SDP (OS) Operator Reference Manual (Rel. 6.2)
Front matter
The reader
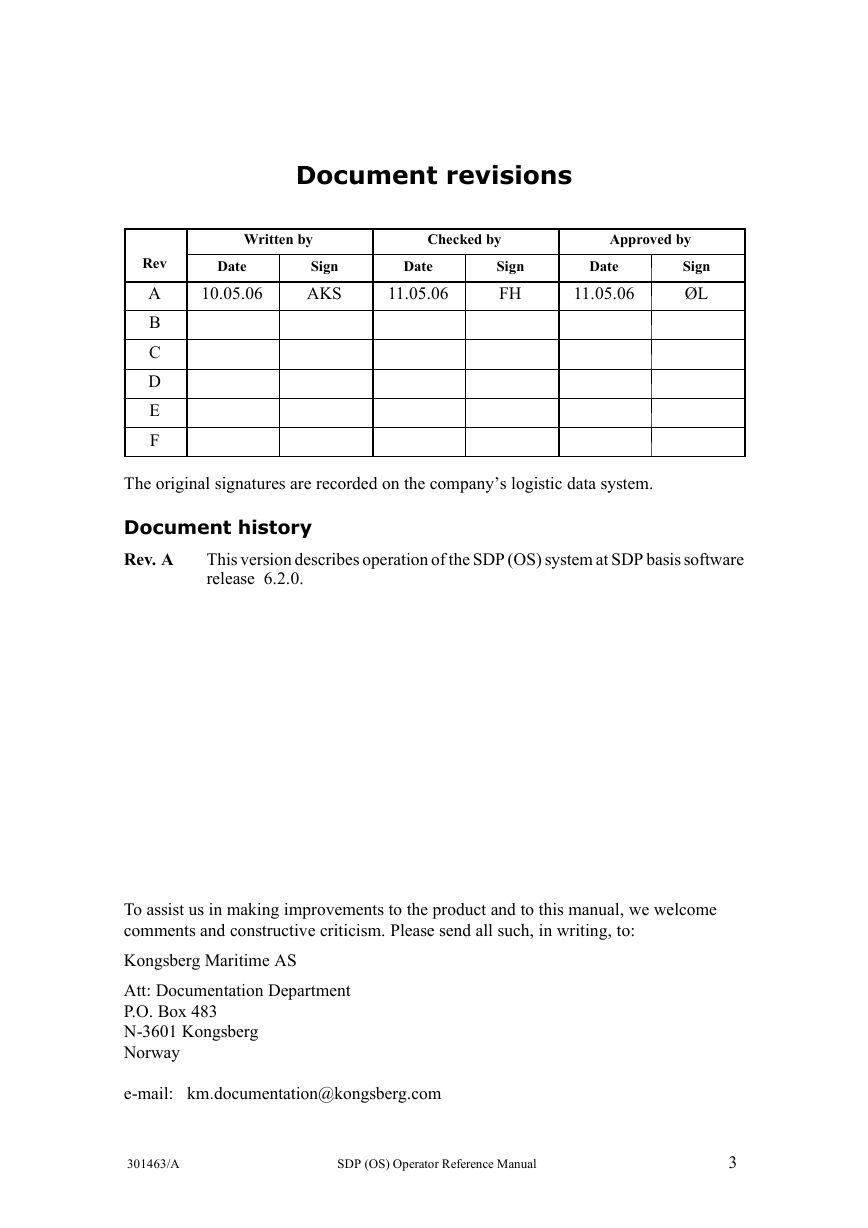
Document revisions
Glossary
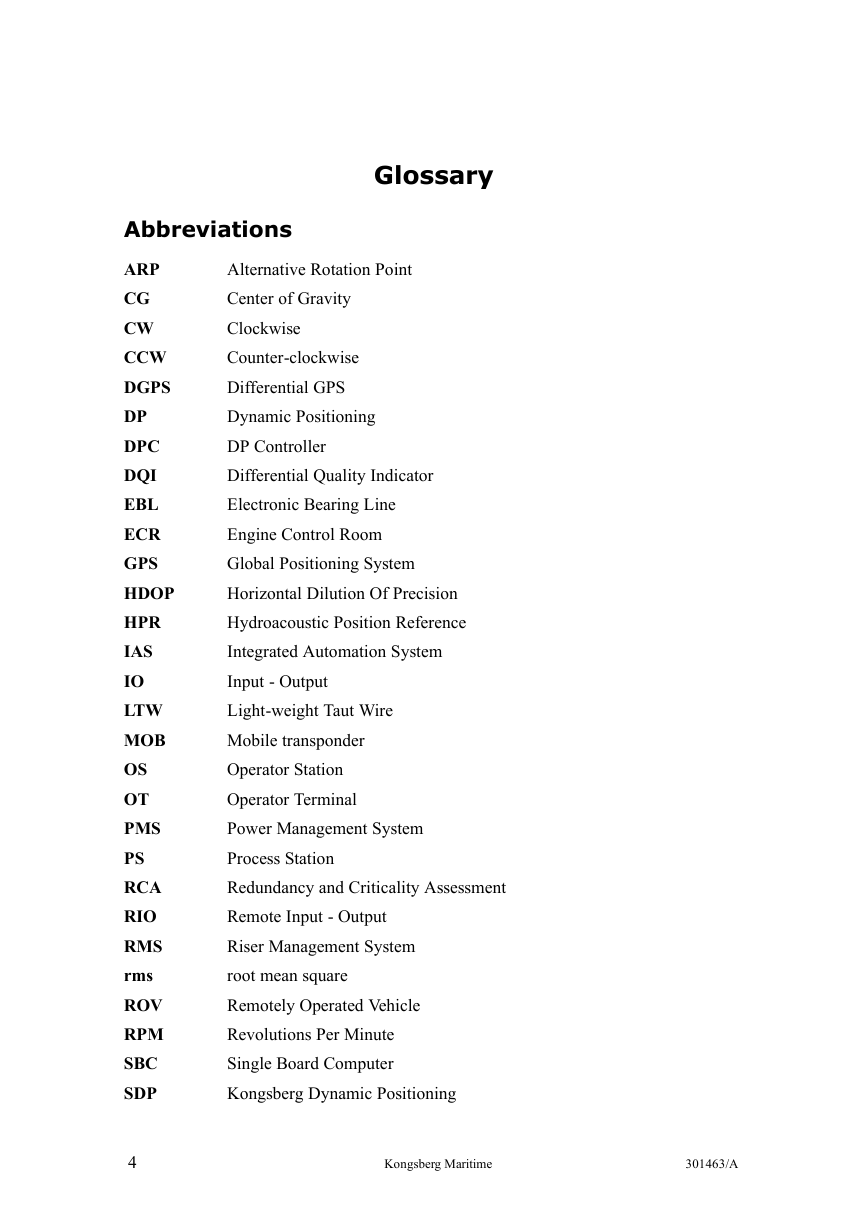
Abbreviations
General terms
Windows terminology
Table of contents
USER INTERFACE
Operator station
Operator panel
Push buttons
Modes
Controls
Sensors
Views
Alarms
Command
Keypad
Trackball
Joystick
Heading wheel
Display layout
Title bar
Menu bar
Active and unavailable commands
Message line
Performance area
Working area
Monitoring area
Status line
Status bar
Overview of labels on the status bar
Dialog boxes
Entering numeric values
Enabling the Enter a New Numeric Value dialog box
Using the Enter a New Numeric Value dialog box
Overview of the keys in the Enter a New Numeric Value dialog box
Input validation of entered values
Display views
Orientation of the OS and effect on display views
Tooltip / hotspot cursor and change of cursor image
Available views
Selecting a display view
View control dialog boxes
Zooming
Preselecting views
Main menus
Menu bar
System menu
View menu
Sensors menu
Thruster menu
Joystick menu
AutoPos menu
Help menu
SYSTEM SETTINGS
Changing user
Printing the display picture
Panel Light Configuration dialog box
Dimming level
Lamp test
Display Units dialog box
Selecting the set of display units to use
Editing Display Units
Additional information
Vessel and sea current speed
Wind, waves and sea current direction
Resetting the display units
System date and time
Date and time
Time zone
Set palette (display colours)
Changing the display palette on Operator Stations that are not set to have an independent palette selection
Changing the display palette on a single Operator Station
Alarm Limits dialog box
Position page
VRS page
Controller Mode and Gain Level selection
Gain Level for High Precision and Relaxed Controller Mode
Display presentation of Controller Mode
High Precision
Relaxed
Green
Quick model update
Quick Model dialog box
Rotation center for automatic control
Additional information
JOYSTICK
Calibrating the joystick
Calibration procedure
Joystick settings
Rotation center for joystick manoeuvring
Rotation Center dialog box
Additional information
THE MESSAGE SYSTEM
System diagnostics
Operational checks
Audible and visual indications
Message priority
Presentation of messages
Defining the time span for the Historic Event Page
Alarm states
Acknowledging messages
Silence button
Alarm lamps
Messages on the printer
Event Printer dialog
Message explanations
Contents
Search
Displayed explanation
Back link
Menu bar
Printing message explanations
Operator advice messages
BUILT-IN TRAINER
Trainer functions
Using the trainer
Setting the start position for the next session
Leaving the trainer
DP ONLINE CONSEQUENCE ANALYSIS
DP Online Consequence Analysis
Selecting the DP class
Consequence analysis status messages
Consequence analysis warning messages
STARTING OPERATIONS
System start-up/shut-down and OS stop/restart
Stop/Restart dialog box
Restart the OS using the Windows Security dialog box
Logon Configuration dialog box
Command transfer
Taking command
Giving command
Command Control dialog box
Command groups
Thr_Propulsion
Thr_Propulsion(Sim)
OS page
Overview page
Give page
Command Groups
Controls and indicators
Taking or giving command of thruster propulsion
Connecting to a controller PS group
CONTROLLER PROCESS STATIONS
Resetting controller process stations
Resetting the controller PS in a single-computer system
Resetting one controller PS in a dual or triple redundant system
Resetting all controller PSes in a dual or triple redundant system
Redundant systems
Error objects
Dual redundant system
Automatic switch- over to the Offline PS
Resetting after an automatic switch-over
Triple redundant system
Hardware voting
Redundant Stations dialog box
SENSORS
Gyrocompasses
Sensors dialog box - Gyro page
Gyro Deviation dialog box
Additional information
Gyro status lamp
Displayed heading information
Rejection of heading measurements
Faulty gyrocompasses
Heading dropout
Wind sensors
Sensors dialog - Wind page
Wind status lamp
Displayed wind information
Faulty wind sensors
Rejection of faulty wind data
Operating without wind sensor input
Vertical reference sensors (VRS)
Sensors dialog - VRS page
VRS status lamp
Displayed VRS information
Faulty VRS
Speed sensors
Sensors dialog box - Speed page
Displayed speed information
Draught sensors
Sensors dialog box - Draught page
Additional information
Depth sensors
Sensors dialog box - Depth page
Displayed water-depth information
Rate Of Turn sensors
Sensors dialog box - Rate Of Turn page
POSITION INFORMATION
Handling position information
Position Presentation dialog box
Additional information
Datum Details dialog box
Local N/E Properties dialog box
UTM Properties dialog box
State Plane Zone
Methods for enabling position-reference systems
Panel buttons
Reference System Settings dialog box
Reference System dialog box
Enable page
Additional information
Weight page
Validation page
Reference System Properties dialog box
UTM Properties
Quality Filter Actions
Coordinate systems
Global and local position-reference systems
System datum
The reference origin
Tests on position measurements
Standard deviation of position measurements
Freeze test
Variance, weight and the Variance test
Prediction test
Divergence test
Median test
Enabling the first position-reference system
Enabling other position-reference systems
Changing the reference origin
Position dropout
MAIN MODES AND OPERATING PROCEDURES
Standby mode
Returning to Standby mode/manual levers
Joystick mode
From Standby mode to Joystick mode
Joystick control of position and heading
Position and heading information
Joystick electrical failure
Mixed joystick/auto modes
Joystick mode with automatic heading control
Selecting automatic heading control
Returning to joystick heading control
Joystick mode with automatic position control in both surge and sway
Selecting automatic position control
Returning to joystick position control
Joystick mode with automatic stabilisation
Selecting automatic stabilisation
Returning to joystick control
Auto Position mode
From Joystick mode to Auto Position mode
CHANGING THE POSITION SETPOINT
Stopping a change of position
Marking a new position setpoint on the Posplot view
Position R/B dialog box (range/bearing)
Position Inc dialog box (incremental)
Position dialog box
Inc page
Additional information
R/B page
Abs page
Speed page
Additional information
Speed Setpoint dialog box
Additional information
Acceleration/Retardation Settings dialog box
CHANGING THE HEADING SETPOINT
Stopping a change of heading
Marking a new heading setpoint on the Posplot view
Heading Wheel and its associated panel buttons
Heading dialog box
Heading page
Additional information
Rate Of Turn page
Additional information
Acceleration/retardation factors in the yaw axis
THRUSTERS
Enabling thrusters
Thruster Enable dialog box
Automatic thruster start (for IAS deliveries)
Automatic Thruster Start dialog box
Thruster Allocation dialog box
Additional information
Allocation Settings dialog box
Rudder/Nozzle control
Thruster biasing
Thruster Biasing dialog box
Manual selection of thruster biasing
Automatically changing bias available
Turn factor
Angle factor
Inwards
Thruster Run-in dialog box
POWER SYSTEM
Power monitoring
Power load monitoring and blackout prevention
SYSTEM STATUS INFORMATION
Panel driver logging
Panel Driver Logging dialog box
Copy Panel Logfiles to floppies dialog box
Selecting panel logfiles from the file list
Copying panel logfiles
Remote diagnostics
pcAnywhere Waiting... dialog box
Printing system status data
Displaying software information
RCA and Vessel Control modes
Vessel Control mode
Redundancy and Criticality Assessment - RCA
Vessel Control Mode dialog box
RCA messages
RCA view
Relation between RCA view and Vessel Control Mode dialog box
Relation between RCA view and status bar
Interface to CyberSea
SYSTEM STATUS MONITORING
Introduction
System architecture
Operator stations
Process stations
Redundancy
WinPS
PS names and numbers
The IO system
Monitoring functions
Station Explorer
PS tree structure
Alarm status indicators
Hotspots
Acknowledging PS system alarms
IO Manager
IO Configurator
PBUS IO Image
Overview level
Detailed level
IO Block
Shortcut menu
Signal Conditioning elements
IO Point Browser
IO Point Browser dialog box
Station
Shortcut menu
Driver Properties
Resetting a disabled serial line
DISPLAY VIEWS
Deviation view
Position and heading
Position and heading deviation
View controls
Diesels view
General view
Position, heading and speed
Position and heading deviation
View controls
Joystick view
LTW view
View controls
Numeric view
View controls
Posplot view
View controls
Mode page
Show page
Chart page
Grid page
Range page
Trace page
EBL function
Panning function
Power view
View controls
Power consumption view
Refsys view
View controls
Mode page
Grid page
Range page
Refsys Status view
Rotation Centers view
Sensors view
View controls
Thruster views
Thruster main view
Tunnel thruster view
Azimuth thruster view
Propeller/rudder view
Subview controls
Setpoint/feedback view
Forces view
Trends view
View controls
SDP SYSTEM THEORY
The SDP system
Basic forces and motions
SDP system principles
The Extended Kalman Filter
The Controller
High Precision and Relaxed Control
Green control
Thruster allocation
Index














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc