INCOSE (MBSE)
Model Based System Engineering
(SoS) System of Systems Activity Introduction
Ron Williamson, Ph.D.
Raytheon
ron.williamson@incose.org
Jan 30-31, 2011
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
MBSE Wiki page: http://www.omgwiki.org/mbse
MBSE SoS/Enterprise Modeling Wiki page:
http://www.omgwiki.org/MBSE/doku.php?id=mbse:enterprise
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
1
�
Outline
Introduction
•
• Conceptual Model Summary for SoS
• Concept Representations
– Languages
– Frameworks
– Patterns
• MBSE SoS Challenges
• Systems Language Models for SoS
– SysML (System Modeling Language)
• Architecture Framework (AF) Models for SoS
– UPDM (UML(Unified Modeling Language) Profile for DoDAF/MODAF
• MBSE SoS Case Studies
– Architecture Eco-System Efforts
– UPDM and DoDAF 2.0 DM2
– UPDM and SysML, SoaML, BPMN, BMM, etc.
• Questions…hold for the end of the session
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
2
�
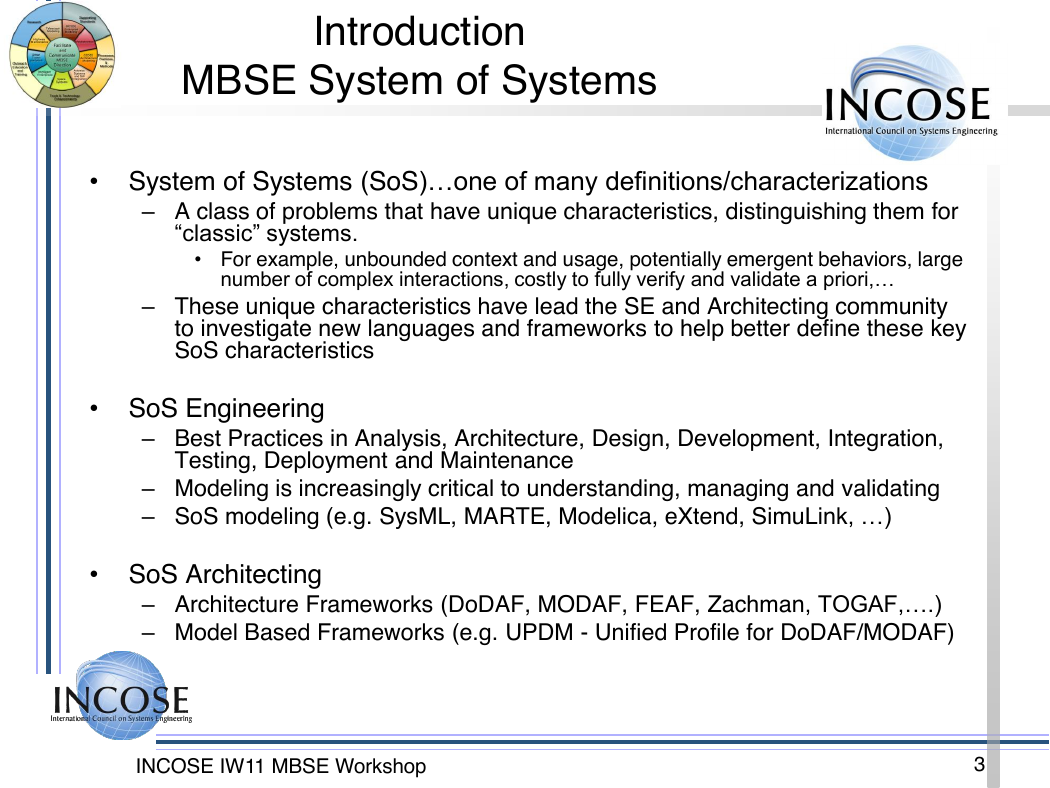
Introduction
MBSE System of Systems
• System of Systems (SoS)…one of many definitions/characterizations
– A class of problems that have unique characteristics, distinguishing them for
“classic” systems.
• For example, unbounded context and usage, potentially emergent behaviors, large
number of complex interactions, costly to fully verify and validate a priori,…
– These unique characteristics have lead the SE and Architecting community
to investigate new languages and frameworks to help better define these key
SoS characteristics
• SoS Engineering
– Best Practices in Analysis, Architecture, Design, Development, Integration,
Testing, Deployment and Maintenance
– Modeling is increasingly critical to understanding, managing and validating
– SoS modeling (e.g. SysML, MARTE, Modelica, eXtend, SimuLink, …)
• SoS Architecting
– Architecture Frameworks (DoDAF, MODAF, FEAF, Zachman, TOGAF,….)
– Model Based Frameworks (e.g. UPDM - Unified Profile for DoDAF/MODAF)
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
3
�
Introduction SoS Engineering
Key Concepts
• SoS Engineering Key
Concepts
– Legacy Systems
– Dynamic Reconfiguration of
Architecture
– Service Oriented Architecture
Enabler
– Protocols and Standards to
Enable Interoperable Systems
– Added “ilities” or Quality
Attributes
– Federated Acquisition
– Independent Systems
– Concept of Operations Critical
– Ongoing Experimentation
– Converging Spirals
SoS Modeling
Implications
Saunders, T. et al, “United States Air Force Scientific Advisory Board Report on System-
of-Systems Engineering for Air Force Capability Development,” SAB-TR-05-04, July 2005
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
4
�
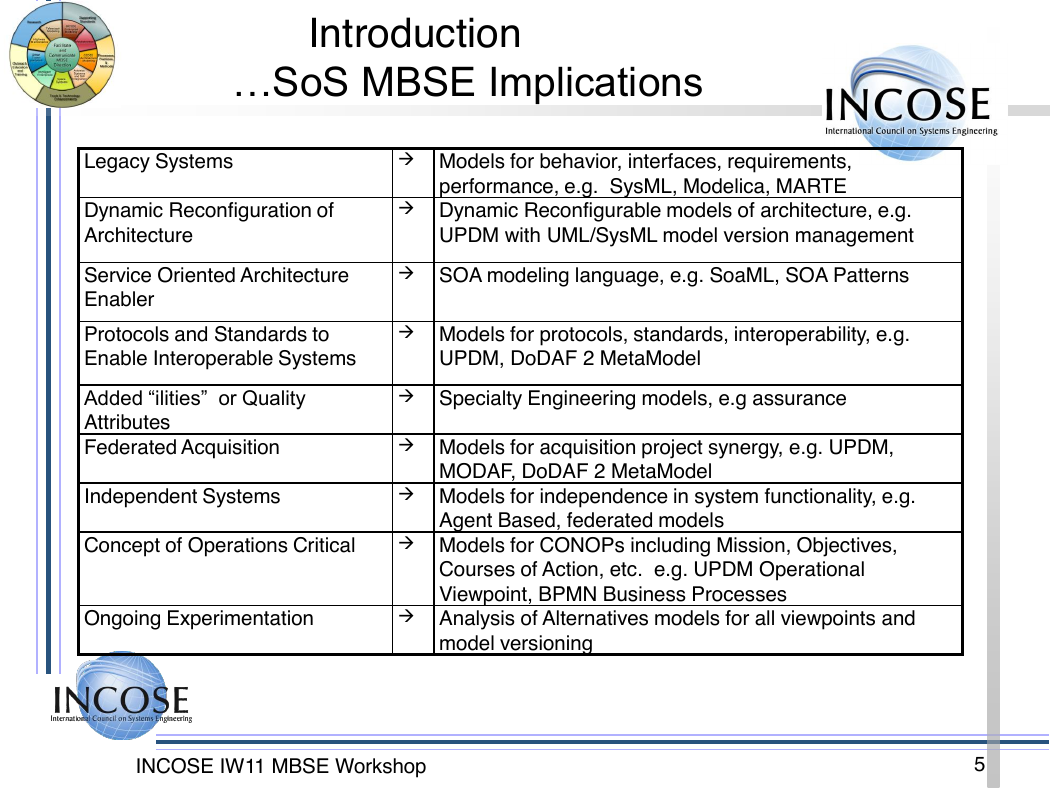
Introduction
…SoS MBSE Implications
Legacy Systems
Models for behavior, interfaces, requirements,
performance, e.g. SysML, Modelica, MARTE
Dynamic Reconfiguration of
Architecture
Dynamic Reconfigurable models of architecture, e.g.
UPDM with UML/SysML model version management
Service Oriented Architecture
Enabler
Protocols and Standards to
Enable Interoperable Systems
Added “ilities” or Quality
Attributes
Federated Acquisition
SOA modeling language, e.g. SoaML, SOA Patterns
Models for protocols, standards, interoperability, e.g.
UPDM, DoDAF 2 MetaModel
Specialty Engineering models, e.g assurance
Models for acquisition project synergy, e.g. UPDM,
MODAF, DoDAF 2 MetaModel
Independent Systems
Models for independence in system functionality, e.g.
Concept of Operations Critical
Models for CONOPs including Mission, Objectives,
Agent Based, federated models
Ongoing Experimentation
Analysis of Alternatives models for all viewpoints and
model versioning
Courses of Action, etc. e.g. UPDM Operational
Viewpoint, BPMN Business Processes
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
5
�
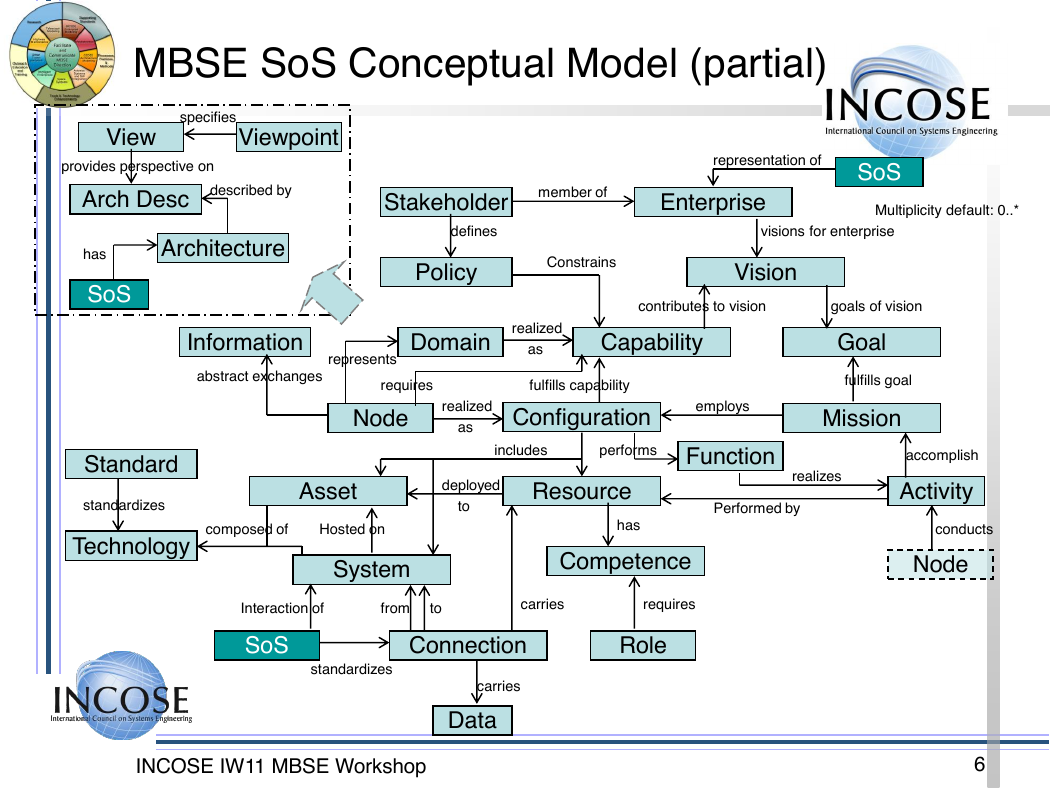
MBSE SoS Conceptual Model (partial)
specifies
View
Viewpoint
provides perspective on
Arch Desc described by
Architecture
has
SoS
Stakeholder
defines
member of
Enterprise
Multiplicity default: 0..*
visions for enterprise
representation of
SoS
Policy
Constrains
Vision
contributes to vision
goals of vision
Information
abstract exchanges
Domain
realized
as
Capability
represents
requires
fulfills capability
Node
realized
as
Configuration
employs
Goal
fulfills goal
Mission
Standard
standardizes
Technology
includes
performs
Function
Asset
deployed
to
Resource
realizes
Performed by
composed of
Hosted on
System
has
Competence
Interaction of
from
to
carries
requires
SoS
Connection
Role
standardizes
carries
Data
accomplish
Activity
conducts
Node
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
6
�
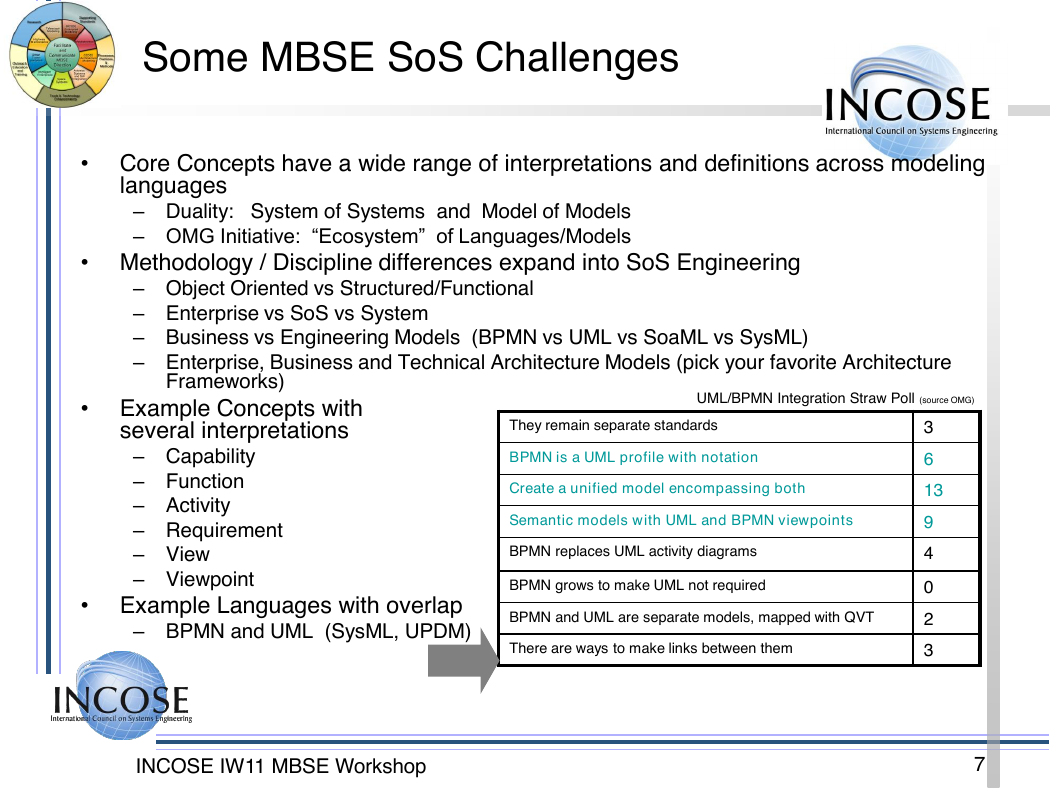
Some MBSE SoS Challenges
• Core Concepts have a wide range of interpretations and definitions across modeling
languages
– Duality: System of Systems and Model of Models
– OMG Initiative: “Ecosystem” of Languages/Models
• Methodology / Discipline differences expand into SoS Engineering
– Object Oriented vs Structured/Functional
– Enterprise vs SoS vs System
– Business vs Engineering Models (BPMN vs UML vs SoaML vs SysML)
– Enterprise, Business and Technical Architecture Models (pick your favorite Architecture
•
•
Frameworks)
Example Concepts with
several interpretations
– Capability
– Function
– Activity
– Requirement
– View
– Viewpoint
Example Languages with overlap
– BPMN and UML (SysML, UPDM)
UML/BPMN Integration Straw Poll (source OMG)
They remain separate standards
BPMN is a UML profile with notation
Create a unified model encompassing both
Semantic models with UML and BPMN viewpoints
BPMN replaces UML activity diagrams
BPMN grows to make UML not required
BPMN and UML are separate models, mapped with QVT
There are ways to make links between them
3
6
13
9
4
0
2
3
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
7
�
Systems Language Models for SoS
• SysML Core Concepts
– Structure, Behavior, Requirements, Parametrics
• View, Viewpoint, Block, Part, Role, Connector, Interface, Item, ItemFlow, Activity, State,
Transition, Requirement, Constraint Block,…
– SoS Core Concepts
• View, Viewpoint, Enterprise, Mission, Projects, Milestone, Vision, Goal, Policy,
Capability, Node, Configuration, Resource, System, Information, Data, Technology,
Standard, Organization, Task, Activity, Measures of Effectiveness, Key Performance
Parameters, “ilities”, Scenario, Workflow…
• SysML/SoS Mapping Example (one of several approaches)
– Structure (Block,…)
• Enterprise, Capability, Configuration, Resource, Systems, Information, Data,
Technology, Organization, Milestone, Vision, Goal, Node, …
– Behavior (Activity, State,…)
• Function, Task, Activity, Scenario, Workflow,
– Requirement
• Policy, Constraint, Standard,…
– Parametrics
• MoE’s, KPP’s, “ilities”…
See UPDM and DoDAF Meta model
References for mapping standards efforts
INCOSE IW11 MBSE Workshop
8
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc