This Presentation is a part
of AnyLogic Standard
Training Program
Java Basics for
AnyLogic
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
�
General remarks
• You do not have to learn full OO programming
• You need to understand Java data types,
expression and statement syntax
• Please note:
– Java is case-sensitive: MyVar is different to myVar!
– Spaces are not allowed in names: “My Var” is illegal name!
– Each statement has to be finished with “;”: MyVar = 150;
– Each function has to have parenthesis: time(), add(a)
– Mind integer division: 3/2 = 1, not 1.5
– Boolean values are only true and false, you cannot use 1 and 0
– Dot “.” brings you “inside” the object: agent.event.restart()
– Array elements have indexes from 0 to N-1
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
2
�
Types
• Primitive Types
– double – represent real numbers: 1.43, 3.6E18, -14.0
– int – represents integer numbers: 12, 16384, -5000
– boolean – represents Boolean (true/false) values
• Compound Types – Classes
– String – represents textual strings, e.g. “MSFT”, “Hi there!”, etc
– ArrayList, LinkedList – collections of objects
– HyperArray – represents multi-dimensional array in System
Dynamics models
– … many others. See AnyLogic and Java Class References
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
3
�
Expressions
• Arithmetic operations
– Notation: +, –, *, /, % (remainder)
– In integer divisions, the fraction part is lost, e.g. 3 / 2 equals 1, and 2 / 3 equals 0
– Multiplication operators have priority over addition operators
– The ‘+‘ operator allows operands of type String
• Comparison operations
– Notation: >, >=, <, <=, ==, !=
• Boolean operations
– Notation: && (AND), || (OR), ! (NOT)
• Conditional operator
– Notation: condition ? value-if-true : value-if-false
• Assignments and shortcuts
– Notation: =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=, ++, --
– Example: a+=b is equivalent to a=a+b
Within most of operators,
left-to-right precedence
holds
Parentheses may be used
to alter the precedence of
operations
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
4
�
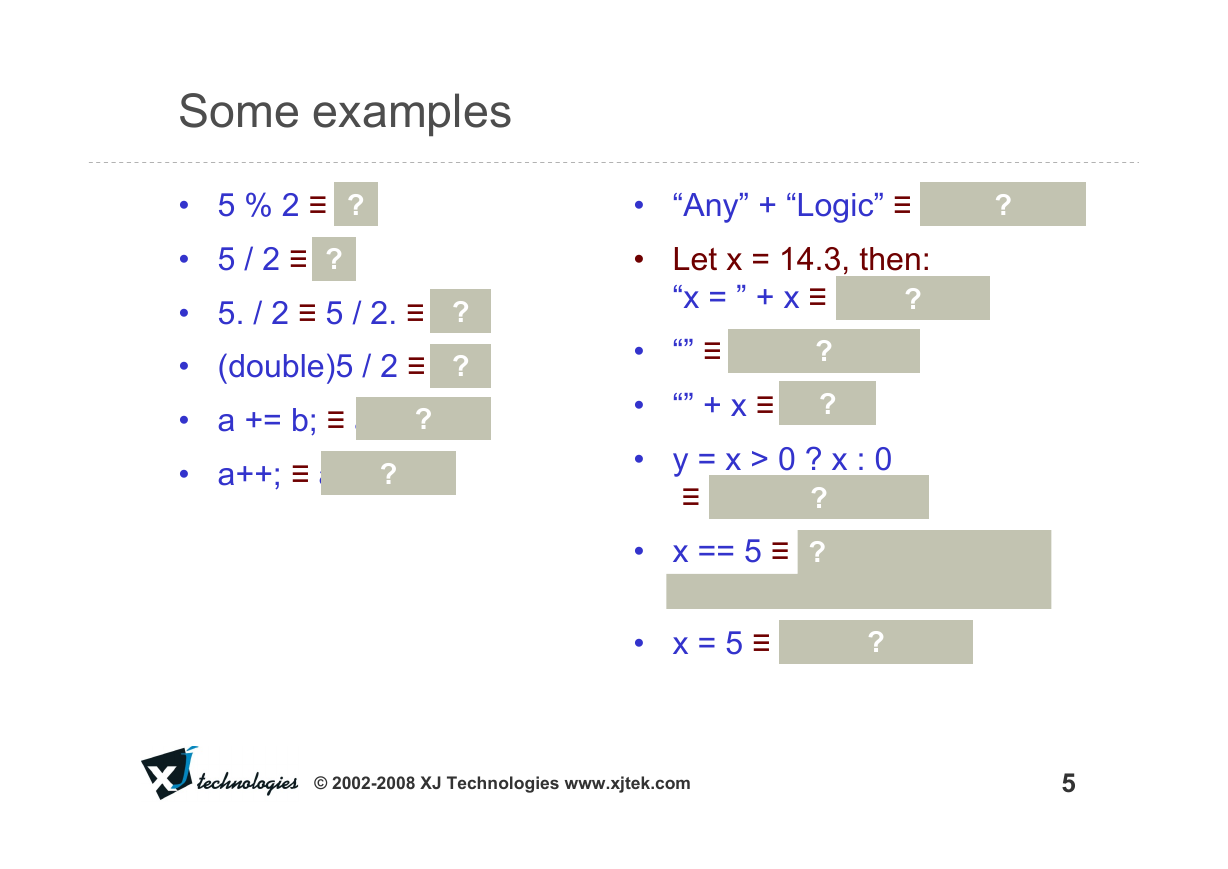
Some examples
• 5 % 2 ≡ 1
?
• 5 / 2 ≡ 2
?
?
• 5. / 2 ≡ 5 / 2. ≡ 2.5
(double)5 / 2 ≡ 2.5
•
?
?
• a += b; ≡ a = a+b;
• a++; ≡ a = a+1;
?
“Any” + “Logic” ≡ “AnyLogic”
?
•
• Let x = 14.3, then:
“x = ” + x ≡ “x = 14.3”
?
“” ≡ empty string
“” + x ≡ “14.3”
•
•
• y = x > 0 ? x : 0
?
?
≡ y = max( 0, x )
?
?
• x == 5 ≡ true if x equals 5,
otherwise false, whereas:
• x = 5 ≡ assign 5 to x
?
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
5
�
Calling Methods and Accessing Fields
• Method call
– To call a method, type its name followed by parenthesis. If
necessary, put parameters separated by commas within the
parenthesis. Examples:
x = time();
moveTo( getX(), getY() + 100 );
traceln( “Population is increasing” );
• Accessing object fields and methods
– To access a field or method of a model element (statechart,
timer, animation), use the model element name followed by
dot ‘.’ followed by the field/method name. Examples:
statechart.fireEvent( “go” );
sum = sum + agents.get(i).x;
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
6
�
Writing comments in Java code
• There are two kinds of comments:
/* text */
A traditional comment: all the text from the ASCII
characters /* to the ASCII characters */ is ignored (as in C
and C++)
/**
* The class represents AnyLogic 3D animation. It contains the canvas object.
*
* @author Daniil Chunosov
* @version 5.0
*/
public class Animation3DPanel extends javax.swing.JPanel …
// text
A end-of-line comment: all the text from the ASCII
characters // to the end of the line is ignored (as in
C++).
// Prepare Engine for simulation:
engine.start( root );
engine.runFast(); // fast mode – no animation
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
7
�
Replicated Objects
• Replicated objects are stored in a
collection.
Items are indexed from 0 to N-1
– Getting the current size of the collection:
people.size()
– Obtaining i-th item of the collection:
people.get( i )
– Adding a new object to the collection:
add_people();
– Removing an object from the collection:
remove_people( person );
© 2002-2008 XJ Technologies www.xjtek.com
8
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc