5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
中国科技论文在线
切换多智能体系统在通信时延下的一致性
http://www.paper.edu.cn
翟付强,周洪涛**
(华中科技大学自动化学院图像信息处理与智能控制教育部重点实验室,武汉 430074)
摘要:围绕有向拓扑图下切换多智能体系统的一致性问题,考虑多智能体线性系统的通信时
延和采样周期的大小问题,其中切换多智能体系统包括连续时间子系统和离散时间子系统。
通过构建带有通信时延的输入调节模型,并运用图论、Lyapunov-Krasovskii 函数和线性矩阵
不等式方法判断了系统的稳定性,同时也得到了切换多智能体系统在变化拓扑和通信时延下
状态达到一致的充分条件。进一步地,通过计算出的不等式,可以得到通信时延和采样周期
的最大范围。最后,仿真实例证明了得出的理论结果的有效性。
关键词:一致性;变化拓扑;通信时延;切换多智能体系统
中图分类号:O23
Consensus of switched multi-agent systems with
communication delay
ZHAI Fuqiang, ZHOU Hongtao
(Automation School, Image Processing and Intelligent Control Key Laboratory of the Education
Ministry, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074)
Abstract: Around the consensus problem of switched multi-agent systems under a directed topology
graph, the size of communication delay and sampling period in the multi-agent linear system composed
of continuous-time and discrete-time subsystems is considered. By building a input adjustment model
with communication delay and employing the graph theory, Lyapunov-Krasovskii function and linear
matrix inequality method, the stability of the system can be judged. Simutaneously, sufficient
conditions are given to guarantee the consensus of all the nodes in the network. Furthermore, several
inqualities are established to determine the maximal allowable upper bound of communication delay
and sampling period. Finally, simulation examples are provided to demostrate the effectiveness of the
theoretical results.
Keywords: consensus; switching topology; communication delay; switched multiagent systems
0 引言
随着通信技术和计算机处理能力的巨大提高,多智能体协同控制的一致性算法在许多领
域有了越来越多的应用,其中给许多人印象最深的无疑是 2017 年元宵节广州 1000 架无人机
的精彩表演。一致性算法现已广泛应用于机器人[1-3]、无人飞行器[4-6]等。此外,许多研究者
也对一致性算法进行了更深入的研究,如编队集结[7-8]、群集[9]、传感器网络[10-12]等。
目前多智能体协同控制的一致性算法已有许多研究成果。在[13-16]文献中只研究了连续系
统在变化拓扑和通信时延下的一致性,并没有考虑离散系统。文献[17-18]正好相反,只研究了
离散系统,却没有考虑连续系统。而实际当中,既要考虑离散系统又要考虑连续系统的情况
却很多,如文献[19]。在[20-24]文献中虽然连续和离散系统都考虑了,但却没有考虑最常见的
拓扑发生变化或者通信出现时延的情况。
作者简介:翟付强(1991-),男,硕士,主要研究方向:切换多智能体的协同控制
通信联系人:周洪涛(1969-),男,副教授,主要研究方向:复杂社会经济系统建模与仿真、多智能体系
统. E-mail: zhouhongtao_hust@sina.com
- 1 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
在协同控制中,通信时延和变化拓扑是影响多智能体系统稳定性的主要因素。基于已有
的研究,我们在典型的输入模型中加入通信时延,而由于切换多智能体系统的切换特征,使
得在连续时间多智能体系统中广泛使用的李雅普诺夫函数很难直接使用。通过运用变化后的
Lyapunov-Krasovskii 函数,本文主要研究了包含连续和离散系统的切换多智能体系统在变化
45
拓扑和通信时延下所有智能体的一致性问题,同时得到了切换多智能体系统在固定通信时延
和变化通信时延下达到一致性的充分条件。
1 图论基础和相关引理
1.1 图论相关知识
50
55
60
65
70
2
1
论文中会用到图论的一些基本知识,这里做下简短介绍,具体图论知识可参考[25]。设
一个多智能体系统含有 n 个智能体,则这 n 个智能体的拓扑图结构可表示为 G=(V,E,A),其
中
邻接矩阵,并且 a
v
i,顶点 的邻居集合表示为 N {
表示有向边集合,而 A [
V= v , v ,..., vn 表示顶点集合, E V V
v v
(
,
ij 。图 G 的有向边 ij
i
V v v
)
,
: (
ija ,
j
iia 。此外,有向图的拉普拉斯矩阵定义
ija 。在整个系统中假设不存在回环,即
j 时,
,表示信息流从智能体 j 传递到智能体
E
}
0
)
j
。如果有边 (
v v 则有 1
i
是对角矩阵,并且
,其中
,而当i
D d
[
a
]ij n n
D A
表示加权
否则
0
d
)
n
,
n
i
j
i
j
]ij n n
j a
1
ij
ii
0
l
为 L [
]ij n n
ijd 。
0
1.2 假设及引理
假设 1:假设 L 是有向拓扑图的拉普拉斯矩阵,则令表示 LT L 的特征值。
假设 2:假设 L 是有向拓扑图的拉普拉斯矩阵,则令 ˆ表示 L +T L 征值。
引理 1[16]:正方形矩阵
引理 2[26]:对任意矩阵
nM 。
,矩阵 AB 和矩阵 BA 有相同的非零特征值。
是平衡矩阵当且仅当 n1
nM R n
A B
R n
,
n
T M 和 1
0
0
2 系统模型
切换多智能体系统包含连续时间子系统和离散时间子系统,连续和离散子系统分别为下
1a 和
式中的
b1 :
t
x ( )
i
x t
(
i
其中 xi 、 iu 和 x (0)
i 表示第 i 个智能体的实时状态、控制输入和初始状态,为表示方便,设
i ,则
u t
( )
i
x t
1)
( )
i
(1 )
a
(1 )
b
x (0)
i
u t
( )
i
x(0)
,...,
x
20
x
10
(1)
。
x
n
I
I
i
i
]T
x
[
,
n
n
0
定
定义 1:对任意的初始条件,切换多智能体系统
使得:
|| 0,
。
x
I
i
0
x t
( )
i
n
lim ||
t
1a ,
b1 达到状态一致仅当存在 x ,
- 2 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
对于连续时间多智能体系统和离散时间多智能体系统广泛使用的控制输入,当存在通信
时延时,切换多智能体系统的控制输入为:
t
)(u
i
n
1
n
j
h
j
1
ta
(
ij
t
(x)[
j
t
(
))
t
(x
i
t
(
))]
ta
(
ij
t
(x)[
j
t
(
))
t
(x
i
t
(
))]
其中 τ 是变化的通信时延,h>0 是采样周期.
那么,由(1)、(2)可得,切换多智能体系统可简写为:
75
t
x(
t
x( )
1)
3 主要结果
t
-L(t)x(t- ( ))
hL t x t
t
x( )
( ) (
t
( ))
)(2
3
( )
主要研究通信时延是固定大小和随时间变化的情况下,切换多智能体系统在变化拓扑下
达到状态一致性。
首先,当通信时延大小固定时, ( )t ,则切换多智能体系统为:
80
t
x(
t
x( )
1)
-L(t)x(t- )
t
hL t x t
x( )
( ) (
)
4
( )
定理 1:对于包含常数时延和切换拓扑的有向通信网络,如果通信网络 G 是强连通和平
衡的,并且满足如下条件,则可以达到一致性。
h
2
1 0
h
2
和
h
ˆ
min
0
-1 0
max
max
85
对定理证明如下:
n
i x t
( )
1
n
c t
( )
设
i
,由图 G 是平衡矩阵,可知 n1
T L t 和
( ) 0
L t
( )1
n
0
dc t
( )
dt
c t
(
1)
dx t
( )
i
dt
1)
1
n
n
i
1
n
i
1
x t
(
i
n
n
x t
( )
i
i
1
n
1)
T
1
n
T
1
n
x t
(
n
也就是说,c(t)是常量,即 c(t)=c(0)。
T
1
n
x t
( )
n
x t
( ) 1
n
T
1
n
L t x t
( ) (
n
)
0
L t x t
( ) (
T
n
)
T
1
n
x t
( )
n
n
x t
( )
i
i
1
n
c t
( )
90
令 (t)
,则:
nc t
x(t) 1 ( )
(t)
L(t) (t
(t)
(t 1)
)
hL t
( ) (t
)
(5a)
b
(5 )
(5)
对 于 连 续 时 间 子 系 统 ( 5a ) 和 离 散 时 间 子 系 统 ( 5b ) , 取 李 雅 普 诺 夫 函 数
,则在连续时间子系统工作期间,
t
t
( ) ( )
V( ( ))
t
T
- 3 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
t
( )
t
令
V
T
t
t
( ) ( )
因为
s ds
T
t-
s
( ) ( )
t
故对任意的 都有:
t
0
t
t
T
T
s ds
s
( ) ( )
t
t-
0
s
s dsd
0
( ) ( )
和
t
t
V
t
( )
V ( )
t
( ) ( )-
t
T
T
s
( ) ( )
s dsd
0
V
令
t
( )
T
t
( - ) ( - )
t
t
( ) ( )
t
T
0
0
T
T
T
t
t
( ) ( )
t
t
t
(
( ) ( )-
-
L
t
t
[ (t) (
( )
)]
T
T
t
t
t
( ) ( )-
(
T
T
-
L
t
t
(t) ( )
-
(
)
T
T
0
t
t
d
) (
(
-
)
-
L
t
t L
t
( ) (t) (
(t) ( )
T
T
)
和
t
( )
T
T
)
t
d
) (
)
t L
t
t
( ) (t) (
( - ) ( - )
d
t
) (
)
t L
t
( ) (t) (
t
( - ) ( - )
t
( ) ( )-
t
( ) ( )-
t
t
T
T
t
t
( ) ( )
)
t
t
T
T
T
L
t
(t) (
)
因为
T
)
t
(
故:
原式
-2
T
)
t
又因为
t
(
)
t
( )
-2
故:
T
t L
t
( ) (t) (
)
t
-2
t L
t
( ) (t) (
)
t
( - ) ( - )
t
( ) ( )-
t
(
t
t
T
T
T
L
T
t
(t) (t) (
T
)-
L
(
d
) ( )
t
t-
s ds
( )
及对任意的
x,
y
R ,
n
都有
2x
T
y
T
x
x
T
y
y
T
t L
t
( ) (t)[ ( )
s ds
( )
]
t L
t
( ) (t) ( )
2
T
L
T
t
t
t
t
t
T
t
t
t
t L
t
( ) (t) ( )
t L
t
( ) (t) ( )
t L
t
( ) (t) ( )
-2
T
-2
T
-2
T
-2
T
t L
( ) (t) ( )
s ds
T
t
T
T
L
T
L
T
s ds
( )
t
(t) ( )
t
(t) ( )
t
(t) ( )
t
(t) ( )
t
2
t L L
( ) (t)
T
t
s ds
s
( ) ( )
t
t
t
(t) (t) (
t
(t) ( )
d
( ) ( )
t
t
( - ) ( - )
T
)-
t-
t
t
( ) ( )-
s
( ) ( )
t
(t) ( )
L
T
T
T
s
( ) ( )
s ds
s ds
T
t
t
( ) ( )
故:原式子
-2
T
t L
t
( ) (t) ( )
T
t L L
( ) (t)
T
T
T
T
t
t
L
t
( - ) ( - )
(
-
)
T
t L
t
t L L
( ) (t) ( )
( ) (t)
-2
T
T
T
L
t
L
t
)
(t) (t) (
(
)
T
T
t L
t
(t) L (t)
( )
( )
-
T
T
T
t
L
t
L
(
)
(t)
(
)
(t)
T
T
L
L L
t
( ) - (t)-L (t)
(t)
(t)
T
T
T
因此,
0
t
V
)(
的充分条件可为:
L
L L
(t)
(t)
- (t)-L (t)
(t) (t)-I
I 0
T
L
L
L
max (
(t) (t)) 0,
min ( (t) L (t)) 0
T
λ
L
T
和
ˆ
min
t L L
( ) (t)
T
t
(t) ( )
max
令
λ
L
0
I
T
T
95
t
( - ) ( - )
t
( ) ( )-
t
t
T
T
L
T
t
( )
t
(
)
T
(t) (t)-I
L
)
t
(
即充分条件可为:
ˆ-
1 0
和
min
max
V
t
t
V ( )
( )
故
t
V ( )
即:
max
T
min
-1 0
t
L
( ) - (t)-L (t)
t
max 1
( )
V
T
L L
(t)
T
(t)
I
t
( )
min
max
1
V
t
( )
0
- 4 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
1)
(
min
max
k
令
,则
1
在离散时间子系统工作期间:
t
V (
t
1) -V ( )
V( (t))
e V( (0))
k t
1
。
同理可得:
2
T
T
t
(
t
hL t
t
hL t
t
t
[ ( )
( ) (
)] [ ( )
( ) (
T
t L t
t
h
t
h
t
L t
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) (
(
)
)
T
T
T
t
t
h
t
L t L t
h
) 2
( ) ( ) (
(
(
)
)
T
T
T
2
L t
t
t
h
h
L t
t
( )[ (
)
2
( ) ( )
(
)
)
T
T
T
t
h
t
t
( ) ( )
)]
h
t
(
)
T
2
t
L t
( ) ( )
T
t
s ds
( )
t
L t
)
2
( ) ( )
T
t
t
)
h
)
h
)
t
( ) ( ) (
L t L t
T
)
)
t
( ) (
t
( ) (
2
2
s ds
L t
T
L t
T
t
(
t
(
t
(
t
(
h
h
]
T
T
T
T
t
T
h
)
2
t
t
1) -V ( )
(
h
则:
t
V (
T
h
t
)
(
h L t L t
t
(
)[
T
2
h
h
(
2
2
λ )
因此,的充分条件可为:
T
T
T
t
(
) 2
t
t
L t
L t L t
(
)
( ) (
)
T
T
h
L t L t
t
( ) ( ) (
)
)
T
T
2
t
L t L t
s
)
( ) ( ) (
( ) ( )
T
t
hL t L t
hL t
t
( ) ( ) 2
( )
( ) ( )] (
T
t
h
t
-
(
) (
)
T
t
)
( ) ( ) (
t
L t
t
(
( ) (
T
t
s ds
h
T
T
)
L t L t
T
t
( ) ( ) (
)
s
( ) ( )
s ds
)
T
h
)
t
T
s
( ) (
t
s
)
ds
V
t
t
( ( )) 0
1))
V( (
t
V
( ( ))
)
(1
V( (
1))
。
t
对任意时刻 t>0,令 t
2h
2
V
t
( ( ))
h
, 其 中 表 示 大 于 0 的 任 意 正 数 , 即
0
h
t
,其中 ct 续时间子系统工作时间, dt 散子系统工作时间,
t
d
c
因此:
其中
V
t
( ( ))
k
= min(
,ln(1
1
t
e
( ) |
|
t
0.5
e
))
(0)
t
)
( (0))
V
d
k t
c
1
。
(1
k
1
k t
c
1
e
t
d
e
V
ln(1
)
( (0))
e V
t
( (0))
t
故
下,切换多智能体系统可以达到状态一致。
其次,当通信时延大小随时间变化时,切换多智能系统如(3)所示。
| x( ) 1 (0) |
,也就是说,
e
0.5
(0)
c
n
t
,因此,在任意变化拓扑
定理 2: 对于包含时延和切换拓扑的有向通行网络,如果通信网络 G 是强连通和平衡
的,并且满足如下条件,则可以达到一致性。
h
2
1 0
h
2
和
ˆ
min
max
h
max
0
-1
0
证明:定理 2 的证明与定理 1 的证明方法一样,证明过程类似,此处省略。
100
105
110
115
4 仿真
这一部分,我们用仿真例子来证明我们的理论分析结果。例子中选取 6 个智能体,系统
的拓扑结构图如图 1 所示。假设每个智能体 0 时刻及以前的初始状态都一样,用生成的随机
值来表示。
120
通信网络如图 1 所示,切换多智能体系统的切换率如图 2 所示,通过计算,通信时延
- 5 -
�
中国科技论文在线
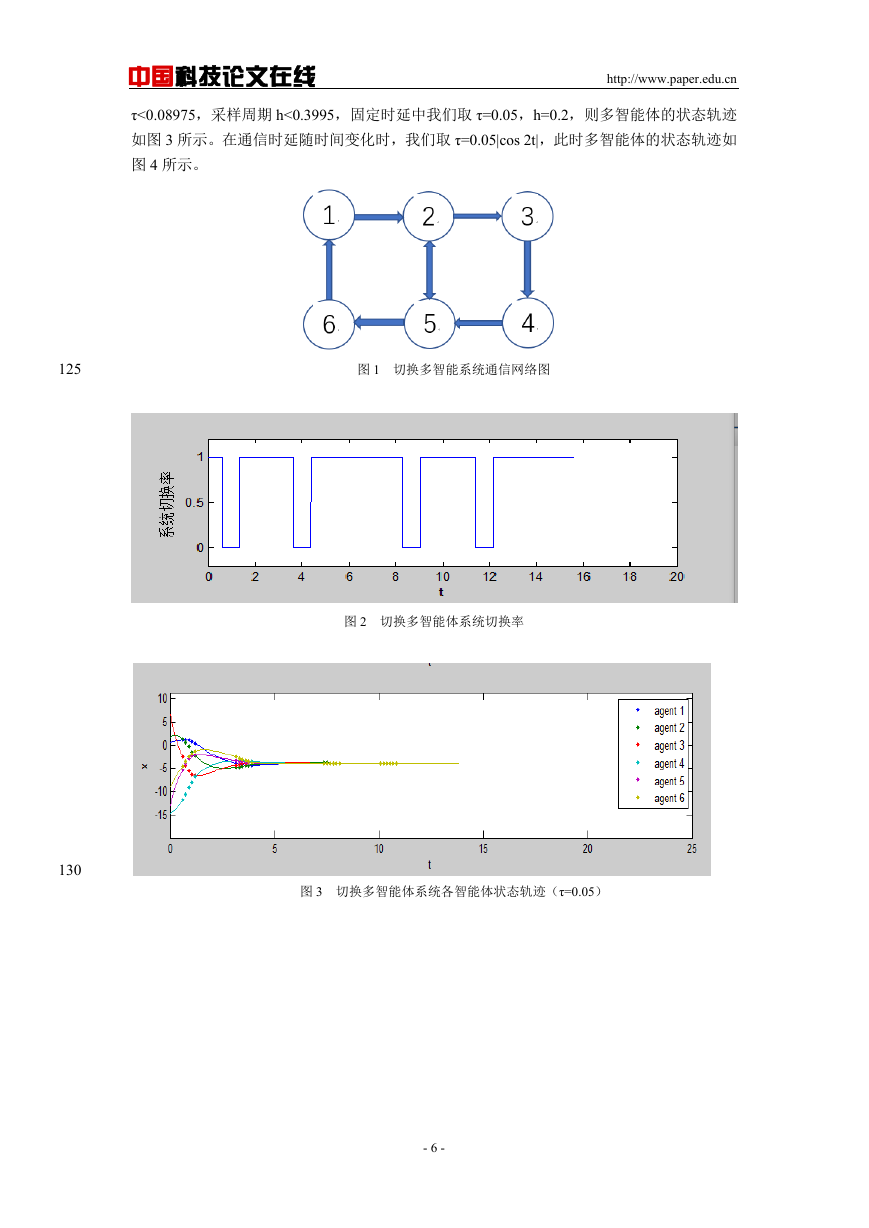
τ<0.08975,采样周期 h<0.3995,固定时延中我们取 τ=0.05,h=0.2,则多智能体的状态轨迹
如图 3 所示。在通信时延随时间变化时,我们取 τ=0.05|cos 2t|,此时多智能体的状态轨迹如
图 4 所示。
http://www.paper.edu.cn
125
图 1 切换多智能系统通信网络图
图 2 切换多智能体系统切换率
130
图 3 切换多智能体系统各智能体状态轨迹(τ=0.05)
- 6 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
135
140
145
150
155
160
165
170
图 4 切换多智能体系统各智能体状态轨迹(τ=0.05|cos 2t|)
5 结论
将严重干扰系统稳定性的变化拓扑和通信时延与切换多智能体系统相结合,研究了切换
多智能体系统通信时延和采样周期的大小对系统稳定性的影响。对于既需要考虑连续又需要
考虑离散的情况,通过运用矩阵不等式和变化的李雅普诺夫函数,给出了系统到达稳定性的
充分条件。
本文研究了切换多智能体系统通信时延固定大小和随时间变化的两种情况,下一步会继
续研究二阶和多阶时切换多智能体系统是否还能达到稳定性。
[参考文献] (References)
[1] Fierro R, Song P, Das A, et al. Cooperative Control of Robot Formations[J]. Applied Optimization, 2002,
66:73-93.
[2] Cao Y, Ren W, Sorensen N, et al. Experiments in Consensus-based Distributed Cooperative Control of
Multiple Mobile Robots[C]// International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation. IEEE, 2007:2819-2824.
[3] Dong W, Farrell J A. Consensus of multiple uncertain mechanical systems and its application in cooperative
control of mobile robots[J]. 2008:1954-1959.
[4] Kuriki Y, Namerikawa T. Consensus-based cooperative control for geometric configuration of UAVs flying in
formation[C]// Sice Conference. IEEE, 2014:1237-1242.
[5] Chandler P R, Pachter M, Rasmussen S. UAV cooperative control[C]// American Control Conference, 2001.
Proceedings of the. IEEE, 2001:50-55 vol.1.
[6] Ryan A, Zennaro M, Howell A, et al. An overview of emerging results in cooperative UAV control[C]//
Decision and Control, 2004. Cdc. IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2004:602-607 Vol.1.
[7] Beard R W, Mclain T W, Nelson D B, et al. Decentralized Cooperative Aerial Surveillance Using Fixed-Wing
Miniature UAVs[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2006, 94(7):1306-1324.
[8] Smith S L, Broucke M E, Francis B A. A hierarchical cyclic pursuit scheme for vehicle networks ☆[J].
Automatica, 2005, 41(6):1045-1053.
[9] Lee D, Spong M W. Stable Flocking of Multiple Inertial Agents on Balanced Graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on
Automatic Control, 2007, 52(8):1469-1475.
[10] Spanos D P, Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. DISTRIBUTED SENSOR FUSION USING DYNAMIC
CONSENSUS[J]. Proc Ifac, 2005.
[11] Olfati-Saber R, Shamma J S. Consensus Filters for Sensor Networks and Distributed Sensor Fusion[C]//
Decision and Control, 2005 and 2005 European Control Conference. Cdc-Ecc '05. IEEE Conference on. IEEE,
2006:6698-6703.
[12] Olfati-Saber R. Distributed Kalman Filter with Embedded Consensus Filters[C]// Decision and Control, 2005
and 2005 European Control Conference. Cdc-Ecc '05. IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2006:8179-8184.
[13] Qin J H, Gao H J, Zheng W X. On average consensus in directed networks of agents with switching topology
and time delay[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2011, 42(12):1947-1956.
[14] Qin J H, Gao H J, Zheng W X. Second-order consensus for multi-agent systems with switching topology and
communication delay ☆[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 2011, 60(6):390-397.
- 7 -
�
http://www.paper.edu.cn
中国科技论文在线
[15] Lin P, Jia Y. Consensus of a Class of Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems With Time-Delay and
Jointly-Connected Topologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(3):778-784.
[16] Lin P, Jia Y. Average consensus in networks of multi-agents with both switching topology and coupling
time-delay[J]. Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2008, 387(1):303-313.
[17] Xiao F, Wang L. State consensus for multi-agent systems with switching topologies and time-varying
delays[J]. International Journal of Control, 2006, 79(10):1277-1284.
[18] Lin P, Jia Y M. Consensus of second-order discrete-time multi-agent systems with nonuniform time-delays
and dynamically changing topologies ☆[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(9):2154-2158.
[19] Halloy J, Sempo G, Caprari G, et al. Social Integration of Robots into Groups of Cockroaches to Control
Self-Organized Choices[J]. Science (New York, N.Y.), 2007, 318(5853):1155-8.
[20] Lin X, Zheng Y S, Wang L. Delta-operator based consensus analysis of multi-agent networks with link
failures[J]. 2017.
[21] Zhu Y R, Zheng Y S, Guan Y Q. Consensus of switched multi-agent systems under quantised
measurements[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2014, 48(3):314-318.
[22] Zheng Y S, Ma J, Wang L. Consensus of Hybrid Multi-Agent Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural
Networks & Learning Systems, 2015, PP(99):1-7.
[23] Zheng Y S, Wang L. Consensus of Switched Multiagent Systems[J]. International Journal of Systems Science,
2014, 48(3):314-318.
[24] Lin X, Zheng Y S,Wang L. Consensus of switched multi-agent systems with random networks[J].
International Journal of Control, 2014, 90(5):1113-1122.
[25] Bondy B A, Murty U S R. Graph Theory[M]. Springer London, 2008.
[26] Horn R A, Johnson C R. Matrix Analysis[J]. Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 1990, 169(8):1-17.
175
180
185
190
195
- 8 -
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc