Cover
Notice
Description of Registers
Notes for CMOS devices
How to Use This Manual
Table of Contents
Section 1 Overview
1.1 RH850/F1L Products Features
1.1.1 RH850/F1L Functions
1.1.2 Internal Block Diagram
Section 2 Pin Function
2.1 Pin Connection Diagram
2.2 Pin Description
2.3 Ports and Pin Functions During and After Reset
2.4 Port State in Standby Mode
2.5 Recommended Connection of Unused Pins
2.6 RH850/F1L Port Features
2.6.1 Port Group
2.6.2 Port Group Index n
2.6.3 Register Base Address
2.7 Port Functions
2.7.1 Functional Overview
2.7.2 Terms
2.7.2.1 JTAG Ports
2.7.3 Overview of Pin Functions
2.7.4 Pin Data Input/Output
2.7.4.1 Output Data
2.7.4.2 Input Data
2.7.4.3 Writing to the Pn Register
2.8 Port Type
2.9 Port Group Configuration Registers
2.9.1 Overview
2.9.2 Pin Function Configuration
2.9.2.1 PMCn / JPMC0 — Port Mode Control Register
2.9.2.2 PMCSRn / JPMCSR0 — Port Mode Control Set/Reset Register
2.9.2.3 PIPCn — Port IP Control Register
2.9.2.4 PMn / APMn / JPM0 — Port Mode Register
2.9.2.5 PMSRn / APMSRn / JPMSR0 — Port Mode Set/Reset Register
2.9.2.6 PIBCn / APIBCn / JPIBC0 / IPIBCn — Port Input Buffer Control Register
2.9.2.7 PFCn / JPFC0 — Port Function Control Register
2.9.2.8 PFCEn — Port Function Control Expansion Register
2.9.2.9 PFCAEn — Port Function Control Additional Expansion Register
2.9.3 Pin Data Input/Output
2.9.3.1 PBDCn / APBDCn / JPBDC0 — Port Bidirection Control Register
2.9.3.2 PPRn / APPRn / JPPR0 / IPPR0 — Port Pin Read Register
2.9.3.3 Pn / APn / JP0 — Port Register
2.9.3.4 PNOTn / APNOTn / JPNOT0 — Port NOT Register
2.9.3.5 PSRn / APSRn / JPSR0 — Port Set/Reset Register
2.9.4 Configuration of Electrical Characteristics Registers
2.9.4.1 PUn / JPU0 — Pull-Up Option Register
2.9.4.2 PDn / JPD0 — Pull-Down Option Register
2.9.4.3 PDSCn — Port Drive Strength Control Register
2.9.4.4 PODCn / JPODC0 — Port Open Drain Control Register
2.9.4.5 PISn — Port Input Buffer Selection Register
2.9.5 Port Register Protection
2.9.6 Flowchart Example for Port Settings
2.9.6.1 Batch Setting
2.9.6.2 Individual Settings
2.10 Port (General I/O) Function Overview
2.10.1 JTAG Port 0 (JP0)
2.10.1.1 Alternative Function
2.10.1.2 Control Registers
2.10.2 Port 0 (P0)
2.10.2.1 Alternative Function
2.10.2.2 Control Registers
2.10.3 Port 1 (P1)
2.10.3.1 Alternative Function
2.10.3.2 Control Registers
2.10.4 Port 2 (P2)
2.10.4.1 Alternative Function
2.10.4.2 Control Registers
2.10.5 Port 8 (P8)
2.10.5.1 Alternative Function
2.10.5.2 Control Registers
2.10.6 Port 9 (P9)
2.10.6.1 Alternative Function
2.10.6.2 Control Registers
2.10.7 Port 10 (P10)
2.10.7.1 Alternative Function
2.10.7.2 Control Registers
2.10.8 Port 11 (P11)
2.10.8.1 Alternative Function
2.10.8.2 Control Registers
2.10.9 Port 12 (P12)
2.10.9.1 Alternative Function
2.10.9.2 Control Registers
2.10.10 Port 18 (P18)
2.10.10.1 Alternative Function
2.10.10.2 Control Registers
2.10.11 Port 20 (P20)
2.10.11.1 Alternative Function
2.10.11.2 Control Registers
2.10.12 Analog Port 0 (AP0)
2.10.12.1 Alternative Function
2.10.12.2 Control Registers
2.10.13 Analog Port 1 (AP1)
2.10.13.1 Alternative Function
2.10.13.2 Control Registers
2.10.14 Input Port 0 (IP0)
2.10.14.1 Alternative Function
2.10.14.2 Control Registers
2.11 Port (Special I/O) Function Overview
2.11.1 Special I/O after Reset
2.11.1.1 P0_0: RESETOUT
2.11.1.2 JP0_0 to JP0_5: Debug Interface
2.11.1.3 JP0_0, JP0_1, JP0_2: Flash Programmer
2.11.1.4 Mode Pins
2.11.2 A/D Input Alternative I/O
2.11.3 Special I/O Control
2.11.3.1 Direct I/O Control (PIPC)
2.11.3.2 Input Buffer Control (PIS)
2.11.3.3 Output Buffer Control (PDSC)
2.12 Noise Filter & Edge/Level Detector
2.12.1 Port Filter Assignment
2.12.1.1 Input Pins that Incorporate Analog Filter Type A
2.12.1.2 Input Pins that Incorporate Analog Filter Type B
2.12.1.3 Input Pins that Incorporate Analog Filter Type C
2.12.1.4 Input Pins that Incorporate Digital Filter Type D
2.12.1.5 Input Pins that Incorporate Digital Filter Type E
2.12.2 Clock Supply for Port Filters
2.13 Description of Port Noise Filter & Edge/Level Detection
2.13.1 Overview
2.13.1.1 Analog Filter Types
2.13.1.2 Digital Filter Types
2.13.2 Analog Filters
2.13.2.1 Analog Filter Characteristic
2.13.2.2 Analog Filters Control Registers
2.13.2.3 Analog Filters in Standby Mode
2.13.3 Digital Filters
2.13.3.1 Digital Filter Characteristic
2.13.3.2 Digital Filter Groups
2.13.3.3 Digital Filters in Standby Mode
2.13.3.4 Digital Filters Control Registers
2.13.4 Filter Control Registers
2.13.4.1 FCLA0CTLm_ — Filter Control Register
2.13.4.2 DNFACTL — Digital Noise Elimination Control Register
2.13.4.3 DNFAEN — Digital Noise Elimination Enable Register
Section 3 CPU System
3.1 Overview
3.1.1 Architectural Features
3.1.1.1 CPU
3.1.1.2 Coprocessor
3.1.1.3 Exceptions and Interrupts
3.1.1.4 Memory Management
3.1.1.5 System Register Protection (SRP)
3.1.1.6 Functions not Supported
3.1.2 Power Supply and Clock
3.1.3 RH850/F1L CPU Subsystem
3.2 Processor Model
3.2.1 CPU Operating Mode
3.2.2 Hardware Thread
3.2.3 CPU Data Address and Physical Program Address Space
3.2.3.1 Program Space and Data Space
3.2.3.2 Wrap-Around of Data Space
3.2.3.3 Wrap-Around of Program Space
3.2.4 RH850/F1L Memory Map
3.2.4.1 Code Flash Area
3.2.4.2 Data Flash Area
3.2.4.3 Primary Local RAM Area
3.2.4.4 Secondary Local RAM Area
3.2.4.5 Retention RAM Area
3.3 Register Reference
3.3.1 PC — Program Counter
3.3.2 Basic System Registers
3.3.2.1 EIPC — Status Save Register when Acknowledging EI Level Exception
3.3.2.2 EIPSW — Status Save Register when Acknowledging EI Level Exception
3.3.2.3 FEPC — Status Save Register when Acknowledging FE Level Exception
3.3.2.4 FEPSW — Status Save Register when Acknowledging FE Level Exception
3.3.2.5 PSW — Program Status Word
3.3.2.6 CTPC — Status Save Register when Executing CALLT
3.3.2.7 CTBP — CALLT Base Pointer
3.3.2.8 HTCFG0 — Thread Configuration
3.3.2.9 MEI — Memory Error Information
3.3.2.10 RBASE — Reset Vector Base Address
3.3.2.11 EBASE — Exception Handler Vector Address
3.3.2.12 INTBP — Base Address of the Interrupt Handler Table
3.3.2.13 PID — Processor ID
3.3.2.14 SCBP — SYSCALL Base Pointer
3.3.2.15 MCFG0 — Machine Configuration 0
3.3.2.16 MCFG1 — Machine Configuration 1
3.3.2.17 MCTL — Machine Control
3.3.3 Interrupt Function Registers
3.3.3.1 ISPR — Priority of Interrupt being Serviced
3.3.3.2 PMR — Interrupt Priority Masking
3.3.3.3 ICSR — Interrupt Control Status
3.3.3.4 INTCFG — Interrupt Function Setting
3.3.4 Hardware Thread Function Registers
3.3.4.1 HTCTL — Hardware Thread Control
3.3.5 Virtualization Support Function Registers
3.3.6 FPU Function Registers
3.3.7 SIMD Function Registers
3.3.8 MMU Function Registers
3.3.9 MPU Function Registers
3.3.9.1 MPM — Memory Protection Operation Mode
3.3.9.2 MPRC — MPU Region Control
3.3.9.3 MPBRGN — MPU Base Region
3.3.9.4 MPTRGN — MPU End Region
3.3.9.5 MCA — Memory Protection Setting Check Address
3.3.9.6 MCS — Memory Protection Setting Check Size
3.3.9.7 MCC — Memory Protection Setting Check Command
3.3.9.8 MCR — Memory Protection Setting Check Result
3.3.9.9 MPLAn — Protection Area Minimum Address
3.3.9.10 MPUAn — Protection Area Maximum Address
3.3.9.11 MPATn — Protection Area Attribute
3.3.10 Cache Operation Function Registers
3.4 Instruction Reference
3.4.1 Number of Instruction Clock Cycles
3.5 System Error Notification Setting Registers
3.5.1 SEG_CONT — SYSERR Exception Notification Setting Registers
3.5.2 SEG_FLAG — System Error Source Storing Registers
3.6 Usage Notes
3.6.1 Completion of Store Instruction and Synchronization of Subsequent Instruction
3.6.2 System Register Hazards
3.6.3 Access to Registers by Bit-Manipulation Instructions
3.6.4 Overwriting Context upon Acceptance of Multiple Exceptions
Section 4 Write-Protected Registers
4.1 Overview
4.1.1 Functional Overview
4.1.2 Write-Protected Register Write Procedure
4.1.3 Interrupt during Write Protection Unlocking
4.1.4 Emulation Break during Write Protection Unlock Sequence
4.1.5 Write-Protection Target Registers
4.2 Registers
4.2.1 List of Registers
4.2.2 Details of Control Protection Cluster Registers
4.2.2.1 PROTCMDn — Protection Command Register
4.2.2.2 PROTSn — Protection Status Register
4.2.3 Details of Clock Monitor Protection Cluster Registers
4.2.3.1 CLMAnPCMD — CLMAn Protection Command Register
4.2.3.2 CLMAnPS — CLMAn Protection Status Register
4.2.3.3 PROTCMDCLMA — Clock Monitor Test Protection Command Register
4.2.3.4 PROTSCLMA — Clock Monitor Test Protection Status Register
4.2.4 Details of Core Voltage Monitor Register
4.2.4.1 PROTCMDCVM — Core Voltage Monitor Protection Command Register
4.2.4.2 PROTSCVM — Core Voltage Monitor Protection Status Register
4.2.5 Details of Port Protection Cluster Registers
4.2.5.1 PPCMDn — Port Protection Command Register
4.2.5.2 PPROTSn — Port Protection Status Register
4.2.6 Details of Self-Programming Protection Cluster Registers
4.2.6.1 FLMDPCMD — FLMD Protection Command Register
4.2.6.2 FLMDPS — FLMD Protection Error Status Register
Section 5 Operating Modes
Section 6 Exception/Interrupts
6.1 Features
6.2 RH850/F1L Interrupt Sources
6.2.1 RH850/F1L Interrupt Sources
6.2.1.1 RH850/F1L FE Level Non-Maskable Interrupts
6.2.1.2 RH850/F1L FE Level Maskable Interrupts
6.2.1.3 EI Level Maskable Interrupts
6.2.2 FE Level Non-Maskable Interrupt Sources
6.2.2.1 WDTNMIF — FENMI Factor Register
6.2.2.2 WDTNMIFC — WDTNMI Factor Clear Register
6.2.3 FE Level Maskable Interrupt Sources
6.2.3.1 FEINTF — FEINT Factor Register
6.2.3.2 FEINTFMSK — FEINT Factor Mask Register
6.2.3.3 FEINTFC — FEINT Factor Clear Register
6.3 Edge Detection
6.4 Interrupt Controller Control Registers
6.4.1 ICxxx — EI Level Interrupt Control Registers
6.4.2 IMRm — EI Level Interrupt Mask Registers (m = 0 to 8)
6.4.3 FNC — FE Level NMI Status Register
6.4.4 FIC — FE Level Maskable Interrupt Status Register
6.5 EI Level Maskable Interrupt Select Registers
6.5.1 SELB_INTC1 — INTC1 Interrupt Select Register
6.5.2 SELB_INTC2 — INTC2 Interrupt Select Register
6.6 Interrupt Function System Registers
6.6.1 ISPR — Priority of Interrupt being Serviced
6.6.2 PMR — Interrupt Priority Masking
6.6.3 ICSR — Interrupt Control Status
6.6.4 INTCFG — Interrupt Function Setting
6.7 Operation when Acknowledging an Interrupt
6.8 Return from Interrupts
6.9 Interrupt Operation
6.9.1 Interrupt Mask Function of EI Level Maskable Interrupt (INTn)
6.9.2 Interrupt Priority Level Judgment
6.9.2.1 Comparison with the Priority Level as the Interrupt Currently being Handled
6.9.2.2 Masking through Priority Mask Register (PMR)
6.9.2.3 The Requested Interrupt Source with the Highest Priority Level is Selected
6.9.2.4 Interrupt Hold by CPU
6.9.3 Interrupt Request Acknowledgement Conditions and the Priority
6.9.4 Exception Priority of Interrupts and the Priority Mask
6.9.5 Interrupt Priority Mask
6.9.6 Priority Mask Function
6.9.7 Exception Management
6.10 Exception Handler Address
6.10.1 Direct Vector Method
6.10.2 Table Reference Method
Section 7 DMA
7.1 Features of RH850/F1L DMA
7.1.1 Number of Channels
7.1.2 Register Base Addresses
7.1.3 Interrupt Requests
7.1.4 DMA Trigger Factors
7.2 Overview
7.2.1 Functional Overview
7.2.1.1 DMA Transfer Function
7.2.1.2 DTFR Function
7.2.1.3 DMA Access Memory Map
7.2.1.4 Prioritization of Channels
7.2.2 Terms
7.2.3 Block Diagram
7.3 Registers
7.3.1 List of Registers
7.3.2 Enabling or Disabling Writing Control Registers
7.3.3 DMAC Control Registers
7.3.3.1 DTRC0 — DMA Transfer Request Control Register 0
7.3.3.2 DMCM0 — DMA Channel Master Setting Register 0
7.3.3.3 DSAm — DMA Source Address Register
7.3.3.4 DDAm — DMA Destination Address Register
7.3.3.5 DTCm — DMA Transfer Count Register (m = 0 to 15)
7.3.3.6 DTCTm — DMA Transfer Control Register (m = 0 to 15)
7.3.3.7 DTSm — DMA Transfer Status Register (m = 0 to 15)
7.3.4 DTFR Control Registers
7.3.4.1 DTFRm — DTFRm Register (m = 0 to 15)
7.3.4.2 DRQCLR — DMA Request Clear Register
7.3.4.3 DRQSTR — DMA Request Check Register
7.4 Functions
7.4.1 DMAC Transfer Modes
7.4.1.1 Single Transfer Mode (when hardware DMA transfer request is generated)
7.4.1.2 Single-Step Transfer Mode (when software DMA transfer request is generated)
7.4.2 DMAC Channel Priority Control
7.4.3 Valid DMAC Transfer Request Conditions
7.4.4 Suspending/Resuming/Forcibly Terminating DMAC Transfer
7.4.4.1 Suspending or Resuming DMA Transfer for All Channels through Software
7.4.4.2 Suspending or Resuming DMA Transfer for Each Channel using DMA Transfer Enable Bit (DTE)
7.4.4.3 Suspending or Resuming DMA Transfer by using Software DMA Transfer Request Bit (SR)
7.4.4.4 Forcibly Terminating Suspended DMA Transfer
7.4.5 Error Response
7.4.5.1 Suspending DMA Transfer by Error Response
7.4.5.2 Canceling Transfer Suspend by Error Response
7.4.6 Stand-By Support
7.5 Protection Function
7.6 DMAC Transfer Setting Flow
Section 8 Resets
8.1 Overview
8.1.1 Reset Sources
8.1.2 Reset Controller Redundancy
8.1.3 Reset Output (RESETOUT)
8.1.4 Reset Flag
8.2 Configuration
8.2.1 Block Diagram
8.3 Registers
8.3.1 Reset Controller Registers Overview
8.3.2 Details of General Reset Flag Registers
8.3.2.1 RESF — Reset Factor Register
8.3.2.2 RESFC — Reset Factor Clear Register
8.3.2.3 RESFR — Redundant Reset Source Register
8.3.2.4 RESFCR — Redundant Reset Source Clear Register
8.3.3 Details of Software Reset Control Registers
8.3.3.1 SWRESA — Software Reset Register
8.4 Functional Description
8.4.1 Reset Flags
8.4.2 Power-On-Clear (POC) Reset
8.4.3 Low-Voltage Detection Circuit (LVI) Reset
8.4.4 Core Voltage Monitor (CVM) Reset
8.4.5 External Reset (RESET)
8.4.6 Watchdog Timer (WDTA) Reset
8.4.7 Software Reset
8.4.8 Clock Monitor (CLMA) Reset
8.4.9 Debugger Reset
Section 9 Supply Voltage Monitor
9.1 Overview
9.1.1 Functional Overview
9.1.2 Power-On Clear (POC)
9.1.3 Low Voltage Indicator Circuit (LVI)
9.1.3.1 LVI Reference Voltage
9.1.3.2 LVI Reset (LVIRES)
9.1.3.3 LVI Interrupt (INTLVIL / INTLVIH)
9.1.3.4 LVI Setting Procedure
9.1.4 Core Voltage Monitor (CVM)
9.1.4.1 CVM Reset (CVMRES)
9.1.4.2 CVM Setting
9.1.4.3 Diagnostic (DIAG) Mode
9.1.5 RAM Retention Voltage Indicator (Very-Low-Voltage Detection Circuit)
9.1.5.1 Retention RAM Content Retention
9.1.6 Block Diagram
9.2 Registers
9.2.1 List of Registers
9.2.2 Low-Voltage Indicator Reset Control Registers
9.2.2.1 LVICNT — LVI Control Register
9.2.3 Core Voltage Monitor Control Registers
9.2.3.1 CVMF — CVM Factor Register
9.2.3.2 CVMDE — CVM Detection Enable Register
9.2.3.3 CVMDIAG — CVM Diagnostic Mode Setting Register
9.2.4 Very-Low-Voltage Detection Control Registers
9.2.4.1 VLVF — Very-Low-Voltage Detection Register
9.2.4.2 VLVFC — Very-Low-Voltage Detection Clear Register
Section 10 Clock Controller
10.1 Features of Clock Controller of RH850/F1L
10.2 Configuration of Clock Controller
10.2.1 Clock Generation Circuits
10.2.2 Clock Selection
10.2.3 Clock Domains
10.2.4 Resetting Clock Oscillators
10.3 Clock Oscillators
10.3.1 Main Oscillator (MainOSC)
10.3.2 Sub Oscillator (SubOSC)
10.3.3 High Speed Internal Oscillator (HS IntOSC)
10.3.4 Low Speed Internal Oscillator (LS IntOSC)
10.3.5 PLL
10.3.5.1 PLL Parameters
10.4 Registers
10.4.1 List of Registers
10.4.2 Clock Oscillator Registers
10.4.2.1 MOSCE — MainOSC Enable Register
10.4.2.2 MOSCS — MainOSC Status Register
10.4.2.3 MOSCC — MainOSC Control Register
10.4.2.4 MOSCST — MainOSC Stabilization Time Register
10.4.2.5 MOSCSTPM — MainOSC Stop Mask Register
10.4.2.6 SOSCE — SubOSC Enable Register
10.4.2.7 SOSCS — SubOSC Status Register
10.4.2.8 SOSCST — SubOSC Stabilization Time Register
10.4.2.9 ROSCE — HS IntOSC Enable Register
10.4.2.10 ROSCS — HS IntOSC Status Register
10.4.2.11 ROSCSTPM — HS IntOSC Stop Mask Register
10.4.2.12 PLLE — PLL Enable Register
10.4.2.13 PLLS — PLL Status Register
10.4.2.14 PLLC — PLLC Control Register
10.4.3 Clock Selector Control Register
10.4.3.1 WDTA0 Clock Domain C_AWO_WDTA
10.4.3.2 TAUJ Clock Domain C_AWO_TAUJ
10.4.3.3 RTCA Clock Domain C_AWO_RTCA
10.4.3.4 ADCA0 Clock Domain C_AWO_ADCA
10.4.3.5 FOUT Clock Domain C_AWO_FOUT
10.4.3.6 CPU Clock Domain C_ISO_CPUCLK
10.4.3.7 Peripheral Clock Domains C_ISO_PERI1 and C_ISO_PERI2
10.4.3.8 RLIN Clock Domains C_ISO_LIN
10.4.3.9 ADCA1 Clock Domain C_ISO_ADCA
10.4.3.10 RS-CAN Clock Domains C_ISO_CAN and C_ISO_CANOSC
10.4.3.11 CSI Clock Domain C_ISO_CSI
10.5 Clock Domain Setting Method
10.5.1 Clock Domain Setting
10.5.1.1 Overview of Clock Selector Register
10.5.1.2 Setting Procedure for Clock Domain
10.5.2 Stopping the Clock in Stand-By Mode
10.5.3 Clock Domain Settings
10.6 Frequency Output Function (FOUT)
10.6.1 Functional Overview
10.6.2 Register
10.6.2.1 List of Registers
10.6.2.2 FOUTDIV — Clock Division Ratio Register
10.6.2.3 FOUTSTAT — Clock Divider Status Register
10.7 Clock Monitor A (CLMA)
10.7.1 Features of RH850/F1L CLMA
10.7.1.1 Number of Channels
10.7.1.2 Register Base Addresses
10.7.1.3 Clock Supply to CLMA
10.7.1.4 Internal Input/Output Signals
10.7.2 Overview
10.7.2.1 Functional Overview
10.7.3 Enabling CLMA
10.7.4 Functions
10.7.4.1 Detection of Abnormal Clock Frequencies
10.7.4.2 Notification of Abnormal Clock Frequency
10.7.4.3 CLMAn Enable (Write to CLMAnCTL0)
10.7.5 Registers
10.7.5.1 List of Registers
10.7.5.2 CLMAnCTL0 — CLMAn Control Register 0
10.7.5.3 CLMAnCMPH — CLMAn Compare Register H
10.7.5.4 CLMAnCMPL — CLMAn Compare Register L
10.7.5.5 CLMATEST — CLMA Test Register
10.7.5.6 CLMATESTS — CLMA Test Status Register
10.7.5.7 CLMAnEMU0 — CLMAn Emulation Register 0
10.7.6 Usage Notes for CLMAn
Section 11 Stand-By Controller (STBC)
11.1 Functions
11.1.1 Types of Stand-By Mode
11.1.2 Wake-Up Control
11.1.2.1 Wake-Up Factors from Stand-By Mode
11.1.2.2 Setting of Wake-Up Factors
11.1.3 On-Chip Debug Wake-Up
11.1.4 I/O Buffer Control
11.1.4.1 I/O Buffer Hold State
11.1.4.2 I/O Buffers during STOP Mode
11.1.4.3 I/O Buffers during DEEPSTOP Mode
11.1.5 Transition to Stand-By Mode
11.2 Registers
11.2.1 List of Registers
11.2.2 Details of Stand-By Controller Control Registers
11.2.2.1 STBC0PSC — Power Save Control Register
11.2.2.2 STBC0STPT — Power Stop Trigger Register
11.2.2.3 WUF0/WUF20/WUF_ISO0 — Wake-Up Factor Registers
11.2.2.4 WUFMSK0/WUFMSK20/WUFMSK_ISO0 — Wake-Up Factor Mask Registers
11.2.2.5 WUFC0/WUFC20/WUFC_ISO0 — Wake-Up Factor Clear Registers
11.2.2.6 IOHOLD — I/O Buffer Hold Control Register
11.3 Mode
11.3.1 STOP Mode
11.3.2 DEEPSTOP Mode
11.3.3 Cyclic RUN Mode
11.3.4 Cyclic STOP Mode
11.4 Writing to the Stand-By Controller Related Registers
11.5 Cautions when Using Stand-By Modes
11.5.1 Cautions when Shifting to DEEPSTOP Mode during Debugger Use
Section 12 Low-Power Sampler (LPS)
12.1 Features of RH850/F1L LPS
12.1.1 Number of Units
12.1.2 Register Base Address
12.1.3 Clock Supply
12.1.4 Interrupt Request
12.1.5 Reset Sources
12.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
12.1.7 Internal Input/Output Signals
12.2 Overview
12.2.1 Functional Overview
12.3 Registers
12.3.1 List of Registers
12.3.2 SCTLR — LPS Control Registers
12.3.3 EVFR — Event Flag Register
12.3.4 DPSELRL0 — DPIN Select Register 0
12.3.5 DPSELRM — DPIN Select Register M
12.3.6 DPSELRH — DPIN Select Register H
12.3.7 DPDSR0 — DPIN Data Set Register 0
12.3.8 DPDSRM — DPIN Data Set Register M
12.3.9 DPDSRH — DPIN Data Set Register H
12.3.10 DPDIMR0 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 0
12.3.11 DPDIMR1 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 1
12.3.12 DPDIMR2 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 2
12.3.13 DPDIMR3 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 3
12.3.14 DPDIMR4 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 4
12.3.15 DPDIMR5 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 5
12.3.16 DPDIMR6 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 6
12.3.17 DPDIMR7 — DPIN Data Input Monitor Register 7
12.3.18 CNTVAL — Count Value Register
12.3.19 SOSTR — LPS Operation Status Register
12.4 Digital Input Mode
12.5 Analog Input Mode
Section 13 External Memory Access (MEMC)
13.1 Features of MEMC
13.1.1 Products that Incorporate MEMC
13.1.2 Register Addresses
13.1.3 Clock Supply
13.1.4 Reset Sources
13.1.5 External Input/Output Signals
13.2 Overview
13.2.1 Functional Overview
13.2.2 Operation Mode, Connectable Memory Types
13.2.2.1 Multiplexed Bus
13.2.3 Chip Select Output Function
13.2.4 Bus Sizing Function
13.2.5 Data Endian Setting Function
13.2.6 Programmable Wait Setting Functions
13.2.7 External Wait Function
13.3 Registers
13.3.1 List of Registers
13.3.2 BSC — Data Bus Width Configuration Register
13.3.3 DEC — Data Endian Configuration Register
13.3.4 DWC — Data Wait Configuration Register
13.3.5 DHC — Data Hold Wait Configuration Register
13.3.6 AWC — Address Wait Configuration Register
13.3.7 ICC — Idle Cycle Configuration Register
13.4 Functions
13.4.1 Bus Control Functions
13.4.1.1 Chip Select Output Function
13.4.1.2 Bus Size Setting Function
13.4.1.3 Data Endian Setting Function
13.4.2 Wait Functions
13.4.2.1 Programmable Data Wait Function
13.4.2.2 External Wait Function
13.4.2.3 Data Hold Wait Function
13.4.2.4 Address Setup Wait and Address Hold Wait Functions
13.4.2.5 Idle Insertion Function
13.4.3 Memory Connection Example
13.4.3.1 SRAM Connection Example
13.4.4 Data Access Flow
13.4.4.1 Data Flow for Byte Access (for Reading and Writing)
13.4.4.2 Data Flow for Half-Word Read Access
13.4.4.3 Data Flow for Half-Word Write Access
13.4.4.4 Data Flow for Word Read Access
13.4.4.5 Data Flow for Word Write Access
Section 14 Clocked Serial Interface G (CSIG)
14.1 Features of RH850/F1L CSIG
14.1.1 Number of Units
14.1.2 Register Base Address
14.1.3 Clock Supply
14.1.4 Interrupt Request
14.1.5 Reset Sources
14.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
14.1.7 Data Consistency Check
14.2 Overview
14.2.1 Functional Overview
14.2.2 Functional Overview Description
14.2.3 Block Diagram
14.3 Registers
14.3.1 List of Registers
14.3.2 CSIGnCTL0 — CSIGn Control Register 0
14.3.3 CSIGnCTL1 — CSIGn Control Register 1
14.3.4 CSIGnCTL2 — CSIGn Control Register 2
14.3.5 CSIGnSTR0 — CSIGn Status Register 0
14.3.6 CSIGnSTCR0 — CSIGn Status Clear Register 0
14.3.7 CSIGnBCTL0 — CSIGn Rx-Only Mode Control Register 0
14.3.8 CSIGnCFG0 — CSIGn Configuration Register 0
14.3.9 CSIGnTX0W — CSIGn Transmission Register 0 for Word Access
14.3.10 CSIGnTX0H — CSIGn Transmission Register 0 for Half Word Access
14.3.11 CSIGnRX0 — CSIGn Reception Register 0
14.3.12 CSIGnEMU — CSIGn Emulation Register
14.3.13 List of Cautions
14.4 Interrupt Sources
14.4.1 Interrupt Delay
14.4.2 INTCSIGTIC (Communication Status Interrupt)
14.4.3 INTCSIGTIR (Reception Status Interrupt)
14.4.4 INTCSIGTIRE (Communication Error Interrupt)
14.5 Operation
14.5.1 Master/Slave Mode
14.5.1.1 Master Mode
14.5.1.2 Slave Mode
14.5.2 Master/Slave Connections
14.5.2.1 One Master and One Slave
14.5.2.2 One Master and Multiple Slaves
14.5.3 Transmission Clock Selection
14.5.4 Data Transfer Modes
14.5.4.1 Transmit-Only Mode
14.5.4.2 Receive-Only Mode
14.5.4.3 Transmit/Receive Mode
14.5.5 Data Length Selection
14.5.5.1 Data Length Selection without Extended Length
14.5.5.2 Data Length Selection with Extended Data Length
14.5.6 Serial Data Direction Select Function
14.5.7 Communication in Slave Mode
14.5.8 Handshake Function
14.5.8.1 Slave Mode
14.5.8.2 Master Mode
14.5.9 Loop-Back Mode
14.5.10 Error Detection
14.5.10.1 Data Consistency Check
14.5.10.2 Parity Check
14.5.10.3 Overrun Error
14.6 Operating Procedure
14.6.1 Master Mode Transmission/Reception by DMA
Section 15 Clocked Serial Interface H (CSIH)
15.1 Features of RH850/F1L CSIH
15.1.1 Number of Units
15.1.2 Register Base Address
15.1.3 Clock Supply
15.1.4 Interrupt Requests
15.1.5 Reset Sources
15.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
15.1.7 Data Consistency Check
15.2 Overview
15.2.1 Functional Overview
15.2.2 Functional Overview Description
15.2.3 Block Diagram
15.3 Registers
15.3.1 List of Registers
15.3.2 CSIHnCTL0 — CSIHn Control Register 0
15.3.3 CSIHnCTL1 — CSIHn Control Register 1
15.3.4 CSIHnCTL2 — CSIHn Control Register 2
15.3.5 CSIHnSTR0 — CSIHn Status Register 0
15.3.6 CSIHnSTCR0 — CSIHn Status Clear Register 0
15.3.7 CSIHnMCTL0 — CSIHn Memory Control Register 0
15.3.8 CSIHnMCTL1 — CSIHn Memory Control Register 1
15.3.9 CSIHnMCTL2 — CSIHn Memory Control Register 2
15.3.10 CSIHnMRWP0 — CSIHn Memory Read/Write Pointer Register 0
15.3.11 CSIHnCFGx — CSIHn Configuration Register x
15.3.12 CSIHnTX0W — CSIHn Transmit Data Register 0 for Word Access
15.3.13 CSIHnTX0H — CSIHn Transmit Data Register 0 for Half Word Access
15.3.14 CSIHnRX0W — CSIHn Receive Data Register 0 for Word Access
15.3.15 CSIHnRX0Hn — CSIHn Receive Data Register 0 for Half Word Access
15.3.16 CSIHnEMU — CSIHn Emulation Register
15.3.17 CSIHnBRSy — CSIHn Baud Rate Setting Register y (y = 0 to 3)
15.3.18 List of Caution
15.4 Interrupt Sources
15.4.1 Overview
15.4.2 Interrupt Delay
15.4.3 INTCSIHTIC (Communication Status Interrupt)
15.4.3.1 INTCSIHTIC in Direct Access Mode
15.4.3.2 INTCSIHTIC in FIFO Mode
15.4.3.3 INTCSIHTIC in Job Mode
15.4.4 INTCSIHTIR (Reception Status Interrupt)
15.4.4.1 INTCSIHTIR in Direct Access Mode
15.4.4.2 INTCSIHTIR in Dual Buffer Mode
15.4.5 INTCSIHTIRE (Communication Error Interrupt)
15.4.6 INTCSIHTIJC (Job Completion Interrupt)
15.5 Operation
15.5.1 Operating Modes (Master/Slave)
15.5.1.1 Master Mode
15.5.1.2 Slave Mode
15.5.2 Master/Slave Connections
15.5.2.1 One Master and One Slave
15.5.2.2 One Master and Multiple Slaves
15.5.3 Chip Selection (CS) Features
15.5.3.1 Configuration Registers
15.5.3.2 CS Example
15.5.3.3 Job Concept
15.5.4 Details of Chip Select Timing
15.5.4.1 Changing the Clock Phase
15.5.4.2 Changing the Data Phase
15.5.5 Transmission Clock Selection
15.5.6 CSIH Buffer Memory
15.5.6.1 FIFO Mode
15.5.6.2 Dual Buffer Mode
15.5.6.3 Transmit-Only Buffer Mode
15.5.6.4 Direct Access Mode
15.5.7 Data Transfer Modes
15.5.7.1 Transmit-Only Mode
15.5.7.2 Receive-Only Mode
15.5.7.3 Transmit/Receive Mode
15.5.7.4 Summary
15.5.8 Data Length Selection
15.5.8.1 Data Length from 2 to 16 Bits
15.5.8.2 Data Length Greater than 16 Bits
15.5.9 Serial Data Direction Selection
15.5.10 Slave Select (SS) Function
15.5.10.1 Communication Timing Using SS Function
15.5.10.2 CSIHTSSO Operation
15.5.11 Handshake Function
15.5.11.1 Slave Mode
15.5.11.2 Master Mode
15.5.12 Error Detection
15.5.12.1 Data Consistency Check
15.5.12.2 Parity Check
15.5.12.3 Time-Out Error
15.5.12.4 Overflow Error
15.5.12.5 Overrun Error
15.5.13 Loop-Back Mode
15.5.14 CPU-Controlled High Priority Communication Function
15.5.15 Enforced Chip Select Idle Setting
15.6 Operating Procedures
15.6.1 Procedures in Direct Access Mode
15.6.1.1 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Disabled
15.6.1.2 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Enabled
15.6.2 Procedures in Transmit-Only Buffer Mode
15.6.2.1 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Disabled
15.6.2.2 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Enabled
15.6.3 Procedures in Dual Buffer Mode
15.6.3.1 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Disabled
15.6.3.2 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Enabled
15.6.3.3 Transmit/Receive in Slave Mode when Job Mode is Disabled
15.6.4 Procedures in FIFO Mode
15.6.4.1 Transmit/Receive in Master Mode when Job Mode is Disabled
15.6.4.2 Transmit/Receive Mode when Job Mode is Enabled in Master Mode
15.7 Detection and Correction of Errors in CSIHn RAM
15.7.1 ECC for the CSIHn RAM
15.7.2 Interrupt Request
15.7.3 ECCCSIHnCTL — CSIHn ECC Control Register
15.7.4 ECCCSIHnTMC — CSIHn ECC Test Mode Control Register
15.7.5 ECCCSIHnTED — CSIHn ECC Encode/Decode Input/Output Replacement Test Register
15.7.6 ECCCSIHnTRC — CSIHn ECC Redundant Bit Data Control Test Register
15.7.7 ECCCSIHnSYND — CSIHn ECC Decode Syndrome Data Register
15.7.8 ECCCSIHnHORD — CSIHn ECC 7-Bit Redundant Bit Data Hold Test Register
15.7.9 ECCCSIHnECRD — CSIHnECC Encode Test Register
15.7.10 ECCCSIHnERDB — CSIHn ECC Redundant Bit Input/Output Replacement Register
15.7.11 SELB_READTEST — ECCREAD Test Select Register
Section 16 LIN Master Interface (RLIN2)
16.1 Features of RH850/F1L RLIN2
16.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
16.1.2 Register Base Address
16.1.3 Clock Supply
16.1.4 Interrupt Request
16.1.5 Reset Sources
16.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
16.2 Overview
16.2.1 Functional Overview
16.2.2 Block Diagram
16.3 Registers
16.3.1 List of Registers
16.3.2 Global Registers
16.3.2.1 RLN24nGLWBR / RLN21nGLWBR — LIN Wake-Up Baud Rate Select Register
16.3.2.2 RLN24nGLBRP0 / RLN21nGLBRP0 — LIN Baud Rate Prescaler 0 Register
16.3.2.3 RLN24nGLBRP1 / RLN21nGLBRP1 — LIN Baud Rate Prescaler 1 Register
16.3.2.4 RLN24nGLSTC / RLN21nGLSTC — LIN Self-Test Control Register
16.3.3 Channel Registers
16.3.3.1 RLN24nmLiMD / RLN21nmLiMD — LIN Mode Register
16.3.3.2 RLN24nmLiBFC / RLN21nmLiBFC — LIN Break Field Configuration Register
16.3.3.3 RLN24nmLiSC / RLN21nmLiSC — LIN Space Configuration Register
16.3.3.4 RLN24nmLiWUP / RLN21nmLiWUP — LIN Wake-Up Configuration Register
16.3.3.5 RLN24nmLiIE / RLN21nmLiIE — LIN Interrupt Enable Register
16.3.3.6 RLN24nmLiEDE / RLN21nmLiEDE — LIN Error Detection Enable Register
16.3.3.7 RLN24nmLiCUC / RLN21nmLiCUC — LIN Control Register
16.3.3.8 RLN24nmLiTRC / RLN21nmLiTRC — LIN Transmission Control Register
16.3.3.9 RLN24nmLiMST / RLN21nmLiMST — LIN Mode Status Register
16.3.3.10 RLN24nmLiST / RLN21nmLiST — LIN Status Register
16.3.3.11 RLN24nmLiEST / RLN21nmLiEST — LIN Error Status Register
16.3.3.12 RLN24nmLiDFC / RLN21nmLiDFC — LIN Data Field Configuration Register
16.3.3.13 RLN24nmLiIDB / RLN21nmLiIDB — LIN ID Buffer Register
16.3.3.14 RLN24nmLiCBR / RLN21nmLiCBR — LIN Checksum Buffer Register
16.3.3.15 RLN24nmLiDBRb / RLN21nmLiDBRb — LIN Data Buffer b Register
16.4 Interrupt Sources
16.5 Modes
16.6 LIN Reset Mode
16.7 LIN Operation Mode
16.8 LIN Wake-Up Mode
16.9 Header Transmission/Response Transmission/Response Reception
16.9.1 Header Transmission
16.9.2 Response Transmission
16.9.3 Response Reception
16.10 Data Transmission/Reception
16.10.1 Data Transmission
16.10.2 Data Reception
16.11 Transmission/Reception Data Buffering
16.11.1 Transmission of LIN Frames
16.11.2 Reception of LIN Frames
16.12 Wake-Up Transmission/Reception
16.12.1 Wake-Up Transmission
16.12.2 Wake-Up Reception
16.12.3 Wake-Up Collision
16.13 Status
16.14 Error Status
16.14.1 Types of Error Statuses
16.14.2 Target Time Area for Error Detection
16.15 LIN Self-Test Mode
16.15.1 Change to LIN Self-Test Mode
16.15.2 Transmission in LIN Self-Test Mode
16.15.3 Reception in LIN Self-Test Mode
16.15.4 Terminating LIN Self-Test Mode
16.16 Baud Rate Generator
Section 17 LIN/UART Interface (RLIN3)
17.1 Features of RH850/F1L RLIN3
17.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
17.1.2 Register Base Address
17.1.3 Clock Supply
17.1.4 Interrupt Request
17.1.5 Reset Sources
17.1.6 External Input/output Signals
17.2 Overview
17.2.1 Functional Overview
17.2.2 Block Diagram
17.2.3 Description of Blocks
17.3 Registers
17.3.1 List of Registers
17.3.2 LIN Master Related Registers
17.3.2.1 RLN3nLWBR — LIN Wake-Up Baud Rate Select Register
17.3.2.2 RLN3nLBRP0 — LIN Baud Rate Prescaler 0 Register
17.3.2.3 RLN3nLBRP1 — LIN Baud Rate Prescaler 1 Register
17.3.2.4 RLN3nLSTC — LIN Self-Test Control Register
17.3.2.5 RLN3nLMD — LIN Mode Register
17.3.2.6 RLN3nLBFC — LIN Break Field Configuration Register
17.3.2.7 RLN3nLSC — LIN Space Configuration Register
17.3.2.8 RLN3nLWUP — LIN Wake-Up Configuration Register
17.3.2.9 RLN3nLIE — LIN Interrupt Enable Register
17.3.2.10 RLN3nLEDE —LIN Error Detection Enable Register
17.3.2.11 RLN3nLCUC — LIN Control Register
17.3.2.12 RLN3nLTRC — LIN Transmission Control Register
17.3.2.13 RLN3nLMST — LIN Mode Status Register
17.3.2.14 RLN3nLST — LIN Status Register
17.3.2.15 RLN3nLEST — LIN Error Status Register
17.3.2.16 RLN3nLDFC — LIN Data Field Configuration Register
17.3.2.17 RLN3nLIDB — LIN ID Buffer Register
17.3.2.18 RLN3nLCBR — LIN Checksum Buffer Register
17.3.2.19 RLN3nLDBRb — LIN Data Buffer b Register (b = 1 to 8)
17.3.3 LIN Slave Related Registers
17.3.3.1 RLN3nLWBR — LIN Wake-Up Baud Rate Select Register
17.3.3.2 RLN3nLBRP01 — LIN Baud Rate Prescaler 01 Register
17.3.3.3 RLN3nLSTC — LIN Self-Test Control Register
17.3.3.4 RLN3nLMD — LIN Mode Register
17.3.3.5 RLN3nLBFC — LIN Break Field Configuration Register
17.3.3.6 RLN3nLSC — LIN Space Configuration Register
17.3.3.7 RLN3nLWUP — LIN Wake-Up Configuration Register
17.3.3.8 RLN3nLIE — LIN Interrupt Enable Register
17.3.3.9 RLN3nLEDE — LIN Error Detection Enable Register
17.3.3.10 RLN3nLCUC — LIN Control Register
17.3.3.11 RLN3nLTRC — LIN Transmission Control Register
17.3.3.12 RLN3nLMST — LIN Mode Status Register
17.3.3.13 RLN3nLST — LIN Status Register
17.3.3.14 RLN3nLEST — LIN Error Status Register
17.3.3.15 RLN3nLDFC — LIN Data Field Configuration Register
17.3.3.16 RLN3nLIDB — LIN/UART ID Buffer Register
17.3.3.17 RLN3nLCBR — LIN Checksum Buffer Register
17.3.3.18 RLN3nLDBRb — LIN Data Buffer b Register (b = 1 to 8)
17.3.4 UART Related Registers
17.3.4.1 RLN3nLWBR — LIN Wake-Up Baud Rate Select Register
17.3.4.2 RLN3nLBRP01 — UART Baud Rate Prescaler 01 Register
17.3.4.3 RLN3nLMD — UART Mode Register
17.3.4.4 RLN3nLBFC — UART Configuration Register
17.3.4.5 RLN3nLSC — UART Space Configuration Register
17.3.4.6 RLN3nLEDE —UART Error Detection Enable Register
17.3.4.7 RLN3nLCUC — UART Control Register
17.3.4.8 RLN3nLTRC — UART Transmission Control Register
17.3.4.9 RLN3nLMST — UART Mode Status Register
17.3.4.10 RLN3nLST — UART Status Register
17.3.4.11 RLN3nLEST — UART Error Status Register
17.3.4.12 RLN3nLDFC — UART Data Field Configuration Register
17.3.4.13 RLN3nLIDB — UART ID Buffer Register
17.3.4.14 RLN3nLUDB0 — UART Data 0 Buffer Register
17.3.4.15 RLN3nLDBRb — UART Data Buffer b Register (b = 1 to 8)
17.3.4.16 RLN3nLUOER — UART Operation Enable Register
17.3.4.17 RLN3nLUOR1 — UART Option Register 1
17.3.4.18 RLN3nLUTDR — UART Transmission Data Register
17.3.4.19 RLN3nLURDR — UART Reception Data Register
17.3.4.20 RLN3nLUWTDR — UART Wait Transmission Data Register
17.4 Interrupt Sources
17.5 Modes
17.6 LIN Reset Mode
17.7 LIN Mode
17.7.1 LIN Master Mode
17.7.1.1 Header Transmission
17.7.1.2 Response Transmission
17.7.1.3 Response Reception
17.7.2 LIN Slave Mode
17.7.2.1 Header Reception
17.7.2.2 Response Transmission
17.7.2.3 Response Reception
17.7.2.4 No-response Request
17.7.3 Data Transmission/Reception
17.7.3.1 Data Transmission
17.7.3.2 Data Reception
17.7.4 Transmission/Reception Data Buffering
17.7.4.1 Transmission of LIN Frames
17.7.4.2 Reception of LIN Frames
17.7.4.3 Multi-Byte Response Transmission/Reception Function
17.7.5 Wake-up Transmission/Reception
17.7.5.1 Wake-up Transmission
17.7.5.2 Wake-up Reception
17.7.5.3 Wakeup Collision
17.7.6 Status
17.7.7 Error Status
17.7.7.1 LIN Master Mode
17.7.7.2 LIN Slave Mode
17.8 UART Mode
17.8.1 Transmission
17.8.1.1 Continuous Transmission
17.8.1.3 Data Transmission
17.8.1.2 UART Buffer Transmission
17.8.1.4 Transmission Start Wait Function
17.8.2 Reception
17.8.2.1 Data Reception
17.8.3 Expansion Bits
17.8.3.1 Expansion Bit Transmission
17.8.3.2 Expansion Bit Reception
17.8.3.3 Expansion Bit Reception (with Expansion Bit Comparison)
17.8.3.4 Expansion Bit Reception (with Data Comparison)
17.8.4 Status
17.8.5 Error Status
17.9 LIN Self-Test Mode
17.9.1 Change to LIN Self-Test Mode
17.9.2 Transmission in LIN Master Self-Test Mode
17.9.3 Reception in LIN Master Self-Test Mode
17.9.4 Transmission in LIN Slave Self-Test Mode
17.9.5 Reception in LIN Slave Self-Test Mode
17.9.6 Terminating LIN Self-Test Mode
17.10 Baud Rate Generator
17.10.1 LIN Master Mode
17.10.2 LIN Slave Mode
17.10.3 UART Mode
17.11 Noise Filter
Section 18 I2C Bus Interface (RIIC)
18.1 Features of RH850/F1L RIIC
18.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
18.1.2 Register Base Address
18.1.3 Clock Supply
18.1.4 Interrupt Requests
18.1.5 Reset Sources
18.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
18.2 Overview
18.2.1 Functional Overview
18.2.2 Block Diagram
18.3 Registers
18.3.1 List of Registers
18.3.2 RIICnCR1 — I2C Bus Control Register 1
18.3.3 RIICnCR2 — I2C Bus Control Register 2
18.3.4 RIICnMR1 — I2C Bus Mode Register 1
18.3.5 RIICnMR2 — I2C Bus Mode Register 2
18.3.6 RIICnMR3 — I2C Bus Mode Register 3
18.3.7 RIICnFER — I2C Bus Function Enable Register
18.3.8 RIICnSER — I2C Bus Status Enable Register
18.3.9 RIICnIER — I2C Bus Interrupt Enable Register
18.3.10 RIICnSR1 — I2C Bus Status Register 1
18.3.11 RIICnSR2 — I2C Bus Status Register 2
18.3.12 RIICnSARy — I2C Slave Address Register y (y = 0 to 2)
18.3.13 RIICnBRL — I2C Bus Bit Rate Low-Level Register
18.3.14 RIICnBRH — I2C Bus Bit Rate High-Level Register
18.3.15 RIICnDRT — I2C Bus Transmit Data Register
18.3.16 RIICnDRR — I2C Bus Receive Data Register
18.3.17 RIICnDRS — I2C Bus Shift Register
18.4 Interrupt Sources
18.5 Operation
18.5.1 Communication Data Format
18.5.2 Initial Settings
18.5.3 Master Transmit Operation
18.5.4 Master Receive Operation
18.5.5 Slave Transmit Operation
18.5.6 Slave Receive Operation
18.6 SCL Synchronization Circuit
18.7 Facility for Delaying SDA Output
18.8 Digital Noise-Filter Circuits
18.9 Address Match Detection
18.9.1 Slave-Address Match Detection
18.9.2 Detection of the General Call Address
18.9.3 Device-ID Address Detection
18.10 Automatically Low-Hold Function for SCL
18.10.1 Function to Prevent Wrong Transmission of Transmit Data
18.10.2 NACK Reception Transfer Suspension Function
18.10.3 Function to Prevent Failure to Receive Data
18.11 Arbitration-Lost Detection Functions
18.11.1 Master Arbitration-Lost Detection (MALE Bit)
18.11.2 Function to Detect Loss of Arbitration during NACK Transmission (NALE Bit)
18.11.3 Slave Arbitration-Lost Detection (SALE Bit)
18.12 Start Condition/Restart Condition/Stop Condition Issuing Function
18.12.1 Issuing a Start Condition
18.12.2 Issuing a Restart Condition
18.12.3 Issuing a Stop Condition
18.13 Bus Hanging
18.13.1 Timeout Function
18.13.2 Extra SCL Clock Cycle Output Function
18.13.3 RIIC Reset and Internal Reset
18.14 Reset Function of RIIC
Section 19 CAN Interface (RS-CAN)
19.1 Features of RH850/F1L RS-CAN
19.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
19.1.2 Register Base Address
19.1.3 Clock Supply
19.1.4 Interrupt Request
19.1.5 Reset Sources
19.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
19.2 Overview
19.2.1 Functional Overview
19.2.2 Block Diagram
19.3 Registers
19.3.1 List of Registers
19.3.2 RSCAN0CmCFG — Channel Configuration Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.3 RSCAN0CmCTR — Channel Control Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.4 RSCAN0CmSTS — Channel Status Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.5 RSCAN0CmERFL — Channel Error Flag Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.6 RSCAN0GCFG — Global Configuration Register
19.3.7 RSCAN0GCTR — Global Control Register
19.3.8 RSCAN0GSTS — Global Status Register
19.3.9 RSCAN0GERFL — Global Error Flag Register
19.3.10 RSCAN0GTINTSTS0 — Global TX Interrupt Status Register 0
19.3.11 RSCAN0GTINTSTS1 — Global TX Interrupt Status Register 1
19.3.12 RSCAN0GTSC — Global Timestamp Counter Register
19.3.13 RSCAN0GAFLECTR — Receive Rule Entry Control Register
19.3.14 RSCAN0GAFLCFG0 — Receive Rule Configuration Register 0
19.3.15 RSCAN0GAFLCFG1 — Receive Rule Configuration Register 1
19.3.16 RSCAN0GAFLIDj — Receive Rule ID Register (j = 0 to 15)
19.3.17 RSCAN0GAFLMj — Receive Rule Mask Register (j = 0 to 15)
19.3.18 RSCAN0GAFLP0j — Receive Rule Pointer 0 Register (j = 0 to 15)
19.3.19 RSCAN0GAFLP1j — Receive Rule Pointer 1 Register (j = 0 to 15)
19.3.20 RSCAN0RMNB — Receive Buffer Number Register
19.3.21 RSCAN0RMNDy — Receive Buffer New Data Register (y = 0 to 2)
19.3.22 RSCAN0RMIDq — Receive Buffer ID Register (q = 0 to 95)
19.3.23 RSCAN0RMPTRq — Receive Buffer Pointer Register (q = 0 to 95)
19.3.24 RSCAN0RMDF0q — Receive Buffer Data Field 0 Register (q = 0 to 95)
19.3.25 RSCAN0RMDF1q — Receive Buffer Data Field 1 Register (q = 0 to 95)
19.3.26 RSCAN0RFCCx — Receive FIFO Buffer Configuration and Control Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.27 RSCAN0RFSTSx — Receive FIFO Buffer Status Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.28 RSCAN0RFPCTRx — Receive FIFO Buffer Pointer Control Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.29 RSCAN0RFIDx — Receive FIFO Buffer Access ID Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.30 RSCAN0RFPTRx — Receive FIFO Buffer Access Pointer Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.31 RSCAN0RFDF0x — Receive FIFO Buffer Access Data Field 0 Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.32 RSCAN0RFDF1x — Receive FIFO Buffer Access Data Field 1 Register (x = 0 to 7)
19.3.33 RSCAN0CFCCk — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Configuration and Control Register k (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.34 RSCAN0CFSTSk — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Status Register (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.35 RSCAN0CFPCTRk — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Pointer Control Register (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.36 RSCAN0CFIDk — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Access ID Register (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.37 RSCAN0CFPTRk — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Access Pointer Register (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.38 RSCAN0CFDF0k — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Access Data Field 0 Register (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.39 RSCAN0CFDF1k — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Access Data Field 1 Register (k = 0 to 17)
19.3.40 RSCAN0FESTS — FIFO Empty Status Register
19.3.41 RSCAN0FFSTS — FIFO Full Status Register
19.3.42 RSCAN0FMSTS — FIFO Message Lost Status Register
19.3.43 RSCAN0RFISTS — Receive FIFO Buffer Interrupt Flag Status Register
19.3.44 RSCAN0CFRISTS — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Receive Interrupt Flag Status Register
19.3.45 RSCAN0CFTISTS — Transmit/receive FIFO Buffer Transmit Interrupt Flag Status Register
19.3.46 RSCAN0TMCp — Transmit Buffer Control Register (p = 0 to 95)
19.3.47 RSCAN0TMSTSp — Transmit Buffer Status Register (p = 0 to 95)
19.3.48 RSCAN0TMTRSTSy — Transmit Buffer Transmit Request Status Register (y = 0 to 2)
19.3.49 RSCAN0TMTARSTSy — Transmit Buffer Transmit Abort Request Status Register (y = 0 to 2)
19.3.50 RSCAN0TMTCSTSy — Transmit Buffer Transmit Complete Status Register (y = 0 to 2)
19.3.51 RSCAN0TMTASTSy — Transmit Buffer Transmit Abort Status Register (y = 0 to 2)
19.3.52 RSCAN0TMIECy — Transmit Buffer Interrupt Enable Configuration Register (y = 0 to 2)
19.3.53 RSCAN0TMIDp — Transmit Buffer ID Register (p = 0 to 95)
19.3.54 RSCAN0TMPTRp — Transmit Buffer Pointer Register (p= 0 to 95)
19.3.55 RSCAN0TMDF0p — Transmit Buffer Data Field 0 Register (p = 0 to 95)
19.3.56 RSCAN0TMDF1p — Transmit Buffer Data Field 1 Register (p = 0 to 95)
19.3.57 RSCAN0TXQCCm — Transmit Queue Configuration and Control Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.58 RSCAN0TXQSTSm — Transmit Queue Status Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.59 RSCAN0TXQPCTRm — Transmit Queue Pointer Control Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.60 RSCAN0THLCCm — Transmit History Configuration and Control Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.61 RSCAN0THLSTSm — Transmit History Status Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.62 RSCAN0THLACCm — Transmit History Access Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.63 RSCAN0THLPCTRm — Transmit History Pointer Control Register (m = 0 to 5)
19.3.64 RSCAN0GTSTCFG — Global Test Configuration Register
19.3.65 RSCAN0GTSTCTR — Global Test Control Register
19.3.66 RSCAN0GLOCKK — Global Lock Key Register
19.3.67 RSCAN0RPGACCr — RAM Test Page Access Register (r = 0 to 63)
19.4 Interrupt Sources
19.5 CAN Modes
19.5.1 Global Modes
19.5.1.1 Global Stop Mode
19.5.1.2 Global Reset Mode
19.5.1.3 Global Test Mode
19.5.1.4 Global Operating Mode
19.5.2 Channel Modes
19.5.2.1 Channel Stop Mode
19.5.2.2 Channel Reset Mode
19.5.2.3 Channel Halt Mode
19.5.2.4 Channel Communication Mode
19.5.2.5 Bus Off State
19.6 Reception Function
19.6.1 Data Processing Using the Receive Rule Table
19.6.1.1 Acceptance Filter Processing
19.6.1.2 DLC Filter Processing
19.6.1.3 Routing Processing
19.6.1.4 Label Addition Processing
19.6.1.5 Mirror Function Processing
19.6.1.6 Timestamp
19.7 Transmission Functions
19.7.1 Transmit Priority Determination
19.7.2 Transmission Using Transmit Buffers
19.7.2.1 Transmit Abort Function
19.7.2.2 One-Shot Transmission Function (Retransmission Disabling Function)
19.7.3 Transmission Using FIFO Buffers
19.7.3.1 Interval Transmission Function
19.7.4 Transmission Using Transmit Queues
19.7.5 Transmit History Function
19.8 Gateway Function
19.9 Test Function
19.9.1 Standard Test Mode
19.9.2 Listen-Only Mode
19.9.3 Self-Test Mode (Loopback Mode)
19.9.3.1 Self-Test Mode 0 (External Loopback Mode)
19.9.3.2 Self-Test Mode 1 (Internal Loopback Mode)
19.9.4 RAM Test
19.9.5 Inter-Channel Communication Test
19.10 RS-CAN Setting Procedure
19.10.1 Initial Settings
19.10.1.1 Clock Setting
19.10.1.2 Bit Timing Setting
19.10.1.3 Communication Speed Setting
19.10.1.4 Receive Rule Setting
19.10.1.5 Buffer Setting
19.10.2 Reception Procedure
19.10.2.1 Receive Buffer Reading Procedure
19.10.2.2 FIFO Buffer Reading Procedure
19.10.3 Transmission Procedure
19.10.3.1 Procedure for Transmission from Transmit Buffers
19.10.3.2 Procedure for Transmission from Transmit/Receive FIFO Buffers
19.10.3.3 Procedure for Transmission from the Transmit Queue
19.10.3.4 Transmit History Buffer Reading Procedure
19.10.4 Test Settings
19.10.4.1 Self-Test Mode Setting Procedure
19.10.4.2 Procedure for Releasing the Protection
19.10.4.3 RAM Test Setting Procedure
19.10.4.4 Inter-Channel Communication Test Setting Procedure
19.11 Detection and Correction of Errors in RS-CAN RAM
19.11.1 ECC for the RSCAN0 RAM
19.11.2 Interrupt Request
19.11.3 ECCRCAN0CTL — RSCAN0 ECC Control Register
19.11.4 ECCRCAN0TMC — RSCAN0 ECC Test Mode Control Register
19.11.5 ECCRCAN0TED — RSCAN0 ECC Encode/Decode Input/Output Replacement Test Register
19.11.6 ECCRCAN0TRC — RSCAN0 ECC Redundant Bit Data Control Test Register
19.11.7 ECCRCAN0SYND — RSCAN0 ECC Decode Syndrome Data Register
19.11.8 ECCRCAN0HORD — RSCAN0 ECC 7-Bit Redundant Bit Data Hold Test Register
19.11.9 ECCRCAN0ECRD — RSCAN0 ECC Encode Test Register
19.11.10 ECCRCAN0ERDB — RSCAN0 ECC Redundant Bit Input/Output Replacement Register
19.11.11 SELB_READTEST — ECCREAD Test Select Register
19.12 Notes on the RS-CAN Module
Section 20 Window Watchdog Timer (WDTA)
20.1 Features of RH850/F1L WDTA
20.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
20.1.2 Register Base Address
20.1.3 Clock Supply
20.1.4 Interrupt Request
20.1.5 Reset Sources
20.2 Overview
20.2.1 Functional Overview
20.2.2 Block Diagram
20.3 Registers
20.3.1 List of Registers
20.3.2 WDTAnWDTE — WDTA Enable Register
20.3.3 WDTAnEVAC — WDTA Enable VAC Register
20.3.4 WDTAnREF — WDTA Reference Value Register
20.3.5 WDTAnMD — WDTA Mode Register
20.4 Interrupt Sources
20.5 Functions
20.5.1 WDTA after Reset Release
20.5.1.1 Start Modes
20.5.1.2 WDTA Settings after Reset Release
20.5.1.3 Default Start Mode Timing
20.5.1.4 Software Trigger Start Mode Timing
20.5.2 WDTA Trigger
20.5.2.1 Calculating an Activation Code when the VAC Function is Used
20.5.3 WDTA Error Detection
20.5.3.1 WDTA Error Mode
20.5.4 75% Interrupt Request Signals
20.5.5 Window Function
Section 21 OS Timer (OSTM)
21.1 Features of RH850/F1L OSTM
21.1.1 Number of Units
21.1.2 Register Base Address
21.1.3 Clock Supply
21.1.4 Interrupt Request
21.1.5 Reset Sources
21.2 Overview
21.2.1 Functional Overview
21.2.2 Block Diagram
21.2.3 Count Clock
21.2.4 Interrupt Sources (OSTMTINT)
21.3 Registers
21.3.1 List of Registers
21.3.2 OSTMnCMP — OSTMn Compare Register
21.3.3 OSTMnCNT — OSTMn Counter Register
21.3.4 OSTMnTE — OSTMn Count Enable Status Register
21.3.5 OSTMnTS — OSTMn Count Start Trigger Register
21.3.6 OSTMnTT — OSTMn Count Stop Trigger Register
21.3.7 OSTMnCTL — OSTMn Control Register
21.3.8 OSTMnEMU — OSTMn Emulation Register
21.4 Operation
21.4.1 Starting and Stopping OSTM
21.4.2 Interval Timer Mode
21.4.2.1 Basic Operation in Interval Timer Mode
21.4.2.2 Operation when OSTMnCMP = 0000 0000H
21.4.2.3 Setting Procedure for Interval Timer Mode
21.4.3 Free-Run Compare Mode
21.4.3.1 Basic Operation in Free-Run Compare Mode
21.4.3.2 Operation when OSTMnCMP = 0000 0000H
21.4.3.3 Setting Procedure for Free-Run Compare Mode
Section 22 Timer Array Unit B (TAUB)
22.1 Features of RH850/F1L TAUB
22.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
22.1.2 Register Base Addresses
22.1.3 Clock Supply
22.1.4 Interrupt Requests
22.1.5 Reset Sources
22.1.6 External I/O Signals
22.2 Overview
22.2.1 Features Summary
22.2.2 Terms
22.2.3 Functional List of Timer Operations
22.2.4 Input/Output Interrupt Request Signals
22.2.5 Block Diagram
22.2.6 Description of Blocks
22.3 Registers
22.3.1 List of Registers
22.3.2 Details of TAUBn Prescaler Registers
22.3.2.1 TAUBnTPS — TAUBn Prescaler Clock Select Register
22.3.3 Details of TAUBn Control Registers
22.3.3.1 TAUBnCDRm — TAUBn Channel Data Register
22.3.3.2 TAUBnCNTm — TAUBn Channel Counter Register
22.3.3.3 TAUBnCMORm — TAUBn Channel Mode OS Register
22.3.3.4 TAUBnCMURm — TAUBn Channel Mode User Register
22.3.3.5 TAUBnCSRm — TAUBn Channel Status Register
22.3.3.6 TAUBnCSCm — TAUBn Channel Status Clear Register
22.3.3.7 TAUBnTS — TAUBn Channel Start Trigger Register
22.3.3.8 TAUBnTE — TAUBn Channel Enable Status Register
22.3.3.9 TAUBnTT — TAUBn Channel Stop Trigger Register
22.3.4 Details of TAUBn Simultaneous Rewrite Registers
22.3.4.1 TAUBnRDE — TAUBn Channel Reload Data Enable Register
22.3.4.2 TAUBnRDS — TAUBn Channel Reload Data Control Channel Select Register
22.3.4.3 TAUBnRDM — TAUBn Channel Reload Data Mode Register
22.3.4.4 TAUBnRDC — TAUBn Channel Reload Data Control Register
22.3.4.5 TAUBnRDT — TAUBn Channel Reload Data Trigger Register
22.3.4.6 TAUBnRSF — TAUBn Channel Reload Status Register
22.3.5 Details of TAUBn Output Registers
22.3.5.1 TAUBnTOE — TAUBn Channel Output Enable Register
22.3.5.2 TAUBnTO — TAUBn Channel Output Register
22.3.5.3 TAUBnTOM — TAUBn Channel Output Mode Register
22.3.5.4 TAUBnTOC — TAUBn Channel Output Configuration Register
22.3.5.5 TAUBnTOL — TAUBn Channel Output Level Register
22.3.6 Details of TAUBn Dead Time Output Registers
22.3.6.1 TAUBnTDE — TAUBn Channel Dead Time Output Enable Register
22.3.6.2 TAUBnTDL — TAUBn Channel Dead Time Output Level Register
22.3.7 TAUBn Emulation Register
22.3.7.1 TAUBnEMU — TAUB Emulation Register
22.4 General Operating Procedure
22.5 Concepts of Synchronous Channel Operation
22.5.1 Rules of Synchronous Channel Operation Function
22.5.2 Simultaneous Start and Stop of Synchronous Channel Counters
22.5.2.1 Simultaneous Start and Stop within a TAUB Unit
22.6 Simultaneous Rewrite
22.6.1 Introduction
22.6.2 How to Control Simultaneous Rewrite
22.6.2.1 Initial Settings
22.6.2.2 Start Counter and Count Operation
22.6.2.3 Simultaneous Rewrite
22.6.3 Other General Rules of Simultaneous Rewrite
22.6.4 Types of Simultaneous Rewrite
22.6.4.1 Simultaneous Rewrite when the Master Channel (Re)Starts Counting (Method A)
22.6.4.2 Simultaneous Rewrite at the Peak of a Triangular Wave of the Slave Channel (Method B)
22.6.4.3 Simultaneous Rewrite when INTTAUBnIm is Generated on an Upper Channel Specified by TAUBnRDC.TAUBnRDCm (Method C1)
22.7 Channel Output Modes
22.7.1 General Procedures for Specifying a Channel Output Mode
22.7.2 Channel Output Modes Controlled Independently by TAUBn Signals
22.7.2.1 Independent Channel Output Mode 1
22.7.2.2 Independent Channel Output Mode 2
22.7.3 Channel Output Modes Controlled Synchronously by TAUBn Signals
22.7.3.1 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 1
22.7.3.2 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2
22.7.3.3 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2 with Dead Time Output
22.8 Start Timing in Each Operating Modes
22.8.1 Interval Timer Mode, Judge Mode, Capture Mode, Count-Up/-Down Mode, and Count Capture Mode
22.8.2 Event Count Mode
22.8.3 Other Operating Modes
22.9 TAUBTTOUTm Output and INTTAUBnIm Generation when Counter Starts or Restarts
22.10 Interrupt Generation upon Overflow
22.10.1 Example of Combination of TAUBTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function and TAUBTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
22.10.2 Example of Combination of TAUBTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function and Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUBTTINm Width Measurement)
22.10.3 Example of Combination of TAUBTTINm Input Position Detection Function and Interval Timer Function
22.10.4 Example of Combination of TAUBTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function and Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUBTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
22.11 TAUBTTINm Edge Detection
22.12 Independent Channel Operation Functions
22.12.1 Interval Timer Function
22.12.1.1 Overview
22.12.1.2 Equations
22.12.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.1.4 Register Settings
22.12.1.5 Operating Procedure for Interval Timer Function
22.12.1.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.12.2 TAUBTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
22.12.2.1 Overview
22.12.2.2 Equations
22.12.2.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.2.4 Register Settings
22.12.2.5 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
22.12.2.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.12.3 Clock Divide Function
22.12.3.1 Overview
22.12.3.2 Equations
22.12.3.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.3.4 Register Settings
22.12.3.5 Operating Procedure for Clock Divide Function
22.12.3.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.12.4 External Event Count Function
22.12.4.1 Overview
22.12.4.2 Equations
22.12.4.3 Block Diagram for External Event Count Function
22.12.4.4 Register Settings
22.12.4.5 Operating Procedure for External Event Count Function
22.12.4.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.12.5 One-Pulse Output Function
22.12.5.1 Overview
22.12.5.2 Equations
22.12.5.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.5.4 Register Settings
22.12.5.5 Operating Procedure for One-Pulse Output Function
22.12.6 TAUBTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function
22.12.6.1 Overview
22.12.6.2 Equations
22.12.6.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.6.4 Register Settings
22.12.6.5 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function
22.12.6.6 Specific Timing Diagrams: Overflow Behavior
22.12.7 TAUBTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function
22.12.7.1 Overview
22.12.7.2 Equations
22.12.7.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.7.4 Register Settings
22.12.7.5 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function
22.12.7.6 Specific Timing Diagrams: Overflow Behavior
22.12.8 TAUBTTINm Input Position Detection Function
22.12.8.1 Overview
22.12.8.2 Equations
22.12.8.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.8.4 Register Settings
22.12.8.5 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Position Detection Function
22.12.8.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.12.9 TAUBTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function
22.12.9.1 Overview
22.12.9.2 Equations
22.12.9.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.9.4 Register Settings
22.12.9.5 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function
22.12.9.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.12.10 TAUBTTINm Input Pulse Interval Judgment Function
22.12.10.1 Overview
22.12.10.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.10.3 Register Settings
22.12.10.4 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Pulse Interval Judgment Function
22.12.11 TAUBTTINm Input Signal Width Judgment Function
22.12.11.1 Overview
22.12.11.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.11.3 Register Settings
22.12.11.4 Operating Procedure for TAUBTTINm Input Signal Width Judgment Function
22.12.12 Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUBTTINm Width Measurement)
22.12.12.1 Overview
22.12.12.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.12.3 Register Settings
22.12.12.4 Operating Procedure for Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUBTTINm Width Measurement)
22.12.13 Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUBTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
22.12.13.1 Overview
22.12.13.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.12.13.3 Register Settings
22.12.13.4 Operating Procedure for Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUBTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
22.13 Independent Channel Simultaneous Rewrite Functions
22.13.1 Simultaneous Rewrite Trigger Generation Function Type 1
22.13.1.1 Overview
22.13.1.2 Equations
22.13.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.13.1.4 Register Settings for The Upper Channel
22.13.1.5 Register Settings for the Lower Channel(s)
22.13.1.6 Operating Procedure for Simultaneous Rewrite Trigger Generation Function Type 1
22.14 Synchronous Channel Operation Functions
22.14.1 PWM Output Function
22.14.1.1 Overview
22.14.1.2 Equations
22.14.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.14.1.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
22.14.1.5 Register Settings for the Slave Channel(s)
22.14.1.6 Operating Procedure for PWM Output Function
22.14.1.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.14.2 One-Shot Pulse Output Function
22.14.2.1 Overview
22.14.2.2 Equations
22.14.2.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.14.2.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
22.14.2.5 Register Settings for the Slave Channel
22.14.2.6 Operating Procedure for One-Shot Pulse Output Function
22.14.2.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.14.3 Delay Pulse Output Function
22.14.3.1 Overview
22.14.3.2 Equations
22.14.3.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.14.3.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
22.14.3.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 1
22.14.3.6 Register Settings For Slave Channel 2
22.14.3.7 Register Settings for Slave Channel 3
22.14.3.8 Operating Procedure for Delay Pulse Output Function
22.14.3.9 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.14.4 AD Conversion Trigger Output Function Type 1
22.14.4.1 Overview
22.14.4.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.14.5 Triangle PWM Output Function
22.14.5.1 Overview
22.14.5.2 Equations
22.14.5.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.14.5.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
22.14.5.5 Register Settings for the Slave Channel(s)
22.14.5.6 Operating Procedure for Triangle PWM Output Function
22.14.5.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.14.6 Triangle PWM Output Function with Dead Time
22.14.6.1 Overview
22.14.6.2 Equations
22.14.6.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
22.14.6.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
22.14.6.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 2
22.14.6.6 Register Settings for Slave Channel 3
22.14.6.7 Operating Procedure for Triangle PWM Output Function with Dead Time
22.14.6.8 Specific Timing Diagrams
22.14.7 AD Conversion Trigger Output Function Type 2
22.14.7.1 Overview
22.14.7.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
Section 23 Timer Array Unit D (TAUD)
23.1 Features of RH850/F1L TAUD
23.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
23.1.2 Register Base Address
23.1.3 Clock Supply
23.1.4 Interrupt Requests
23.1.5 Reset Sources
23.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
23.1.7 Internal Input/Output Signals
23.1.8 TAUD0 Input Selection
23.1.8.1 SELB_TAUD0I — TAUDTTINm Input Signal Selection Register
23.2 Overview
23.2.1 Functional Overview
23.2.2 Terms
23.2.3 Functional List of Timer Operations
23.2.4 TAUD I/O and Interrupt Request Signals
23.2.5 Block Diagram
23.2.6 Description of Blocks
23.3 Registers
23.3.1 List of Registers
23.3.2 Details of TAUDn Prescaler Registers
23.3.2.1 TAUDnTPS — TAUDn Prescaler Clock Select Register
23.3.2.2 TAUDnBRS — TAUDn Prescaler Baud Rate Setting Register
23.3.3 Details of TAUDn Control Registers
23.3.3.1 TAUDnCDRm — TAUDn Channel Data Register
23.3.3.2 TAUDnCNTm — TAUDn Channel Counter Register
23.3.3.3 TAUDnCMORm — TAUDn Channel Mode OS Register
23.3.3.4 TAUDnCMURm — TAUDn Channel Mode User Register
23.3.3.5 TAUDnCSRm — TAUDn channel status register
23.3.3.6 TAUDnCSCm — TAUDn Channel Status Clear Register
23.3.3.7 TAUDnTS — TAUDn Channel Start Trigger Register
23.3.3.8 TAUDnTE — TAUDn Channel Enable Status Register
23.3.3.9 TAUDnTT — TAUDn Channel Stop Trigger Register
23.3.4 Details of TAUDn Simultaneous Rewrite Registers
23.3.4.1 TAUDnRDE — TAUDn Channel Reload Data Enable Register
23.3.4.2 TAUDnRDS — TAUDn Channel Reload Data Control Channel Select Register
23.3.4.3 TAUDnRDM — TAUDn Channel Reload Data Mode Register
23.3.4.4 TAUDnRDC — TAUDn Channel Reload Data Control Register
23.3.4.5 TAUDnRDT — TAUDn Channel Reload Data Trigger Register
23.3.4.6 TAUDnRSF — TAUDn Channel Reload Status Register
23.3.5 Details of TAUDn Output Registers
23.3.5.1 TAUDnTOE — TAUDn Channel Output Enable Register
23.3.5.2 TAUDnTO — TAUDn Channel Output Register
23.3.5.3 TAUDnTOM — TAUDn Channel Output Mode Register
23.3.5.4 TAUDnTOC — TAUDn Channel Output Configuration Register
23.3.5.5 TAUDnTOL — TAUDn Channel Output Level Register
23.3.6 Details of TAUDn Dead Time Output Registers
23.3.6.1 TAUDnTDE — TAUDn Channel Dead Time Output Enable Register
23.3.6.2 TAUDnTDM — TAUDn Channel Dead Time Output Mode Register
23.3.6.3 TAUDnTDL — TAUDn Channel Dead Time Output Level Register
23.3.7 Details of TAUDn Real-time/Modulation Output Registers
23.3.7.1 TAUDnTRE — TAUDn Channel Real-time Output Enable Register
23.3.7.2 TAUDnTRC — TAUDn Channel Real-time Output Control Register
23.3.7.3 TAUDnTRO — TAUDn Channel Real-time Output Register
23.3.7.4 TAUDnTME — TAUDn Channel Modulation Output Enable Register
23.3.8 TAUDn Emulation Register
23.3.8.1 TAUDnEMU — TAUDn Emulation Register
23.4 Operating Procedure
23.5 Concepts of Synchronous Channel Operation
23.5.1 Rules of Synchronous Channel Operation
23.5.2 Simultaneous Start and Stop of Synchronous Channel Counters
23.5.2.1 Simultaneous Start and Stop within the Same Unit
23.5.2.2 Simultaneous Start between the Units
23.6 Simultaneous Rewrite
23.6.1 Overview of Operations
23.6.2 How to Control Simultaneous Rewrite
23.6.2.1 Initial Settings
23.6.2.2 Start Counter and Count Operation
23.6.2.3 Simultaneous Rewrite
23.6.3 Other General Rules of Simultaneous Rewrite
23.6.4 Types of Simultaneous Rewrite
23.6.4.1 Simultaneous Rewrite when the Master Channel (Re)starts Counting (Method A)
23.6.4.2 Simultaneous Rewrite at the Peak of a Triangular Wave of Slave Channel (Method B)
23.6.4.3 Simultaneous Rewrite when INTTAUDnIm is Generated on an Upper Channel Specified by TAUDnRDC.TAUDnRDCm (Method C1)
23.6.4.4 Simultaneous Rewrite when INTTAUDnIm is Generated on an Upper Channel Specified by TAUDnRDC.TAUDnRDCm that in Turn is Triggered by an External Signal (Method C2)
23.7 Channel Output Modes
23.7.1 General Procedures for Specifying a Channel Output Mode
23.7.2 Channel Output Modes Controlled Independently by TAUDn Signals
23.7.2.1 Independent Channel Output Mode 1
23.7.2.2 Independent Channel Output Mode 1 with Real-Time Output
23.7.2.3 Independent Channel Output Mode 2
23.7.3 Channel Output Modes Controlled Synchronously by TAUDn Signals
23.7.3.1 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 1
23.7.3.2 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 1 with Non-Complementary Modulation Output
23.7.3.3 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2
23.7.3.4 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2 with Dead Time Output
23.7.3.5 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2 with One-Phase PWM Output
23.7.3.6 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2 with Complementary Modulation Output
23.7.3.7 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 2 with Non-Complementary Modulation Output
23.8 Start Timing in Each Operating Modes
23.8.1 Interval Timer Mode, Judge Mode, Capture Mode, Count-up/-down Mode, and Count Capture Mode
23.8.2 Event Count Mode
23.8.3 Other Operating Modes
23.9 TAUDTTOUTm Output and INTTAUDnIm Generation when Counter Starts or Restarts
23.10 Interrupt Generation upon Overflow
23.10.1 Combination of the TAUDTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function and the TAUDTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
23.10.2 Combination of the TAUDTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function and the Overflow Interrupt Output Function (at Measuring the TAUDTTINm Width)
23.10.3 Combination of the TAUDTTINm Input Position Detection Function and the Interval Timer Function
23.10.4 Combination of the TAUDTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function and the Overflow Interrupt Output Function (at Detecting the TAUDTTINm Input Period Count)
23.11 TAUDTTINm Edge Detection
23.12 Independent Channel Operation Functions
23.12.1 Interval Timer Function
23.12.1.1 Overview
23.12.1.2 Equations
23.12.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.1.4 Register Settings
23.12.1.5 Operating Procedure for Interval Timer Function
23.12.1.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.12.2 TAUDTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
23.12.2.1 Overview
23.12.2.2 Equations
23.12.2.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.2.4 Register Settings
23.12.2.5 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
23.12.2.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.12.3 Clock Divide Function
23.12.3.1 Overview
23.12.3.2 Equations
23.12.3.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.3.4 Register Settings
23.12.3.5 Operating Procedure for Clock Divide Function
23.12.3.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.12.4 External Event Count Function
23.12.4.1 Overview
23.12.4.2 Equations
23.12.4.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.4.4 Register Settings
23.12.4.5 Operating Procedure for External Event Count Function
23.12.4.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.12.5 Delay Count Function
23.12.5.1 Overview
23.12.5.2 Equations
23.12.5.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.5.4 Register Settings
23.12.5.5 Operating Procedure for Delay Count Function
23.12.6 One-Pulse Output Function
23.12.6.1 Overview
23.12.6.2 Equations
23.12.6.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.6.4 Register Settings
23.12.6.5 Operating Procedure for One-Pulse Output Function
23.12.7 TAUDTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function
23.12.7.1 Overview
23.12.7.2 Equations
23.12.7.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.7.4 Register Settings
23.12.7.5 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function
23.12.7.6 Specific Timing Diagrams: Overflow Operation
23.12.8 TAUDTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function
23.12.8.1 Overview
23.12.8.2 Equations
23.12.8.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.8.4 Register Settings
23.12.8.5 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function
23.12.8.6 Specific Timing Diagrams: Overflow Operation
23.12.9 TAUDTTINm Input Position Detection Function
23.12.9.1 Overview
23.12.9.2 Equations
23.12.9.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.9.4 Register Settings
23.12.9.5 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Position Detection Function
23.12.9.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.12.10 TAUDTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function
23.12.10.1 Overview
23.12.10.2 Equations
23.12.10.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.10.4 Register Settings
23.12.10.5 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function
23.12.10.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.12.11 TAUDTTINm Input Pulse Interval Judgment Function
23.12.11.1 Overview
23.12.11.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.11.3 Register Settings
23.12.11.4 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Pulse Interval Judgment Function
23.12.12 TAUDTTINm Input Signal Width Judgment Function
23.12.12.1 Overview
23.12.12.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.12.3 Register Settings
23.12.12.4 Operating Procedure for TAUDTTINm Input Signal Width Judgment Function
23.12.13 Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUDTTINm Width Measurement)
23.12.13.1 Overview
23.12.13.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.13.3 Register Settings
23.12.13.4 Operating Procedure for Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUDTTINm Width Measurement)
23.12.14 Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUDTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
23.12.14.1 Overview
23.12.14.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.14.3 Register Settings
23.12.14.4 Operating Procedure for Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUDTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
23.12.15 One-Phase PWM Output Function
23.12.15.1 Overview
23.12.15.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.12.15.3 Register Settings for Lower Channels
23.12.15.4 Register Settings for Upper Channels
23.12.15.5 Operating Procedure for One-phase PWM Output Function
23.13 Independent Channel Real-Time Functions
23.13.1 Real-Time Output Function Type 1
23.13.1.1 Overview
23.13.1.2 Equations
23.13.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.13.1.4 Register Settings for Upper Channels
23.13.1.5 Register Settings for Lower Channels
23.13.1.6 Operating Procedure for Real-Time Output Function Type 1
23.13.1.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.13.2 Real-Time Output Function Type 2
23.13.2.1 Overview
23.13.2.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.13.2.3 Register Settings for Upper Channels
23.13.2.4 Register Settings for Lower Channels
23.13.2.5 Operating Procedure for Real-Time Output Function Type 2
23.13.2.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.14 Independent Channel Simultaneous Rewrite Functions
23.14.1 Simultaneous Rewrite Trigger Generation Function Type 1
23.14.1.1 Overview
23.14.1.2 Equations
23.14.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.14.1.4 Register Settings for Upper Channels
23.14.1.5 Register Settings for Lower Channels
23.14.1.6 Operating Procedure for Simultaneous Rewrite Trigger Generation Function Type 1
23.14.2 Simultaneous Rewrite Trigger Generation Function Type 2
23.14.2.1 Overview
23.14.2.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.14.2.3 Register Settings for Upper Channels
23.14.2.4 Register Settings for Lower Channels
23.14.2.5 Operating Procedure for Simultaneous Rewrite Trigger Generation Function Type 2
23.15 Synchronous Channel Operation Functions
23.15.1 PWM Output Function
23.15.1.1 Overview
23.15.1.2 Equations
23.15.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.1.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.1.5 Register Settings for Slave Channels
23.15.1.6 Operating Procedure for PWM Output Function
23.15.1.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.2 One-Shot Pulse Output Function
23.15.2.1 Overview
23.15.2.2 Equations
23.15.2.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.2.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.2.5 Register Settings for Slave Channels
23.15.2.6 Operating Procedure for One-Shot Pulse Output Function
23.15.2.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.3 Trigger Start PWM Output Function
23.15.3.1 Overview
23.15.3.2 Equations
23.15.3.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.3.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.3.5 Register Settings for Slave Channels
23.15.3.6 Operating Procedure for Trigger Start PWM Output Function
23.15.3.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.4 Delay Pulse Output Function
23.15.4.1 Overview
23.15.4.2 Equations
23.15.4.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.4.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.4.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 1
23.15.4.6 Register Settings for Slave Channel 2
23.15.4.7 Register Settings for Slave Channel 3
23.15.4.8 Operating Procedure for Delay Pulse Output Function
23.15.4.9 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.5 Offset Trigger Output Function
23.15.5.1 Overview
23.15.5.2 Equations
23.15.5.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.5.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.5.5 Register Settings for Slave Channels
23.15.5.6 Operating Procedure for Offset Trigger Output Function
23.15.5.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.6 A/D Conversion Trigger Output Function Type 1
23.15.6.1 Overview
23.15.6.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.7 Triangle PWM Output Function
23.15.7.1 Overview
23.15.7.2 Equations
23.15.7.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.7.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.7.5 Register Settings for Slave Channels
23.15.7.6 Operating Procedure for Triangle PWM Output Function
23.15.7.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.8 Triangle PWM Output Function with Dead Time
23.15.8.1 Overview
23.15.8.2 Equations
23.15.8.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.8.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.8.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 2
23.15.8.6 Register Settings for Slave Channel 3
23.15.8.7 Operating Procedure for Triangle PWM Output Function with Dead Time
23.15.8.8 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.15.9 A/D Conversion Trigger Output Function Type 2
23.15.9.1 Overview
23.15.9.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.10 Interrupt Request Signals Culling Function
23.15.10.1 Overview
23.15.10.2 Equations
23.15.10.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.15.10.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.15.10.5 Register Settings for the Slave Channel
23.15.10.6 Operating Procedure for Interrupt Request Signals Culling Function
23.15.10.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.16 Synchronous Non-Complementary and Complementary Modulation Output Functions
23.16.1 Non-Complementary Modulation Output Function Type 1
23.16.1.1 Overview
23.16.1.2 Equations
23.16.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.16.1.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.16.1.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 1
23.16.1.6 Register Settings for Slave Channels 2 to 7
23.16.1.7 Operating Procedure for Non-Complementary Modulation Output Function Type 1
23.16.1.8 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.16.2 Non-Complementary Modulation Output Function Type 2
23.16.2.1 Overview
23.16.2.2 Equations
23.16.2.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.16.2.4 Register Settings the Master Channel
23.16.2.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 1
23.16.2.6 Register settings for slave channels 2 to 7
23.16.2.7 Operating Procedure for Non-Complementary Modulation Output Function Type 2
23.16.2.8 Specific Timing Diagrams
23.16.3 Complementary Modulation Output Function
23.16.3.1 Overview
23.16.3.2 Equations
23.16.3.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
23.16.3.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
23.16.3.5 Register Settings for Slave Channel 1
23.16.3.6 Register settings for slave channels 2, 4, and 6
23.16.3.7 Register settings for slave channels 3, 5, and 7
23.16.3.8 Operating Procedure for Complementary Modulation Output Function
23.16.3.9 Specific Timing Diagrams
Section 24 Timer Array Unit J (TAUJ)
24.1 Features of RH850/F1L TAUJ
24.1.1 Number of Units
24.1.2 Register Base Address
24.1.3 Clock Supply
24.1.4 Interrupt Requests
24.1.5 Reset Sources
24.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
24.1.7 Internal Input/Output Signals
24.1.8 TAUJ0 Input Selection
24.1.8.1 SELB_TAUJ0I — TAUJTTINm Input Signal Selection Register
24.2 Overview
24.2.1 Functional Overview
24.2.2 Terms
24.2.3 Functional List of Timer Operations
24.2.4 TAUJ I/O and Interrupt Request Signals
24.2.5 Block Diagram
24.2.6 Description of Blocks
24.3 Registers
24.3.1 List of Registers
24.3.2 Details of TAUJn Prescaler Registers
24.3.2.1 TAUJnTPS — TAUJn Prescaler Clock Select Register
24.3.2.2 TAUJnBRS — TAUJn Prescaler Baud Rate Setting Register
24.3.3 Details of TAUJn Control Registers
24.3.3.1 TAUJnCDRm — TAUJn Channel Data Register
24.3.3.2 TAUJnCNTm — TAUJn Channel Counter Register
24.3.3.3 TAUJnCMORm — TAUJn Channel Mode OS Register
24.3.3.4 TAUJnCMURm — TAUJn Channel Mode User Register
24.3.3.5 TAUJnCSRm — TAUJn Channel Status Register
24.3.3.6 TAUJnCSCm — TAUJn Channel Status Clear Trigger Register
24.3.3.7 TAUJnTS — TAUJn Channel Start Trigger Register
24.3.3.8 TAUJnTE — TAUJn Channel Enable Status Register
24.3.3.9 TAUJnTT — TAUJn Channel Stop Trigger Register
24.3.4 Details of TAUJn Simultaneous Rewrite Register
24.3.4.1 TAUJnRDE — TAUJn Channel Reload Data Enable Register
24.3.4.2 TAUJnRDM — TAUJn Channel Reload Data Mode Register
24.3.4.3 TAUJnRDT — TAUJn Channel Reload Data Trigger Register
24.3.4.4 TAUJnRSF — TAUJn Channel Reload Status Register
24.3.5 Details of TAUJn Output Registers
24.3.5.1 TAUJnTOE — TAUJn Channel Output Enable Register
24.3.5.2 TAUJnTO — TAUJn Channel Output Register
24.3.5.3 TAUJnTOM — TAUJn Channel Output Mode Register
24.3.5.4 TAUJnTOC — TAUJn Channel Output Configuration Register
24.3.5.5 TAUJnTOL — TAUJn Channel Output Level Register
24.3.5.6 TAUJnEMU — TAUJn Emulation Register
24.4 Operating Procedure
24.5 Concepts of Synchronous Channel Operation Function
24.5.1 Rules of Synchronous Channel Operation Function
24.5.2 Simultaneous Start and Stop of Synchronous Channel Counters
24.5.2.1 Simultaneous Start and Stop within a TAUJ Unit
24.5.2.2 Simultaneous Start between TAUJ Units
24.6 Simultaneous Rewrite
24.6.1 How to Control Simultaneous Rewrite
24.6.1.1 Initial Settings
24.6.1.2 Start Counter and Count Operation
24.6.1.3 Simultaneous Rewrite
24.6.2 Other General Rules for Simultaneous Rewrite
24.6.3 Simultaneous Rewrite Procedure
24.7 Channel Output Modes
24.7.1 General Procedures for Specifying a Channel Output Mode
24.7.2 Channel Output Modes Controlled Independently by TAUJn Signals
24.7.2.1 Independent Channel Output Mode 1
24.7.3 Channel Output Modes Controlled Synchronously by TAUJn Signals
24.7.3.1 Synchronous Channel Output Mode 1
24.8 Start Timing in Each Operating Modes
24.8.1 Interval Timer Mode, Judge Mode, Capture Mode, Count-Up/-Down Mode, and Count Capture Mode
24.8.2 Other Operating Modes
24.9 TAUJTTOUTm Output and INTTAUJnIm Generation when Counter Starts or Restarts
24.10 Interrupt Generation upon Overflow
24.10.1 Combination of the TAUJTTINm Input Position Detection Function and the Interval Timer Function
24.11 TAUJTTINm Edge Detection
24.12 Independent Channel Operation Functions
24.12.1 Interval Timer Function
24.12.1.1 Overview
24.12.1.2 Equations
24.12.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.1.4 Register Settings
24.12.1.5 Operating Procedure for Interval Timer Function
24.12.1.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
24.12.2 TAUJTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
24.12.2.1 Overview
24.12.2.2 Equations
24.12.2.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.2.4 Register Settings
24.12.2.5 Operating Procedure for TAUJTTINm Input Interval Timer Function
24.12.2.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
24.12.3 TAUJTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function
24.12.3.1 Overview
24.12.3.2 Equations
24.12.3.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.3.4 Register Settings
24.12.3.5 Operating Procedure for TAUJTTINm Input Pulse Interval Measurement Function
24.12.3.6 Specific Timing Diagrams: Overflow Behavior
24.12.4 TAUJTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function
24.12.4.1 Overview
24.12.4.2 Equations
24.12.4.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.4.4 Register Settings
24.12.4.5 Operating Procedure for TAUJTTINm Input Signal Width Measurement Function
24.12.4.6 Specific Timing Diagrams: Overflow Behavior
24.12.5 TAUJTTINm Input Position Detection Function
24.12.5.1 Overview
24.12.5.2 Equations
24.12.5.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.5.4 Register Settings
24.12.5.5 Operating Procedure for TAUJTTINm Input Position Detection Function
24.12.5.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
24.12.6 TAUJTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function
24.12.6.1 Overview
24.12.6.2 Equations
24.12.6.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.6.4 Register Settings
24.12.6.5 Operating Procedure for TAUJTTINm Input Period Count Detection Function
24.12.6.6 Specific Timing Diagrams
24.12.7 Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUJTTINm Width Measurement)
24.12.7.1 Overview
24.12.7.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.7.3 Register Settings
24.12.7.4 Operating Procedure for Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUJTTINm Width Measurement)
24.12.8 Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUJTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
24.12.8.1 Overview
24.12.8.2 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.12.8.3 Register Settings
24.12.8.4 Operating Procedure for Overflow Interrupt Output Function (during TAUJTTINm Input Period Count Detection)
24.13 Synchronous Channel Operation Functions
24.13.1 PWM Output Function
24.13.1.1 Overview
24.13.1.2 Equations
24.13.1.3 Block Diagram and General Timing Diagram
24.13.1.4 Register Settings for the Master Channel
24.13.1.5 Register Settings for the Slave Channel(s)
24.13.1.6 Operating Procedure for PWM Output Function
24.13.1.7 Specific Timing Diagrams
Section 25 Real-Time Clock (RTCA)
25.1 Features of RH850/F1L RTCA
25.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
25.1.2 Register Base Address
25.1.3 Clock Supply
25.1.4 Interrupt Requests
25.1.5 Reset Sources
25.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
25.2 Overview
25.2.1 Functional Overview
25.2.2 Block Diagram
25.2.3 Description of Blocks
25.3 Registers
25.3.1 List of Registers
25.3.2 Details of RTCA Control Registers
25.3.2.1 RTCAnCTL0 — RTCA Control Register 0
25.3.2.2 RTCAnCTL1 — RTCA Control Register 1
25.3.2.3 RTCAnCTL2 — RTCA Control Register 2
25.3.3 Details of RTCA Sub-Counter Registers
25.3.3.1 RTCAnSUBC — RTCA Sub-Count Register
25.3.3.2 RTCAnSRBU — RTCA Sub-Count Register Read Buffer
25.3.3.3 RTCAnSUBU — RTCA Clock Error Correction Register
25.3.3.4 RTCAnSCMP — RTCA Sub-Counter Compare Register
25.3.4 Details of RTCA Clock Counter and Buffer Registers
25.3.4.1 RTCAnSECC — RTCA Seconds Count Register
25.3.4.2 RTCAnSEC — RTCA Seconds Count Buffer Register
25.3.4.3 RTCAnMINC — RTCA Minutes Count Register
25.3.4.4 RTCAnMIN — RTCA Minutes Count Buffer Register
25.3.4.5 RTCAnHOURC — RTCA Hours Count Register
25.3.4.6 RTCAnHOUR — RTCA Hours Count Buffer Register
25.3.4.7 RTCAnWEEKC — RTCA Day of the Week Count Register
25.3.4.8 RTCAnWEEK — RTCA Day of the Week Count Buffer Register
25.3.4.9 RTCAnDAYC — RTCA Day of the Month Count Register
25.3.4.10 RTCAnDAY — RTCA Day of the Month Count Buffer Register
25.3.4.11 RTCAnMONC — RTCA Month Count Register
25.3.4.12 RTCAnMONTH — RTCA Month Count Buffer Register
25.3.4.13 RTCAnYEARC — RTCA Year Count Register
25.3.4.14 RTCAnYEAR — RTCA Year Count Buffer Register
25.3.5 Details of RTCA Special Counter and Buffer Registers
25.3.5.1 RTCAnTIMEC — RTCA Time Count Register
25.3.5.2 RTCAnTIME — RTCA Time Count Buffer Register
25.3.5.3 RTCAnCALC — RTCA Calendar Count Register
25.3.5.4 RTCAnCAL — RTCA Calendar Count Buffer Register
25.3.6 Details of RTCA Alarm Setting Registers
25.3.6.1 RTCAnALM — RTCA Alarm Minute Setting Register
25.3.6.2 RTCAnALH — RTCA Alarm Hour Setting Register
25.3.6.3 RTCAnALW — RTCA Alarm Day of the Week Setting Register
25.3.7 RTCA Emulation Register
25.3.7.1 RTCAnEMU — RTCA Emulation Register
25.4 Operation
25.4.1 Clock Counter Format
25.4.2 Fixed Interval Interrupt Function
25.4.3 Alarm Interrupt Function
25.4.4 Clock Error Correction
25.4.4.1 Setting the Correction Value and the Operator
25.4.4.2 Impact of the Repetition Interval
25.4.4.3 Sample Settings
25.5 Procedures for Setup, Writing and Reading
25.5.1 Initial Setting of the RTCA
25.5.1.1 RTCA Stop Procedure
25.5.1.2 RTCA Initialization Procedure
25.5.2 Updating Clock Counters
25.5.3 Reading Clock Counters
25.5.3.1 Procedure for Reading Count Buffer Registers
25.5.3.2 Procedure for Reading Counter Registers Directly
25.5.4 Reading RTCAnSRBU
25.5.5 Writing to RTCAnSUBU
25.5.6 Writing to RTCAnSCMP
25.6 Timing Diagrams
25.6.1 Timing of Counter Start
25.6.2 Timing of Clock Counter Update while Counter Is Enabled
25.6.3 Timing of Sub-Counter Read Buffer Reading while Counter is Enabled
Section 26 Encoder Timer (ENCA)
26.1 Features of RH850/F1L ENCA
26.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
26.1.2 Register Base Address
26.1.3 Clock Supply
26.1.4 Interrupt Requests
26.1.5 Reset Sources
26.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
26.1.7 Internal Input/Output Signals
26.2 Overview
26.2.1 Functional Overview
26.2.2 Block Diagram
26.3 Registers
26.3.1 List of Registers
26.3.2 ENCAnCTL — ENCAn Control Register
26.3.3 ENCAnIOC0 — ENCAn I/O Control Register 0
26.3.4 ENCAnIOC1 — ENCAn I/O Control Register 1
26.3.5 ENCAnFLG — ENCAn Status Flag Register
26.3.6 ENCAnFGC — ENCAn Status Flag Clear Register
26.3.7 ENCAnCCR0 — ENCAn Capture/Compare Register 0
26.3.8 ENCAnCCR1 – ENCAn Capture/Compare Register 1
26.3.9 ENCAnCNT — ENCAn Counter Register
26.3.10 ENCAnTE — ENCAn Timer Enable Status Register
26.3.11 ENCAnTS — ENCAn Timer Start Trigger Register
26.3.12 ENCAnTT — ENCAn Timer Stop Trigger Register
26.3.13 ENCAnEMU — ENCAn Emulation Register
26.4 Operation
26.4.1 Timer Counter Operation
26.4.2 Up/Down Control of Timer Counter
26.4.2.1 When the ENCAnUDS1/ENCAnUDS0 Bits in the ENCAnCTL Register = 00B
26.4.2.2 When the ENCAnUDS1/ENCAnUDS0 Bits in the ENCAnCTL Register = 01B
26.4.2.3 When the ENCAnUDS1 and ENCAnUDS0 Bits in the ENCAnCTL Register = 10B
26.4.2.4 When ENCAnUDS1 / ENCAnUDS0 Bits in the ENCAnCTL Register = 11B
26.4.3 Timer Counter Clear Control by Encoder Input
26.4.3.1 Clearing Method when ENCAnSCE = 0
26.4.3.2 Clearing Method when ENCAnSCE = 1
26.4.4 Functions of ENCAnCCR0
26.4.4.1 Compare Function
26.4.4.2 Capture Function
26.4.5 Functions of ENCAnCCR1
26.4.5.1 Compare Function
26.4.5.2 Capture Function
26.4.5.3 Timer Counter Clearing upon Compare Register Match
26.4.6 Startup/Stop of Timer Counter
26.4.6.1 Startup of Timer
26.4.6.2 Stop of Timer
26.5 ENCAn Setting Sequences
26.5.1 ENCAn Setting Procedure
26.5.1.1 Initial Setting Procedure for the Counter
26.5.1.2 Initial Setting Procedure for Counter Clear
26.5.1.3 Setting Procedure for ENCAnCCR0 Register
26.5.1.4 Setting Procedure for ENCAnCCR1 Register
26.6 Timing Chart
26.6.1 Overflow Occurrence and Overflow Flag Clear Operation
26.6.2 Underflow Occurrence and Underflow Flag Clear Operation
26.6.3 Count Clearing and Capture Operation by Encoder Clear Input (ENCAnEC Pin)
26.6.4 Conflict between Overflow Occurrence and Clear Operation by Encoder Clear Input (ENCAnEC Pin)
26.6.5 Conflict between Underflow Occurrence and Clear Operation by Encoder Clear Input (ENCAnEC Pin)
26.6.6 Overflow Operation Immediately after Startup
26.6.7 Underflow Operation Immediately after Startup
26.6.8 Using the ENCAnLDE Function Immediately after Startup
26.6.9 ENCAnLDE Function (Loading Count Value)
26.6.10 Conflict between ENCAnLDE Function (Loading Counter Value) and Rewrite of ENCAnCCR0 Register
26.6.11 Conflict between ENCAnLDE Function (Loading Counter Value) and Clear Operation by Encoder Clear Input (ENCAnEC Pin)
26.6.12 Up-count after Conflict between ENCAnLDE Function (Loading Counter Value) and Clear Operation by Encoder Clear Input
26.6.13 Capture Operation between Count Clocks (ENCAnCCR1)
26.6.14 Capture Operation between Count Clocks (ENCAnCCR0)
26.6.15 Encoder Operation when Compare Match Clear Control is Enabled and ENCAnCTS = 0
26.6.16 Encoder Operation when Compare Match Clear Control is Enabled and ENCAnCTS = 1
26.6.17 Encoder Operation when Compare Match Clear Control is Disabled
26.6.18 Capture Operation Performed upon Clearing by ENCAnEC when ENCAnSCE = 1
26.6.18.1 Accompanying capture operation
26.6.18.2 When the Timing of the ENCAnEC Input is Later than that of the ENCAnE1 Input during Up-count (When ENCAnACL = 1, ENCAnBCL = 0, ENCAnZCL = 1, and ENCAnUDS[1:0] = 11B)
26.6.18.3 When the Timing of the ENCAnEC Input is the Same as that of the ENCAnE1 Input during Up-count (When ENCAnACL = 1, ENCAnBCL = 0, ENCAnZCL = 1, and ENCAnUDS[1:0] = 11B)
26.6.18.4 When the Timing of the ENCAnEC Input is Earlier than that of the ENCAnE1 Input during Up-count (When ENCAnACL = 1, ENCAnBCL = 0, ENCAnZCL = 1, and ENCAnUDS[1:0] = 11B)
26.6.18.5 When the Timing of the ENCAnEC Input is Later than that of the ENCAnE1 Input during Down-count (When ENCAnACL = 1, ENCAnBCL = 0, ENCAnZCL = 1, and ENCAnUDS[1:0] = 11B)
26.6.19 Capture Operation Performed upon Clearing by ENCAnEC when ENCAnSCE = 0
Section 27 Motor Control
27.1 Features of RH850/F1L Motor Control
27.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
27.1.2 Register Base Address
27.1.3 Clock Supply
27.1.4 Interrupt Request
27.1.5 Reset Sources
27.1.6 External Input/Output Signal
27.1.7 Internal Output Signal
27.2 Overview
27.2.1 Functional Overview
27.2.2 Basic Structure of Motor Control
27.2.3 Block Diagram
27.2.4 Definition of Terms
27.3 Registers
27.3.1 List of Registers
27.3.2 TAPAnCTL0 — TAPA Control Register 0
27.3.3 TAPAnCTL1 — TAPA Control Register 1
27.3.4 TAPAnFLG — TAPA Flag Register
27.3.5 TAPAnACWE — TAPA Asynchronous Hi-Z Control Write Enable Register
27.3.6 TAPAnACTS — TAPA Asynchronous Hi-Z Control Start Trigger Register
27.3.7 TAPAnACTT — TAPA Asynchronous Hi-Z Control Stop Trigger Register
27.3.8 TAPAnOPHS — TAPA Hi-Z Start Trigger Register
27.3.9 TAPAnOPHT — TAPA Hi-Z Stop Trigger Register
27.3.10 TAPAnEMU — TAPA Emulation Register
27.4 Asynchronous Hi-Z Control Function
27.4.1 Overview
27.4.2 System Configuration Example
27.4.3 Basic Operation
27.4.4 Asynchronous Hi-Z Control Using Software Trigger
27.4.5 Operating Procedure
27.4.6 TAPA0 Hi-Z Control Input Selection
27.4.7 Registers
27.4.7.1 PIC0HIZCENn — Hi-Z Output Control Register n (n = 0)
27.5 INT Signal Output Selection Function
27.5.1 Configuration of the INT Signal Output Selection Function
27.5.2 Block Diagram
27.5.3 Registers
27.5.3.1 PIC0REG2n0 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n0 (n = 0)
27.6 A/D Conversion Trigger Selection Function
27.6.1 Configuration of A/D Conversion Trigger Selection Function
27.6.2 Block Diagram
27.6.3 Waveforms of A/D Conversion Trigger Output Control Operation in Triangle PWM Mode
27.6.4 Operating Procedure for A/D Conversion Trigger Selection Function
27.7 ADCA Trigger Selection Function
27.7.1 Outline of Functions
27.7.2 Configuration
27.7.3 Registers
27.7.3.1 PIC0ADTEN4nj — A/D Conversion Trigger Output Control Register 4nj (n = 0, j = 0 to 2)
27.7.4 Example of Operation
27.7.5 Setup Flow
27.8 Simultaneous Start Trigger Function
27.8.1 Outline of Functions
27.8.2 Configuration
27.8.3 Registers
27.8.3.1 PIC0SSER0 — Simultaneous Start Control Register 0
27.8.3.2 PIC0SSER2 — Simultaneous Start Control Register 2
27.8.3.3 PIC0SST — Simultaneous Start Control Register
27.8.4 Example of Operation
27.8.5 Setup Flow
27.9 Trigger & Pulse Width Measuring Function
27.9.1 Overview of Functions
27.9.2 Configuration
27.9.3 Registers
27.9.3.1 PIC0REG31 — Timer I/O Control Register 31
27.9.4 Example of Operation
27.9.5 Setup Flow
27.9.6 Example of Setting Up Operation Functions
27.10 A/D Trigger Encoder Capture Function
27.10.1 Overview of Functions
27.10.2 Configuration
27.10.3 Registers
27.10.3.1 PIC0REG30 — Timer I/O Control Register 30
27.10.4 Example of Operation
27.10.5 Setup Flow
27.10.6 Example of Setting Up Operation Functions
27.11 Three-Phase PWM Output with Dead Time
27.11.1 Functional Overview
27.11.2 Configuration
27.11.3 Registers
27.11.3.1 PIC0REG2n2 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n2
27.11.3.2 PIC0HIZCENn — Hi-Z Output Control Register n (n = 0)
27.11.4 Operation Example
27.11.4.1 Pwm Output
27.11.4.2 One-Phase PWM Output
27.11.4.3 SR Flip-Flop Circuit
27.11.5 Setup Flow
27.11.6 Example of Setting Up Operation Functions
27.11.6.1 TAUDn Settings (Active High Example)
27.11.6.2 PIC Settings
27.12 High-accuracy Triangle PWM Output with Dead Time
27.12.1 Functional Overview
27.12.2 Configuration
27.12.3 Registers
27.12.3.1 PIC0REG2n0 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n0 (n = 0)
27.12.3.2 PIC0REG2n1 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n1 (n = 0)
27.12.3.3 PIC0REG2n2 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n2 (n = 0)
27.12.3.4 PIC0REG2n3 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n3 (n = 0)
27.12.3.5 PIC0HIZCENn — Hi-Z Output Control Register n (n = 0)
27.12.4 Operation Example
27.12.4.1 Triangle PWM Output with Dead Time
27.12.4.2 One-shot Pulse Output
27.12.4.3 U-phase Combination Circuit (PFN001)
27.12.4.4 Logical Operation Circuit (FN0i) (i = 0 or 1)
27.12.5 Setup Flow
27.12.6 Example of Setting Up Operation Functions
27.12.6.1 TAUDn settings (active high example)
27.12.6.2 PIC Settings (Active High Example)
27.13 Delay Pulse Output with Dead Time
27.13.1 Functional Overview
27.13.2 Configuration
27.13.2.1 TAUDn configuration
27.13.3 Registers
27.13.3.1 PIC0REG2n2 — Timer I/O Control Register 2n2 (n = 0)
27.13.3.2 PIC0HIZCENn — Hi-Z Output Control Register n (n = 0)
27.13.4 Operation Example
27.13.4.1 Delay pulse output function
27.13.4.2 One-phase PWM output
27.13.5 Setup Flow
27.13.6 Example of Setting Up Operation Functions
27.13.6.1 TAUDn Settings
27.13.6.2 Peripheral Interconnections Settings
Section 28 PWM Output/Diagnostic (PWM-Diag)
28.1 Features of RH850/F1L PWM-Diag
28.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
28.1.2 Register Base Address
28.1.3 Clock Supply
28.1.4 Interrupt Requests
28.1.5 Reset Sources
28.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
28.1.7 Internal Signals
28.1.8 Outline of Functions
28.1.9 Block Diagram
28.2 Registers
28.2.1 List of Registers
28.2.1.1 PWBAnBRSm Register
28.2.1.2 PWBAnTE Register
28.2.1.3 PWBAnTS Register
28.2.1.4 PWBAnTT Register
28.2.1.5 PWBA0EMU Register
28.2.1.6 PWGAnCTL — PWGA Control Register
28.2.1.7 PWGAnCNT — PWM Cycle Count Register
28.2.1.8 PWGAnCSDR — PWM Output Set Condition Register
28.2.1.9 PWGAnCRDR — PWM Output Reset Condition Register
28.2.1.10 PWGAnCTDR — PWGA_TRGOUTn Generation Condition Register
28.2.1.11 PWGAnCSBR — PWGAnCSDR Buffer Register
28.2.1.12 PWGAnCRBR — PWGAnCRDR Buffer Register
28.2.1.13 PWGAnCTBR — PWGAnCTDR Buffer Register
28.2.1.14 PWGAnRSF — Buffer Register Reload Status Register
28.2.1.15 PWGAnRDT — Buffer Register Reload Trigger Register
28.2.1.16 SLPWGAk — PWGA Simultaneous Trigger Register (k = 0 to 2)
28.2.1.17 PWSAnCTL Register
28.2.1.18 PWSAnSTR Register
28.2.1.19 PWSAnSTC Register
28.2.1.20 PWSAnQUEj (j = 0 to 7) Register
28.2.1.21 PWSAnPVCRx_y (x = 00, 02, 04 ... 70, y = 01, 03, 05 ... 71) Register
28.2.1.22 PWSAnEMU — Emulation Control Register
28.3 Operating Procedure
28.4 Operation Waveform of PWM-Diag
28.4.1 PWM Waveform Output by PWGA and Operation Waveform for A/D Conversion Trigger Output
28.4.1.1 Basic Operation Waveform of PWGA
28.4.1.2 Operation Waveform when Simultaneous Rewrite for PWGA is Executed
28.4.1.3 Operation Waveform when Stopping and Restarting PWGA Operation
28.4.1.4 Waveforms of PWGA Operation with Specific Settings
28.4.2 Operation Waveform when A/D Conversion Trigger Occurs in PWSA
28.5 PWM-Diag Related Function in A/D Converter (ADCA)
28.5.1 ADCA registers when the PWM-Diag function is used
Section 29 A/D Converter (ADCA)
29.1 Features of RH850/F1L ADCA
29.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
29.1.2 Register Base Address
29.1.3 Clock Supply
29.1.4 Interrupt Requests
29.1.5 Reset Sources
29.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
29.2 Overview
29.2.1 Functional Overview
29.2.2 Block Diagram
29.3 Registers
29.3.1 List of Registers
29.3.2 ADCA Specific Registers
29.3.2.1 ADCAnVCRj — Virtual Channel Register j
29.3.2.2 ADCAnPWDVCR — PWM-Diag Virtual Channel Register
29.3.2.3 ADCAnDRj — Data Register j
29.3.2.4 ADCAnDIRj — Data Supplementary Information Register j
29.3.2.5 ADCAnPWDTSNDR — PWM-Diag Data Register
29.3.2.6 ADCAnPWDDIR — PWM-Diag Data Supplementary Information Register
29.3.2.7 ADCAnADHALTR — A/D Force Halt Register
29.3.2.8 ADCAnADCR — A/D Control Register
29.3.2.9 ADCAnMPXCURR — MPX Current Register
29.3.2.10 ADCAnTHSMPSTCR — T&H Sampling Start Control Register
29.3.2.11 ADCAnTHCR — T&H Control Register
29.3.2.12 ADCAnTHAHLDSTCR — T&H Group A Hold Start Control Register
29.3.2.13 ADCAnTHBHLDSTCR — T&H Group B Hold Start Control Register
29.3.2.14 ADCAnTHACR — T&H Group A Control Register
29.3.2.15 ADCAnTHBCR — T&H Group B Control Register
29.3.2.16 ADCAnTHER — T&H Enable Register
29.3.2.17 ADCAnTHGSR — T&H Group Select Register
29.3.2.18 ADCAnSMPCR — Sampling Control Register
29.3.2.19 ADCAnSFTCR — Safety Control Register
29.3.2.20 ADCAnULLMTBR0 to 2 — Upper Limit/Lower Limit Table Registers 0 to 2
29.3.2.21 ADCAnECR — Error Clear Register
29.3.2.22 ADCAnULER — Upper Limit/Lower Limit Error Register
29.3.2.23 ADCAnOWER — Overwrite Error Register
29.3.3 Scan Group (SG) Unique Registers
29.3.3.1 ADCAnSGSTCRx — Scan Group x Start Control Register
29.3.3.2 ADCAnSGCRx — Scan Group x Control Register
29.3.3.3 ADCAnPWDSGCR — PWM-Diag Scan Group Control Register
29.3.3.4 ADCAnSGVCSPx — Scan Group x Start Virtual Channel Pointer
29.3.3.5 ADCAnSGVCEPx — Scan Group x End Virtual Channel Pointer
29.3.3.6 ADCAnSGMCYCRx — Scan Group x Multicycle Register
29.3.3.7 ADCAnPWDSGSEFCR — PWM-Diag Scan End Flag Clear Register
29.3.3.8 ADCAnSGSEFCRx — Scan Group x Scan End Flag Clear Register
29.3.3.9 ADCAnSGSTR — Scan Group x Status Register
29.3.4 Hardware Trigger Specific Register
29.3.4.1 ADCAnSGTSELx — Scan Group x Start Trigger Control Register x
29.3.5 Self-Diagnosis Specific Registers
29.3.5.1 ADCAnDGCTL0 — Self-Diagnosis Control Register 0
29.3.5.2 ADCAnDGCTL1 — Self-Diagnosis Control Register 1
29.3.5.3 ADCAnPDCTL1 — Pull Down Control Register 1
29.3.5.4 ADCAnPDCTL2 — Pull Down Control Register 2
29.3.6 Emulation Specific Register
29.3.6.1 ADCAnEMU — Emulation Control Register
29.4 Operation
29.4.1 Initial Setting
29.4.2 Trigger Input
29.4.3 Ending A/D Conversion
29.4.4 Example of Scan Group Operation
29.4.5 Channel Repeat Mode
29.4.6 Example of Simultaneous Track and Hold Operation
29.4.7 A/D Conversion with External Analog Multiplexer
29.4.7.1 A/D Conversion with PWM-Diag Enabled
29.4.8 Example of Synchronous Suspend and Resume Operation
29.4.9 Example of Asynchronous Suspend and Resume Operation
29.4.10 Error Detecting Functions
29.4.10.1 Upper-Limit/Lower-Limit Error Detecting Function
29.4.10.2 Overwrite Error Detecting Function
29.4.10.3 SVSTOP Operation
29.4.11 Activating Scan Group by a Hardware Trigger
29.4.11.1 Stopping Scan Group by ADHALT
29.4.12 Scan End Interrupt Request
29.4.13 A/D Error Interrupt Request
29.5 Self-Diagnostic Function
29.5.1 Diagnosis of A/D Conversion Circuit
29.5.1.1 Diagnostic procedure
29.5.2 Diagnosis of Channel Multiplexer
29.5.2.1 Diagnostic procedure
29.5.3 Diagnosis of Open Pins
29.5.3.1 Diagnostic procedure
29.5.4 Diagnosis of T&H Circuit
29.5.4.1 Diagnostic Procedure (in case of T&H circuit ch0 diagnosis)
29.5.4.2 Diagnosis Mechanism
29.6 Definition of A/D Conversion Accuracy
29.7 Usage Notes
29.7.1 Range of Channel Input Voltage
29.7.2 Notes on Application Design
Section 30 Key Return (KR)
30.1 Features of RH850/F1L KR
30.1.1 Number of Units and Channels
30.1.2 Register Base Address
30.1.3 Clock Supply
30.1.4 Interrupt Requests
30.1.5 Reset Sources
30.1.6 External Input/Output Signals
30.2 Overview
30.2.1 Functional Overview
30.2.2 Block Diagram
30.3 Registers
30.3.1 List of Registers
30.3.2 KRnKRM — Key Return Mode Register
30.4 Operation
30.4.1 Interrupt Request KRnTIKR
Section 31 Functional Safety
31.1 Overview
Section 32 Data CRC (DCRA)
32.1 Features of RH850/F1L DCRA
32.1.1 Number of Units
32.1.2 Register Base Address
32.1.3 Clock Supply
32.1.4 Reset Sources
32.2 Overview
32.2.1 Functional Overview
32.2.2 Block Diagram
32.2.3 Operational Circuit
32.3 Registers
32.3.1 List of Registers
32.3.2 DCRAnCIN — CRC Input Register
32.3.3 DCRAnCOUT — CRC Data Register
32.3.4 DCRAnCTL — CRC Control Register
32.4 Operation
Section 33 Integrated Cryptographic Unit (ICUSB)
Section 34 On-Chip Debug Unit (OCD)
34.1 Overview of RH850/F1L OCD
34.1.1 Functional Overview
34.2 Peripheral Break Control
34.3 Registers
34.3.1 EPC — Emulation Peripheral Control Register
34.4 Caution on Using On-Chip Debugging
34.4.1 Treatment of Devices Used for Debugging
Section 35 Flash Memory
35.1 Features
35.2 Structure of Memory
35.2.1 Mapping of Code Flash Memory
35.2.2 Mapping of Data Flash Memory
35.3 Operating Modes Associated with Flash Memory
35.4 Functions
35.4.1 Overview of Functions
35.5 Serial Programming
35.5.1 Environments for Programming
35.6 Communication Modes
35.6.1 Asynchronous Flash Programming Interface - 1-Wire UART
35.6.2 Asynchronous Flash Programming Interface - 2-Wire UART
35.6.3 Synchronous Flash Programming Interface CSI
35.6.4 Selection of Communication Method
35.7 Self Programming
35.7.1 Outline
35.7.2 Background Operation
35.7.3 Enabling of Self-Programming
35.7.3.1 FLMDCNT Register
35.8 Reading Flash Memory
35.8.1 Reading Code Flash Memory
35.8.2 Reading Data Flash Memory
35.8.2.1 EEPRDCYCL — Data Flash Wait Cycle Control Register
35.8.2.2 PRDNAMEn — Product Name Storage Register (n = 1 to 3)
35.10 ECC Error Detection and Correction for Data Flash Memory
35.9 ECC Error Detection and Correction for Code Flash Memory
35.9.1 Outline of ECC Functions for Code Flash Memory
35.9.2 Interrupt Request
35.9.3 Registers
35.9.3.1 List of Registers
35.9.3.2 CFECCCTL — Code Flash ECC Control Register
35.9.3.3 CFFSTERSTR — Code Flash First Error Status Register
35.9.3.4 CFFSTSTC — Code Flash Error Status Clear Register
35.9.3.5 CFOVFSTR — Code Flash Error Overflow Status Register
35.9.3.6 CFOVFSTC — Code Flash Error Overflow Status Clear Register
35.9.3.7 CFERRINT — Code Flash Error Notification Control Register
35.9.3.8 CFFSTEADR — Code Flash First Error Address Register
35.9.3.9 CFTSTCTL — Code Flash Test Control Register
35.9.4 ECC Test Function for the Code Flash
35.10.1 Outline of ECC Functions for Data Flash Memory
35.10.2 Interrupt Request
35.10.3 Registers
35.10.3.1 List of Registers
35.10.3.2 DFECCCTL — Data Flash ECC Control Register
35.10.3.3 DFERSTR — Data Flash Error Status Register
35.10.3.4 DFERSTC — Data Flash Error Status Clear Register
35.10.3.5 DFERRINT — Data Flash Error Notification Control Register
35.10.3.6 DFTSTCTL — Data Flash Test Control Register
35.10.4 ECC Test Function for the Data Flash
35.11 Option Bytes
35.11.1 Option Byte Setting
35.11.2 OPBT0 — Option Byte 0 Register
35.12 Usage Notes
Section 36 RAM
36.1 Features
36.2 Memory Configuration
36.3 ECC Error Detection and Correction for Local RAM
36.3.1 Outline of ECC Functions for Local RAM
36.3.2 Interrupt Request
36.4 Registers
36.4.1 List of Registers
36.4.2 LRECCCTL — Local RAM ECC Control Register
36.4.3 LRFSTERSTR — Local RAM First Error Status Register
36.4.4 LRSTCLR — Local RAM Error Status Clear Register
36.4.5 LROVFSTR — Local RAM Error Overflow Status Register
36.4.6 LROVFSTC — Local RAM Error Overflow Status Clear Register
36.4.7 LRFSTEADR0 — Local RAM First Error Address Register 0
36.4.8 LRERRINT — Local RAM Error Notification Control Register
36.4.9 LRTSTCTL — Local RAM Test Control Register
36.4.10 LRTDATBF0 — Local RAM Test Data Read Buffer 0
Section 37 Boundary Scan
37.1 Overview
37.2 Features
37.3 External Input/Output Pins
37.4 Register Descriptions
37.4.1 Instruction Register (SDIR)
37.4.2 ID Register (SDID)
37.4.3 Bypass Register (SDBPR)
37.4.4 Boundary Scan Register (SDBSR)
37.5 Operation
37.5.1 TAP Controller
37.5.2 Supported Commands
37.5.2.1 BYPASS
37.5.2.2 SAMPLE/PRELOAD
37.5.2.3 EXTEST
37.5.2.4 IDCODE
37.5.3 Pins Subjected to Boundary Scan
37.6 Usage Notes
Section 38 Power Supply and Power Domains
38.1 Function
38.1.1 Power Supply Pins
38.1.2 Block Diagram of Power Domains
38.1.3 Power Domains Arrangement
Appendix A. Pin List
Colophon
Address List
Back Cover




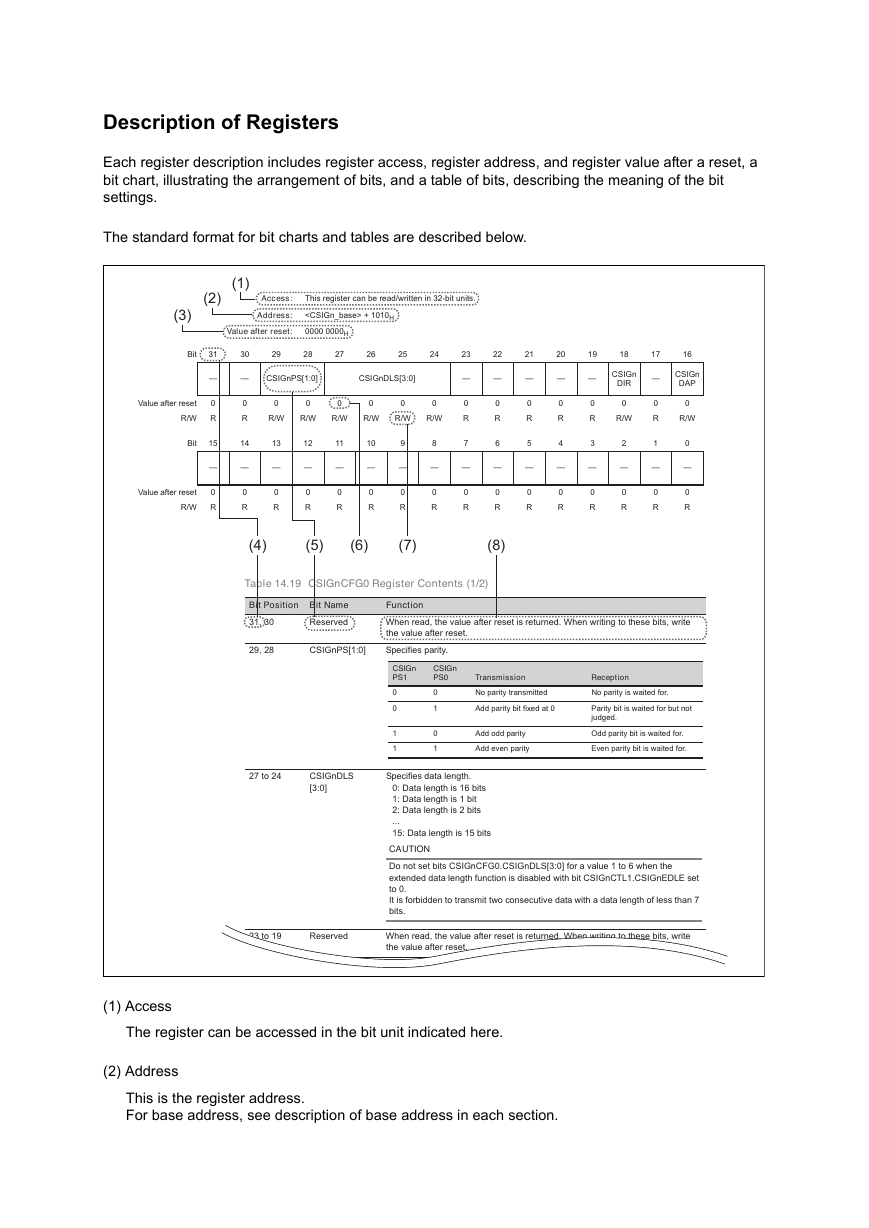










 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc