1912 制作
C++/C 试题
本试题仅用于考查 C++/C 程序员的基本编程技能。内容限于 C++/C 常用语法,不涉及
数据结构、算法以及深奥的语法。考试成绩能反映出考生的编程质量以及对 C++/C 的理解
程度,但不能反映考生的智力和软件开发能力。
笔试时间 90 分钟。请考生认真答题,切勿轻视。
一、请填写 BOOL , float, 指针变量 与“零值”比较的 if 语句。(10 分)
提示:这里“零值”可以是 0, 0.0 , FALSE 或者“空指针”。例如 int 变量 n 与“零值”比较的 if
语句为:
if ( n == 0 )
if ( n != 0 )
以此类推。
请写出 BOOL flag 与“零值”比较的 if 语句:
请写出 float x 与“零值”比较的 if 语句:
请写出 char *p 与“零值”比较的 if 语句:
二、以下为 Windows NT 下的 32 位 C++程序,请计算 sizeof 的值(10 分)
char str[] = “Hello” ;
char *p = str ;
int n = 10;
请计算
void Func ( char str[100])
{
请计算
sizeof( str ) =
sizeof (str ) =
}
sizeof ( p ) =
请计算
void *p = malloc( 100 );
sizeof ( p ) =
sizeof ( n ) =
三、简答题(25 分)
1、头文件中的 ifndef/define/endif 干什么用?
2、#include
和 #include “filename.h” 有什么区别?
3、const 有什么用途?(请至少说明两种)
4、在 C++ 程序中调用被 C 编译器编译后的函数,为什么要加 extern “C”声明?
5、请简述以下两个 for 循环的优缺点
// 第一个
for (i=0; i优点:
缺点:
for (i=0; i
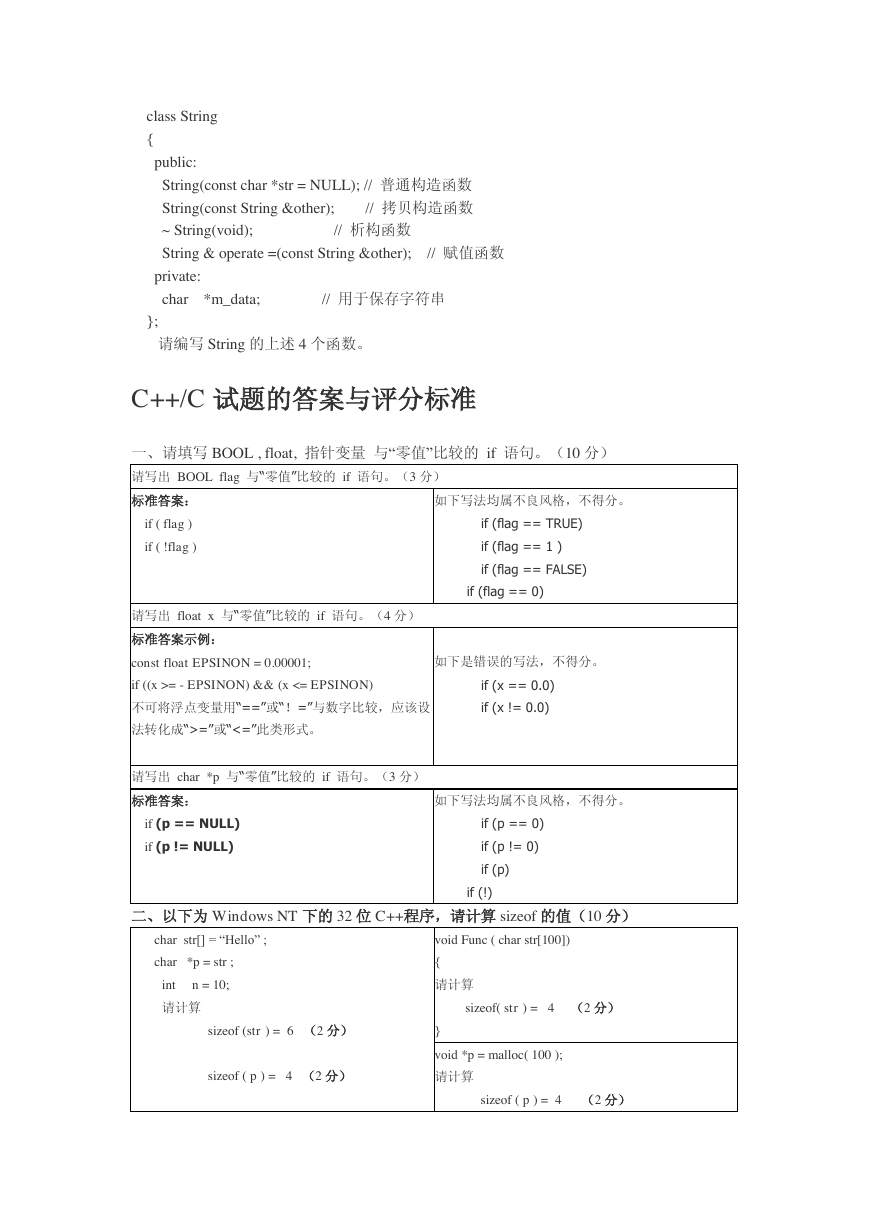
class String
{
public:
String(const char *str = NULL); // 普通构造函数
String(const String &other); // 拷贝构造函数
~ String(void); // 析构函数
String & operate =(const String &other); // 赋值函数
private:
char *m_data; // 用于保存字符串
};
请编写 String 的上述 4 个函数。
C++/C 试题的答案与评分标准
一、请填写 BOOL , float, 指针变量 与“零值”比较的 if 语句。(10 分)
请写出 BOOL flag 与“零值”比较的 if 语句。(3 分)
标准答案:
if ( flag )
if ( !flag )
如下写法均属不良风格,不得分。
if (flag == TRUE)
if (flag == 1 )
if (flag == FALSE)
if (flag == 0)
请写出 float x 与“零值”比较的 if 语句。(4 分)
标准答案示例:
const float EPSINON = 0.00001;
如下是错误的写法,不得分。
if ((x >= - EPSINON) && (x <= EPSINON)
if (x == 0.0)
不可将浮点变量用“==”或“!=”与数字比较,应该设
if (x != 0.0)
法转化成“>=”或“<=”此类形式。
请写出 char *p 与“零值”比较的 if 语句。(3 分)
标准答案:
if (p == NULL)
if (p != NULL)
如下写法均属不良风格,不得分。
if (p == 0)
if (p != 0)
if (p)
if (!)
二、以下为 Windows NT 下的 32 位 C++程序,请计算 sizeof 的值(10 分)
char str[] = “Hello” ;
char *p = str ;
int n = 10;
请计算
void Func ( char str[100])
{
请计算
sizeof( str ) = 4 (2 分)
sizeof (str ) = 6 (2 分)
}
sizeof ( p ) = 4 (2 分)
请计算
void *p = malloc( 100 );
sizeof ( p ) = 4 (2 分)
�
sizeof ( n ) = 4 (2 分)
三、简答题(25 分)
1、头文件中的 ifndef/define/endif 干什么用?(5 分)
答:防止该头文件被重复引用。
2、#include
和 #include “filename.h” 有什么区别?(5 分)
答:对于#include ,编译器从标准库路径开始搜索 filename.h
对于#include “filename.h” ,编译器从用户的工作路径开始搜索 filename.h
3、const 有什么用途?(请至少说明两种)(5 分)
答:(1)可以定义 const 常量
(2)const 可以修饰函数的参数、返回值,甚至函数的定义体。被 const 修饰的东西都
受到强制保护,可以预防意外的变动,能提高程序的健壮性。
4、在 C++ 程序中调用被 C 编译器编译后的函数,为什么要加 extern “C”? (5 分)
答:C++语言支持函数重载,C 语言不支持函数重载。函数被 C++编译后在库中的名字与 C
语言的不同。假设某个函数的原型为: void foo(int x, int y);
该函数被 C 编译器编译后在库中的名字为_foo,而 C++编译器则会产生像_foo_int_int
之类的名字。
C++提供了 C 连接交换指定符号 extern“C”来解决名字匹配问题。
5、请简述以下两个 for 循环的优缺点(5 分)
for (i=0; i}
}
请问运行 Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
请问运行 Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
答:程序崩溃。
答:可能是乱码。
因为 GetMemory 并不能传递动态内存,
因为 GetMemory 返回的是指向“栈内存”的指针,该
Test 函数中的 str 一直都是 NULL。
指针的地址不是 NULL,但其原现的内容已经被清
strcpy(str, "hello world");将使程序崩溃。
除,新内容不可知。
void GetMemory2(char **p, int num)
void Test(void)
{
{
*p = (char *)malloc(num);
char *str = (char *) malloc(100);
}
void Test(void)
{
}
char *str = NULL;
GetMemory(&str, 100);
strcpy(str, "hello");
printf(str);
strcpy(str, “hello”);
free(str);
if(str != NULL)
{
strcpy(str, “world”);
printf(str);
}
}
请问运行 Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
请问运行 Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
答:
(1)能够输出 hello
(2)内存泄漏
答:篡改动态内存区的内容,后果难以预料,非常危
险。
因为 free(str);之后,str 成为野指针,
if(str != NULL)语句不起作用。
五、编写 strcpy 函数(10 分)
已知 strcpy 函数的原型是
char *strcpy(char *strDest, const char *strSrc);
其中 strDest 是目的字符串,strSrc 是源字符串。
(1)不调用 C++/C 的字符串库函数,请编写函数 strcpy
char *strcpy(char *strDest, const char *strSrc);
{
assert((strDest!=NULL) && (strSrc !=NULL)); // 2 分
char *address = strDest; // 2 分
while( (*strDest++ = * strSrc++) != „\0‟ ) // 2 分
NULL ;
return address ; // 2 分
}
(2)strcpy 能把 strSrc 的内容复制到 strDest,为什么还要 char * 类型的返回值?
答:为了实现链式表达式。 // 2 分
例如 int length = strlen( strcpy( strDest, “hello world”) );
六、编写类 String 的构造函数、析构函数和赋值函数(25 分)
已知类 String 的原型为:
class String
{
public:
�
String(const char *str = NULL); // 普通构造函数
String(const String &other); // 拷贝构造函数
~ String(void); // 析构函数
String & operate =(const String &other); // 赋值函数
private:
char *m_data; // 用于保存字符串
};
请编写 String 的上述 4 个函数。
标准答案:
// String 的析构函数
String::~String(void) // 3 分
{
delete [] m_data;
// 由于 m_data 是内部数据类型,也可以写成 delete m_data;
}
// String 的普通构造函数
String::String(const char *str) // 6 分
{
if(str==NULL)
{
m_data = new char[1]; // 若能加 NULL 判断则更好
*m_data = „\0‟;
}
else
{
int length = strlen(str);
m_data = new char[length+1]; // 若能加 NULL 判断则更好
strcpy(m_data, str);
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
String::String(const String &other) // 3 分
{
int length = strlen(other.m_data);
m_data = new char[length+1]; // 若能加 NULL 判断则更好
strcpy(m_data, other.m_data);
}
// 赋值函数
String & String::operate =(const String &other) // 13 分
{
// (1) 检查自赋值 // 4 分
if(this == &other)
return *this;
�
// (2) 释放原有的内存资源 // 3 分
delete [] m_data;
// (3)分配新的内存资源,并复制内容 // 3 分
int length = strlen(other.m_data);
m_data = new char[length+1]; // 若能加 NULL 判断则更好
strcpy(m_data, other.m_data);
// (4)返回本对象的引用 // 3 分
return *this;
}
�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc