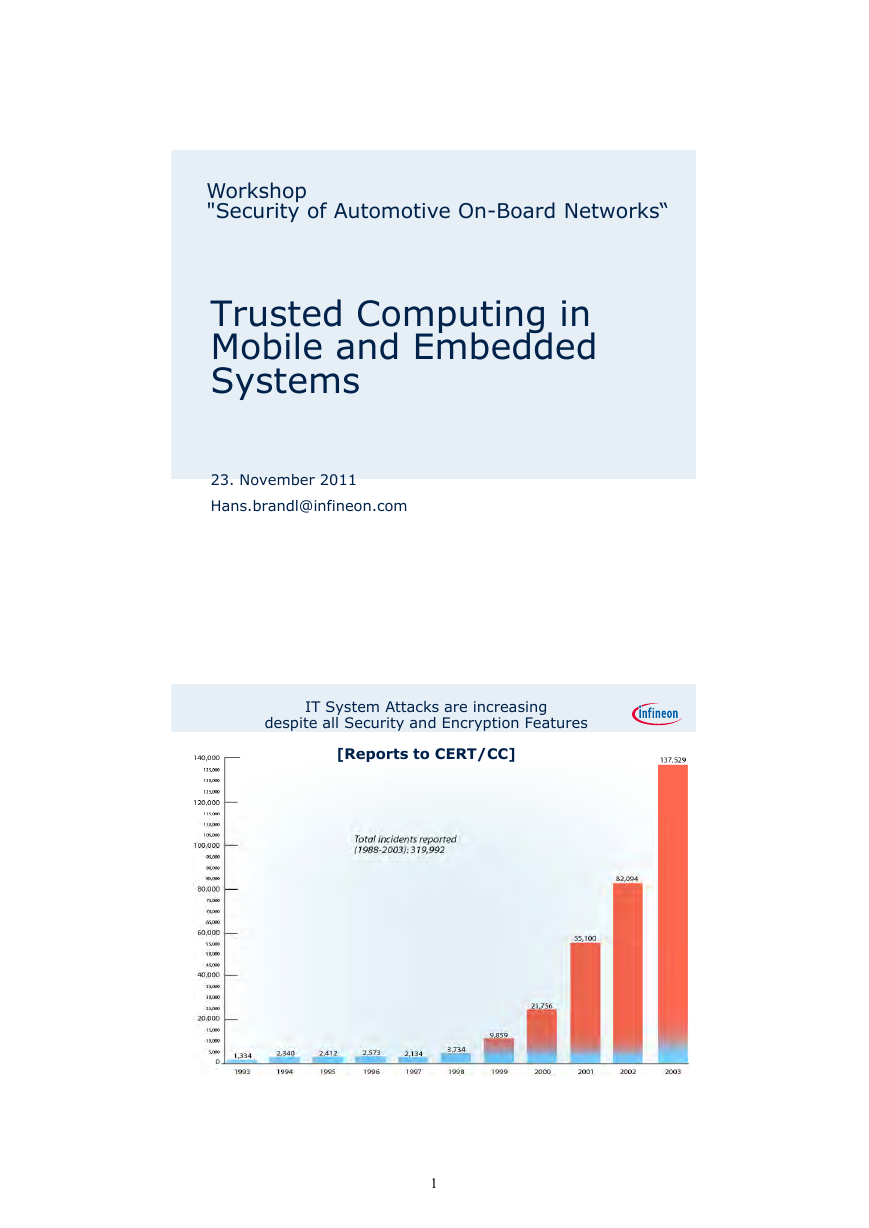
IT System Attacks are increasing
despite all Security and Encryption Features
[Reports to CERT/CC]
Page 2
1�
Computing Platforms:
The Problem and the Solution
Inadequate Security on standard computing Platforms
The problem of platform security exists since the early 70’s
General purpose Computers lack fundamental security
mechanisms. There are encryption modules , but attacks
circumventing.
Most attacks occur through manipulations of the integrity,
not on hacking algorithm!
What is necessary, is an affordable hardware security module
and the necessary OS functionality for the computing
platform, which allows at least
Measurement of the integrity of the platform
Secure storage and digital signing of data, keys and
certificates
Today’s Perception of System Trust
Page 3
Page 4
2�
Who is TCG?
The Trusted Computing Group (TCG) is an international industry
standards group
The TCG develops specifications amongst its members
Upon completion, the TCG publishes the specifications
Anyone may use the specifications once they are published
The TCG publicizes the specifications and uses membership
implementations as examples of the use of TCG Technology
The TCG is organized into a work group model whereby experts
from each technology category can work together to develop the
from each technology category can work together to develop the
specifications
This fosters a neutral environment where competitors and
collaborators can develop industry best capabilities that are
vendor neutral and interoperable
Page 5
TCG Standards and its Community
Global Standardization:
TPM 1.2 spec (2003) is
ISO/IEC 11889 standard
(2008)
(2008)
91 TCG Specifications
published to-date (since
2003)
Worldwide TPM
shipment:
400 million -500 million
Adoption Examples:
Healthcare
Government
E-Commerce
Financial Applications
TCG Community
# of
Organizations
Australia
Austria
Belgium
elgium
Canada
Greater China
Finland
France
Germany
India
Israel
Japan
Korea
Netherlands
Norway
Russia
Sweden
Switzerland
United Kingdom
United States
1
2
1
8
5
1
6
12
1
4
12
3
2
1
1
1
2
11
79
Page 6
3�
Where do we see TCG Technology today?
Commercialized and available
1. High Assurance Platforms (HAP)
2. Self-encrypting drives (SEDs)
3 N t
it (TNC)
3. Network security (TNC)
4. Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs)
k
Applications/solutions that use TCG Technology
1. Machine Identity
2. VPN/wireless access
3. Data at rest
4 SCADA
4. SCADA
5. Clientless endpoint meta data management
6. Hardware-based cloud subscriber management
7. Trusted execution
Page 7
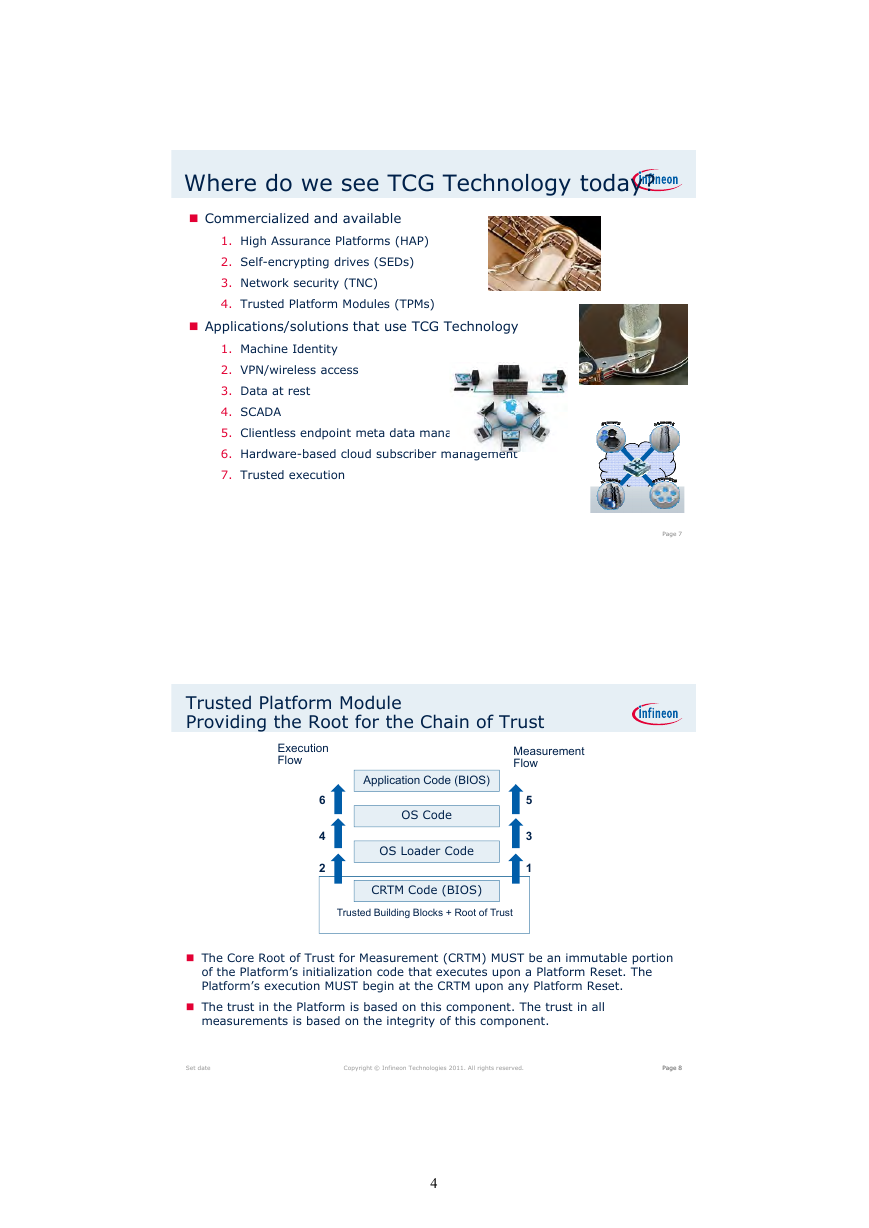
Trusted Platform Module
Providing the Root for the Chain of Trust
Execution
Flow
6
4
2
Measurement
Flow
Application Code (BIOS)
OS Code
OS Code
OS Loader Code
5
3
1
CRTM Code (BIOS)
Trusted Building Blocks + Root of Trust
The Core Root of Trust for Measurement (CRTM) MUST be an immutable portion
of the Platform’s initialization code that executes upon a Platform Reset. The
Platform’s execution MUST begin at the CRTM upon any Platform Reset.
The trust in the Platform is based on this component. The trust in all
measurements is based on the integrity of this component.
Set date
Copyright © Infineon Technologies 2011. All rights reserved.
Page 8
Page 8
4�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc