A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Features and Benefits
• Low RDS(on) outputs
• Overcurrent protection (OCP)
▫ Motor short protection
▫ Motor lead short to ground protection
▫ Motor lead short to battery protection
• Low Power Standby mode
• Adjustable PWM current limit
• Synchronous rectification
• Internal undervoltage lockout (UVLO)
• Crossover-current protection
Package: 8-pin SOICN with exposed
thermal pad (suffix LJ)
Description
Designed for pulse width modulated (PWM) control of DC
motors, the A4950 is capable of peak output currents to ±3.5 A
and operating voltages to 40 V.
Input terminals are provided for use in controlling the speed and
direction of a DC motor with externally applied PWM control
signals. Internal synchronous rectification control circuitry is
provided to lower power dissipation during PWM operation.
Internal circuit protection includes overcurrent protection,
motor lead short to ground or supply, thermal shutdown with
hysteresis, undervoltage monitoring of VBB, and crossover-
current protection.
The A4950 is provided in a low-profile 8-pin SOICN package
with exposed thermal pad (suffix LJ) that is lead (Pb) free, with
100% matte tin leadframe plating.
Not to scale
IN1
IN2
GND
VREF
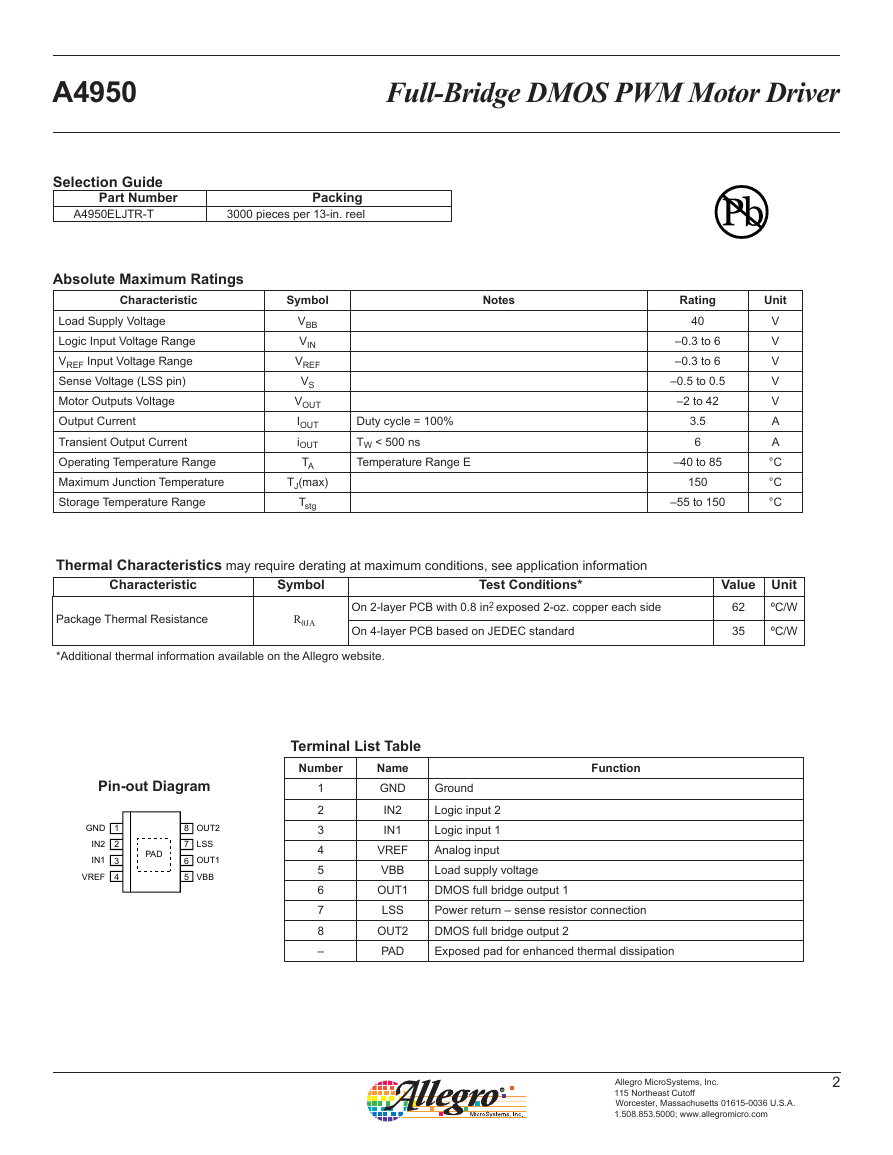
Functional Block Diagram
OSC
Charge
Pump
Control
Logic
Disable
TSD
UVLO
7V
Load Supply
VBB
OUT1
OUT2
LSS
÷
10
(Optional)
A4950-DS, Rev. 2
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Selection Guide
Part Number
A4950ELJTR-T
Packing
3000 pieces per 13-in. reel
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Characteristic
Symbol
Notes
Load Supply Voltage
Logic Input Voltage Range
VREF Input Voltage Range
Sense Voltage (LSS pin)
Motor Outputs Voltage
Output Current
Transient Output Current
Operating Temperature Range
Maximum Junction Temperature
Storage Temperature Range
VBB
VIN
VREF
VS
VOUT
IOUT
iOUT
TA
TJ(max)
Tstg
Duty cycle = 100%
TW < 500 ns
Temperature Range E
Rating
40
–0.3 to 6
–0.3 to 6
–0.5 to 0.5
–2 to 42
3.5
6
–40 to 85
150
–55 to 150
Unit
V
V
V
V
V
A
A
°C
°C
°C
Thermal Characteristics may require derating at maximum conditions, see application information
Characteristic
Package Thermal Resistance
Symbol
RθJA
Test Conditions*
On 2-layer PCB with 0.8 in2. exposed 2-oz. copper each side
On 4-layer PCB based on JEDEC standard
Value Unit
ºC/W
62
35
ºC/W
*Additional thermal information available on the Allegro website.
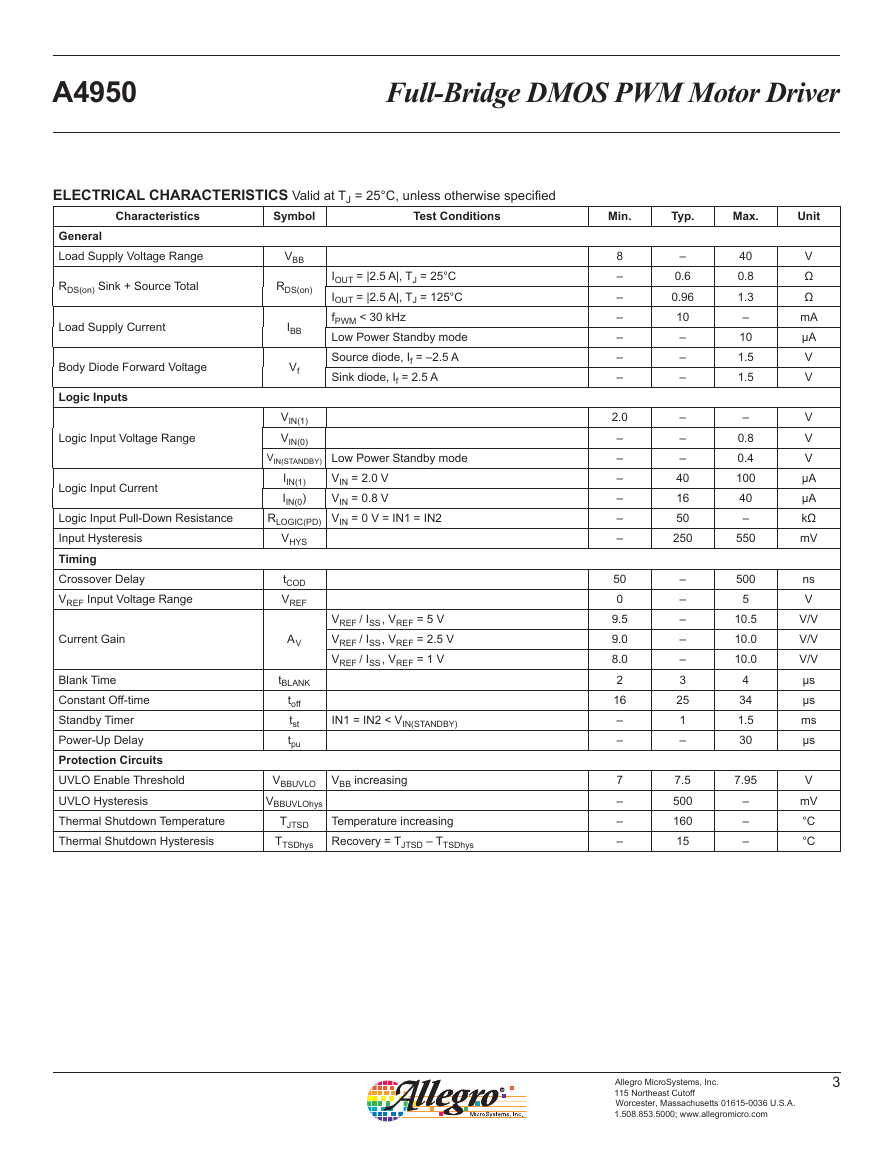
Pin-out Diagram
GND
IN2
IN1
VREF
1
2
3
4
PAD
8
7
6
5
OUT2
LSS
OUT1
VBB
Terminal List Table
Number
Name
GND
IN2
IN1
VREF
VBB
OUT1
LSS
OUT2
PAD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
–
Function
Ground
Logic input 2
Logic input 1
Analog input
Load supply voltage
DMOS full bridge output 1
Power return – sense resistor connection
DMOS full bridge output 2
Exposed pad for enhanced thermal dissipation
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
2
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Valid at TJ = 25°C, unless otherwise specified
Characteristics
Symbol
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
General
Load Supply Voltage Range
RDS(on) Sink + Source Total
Load Supply Current
Body Diode Forward Voltage
Logic Inputs
Logic Input Voltage Range
Logic Input Current
Logic Input Pull-Down Resistance
Input Hysteresis
Timing
Crossover Delay
VREF Input Voltage Range
Current Gain
Blank Time
Constant Off-time
Standby Timer
Power-Up Delay
Protection Circuits
UVLO Enable Threshold
UVLO Hysteresis
Thermal Shutdown Temperature
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis
IOUT = |2.5 A|, TJ = 25°C
IOUT = |2.5 A|, TJ = 125°C
fPWM < 30 kHz
Low Power Standby mode
Source diode, If = –2.5 A
Sink diode, If = 2.5 A
VBB
RDS(on)
IBB
Vf
VIN(1)
VIN(0)
VIN(STANDBY) Low Power Standby mode
IIN(1)
IIN(0)
VIN = 2.0 V
VIN = 0.8 V
RRRLOGIC(PD) VIN = 0 V = IN1 = IN2
VHYS
tCOD
VREF
A V
tBLANK
toff
tst
tpu
VREF / ISS , VREF = 5 V
VREF / ISS , VREF = 2.5 V
VREF / ISS , VREF = 1 V
IN1 = IN2 < VIN(STANDBY)
VBBUVLO
VBBUVLOhys
VBB increasing
TJTSD
TTSDhys
Temperature increasing
Recovery = TJTSD – TTSDhys
8
–
–
–
–
–
–
2.0
–
–
–
–
–
–
50
0
9.5
9.0
8.0
2
16
–
–
7
–
–
–
–
0.6
0.96
10
–
–
–
–
–
–
40
16
50
250
–
–
–
–
–
3
25
1
–
7.5
500
160
15
40
0.8
1.3
–
10
1.5
1.5
–
0.8
0.4
100
40
–
550
500
5
10.5
10.0
10.0
4
34
1.5
30
7.95
–
–
–
V
Ω
Ω
mA
μA
V
V
V
V
V
μA
μA
kΩ
mV
ns
V
V/V
V/V
V/V
μs
μs
ms
μs
V
mV
°C
°C
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
3
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Characteristic Performance
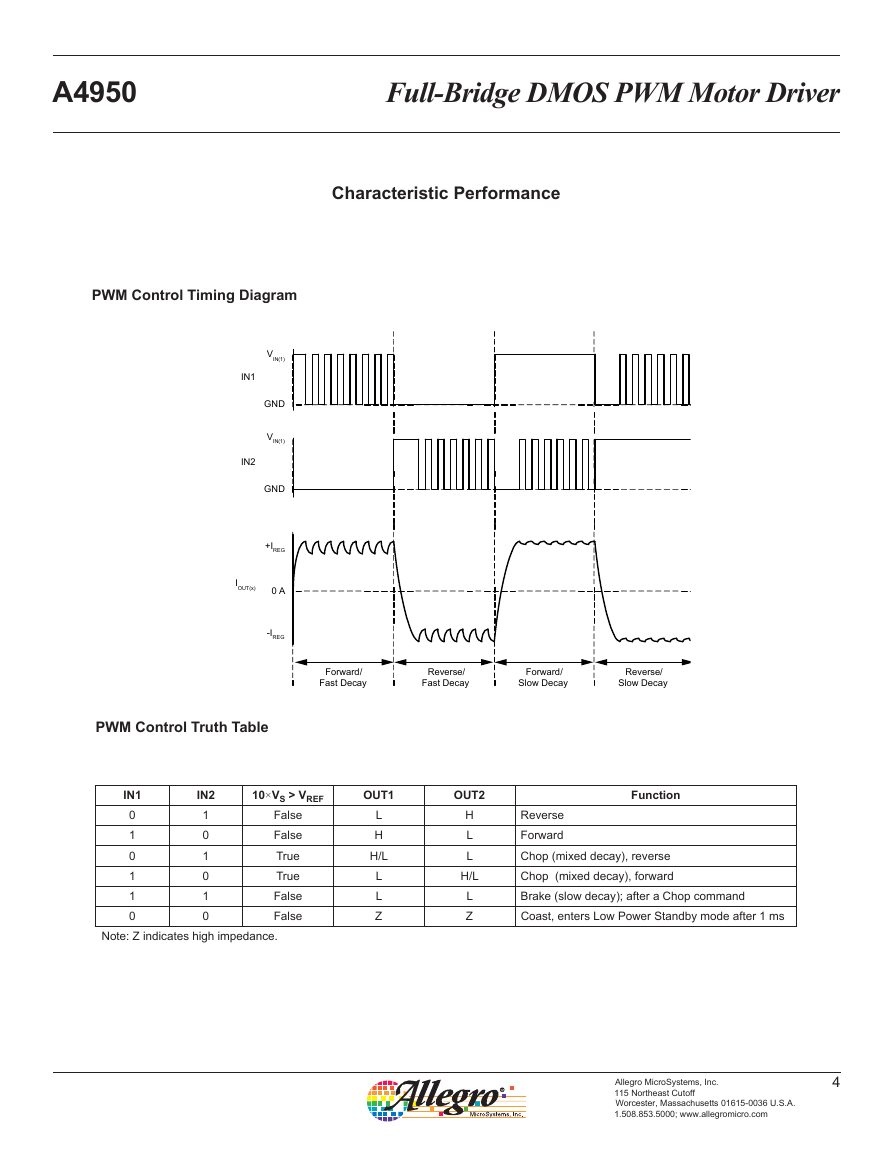
PWM Control Timing Diagram
IN1
IN2
VIN(1)
GND
VIN(1)
GND
+IREG
IOUT(x)
0 A
-IREG
Forward/
Fast Decay
Reverse/
Fast Decay
Forward/
Slow Decay
Reverse/
Slow Decay
PWM Control Truth Table
IN1
0
1
0
1
1
0
IN2
1
0
1
0
1
0
10×VS > VREF
OUT1
OUT2
Function
False
False
True
True
False
False
L
H
H/L
L
L
Z
H
L
L
H/L
L
Z
Reverse
Forward
Chop (mixed decay), reverse
Chop (mixed decay), forward
Brake (slow decay); after a Chop command
Coast, enters Low Power Standby mode after 1 ms
Note: Z indicates high impedance.
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
4
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Functional Description
Device Operation
The A4950 is designed to operate DC motors. The output drivers
are all low-RDS(on) , N-channel DMOS drivers that feature inter-
nal synchronous rectification to reduce power dissipation. The
current in the output full bridge is regulated with fixed off-time
pulse width modulated (PWM) control circuitry. The IN1 and IN2
inputs allow two-wire control for the bridge.
Protection circuitry includes internal thermal shutdown, and pro-
tection against shorted loads, or against output shorts to ground
or supply. Undervoltage lockout prevents damage by keeping the
outputs off until the driver has enough voltage to operate nor-
mally.
Standby Mode
Low Power Standby mode is activated when both input (INx)
pins are low for longer than 1 ms. Low Power Standby mode
disables most of the internal circuitry, including the charge pump
and the regulator. When the A4950 is coming out of standby
mode, the charge pump should be allowed to reach its regulated
voltage (a maximum delay of 200 μs) before any PWM com-
mands are issued to the device.
Internal PWM Current Control
Initially, a diagonal pair of source and sink FET outputs are
enabled and current flows through the motor winding and the
optional external current sense resistor, RS . When the voltage
across RS equals the comparator trip value, then the current sense
comparator resets the PWM latch. The latch then turns off the
sink and source FETs (Mixed Decay mode).
VREF
The maximum value of current limiting is set by the selection of
RSx and the voltage at the VREF pin. The transconductance func-
tion is approximated by the maximum value of current limiting,
ITripMAX (A), which is set by:
VREF
ITripMAX = 10 RS
where VREF is the input voltage on the VREF pin (V) and RS is
the resistance of the sense resistor (Ω) on the LSS terminal.
Overcurrent Protection
A current monitor will protect the IC from damage due to output
shorts. If a short is detected, the IC will latch the fault and disable
the outputs. The fault latch can only be cleared by coming out of
Low Power Standby mode or by cycling the power to VBB. Dur-
ing OCP events, Absolute Maximum Ratings may be exceeded
for a short period of time before the device latches.
Shutdown
If the die temperature increases to approximately 160°C, the full
bridge outputs will be disabled until the internal temperature falls
below a hysteresis, TTSDhys , of 15°C. Internal UVLO is present
on VBB to prevent the output drivers from turning-on below the
UVLO threshold.
Braking
The braking function is implemented by driving the device in
Slow Decay mode, which is done by applying a logic high to both
inputs, after a bridge-enable Chop command (see PWM Control
Truth Table). Because it is possible to drive current in both direc-
tions through the DMOS switches, this configuration effectively
shorts-out the motor-generated BEMF, as long as the Chop com-
mand is asserted. The maximum current can be approximated by
VBEMF / RL . Care should be taken to ensure that the maximum
ratings of the device are not exceeded in worse case braking situ-
ations: high speed and high-inertia loads.
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
5
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Synchronous Rectification
When a PWM off-cycle is triggered by an internal fixed off-time
cycle, load current will recirculate. The A4950 synchronous rec-
tification feature turns-on the appropriate DMOSFETs during the
current decay, and effectively shorts out the body diodes with the
low RDS(on) driver. This significantly lowers power dissipation.
When a zero current level is detected, synchronous rectification is
turned off to prevent reversal of the load current.
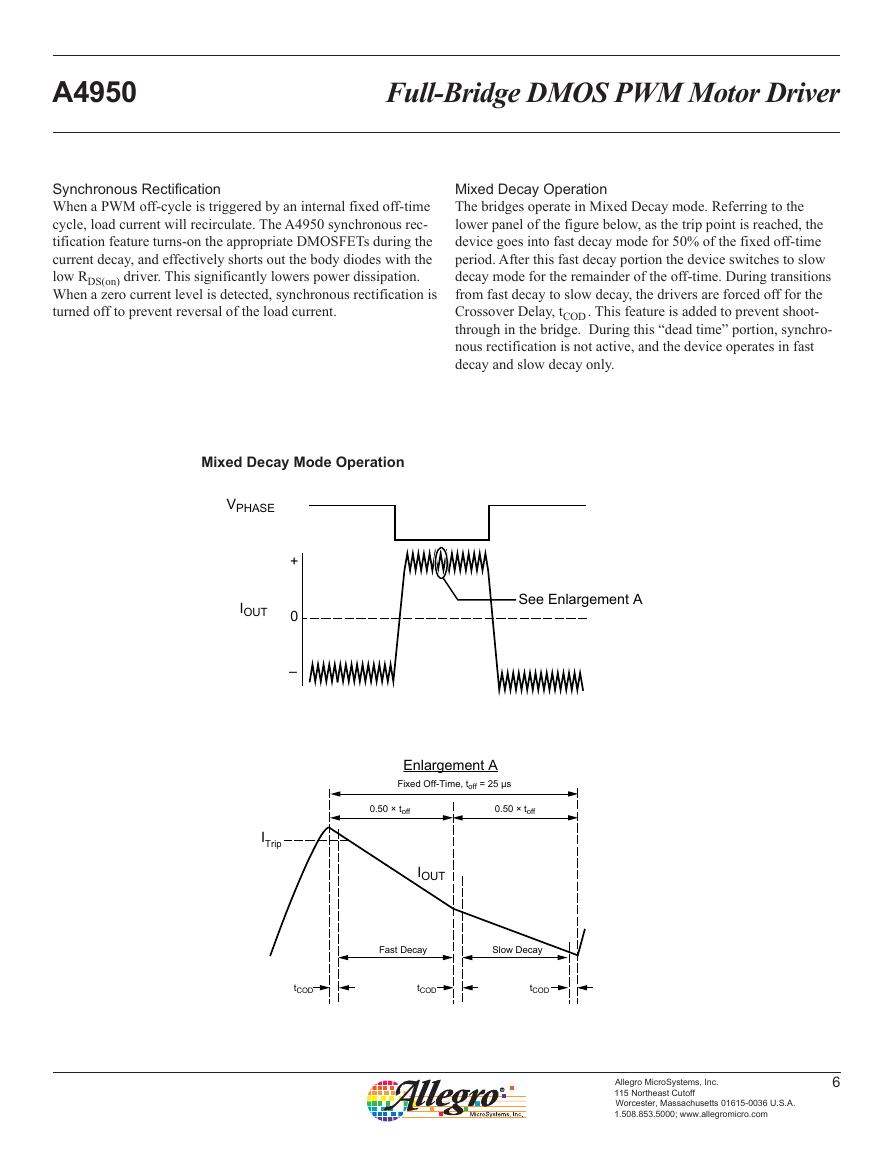
Mixed Decay Operation
The bridges operate in Mixed Decay mode. Referring to the
lower panel of the figure below, as the trip point is reached, the
device goes into fast decay mode for 50% of the fixed off-time
period. After this fast decay portion the device switches to slow
decay mode for the remainder of the off-time. During transitions
from fast decay to slow decay, the drivers are forced off for the
Crossover Delay, tCOD . This feature is added to prevent shoot-
through in the bridge. During this “dead time” portion, synchro-
nous rectification is not active, and the device operates in fast
decay and slow decay only.
Mixed Decay Mode Operation
VPHASE
IOUT
+
0
–
See Enlargement A
Enlargement A
Fixed Off-Time, toff = 25 μs
0.50 × toff
0.50 × toff
ITrip
IOUT
Fast Decay
Slow Decay
tCOD
tCOD
tCOD
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
6
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Application Information
Sense Pin (LSS)
In order to use PWM current control, a low-value resistor is
placed between the LSS pin and ground for current sensing pur-
poses. To minimize ground-trace IR drops in sensing the output
current level, the current sensing resistor should have an indepen-
dent ground return to the star ground point. This trace should be
as short as possible. For low-value sense resistors, the IR drops in
the PCB can be significant, and should be taken into account.
When selecting a value for the sense resistor be sure not to
exceed the maximum voltage on the LSS pin of ±500 mV at
maximum load. During overcurrent events, this rating may be
exceeded for short durations.
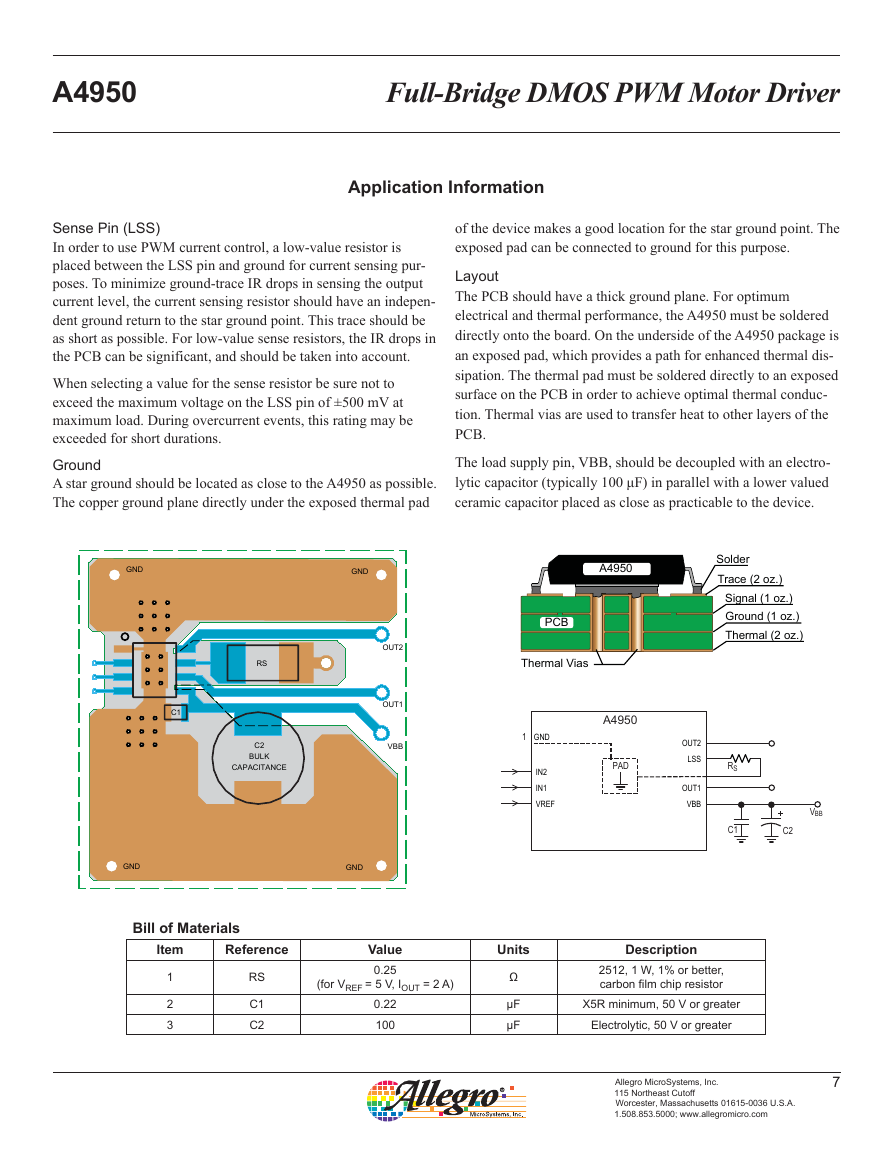
Ground
A star ground should be located as close to the A4950 as possible.
The copper ground plane directly under the exposed thermal pad
of the device makes a good location for the star ground point. The
exposed pad can be connected to ground for this purpose.
Layout
The PCB should have a thick ground plane. For optimum
electrical and thermal performance, the A4950 must be soldered
directly onto the board. On the underside of the A4950 package is
an exposed pad, which provides a path for enhanced thermal dis-
sipation. The thermal pad must be soldered directly to an exposed
surface on the PCB in order to achieve optimal thermal conduc-
tion. Thermal vias are used to transfer heat to other layers of the
PCB.
The load supply pin, VBB, should be decoupled with an electro-
lytic capacitor (typically 100 μF) in parallel with a lower valued
ceramic capacitor placed as close as practicable to the device.
GND
GND
A4950
C1
RS
C2
BULK
CAPACITANCE
OUT2
OUT1
VBB
GND
GND
PCB
Thermal Vias
A4950
PAD
1
GND
IN2
IN1
VREF
Solder
Trace (2 oz.)
Signal (1 oz.)
Ground (1 oz.)
Thermal (2 oz.)
OUT2
LSS
OUT1
VBB
RS
C1
VBB
C2
Bill of Materials
Item
Reference
1
2
3
RS
C1
C2
Value
0.25
(for VREF = 5 V, IOUT = 2 A)
0.22
100
Units
Ω
μF
μF
Description
2512, 1 W, 1% or better,
carbon film chip resistor
X5R minimum, 50 V or greater
Electrolytic, 50 V or greater
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
7
�
A4950
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver
Package LJ, 8-Pin SOICN
with exposed thermal pad
4.90 ±0.10
8
A
2.41 NOM
B
3.90 ±0.10
6.00 ±0.20
1
2
3.30 NOM
8X
0.10
C
0.51
0.31
1.27 BSC
Branded Face
C
C
SEATING
SEATING
PLANE
PLANE
1.70 MAX
0.15
0.00
8°
0°
0.25
0.17
1.04 REF
1.27
0.40
0.25 BSC
SEATING PLANE
GAUGE PLANE
1.27
2.41
5.60
0.65
1.75
8
1
2
3.30
C
PCB Layout Reference View
For Reference Only; not for tooling use (reference MS-012BA)
Dimensions in millimeters
Dimensions exclusive of mold flash, gate burrs, and dambar protrusions
Exact case and lead configuration at supplier discretion within limits shown
A Terminal #1 mark area
B
C
Exposed thermal pad (bottom surface); dimensions may vary with device
Reference land pattern layout (reference IPC7351
SOIC127P600X175-9AM); all pads a minimum of 0.20 mm from all
adjacent pads; adjust as necessary to meet application process
requirements and PCB layout tolerances; when mounting on a multilayer
PCB, thermal vias at the exposed thermal pad land can improve thermal
dissipation (reference EIA/JEDEC Standard JESD51-5)
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
8
�









 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc