Global Mobile Trends 2021
Navigating Covid-19 and beyond
December 2020
Copyright © 2020 GSM Association
gsmaintelligence.com @GSMAi
�
The GSMA represents the interests of mobile operators worldwide, uniting
more than 750 operators with nearly 400 companies in the broader mobile
ecosystem, including handset and device makers, software companies,
equipment providers and internet companies, as well as organisations in
adjacent industry sectors. The GSMA also produces the industry-leading
MWC events held annually in Barcelona, Los Angeles and Shanghai, as well
as the Mobile 360 Series of regional conferences.
For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at
www.gsma.com
Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA
GSMA Intelligence is the definitive source of global mobile operator data,
analysis and forecasts, and publisher of authoritative industry reports and
research. Our data covers every operator group, network and MVNO in every
country worldwide – from Afghanistan to Zimbabwe. It is the most accurate
and complete set of industry metrics available, comprising tens of millions of
individual data points, updated daily.
GSMA Intelligence is relied on by leading operators, vendors, regulators,
financial institutions and third-party industry players, to support strategic
decision-making and long-term investment planning. The data is used as
an industry reference point and is frequently cited by the media and by the
industry itself.
Our team of analysts and experts produce regular thought-leading research
reports across a range of industry topics.
www.gsmaintelligence.com
info@gsmaintelligence.com
�
3
GLOBAL MOBILE TRENDS
Growth beyond connectivity
5G outlook
Network transformation
IoT and enterprise verticals
The digital consumer
The next billion
Regional outlook
Telecoms in the
global macro
context
Covid-19 emerges
into an already
uncertain world
�
Telecoms in the global macro context
4
A shock to the world at large
• The arrival of a global pandemic could hardly
have been a more inauspicious welcome to the
new decade.
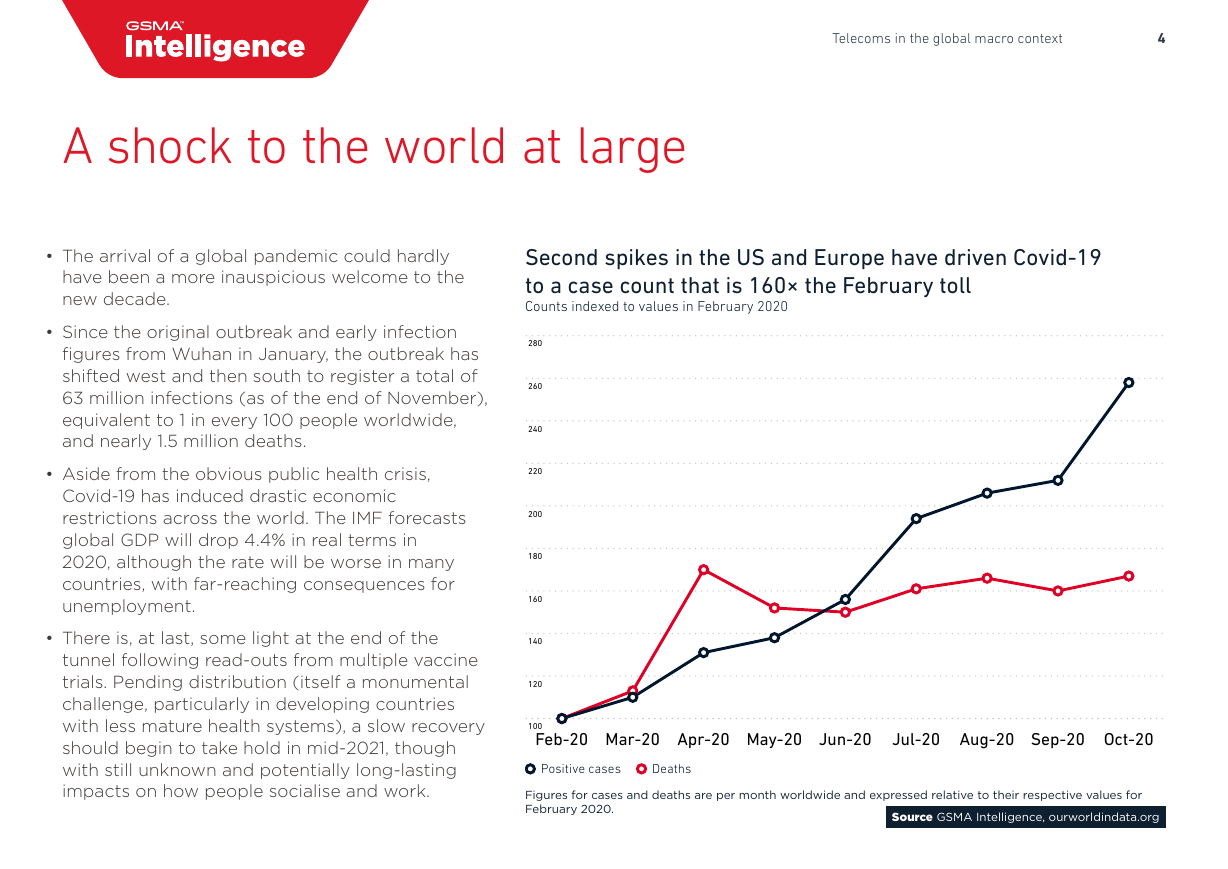
Second spikes in the US and Europe have driven Covid-19
to a case count that is 160× the February toll
Counts indexed to values in February 2020
• Since the original outbreak and early infection
figures from Wuhan in January, the outbreak has
shifted west and then south to register a total of
63 million infections (as of the end of November),
equivalent to 1 in every 100 people worldwide,
and nearly 1.5 million deaths.
• Aside from the obvious public health crisis,
Covid-19 has induced drastic economic
restrictions across the world. The IMF forecasts
global GDP will drop 4.4% in real terms in
2020, although the rate will be worse in many
countries, with far-reaching consequences for
unemployment.
• There is, at last, some light at the end of the
tunnel following read-outs from multiple vaccine
trials. Pending distribution (itself a monumental
challenge, particularly in developing countries
with less mature health systems), a slow recovery
should begin to take hold in mid-2021, though
with still unknown and potentially long-lasting
impacts on how people socialise and work.
280
260
240
220
200
180
160
140
120
100
Feb-20
Mar-20
Apr-20
May-20
Jun-20
Jul-20
Aug-20
Sep-20
Oct-20
Positive cases
Deaths
Figures for cases and deaths are per month worldwide and expressed relative to their respective values for
February 2020.
Source GSMA Intelligence, ourworldindata.org
�
Telecoms in the global macro context
5
Telecoms takes a hit but the impact is less severe
than on the broader economy
• Because of its consumer-facing nature, the telecoms sector
behaves cyclically relative to the economy. Precedents – most
recently the 2008 financial crash – suggest that the impact
compared to that on GDP in a recession is less severe and
lags by 3–6 months.
• A lot, however, has changed since 2008, when the iPhone
had barely arrived and 4G did not exist. Smartphones
are now ubiquitous, LTE is widespread (or on the rise in
emerging markets) and businesses are undertaking digital
transformation, powered by cloud capacity and low-latency
networking (including 5G). In short, mobile and fixed
networks are more in demand than they used to be.
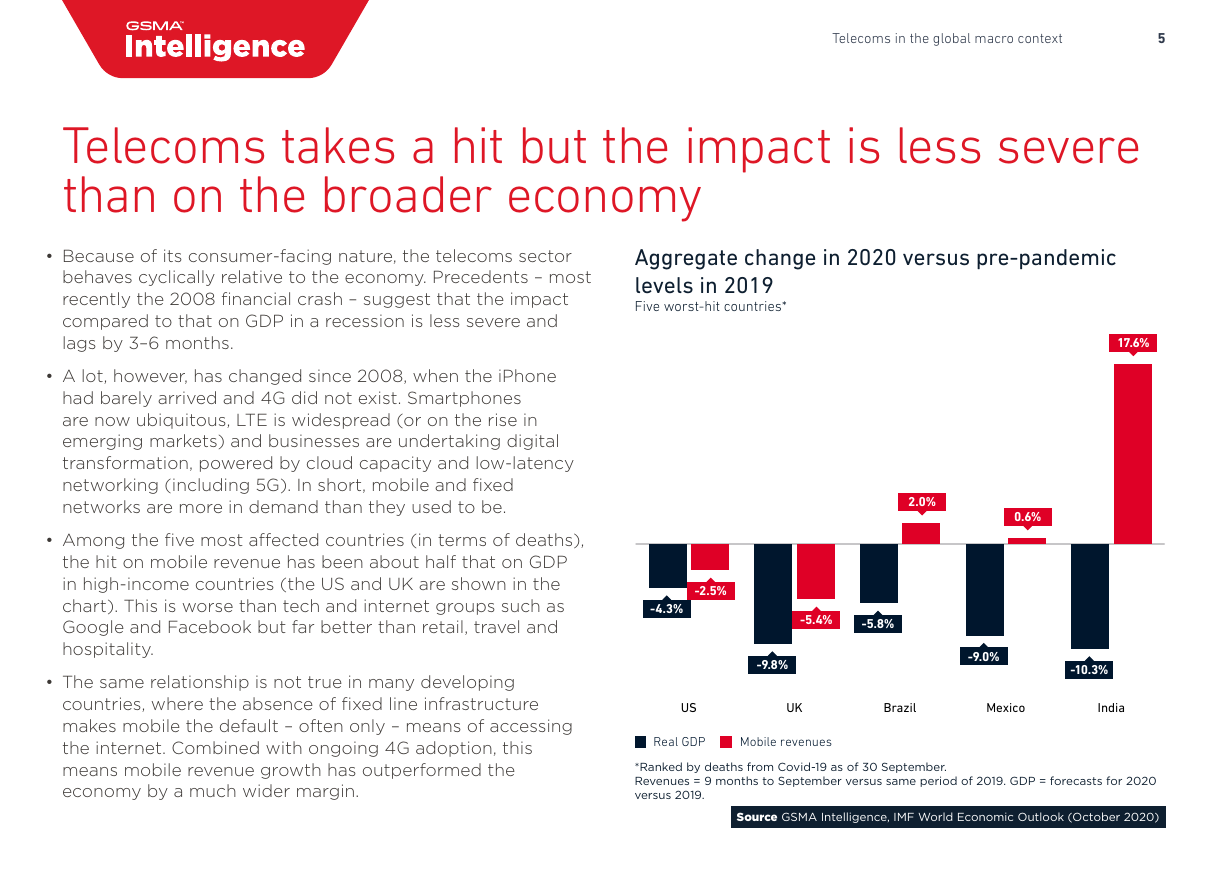
• Among the five most affected countries (in terms of deaths),
the hit on mobile revenue has been about half that on GDP
in high-income countries (the US and UK are shown in the
chart). This is worse than tech and internet groups such as
Google and Facebook but far better than retail, travel and
hospitality.
• The same relationship is not true in many developing
countries, where the absence of fixed line infrastructure
makes mobile the default – often only – means of accessing
the internet. Combined with ongoing 4G adoption, this
means mobile revenue growth has outperformed the
economy by a much wider margin.
Aggregate change in 2020 versus pre-pandemic
levels in 2019
Five worst-hit countries*
17.6%
2.0%
0.6%
-2.5%
-4.3%
-5.4%
-5.8%
-9.8%
-9.0%
-10.3%
US
UK
Brazil
Mexico
India
Real GDP
Mobile revenues
*Ranked by deaths from Covid-19 as of 30 September.
Revenues = 9 months to September versus same period of 2019. GDP = forecasts for 2020
versus 2019.
Source GSMA Intelligence, IMF World Economic Outlook (October 2020)
�
Telecoms in the global macro context
6
The Covid-19 impact has focussed on roaming,
handsets and enterprise
• While Covid-19 has impacted revenues for many sectors,
for telcos – which have multi-faceted business models – it is
important to understand which parts of the business have
been most exposed.
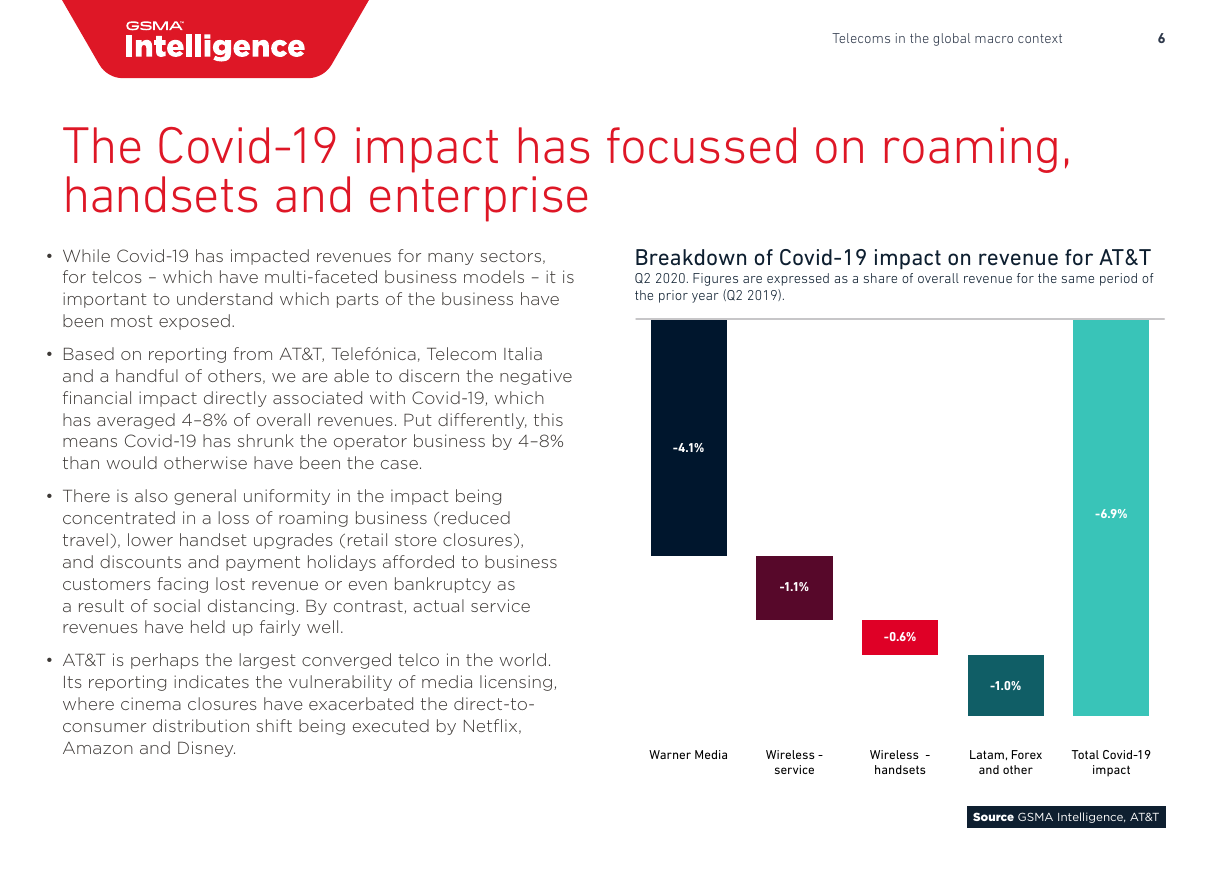
• Based on reporting from AT&T, Telefónica, Telecom Italia
and a handful of others, we are able to discern the negative
financial impact directly associated with Covid-19, which
has averaged 4–8% of overall revenues. Put differently, this
means Covid-19 has shrunk the operator business by 4–8%
than would otherwise have been the case.
• There is also general uniformity in the impact being
concentrated in a loss of roaming business (reduced
travel), lower handset upgrades (retail store closures),
and discounts and payment holidays afforded to business
customers facing lost revenue or even bankruptcy as
a result of social distancing. By contrast, actual service
revenues have held up fairly well.
• AT&T is perhaps the largest converged telco in the world.
Its reporting indicates the vulnerability of media licensing,
where cinema closures have exacerbated the direct-to-
consumer distribution shift being executed by Netflix,
Amazon and Disney.
Breakdown of Covid-19 impact on revenue for AT&T
Q2 2020. Figures are expressed as a share of overall revenue for the same period of
the prior year (Q2 2019).
-4.1%
-6.9%
-1.1%
-0.6%
-1.0%
Warner Media
Wireless -
service
Wireless -
handsets
Latam, Forex
and other
Total Covid-19
impact
Source GSMA Intelligence, AT&T
�
Telecoms in the global macro context
7
Network resilience has been an out and out positive
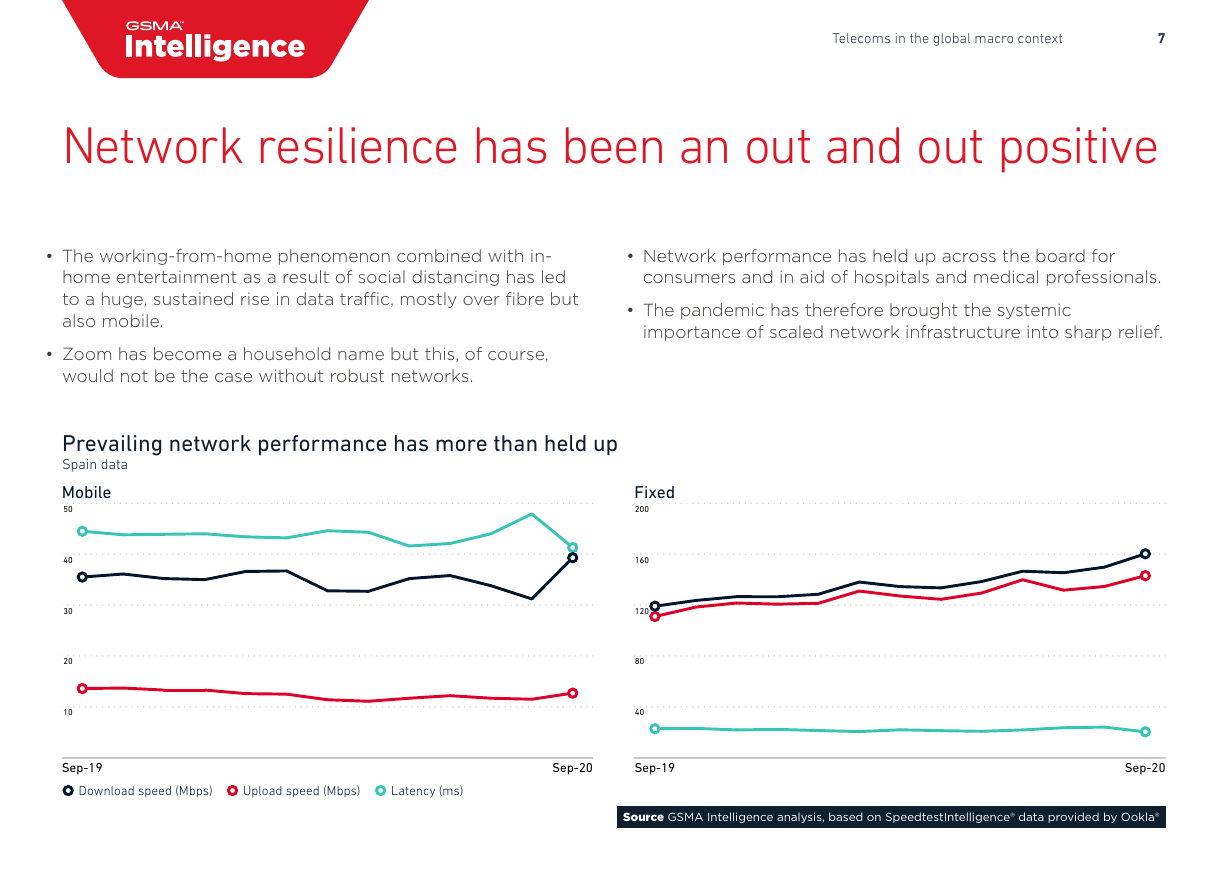
• The working-from-home phenomenon combined with in-
• Network performance has held up across the board for
home entertainment as a result of social distancing has led
to a huge, sustained rise in data traffic, mostly over fibre but
also mobile.
• Zoom has become a household name but this, of course,
would not be the case without robust networks.
consumers and in aid of hospitals and medical professionals.
• The pandemic has therefore brought the systemic
importance of scaled network infrastructure into sharp relief.
Prevailing network performance has more than held up
Spain data
Mobile
50
40
30
20
10
Fixed
200
160
120
80
40
Sep-19
Sep-20
Sep-19
Sep-20
Download speed (Mbps)
Upload speed (Mbps)
Latency (ms)
Source GSMA Intelligence analysis, based on SpeedtestIntelligence® data provided by Ookla®
�
Market valuations shift: the short versus long term
Telecoms in the global macro context
8
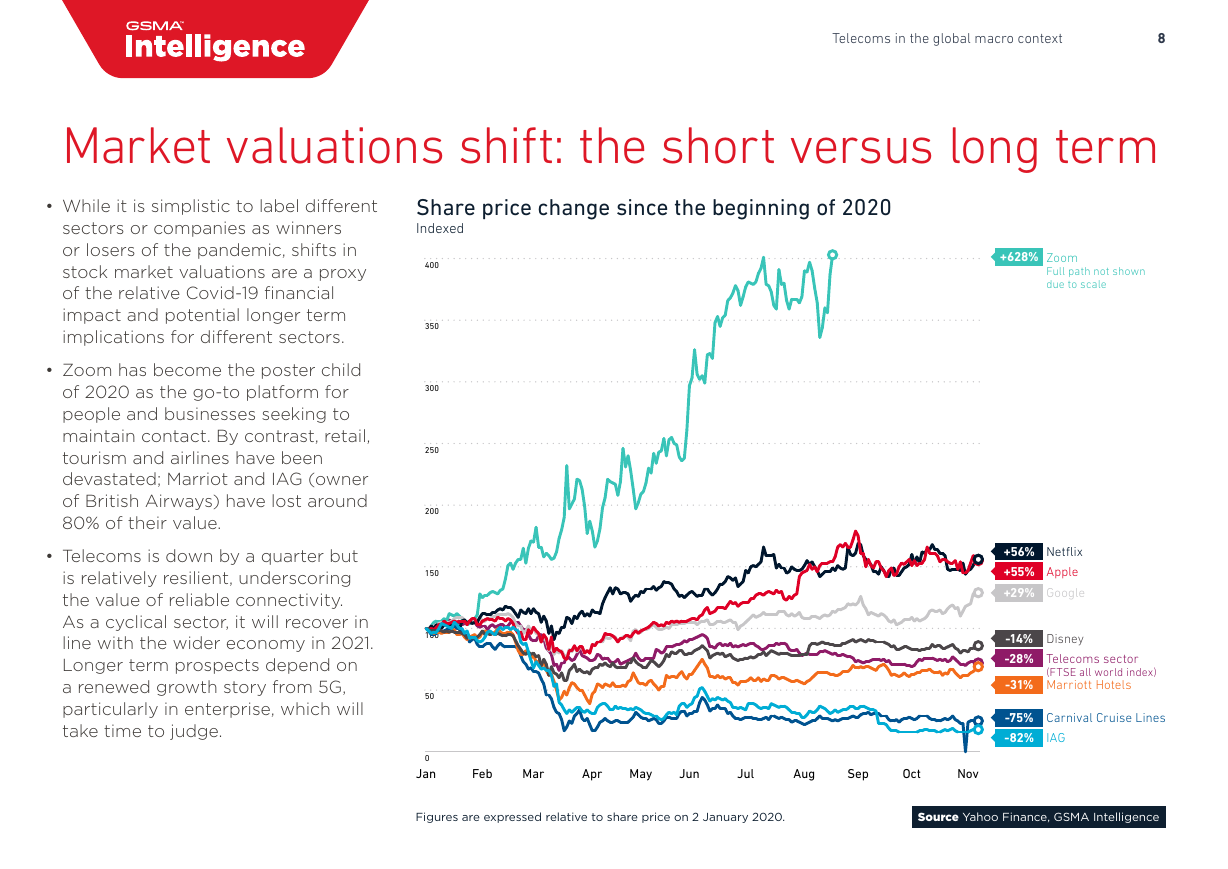
• While it is simplistic to label different
sectors or companies as winners
or losers of the pandemic, shifts in
stock market valuations are a proxy
of the relative Covid-19 financial
impact and potential longer term
implications for different sectors.
• Zoom has become the poster child
of 2020 as the go-to platform for
people and businesses seeking to
maintain contact. By contrast, retail,
tourism and airlines have been
devastated; Marriot and IAG (owner
of British Airways) have lost around
80% of their value.
• Telecoms is down by a quarter but
is relatively resilient, underscoring
the value of reliable connectivity.
As a cyclical sector, it will recover in
line with the wider economy in 2021.
Longer term prospects depend on
a renewed growth story from 5G,
particularly in enterprise, which will
take time to judge.
Share price change since the beginning of 2020
Indexed
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
Jan
+628% Zoom
Full path not shown
due to scale
+56% Netflix
+55% Apple
+29% Google
-14% Disney
-28% Telecoms sector
(FTSE all world index)
-31% Marriott Hotels
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
-75% Carnival Cruise Lines
-82% IAG
Figures are expressed relative to share price on 2 January 2020.
Source Yahoo Finance, GSMA Intelligence
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc