IEEE Std 1101.1-1998
(Revision of
IEEE Std 1101.1-1991)
IEEE Standard for Mechanical Core
Specications for Microcomputers
Using IEC 60603-2 Connectors
Sponsor
Microprocessor and Microcomputer Standards Subcommittee
of the
IEEE Computer Society
Approved 28 September 1998
IEEE-SA Standards Board
Abstract:
The basic dimensions of a range of modular subracks conforming to IEC 60297-3 (1984-
01) and IEC 60297-4 (1995-03) for mounting in equipment according to IEC 60297-1 (1986-09) and
ANSI/EIA 310-D-1992, together with the basic dimensions of a compatible range of plug-in units,
printed boards, and backplanes, are covered. The dimensions and tolerances necessary to ensure
mechanical function compatibility are provided. This standard offers total system integration guide-
lines with attendant advantages, such as reduction in design and development time, manufacturing
cost savings, and distinct marketing advantages.
Keywords:
compatibility, mechanical interchangeability, plug-in units, subracks
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
345 East 47th Street, New York, NY 10017-2394, USA
Copyright ' 1998 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
All rights reserved. Published 18 December 1998. Printed in the United States of America.
Print:
PDF:
ISBN 0-7381-1449-9 SH94691
ISBN 0-7381-1450-2 SS94691
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form, in an electronic retrieval system or otherwise, without the prior
written permission of the publisher.
�
IEEE Standards
documents are developed within the IEEE Societies and the Standards Coordinat-
ing Committees of the IEEE Standards Association (IEEE-SA) Standards Board. Members of the
committees serve voluntarily and without compensation. They are not necessarily members of the
Institute. The standards developed within IEEE represent a consensus of the broad expertise on the
subject within the Institute as well as those activities outside of IEEE that have expressed an inter-
est in participating in the development of the standard.
Use of an IEEE Standard is wholly voluntary. The existence of an IEEE Standard does not imply
that there are no other ways to produce, test, measure, purchase, market, or provide other goods and
services related to the scope of the IEEE Standard. Furthermore, the viewpoint expressed at the
time a standard is approved and issued is subject to change brought about through developments in
the state of the art and comments received from users of the standard. Every IEEE Standard is sub-
jected to review at least every ve years for revision or reafrmation. When a document is more
than ve years old and has not been reafrmed, it is reasonable to conclude that its contents,
although still of some value, do not wholly reect the present state of the art. Users are cautioned to
check to determine that they have the latest edition of any IEEE Standard.
Comments for revision of IEEE Standards are welcome from any interested party, regardless of
membership afliation with IEEE. Suggestions for changes in documents should be in the form of a
proposed change of text, together with appropriate supporting comments.
Interpretations: Occasionally questions may arise regarding the meaning of portions of standards as
they relate to specic applications. When the need for interpretations is brought to the attention of
IEEE, the Institute will initiate action to prepare appropriate responses. Since IEEE Standards rep-
resent a consensus of all concerned interests, it is important to ensure that any interpretation has
also received the concurrence of a balance of interests. For this reason, IEEE and the members of its
societies and Standards Coordinating Committees are not able to provide an instant response to
interpretation requests except in those cases where the matter has previously received formal
consideration.
Comments on standards and requests for interpretations should be addressed to:
Secretary, IEEE-SA Standards Board
445 Hoes Lane
P.O. Box 1331
Piscataway, NJ 08855-1331
USA
Note: Attention is called to the possibility that implementation of this standard may
require use of subject matter covered by patent rights. By publication of this standard,
no position is taken with respect to the existence or validity of any patent rights in
connection therewith. The IEEE shall not be responsible for identifying patents for
which a license may be required by an IEEE standard or for conducting inquiries into
the legal validity or scope of those patents that are brought to its attention.
Authorization to photocopy portions of any individual standard for internal or personal use is
granted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., provided that the appropriate
fee is paid to Copyright Clearance Center. To arrange for payment of licensing fee, please contact
Copyright Clearance Center, Customer Service, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923 USA;
(978) 750-8400. Permission to photocopy portions of any individual standard for educational class-
room use can also be obtained through the Copyright Clearance Center.
�
Introduction
(This introduction is not a part of IEEE Std 1101.1-1998, IEEE Standard for Mechanical Core Specications for Micro-
computers Using IEC 60603-2 Connectors.)
With the introduction of international (IEC) microcomputer architectures based on the Euroboard form fac-
tor, the IEEE Computer Society Technical Committee on Microprocessors and Microcomputers found it
appropriate to form a separate IEEE standard to expand upon the IEC 60297 series of standards, Dimensions
of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series. (See Clause 3 of this standard.)
This standard provides design engineers with the dimensions and tolerances necessary to ensure mechanical
function compatibility. This standard also provides environmental specications as an addendum to IEC
60297-3 (1984-01).
This mechanical standard offers total system integration guidelines. It offers advantages such as reduction in
design and development time, manufacturing cost savings, and distinct marketing advantages.
This standard covers standardized dimensions of a range of modular subracks and a compatible range of
plug-in units, printed boards, backplanes, and connectors.
This standard was revised from IEEE Std 1101.1-1991.
At the time that the revision was completed, the P1101.1 Working Group had the following membership:
Ralf Behrens
Martin Blake
Robert Downing
Jean-Jacques Dumont
Eike Waltz,
Chair
Frank Hom,
Secretary
Wayne P. Fischer
Tad Kubic
Paul Mazura
Michael Munroe
Joe P. Norris
Elwood T. Parsons
Holly Shernsky
Michael G. Thompson
Sue Wong
The following persons were on the balloting committee that approved this document for submission to the
IEEE-SA Standards Board:
Ghassan A. Abbas
Malcolm J. Airst
Ray S. Alderman
Keith D. Anthony
Edmund H. Baulsir
Martin Blake
Ralf Bokaemper
David Brearley
Charles Brill
C. H. Chen
Jean-Jacques Dumont
Jean Paul Emard
Wayne P. Fischer
Kenneth C. Heck
Roger Hinsdale
Frank Hom
Jing Kwok
Conrad A. Laurvick
Gerald E. Laws
Rollins Linser
Gary S. Manchester
Joseph R. Marshall
Thanos Mentzelopoulos
Gene E. Milligan
Klaus-Dieter Mueller
Michael Munroe
Joe P. Norris
Peter G. Odell
Elwood T. Parsons
Hermann H. Strass
Michael G. Thompson
Robert C. Tripi
Bruce Wallace
David L. Wright
Copyright ' 1998 IEEE. All rights reserved.
iii
�
The nal conditions for approval of this standard were met on 28 September 1998. This standard was condi-
tionally approved by the IEEE-SA Standards Board on 16 September 1998, with the following membership:
Richard J. Holleman,
Chair
Donald N. Heirman,
Vice Chair
Judith Gorman,
Secretary
Satish K. Aggarwal
Clyde R. Camp
James T. Carlo
Gary R. Engmann
Harold E. Epstein
Jay Forster*
Thomas F. Garrity
Ruben D. Garzon
*Member Emeritus
James H. Gurney
Jim D. Isaak
Lowell G. Johnson
Robert Kennelly
E. G. Al Kiener
Joseph L. Koepnger*
Stephen R. Lambert
Jim Logothetis
Donald C. Loughry
L. Bruce McClung
Louis-Franois Pau
Ronald C. Petersen
Gerald H. Peterson
John B. Posey
Gary S. Robinson
Hans E. Weinrich
Donald W. Zipse
Catherine Berger
IEEE Standards Project Editor
iv
Copyright ' 1998 IEEE. All rights reserved.
�
Contents
1.
Scope.................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Basic dimensions of subracks ...................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Dimensions of plug-in units......................................................................................................... 1
1.3 Environmental requirements of subracks..................................................................................... 1
Purpose................................................................................................................................................. 1
References............................................................................................................................................ 1
General arrangement............................................................................................................................ 3
Euroboard matrix ................................................................................................................................. 4
Euroboard sizes.................................................................................................................................... 5
6.1 Euroboard height.......................................................................................................................... 5
6.2 Euroboard depth........................................................................................................................... 5
6.3 Euroboard thickness..................................................................................................................... 5
6.4 Conductive elements and guide rails ........................................................................................... 5
Position of plug-in unit mounted connectors, board-type and box-type.............................................. 9
Plug-in unit description...................................................................................................................... 12
Plug-in unit dimensions ..................................................................................................................... 12
9.1 Board-type plug-in units ............................................................................................................ 12
9.2 Box-type, box/board-type plug-in units..................................................................................... 12
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Backplane design and mounting positions......................................................................................... 13
10.1 Rigidity ...................................................................................................................................... 13
10.2 Dimensions ................................................................................................................................ 13
11.
Subracks............................................................................................................................................. 34
12.
Environmental specifications............................................................................................................. 42
12.1 Introduction................................................................................................................................ 42
12.2 Climatic tests.............................................................................................................................. 42
12.3 Mechanical load ......................................................................................................................... 42
12.4 Vibration .................................................................................................................................... 44
12.5 Shock.......................................................................................................................................... 44
12.6 Safety tests ................................................................................................................................. 44
Annex A (informative) Bibliography .......................................................................................................... 47
Copyright ' 1998 IEEE. All rights reserved.
v
�
IEEE Standard for Mechanical Core
Specications for Microcomputers
Using IEC 60603-2 Connectors
1. Scope
1.1 Basic dimensions of subracks
This standard covers the basic dimensions of a range of modular subracks conforming to IEC 60297-3
(1984-01) and IEC 60297-4 (1995-03) for mounting in equipment according to IEC 60297-1 (1986-09) and
ANSI/EIA 310-D-1992, together with the basic dimensions of a compatible range of plug-in units, printed
boards, and backplanes.
1.2 Dimensions of plug-in units
This standard will give the dimensions of associated plug-in units and connector-mounting details together
with applicable detail dimensions of the subrack.
1.3 Environmental requirements of subracks
This standard will state environmental requirements of subracks and their associated plug-in units.
2. Purpose
The purpose of this standard is the specication of dimensions that will ensure the mechanical interchange-
ability and environmental requirements of subracks and of plug-in units.
3. References
The following publications shall be used in conjunctions with this standard. When they are superseded by an
approved revision, the revision shall apply.
1
ANSI/EIA 310-D-1992: Racks, Panels, and Associated Equipment.
1
ANSI publications are available from the Sales Department, American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street, 13th Floor,
New York, NY 10036, USA (www.ansi.org/).
Copyright ' 1998 IEEE. All rights reserved.
1
�
IEEE
Std 1101.1-1998
IEEE STANDARD FOR MECHANICAL CORE SPECIFICATIONS
CFR (Code of Federal Regulations), Title 47: Telecommunications, Part 15J, published by Ofce of the Fed-
2
eral Register (FCC Rules and Regulations are contained within this document).
3
IEC 60068-2-1 (1990-05), Environmental testingPart 2: Tests. Tests A: Cold.
IEC 60068-2-2 (1974-01), Environmental testingPart 2: Tests. Test B: Dry Heat.
IEC 60068-2-6 (1995-03), Environmental testingPart 2: Tests. Test Fc: Vibration (sinusoidal).
IEC 60068-2-11 (1981-01), Environmental testingPart 2: Tests. Test Ka: Salt mist.
IEC 60068-2-27 (1987-06), Environmental testingPart 2: Tests. Test Ea and guidance: Shock.
IEC 60097 (1991-05), Grid systems for printed circuits.
IEC 60249-2-1 (1985-01), Base materials for printed circuits. Part 2: Specications. Specication No. 1:
Phenolic cellulose paper copper-clad laminated sheet, high electrical quality.
IEC 60249-2-2 (1985-01), Base materials for printed circuits. Part 2: Specications. Specication No. 2:
Phenolic cellulose paper copper-clad laminated sheet, economic quality.
IEC 60249-2-3 (1987-04), Base materials for printed circuits. Part 2: Specications. Specication No. 3:
Epoxide cellulose paper copper-clad laminated sheet of dened ammability (vertical burning test).
IEC 60249-2-4 (1987-06), Base materials for printed circuits. Part 2: Specications. Specication No. 4:
Epoxide woven glass fabric copper-clad laminated sheet, general purpose grade.
IEC 60249-2-5 (1987-06), Base materials for printed circuits. Part 2: Specications. Specication No. 5:
Epoxide woven glass fabric copper-clad laminated sheet of dened ammability (vertical burning test).
IEC 60297-1 (1986-09), Dimensions of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series. Part 1: Panels
and racks.
IEC 60297-3 (1984-01), Dimensions of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series. Part 3: Sub-
racks and associated plug-in units.
IEC 60297-4 (1995-03), Mechanical structures of electronic equipmentDimensions of mechanical struc-
tures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series. Part 4: Subracks and associated plug-in unitsAdditional dimensions.
IEC 60603-2 (1995-09), Connectors for frequencies below 3 MHz for use with printed boardsPart 2:
Detail specication for two-part connectors with assessed quality, for printed boards, for basic grid of
2.54 mm (0.1 in), with common mounting features.
IEC 60651 (1979-01), Sound level meters.
IEC 60707 (1981-01), Methods of test for the determination of the ammability of solid electrical insulating
materials when exposed to an igniting source.
IEC 61010-1 (1990-09), Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and labora-
4
tory usePart 1: General requirements.
2
CFR publications are available from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Ofce, P.O. Box 37082, Washing-
ton, DC 20013-7082, USA.
3
IEC publications are available from the Sales Department of the International Electrotechnical Commission, Case Postale 131, 3, rue
de Varemb, CH-1211, Genve 20, Switzerland/Suisse (www.iec.ch/). IEC publications are also available from the Sales Department,
American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street, 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036, USA (www.ansi.org/).
4
IEC 61010-1 (1990-09) replaces withdrawn standard IEC 60348 (1978).
2
Copyright ' 1998 IEEE. All rights reserved.
�
FOR MICROCOMPUTERS USING IEC 60603-2 CONNECTORS
IEEE
Std 1101.1-1998
IEEE Std 1101.10-1996, IEEE Standard for Additional Mechanical Specications for Microcomputers
5
Using the IEEE 1101.1-1991 Equipment Practice.
IEEE 1101.11-1998, IEEE Standard for Mechanical Rear Plug-in Units Specications for Microcomputers
Using the IEEE 1101.1 and the IEEE 1101.10 Equipment Practice.
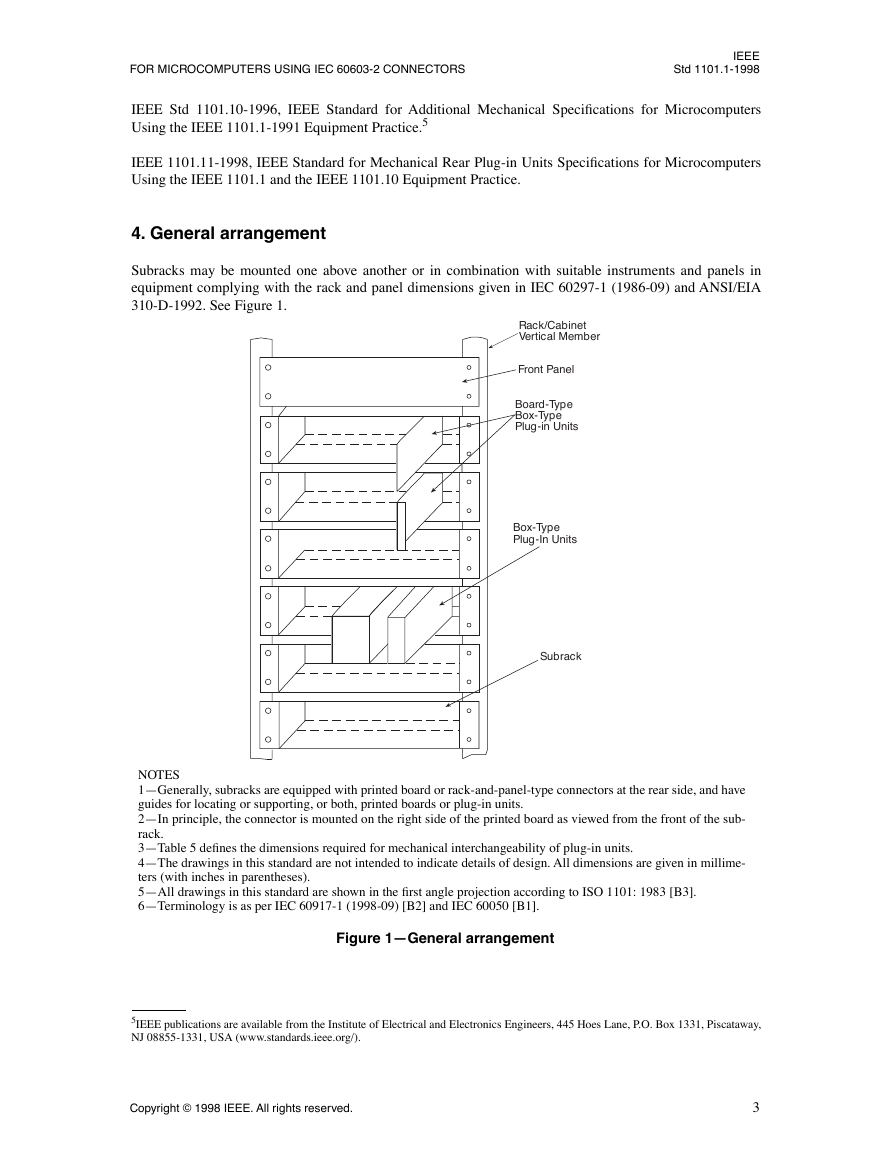
4. General arrangement
Subracks may be mounted one above another or in combination with suitable instruments and panels in
equipment complying with the rack and panel dimensions given in IEC 60297-1 (1986-09) and ANSI/EIA
310-D-1992. See Figure 1.
Rack/Cabinet
Vertical Member
Front Panel
Board-Type
Box-Type
Plug-in Units
Box-Type
Plug-In Units
Subrack
NOTES
1Generally, subracks are equipped with printed board or rack-and-panel-type connectors at the rear side, and have
guides for locating or supporting, or both, printed boards or plug-in units.
2In principle, the connector is mounted on the right side of the printed board as viewed from the front of the sub-
rack.
3Table 5 denes the dimensions required for mechanical interchangeability of plug-in units.
4The drawings in this standard are not intended to indicate details of design. All dimensions are given in millime-
ters (with inches in parentheses).
5All drawings in this standard are shown in the rst angle projection according to ISO 1101: 1983 [B3].
6Terminology is as per IEC 60917-1 (1998-09) [B2] and IEC 60050 [B1].
Figure 1General arrangement
5
IEEE publications are available from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 445 Hoes Lane, P.O. Box 1331, Piscataway,
NJ 08855-1331, USA (www.standards.ieee.org/).
Copyright ' 1998 IEEE. All rights reserved.
3
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc