浅谈汽车以太网网络架构
13/12/2018
蔚来汽车 盛莹莹
�
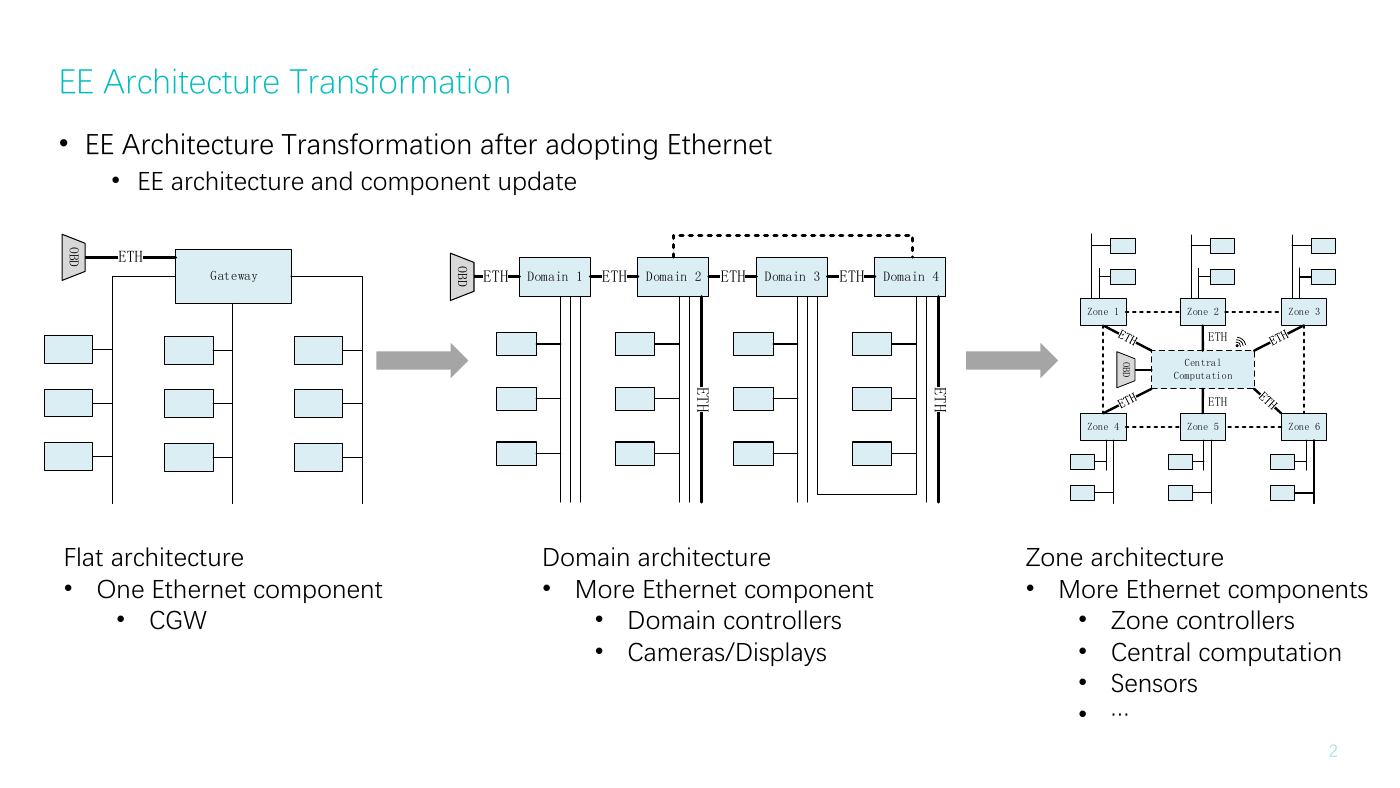
EE Architecture Transformation
• EE Architecture Transformation after adopting Ethernet
• EE architecture and component update
Flat architecture
• One Ethernet component
• CGW
Domain architecture
• More Ethernet component
• Domain controllers
• Cameras/Displays
Zone architecture
• More Ethernet components
• Zone controllers
• Central computation
• Sensors
• …
2
GatewayETHOBDDomain 1Domain 2ETHDomain 3Domain 4ETHETHETHETHETHOBDZone 4Zone 5Zone 6Zone 1Central ComputationZone 2Zone 3OBDETHETH�
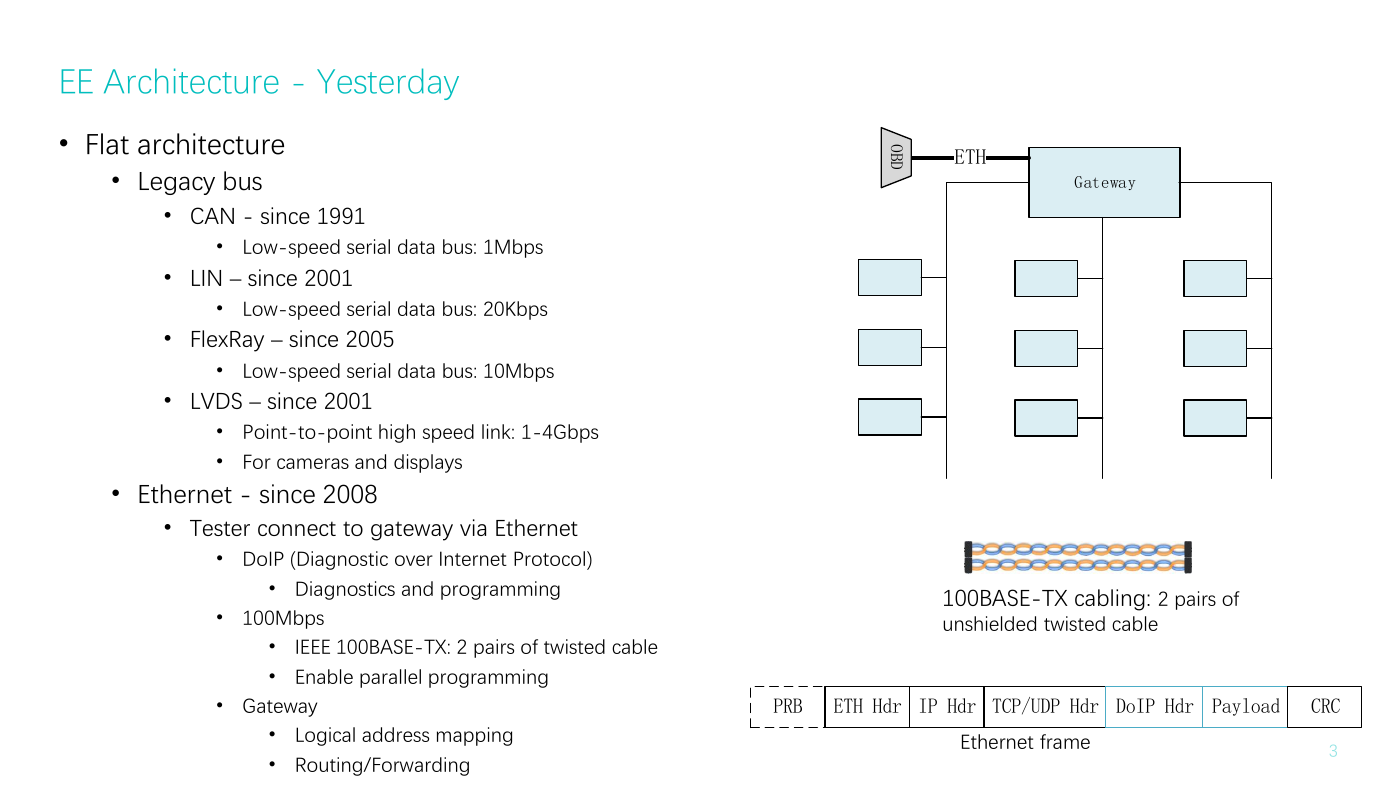
EE Architecture - Yesterday
• Flat architecture
• Legacy bus
• CAN - since 1991
•
Low-speed serial data bus: 1Mbps
• LIN – since 2001
•
Low-speed serial data bus: 20Kbps
• FlexRay – since 2005
•
Low-speed serial data bus: 10Mbps
• LVDS – since 2001
• Point-to-point high speed link: 1-4Gbps
• For cameras and displays
• Ethernet - since 2008
• Tester connect to gateway via Ethernet
• DoIP (Diagnostic over Internet Protocol)
• Diagnostics and programming
• 100Mbps
IEEE 100BASE-TX: 2 pairs of twisted cable
•
• Enable parallel programming
• Gateway
Logical address mapping
•
• Routing/Forwarding
100BASE-TX cabling: 2 pairs of
unshielded twisted cable
Ethernet frame
3
GatewayETHOBDPRBETH HdrIP HdrTCP/UDP HdrDoIP HdrPayloadCRC�
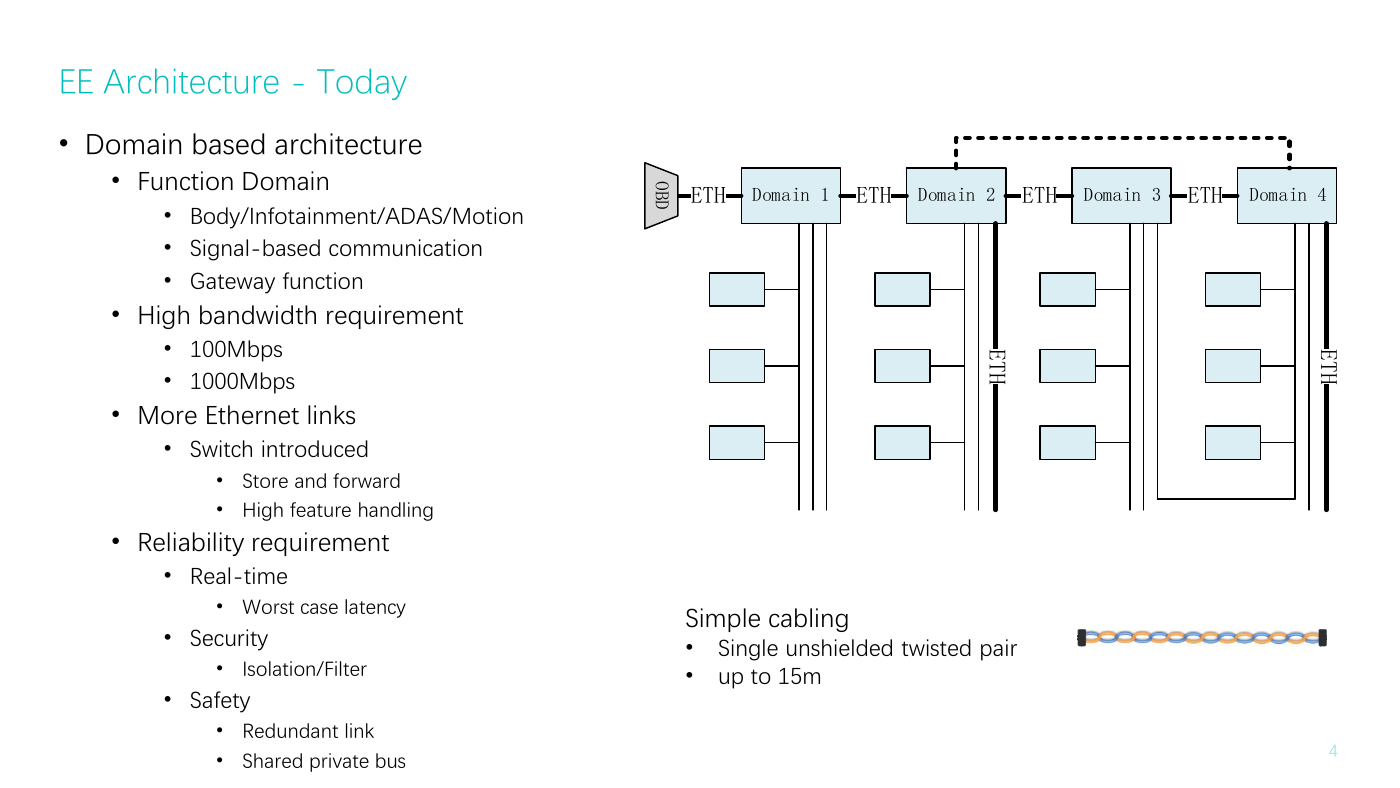
EE Architecture - Today
• Domain based architecture
• Function Domain
• Body/Infotainment/ADAS/Motion
• Signal-based communication
• Gateway function
• High bandwidth requirement
• 100Mbps
• 1000Mbps
• More Ethernet links
• Switch introduced
• Store and forward
• High feature handling
• Reliability requirement
• Real-time
• Worst case latency
• Security
•
Isolation/Filter
• Safety
• Redundant link
• Shared private bus
Simple cabling
•
• up to 15m
Single unshielded twisted pair
4
Domain 1Domain 2ETHDomain 3Domain 4ETHETHETHETHETHOBD�
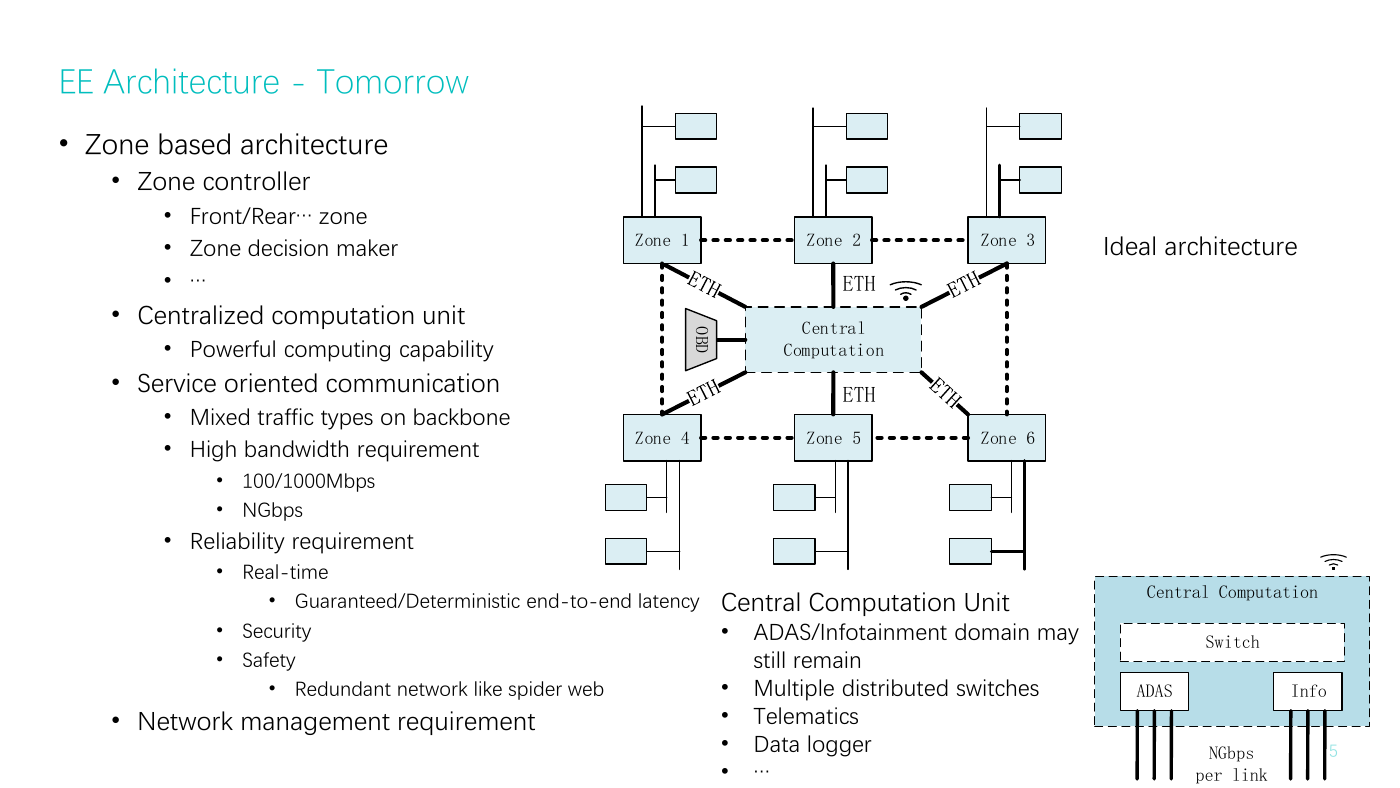
EE Architecture - Tomorrow
• Zone based architecture
• Zone controller
• Front/Rear… zone
• Zone decision maker
• …
• Centralized computation unit
• Powerful computing capability
• Service oriented communication
• Mixed traffic types on backbone
• High bandwidth requirement
• 100/1000Mbps
• NGbps
• Reliability requirement
• Real-time
Ideal architecture
• Guaranteed/Deterministic end-to-end latency
• Security
• Safety
• Redundant network like spider web
• Network management requirement
Central Computation Unit
• ADAS/Infotainment domain may
still remain
Telematics
• Multiple distributed switches
•
• Data logger
• …
5
Central ComputationADASInfoSwitchNGbps per linkZone 4Zone 5Zone 6Zone 1Central ComputationZone 2Zone 3OBDETHETH�
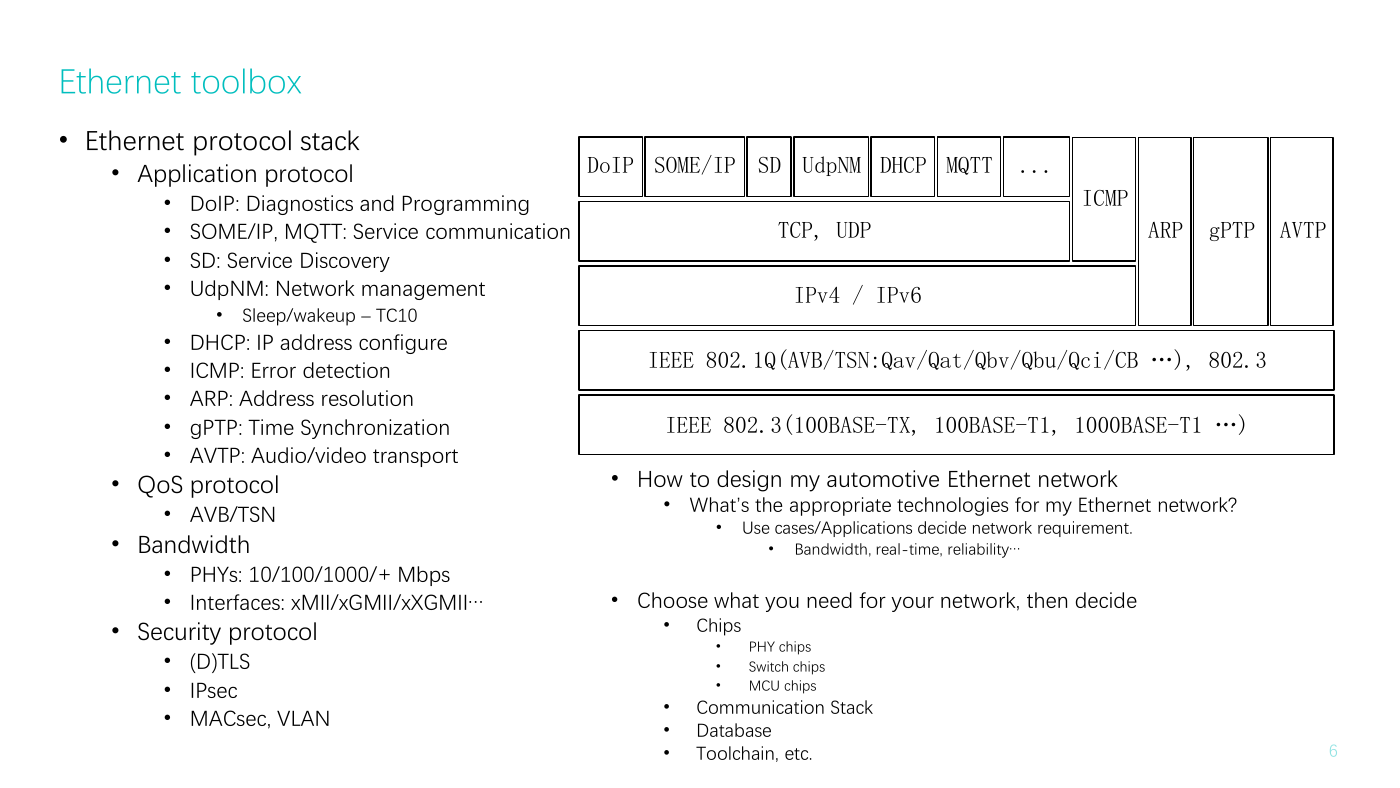
Ethernet toolbox
• Ethernet protocol stack
• Application protocol
• DoIP: Diagnostics and Programming
• SOME/IP, MQTT: Service communication
• SD: Service Discovery
• UdpNM: Network management
•
Sleep/wakeup – TC10
ICMP: Error detection
• DHCP: IP address configure
•
• ARP: Address resolution
• gPTP: Time Synchronization
• AVTP: Audio/video transport
• QoS protocol
• AVB/TSN
• Bandwidth
• How to design my automotive Ethernet network
• What’s the appropriate technologies for my Ethernet network?
• Use cases/Applications decide network requirement.
•
Bandwidth, real-time, reliability…
• PHYs: 10/100/1000/+ Mbps
•
Interfaces: xMII/xGMII/xXGMII…
• Choose what you need for your network, then decide
• Security protocol
(D)TLS
IPsec
•
•
• MACsec, VLAN
•
•
•
•
Chips
•
•
•
PHY chips
Switch chips
MCU chips
Communication Stack
Database
Toolchain, etc.
6
IEEE 802.3(100BASE-TX, 100BASE-T1, 1000BASE-T1 …)IEEE 802.1Q(AVB/TSN:Qav/Qat/Qbv/Qbu/Qci/CB …), 802.3IPv4 / IPv6TCP, UDPARPDoIPSOME/IPSDUdpNMDHCPMQTT...ICMPgPTPAVTP�
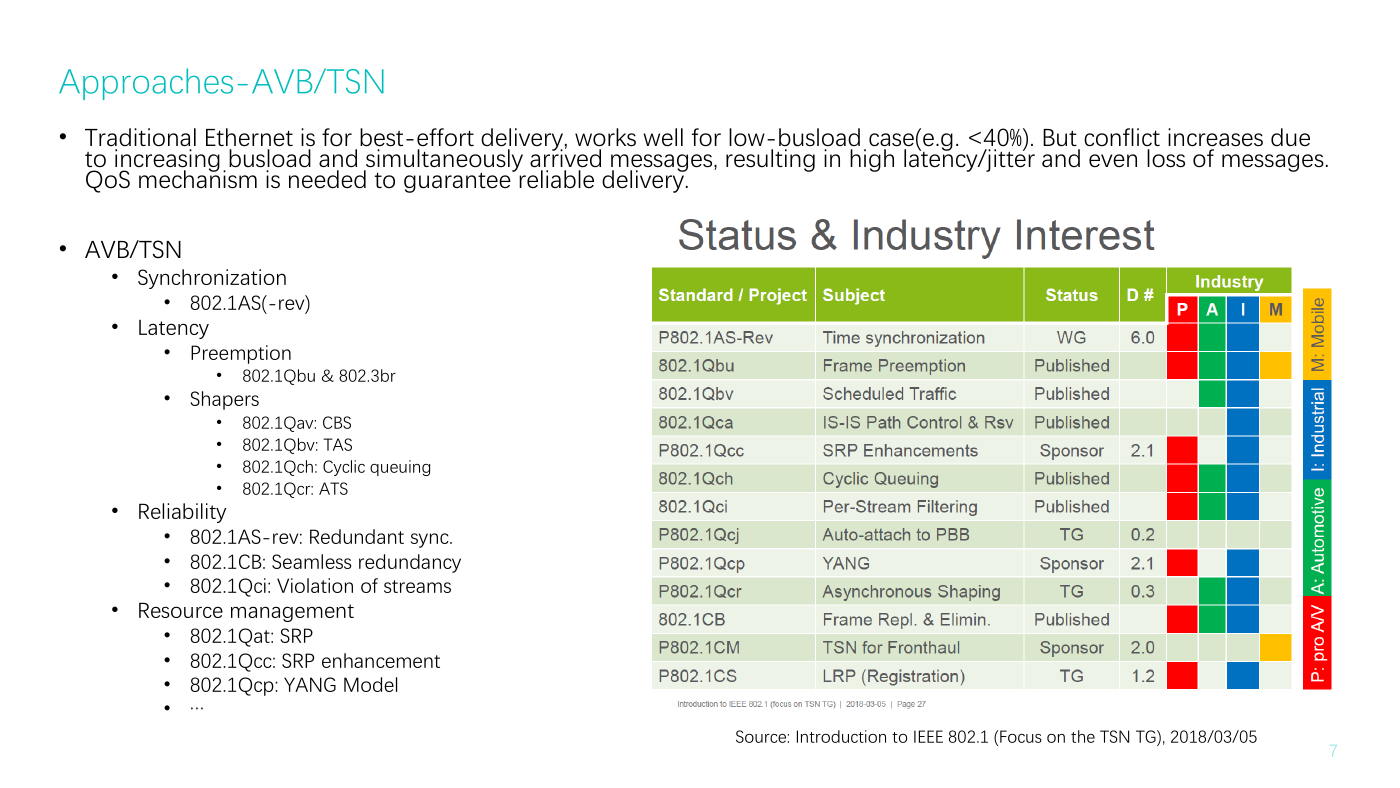
Approaches-AVB/TSN
• Traditional Ethernet is for best-effort delivery, works well for low-busload case(e.g. <40%). But conflict increases due
to increasing busload and simultaneously arrived messages, resulting in high latency/jitter and even loss of messages.
QoS mechanism is needed to guarantee reliable delivery.
• AVB/TSN
• Synchronization
• 802.1AS(-rev)
• Latency
• Preemption
•
802.1Qbu & 802.3br
• Shapers
•
•
•
•
• Reliability
802.1Qav: CBS
802.1Qbv: TAS
802.1Qch: Cyclic queuing
802.1Qcr: ATS
• 802.1AS-rev: Redundant sync.
• 802.1CB: Seamless redundancy
• 802.1Qci: Violation of streams
• Resource management
• 802.1Qat: SRP
• 802.1Qcc: SRP enhancement
• 802.1Qcp: YANG Model
• …
Source: Introduction to IEEE 802.1 (Focus on the TSN TG), 2018/03/05
7
�
Some gaps/challenges of in-vehicle Ethernet
• Even Ethernet is widely used in consumer industry, it cannot be used in automotive directly, due to
• Harsher environment (EMC, temperature…)
• Higher reliability requirement (Hardware Qualification, Software Validation…)
• Shorter Startup time and Latency requirement
• Safety …
•
In-vehicle Ethernet network challenges, e.g.
• Bandwidth
• Higher bandwidth requirement from sensor
•
•
Beyond current Ethernet capability
If compressed data
• Compression efficiency
•
• Code/Decode latency
• Maybe other high-speed bus
Pixel loss tolerance
• GMSL, FPD-link…
• Cost
•
• Maybe IEEE 10BASE-T1S?
Legacy bus is much cheaper
• Function safety
• End-to-end protection
• Ethernet network management
• Sleep/wakeup of different-speed PHYs
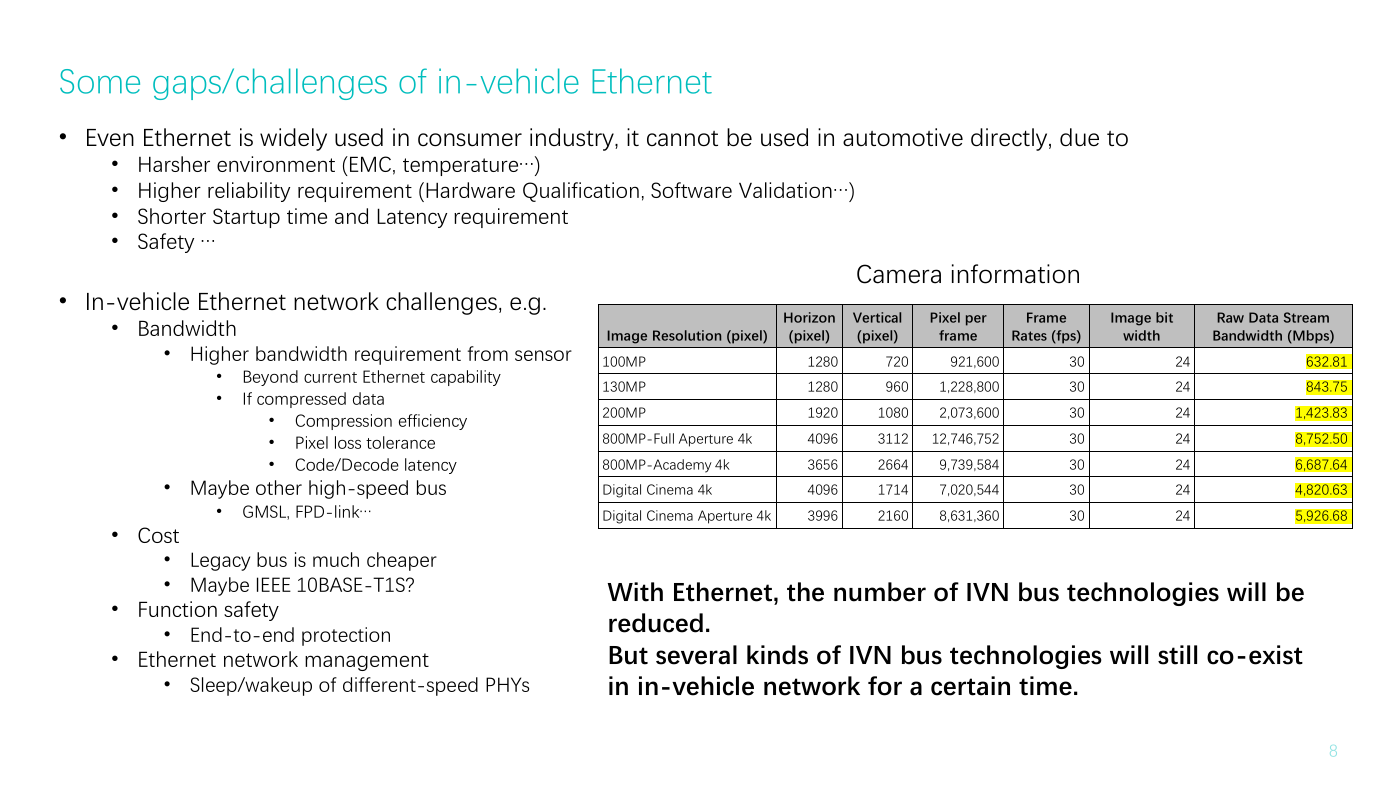
Camera information
Image Resolution (pixel)
Horizon
(pixel)
Vertical
(pixel)
Pixel per
frame
Frame
Rates (fps)
Image bit
width
Raw Data Stream
Bandwidth (Mbps)
100MP
130MP
200MP
800MP-Full Aperture 4k
800MP-Academy 4k
Digital Cinema 4k
Digital Cinema Aperture 4k
1280
1280
1920
4096
3656
4096
3996
720
960
1080
3112
2664
1714
2160
921,600
1,228,800
2,073,600
12,746,752
9,739,584
7,020,544
8,631,360
30
30
30
30
30
30
30
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
632.81
843.75
1,423.83
8,752.50
6,687.64
4,820.63
5,926.68
With Ethernet, the number of IVN bus technologies will be
reduced.
But several kinds of IVN bus technologies will still co-exist
in in-vehicle network for a certain time.
8
�









 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc