�
课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知!
Introduction
(Solution to Practice Set)
CHAPTER 1
khdaw.com
Review Questions
1. The three security goals are confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Confidentiality means protecting confidential information.
Integrity means that changes to the information need to be done only by
Availability means that information needs to be available to authorized enti-
authorized entities.
课后答案网
www.hackshp.cn
ties.
2.
In a passive attack, the attacker’s goal is just to obtain information. This
means that the attack does not modify data or harm the system. Examples of
passive attacks are snooping and traffic analysis.
An active attack may change the data or harm the system. Attacks that
threaten the integrity and availability are active attacks. Examples of active
attacks are modification, masquerading, replaying, repudiation, and denial of
service.
3. We mentioned five security services: data confidentiality, data integrity, authenti-
cation, nonrepudiation, and access control.
Data confidentiality is to protect data from disclosure attack.
Data integrity is to protect data from modification, insertion, deletion, and
khdaw.com
1
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com
replaying.
the line.
Authentication means to identify and authenticate the party at the other end of
Nonrepudiation protects against repudiation by either the sender or the
receiver of the data.
Access control provides protection against unauthorized access to data.
课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知!
2
4. Eight security mechanisms were discussed in this chapter. encipherment, data
integrity, digital signature, authentication exchange, traffic padding, routing con-
trol, notarization, and access control.
Encipherment provides confidentiality.
The data integrity mechanism appends a short checkvalue to the data. The
checkvalue is created by a specific process from the data itself.
A digital signature is a means by which the sender can electronically sign the
data and the receiver can electronically verify the signature.
In authentication exchange, two entities exchange some messages to prove
their identity to each other.
khdaw.com
Traffic padding means inserting some bogus data into the data traffic to thwart
the adversary’s attempt to use the traffic analysis.
Routing control means selecting and continuously changing different avail-
able routes between the sender and the receiver to prevent the opponent from
eavesdropping on a particular route.
Notarization means selecting a third trusted party to control the communica-
Access control uses methods to prove that a user has access right to the data or
tion between two entities.
课后答案网
www.hackshp.cn
resources owned by a system.
5.
Cryptography, a word with origin in Greek, means “secret writing.” We used
the term to refer to the science and art of transforming messages to make them
secure and immune to attacks.
Steganography, a word with origin in Greek, means "covered writing." Stega-
nography refers to concealing the message itself by covering it with some-
thing else.
Exercises
6.
a. A regular mail guarantees no security services. It is the best-effort delivery ser-
vice. The mail can be lost, altered in the mail, opened by somebody other than
the intended recipient.
b. A regular mail with delivery confirmation can only show that the mail has been
delivered. This can only give peace of mind to the sender that the packet is not
lost. However, since there is no signature from the recipient, it does not guaran-
tee any of the security services.
c. A regular mail with delivery confirmation and the recipient signature can pro-
vide nonrepudiation service only at the mail level, not the contents level. In
other words, the recipient of the mail cannot deny that she has not received the
mail, but she can deny that the mail contained some specific information. For
khdaw.com
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com
�
3
khdaw.com
example, if Alice sends a mail with $100 cash inside to Bob via this type of
mail, Bob cannot deny that he has received the mail, but he can deny that the
mail contained some cash inside. In some cases, the sender is an authority and it
is enough that Bob accepts he has received the mail. In this case, if there is a
dispute, the court accept the testimony of the sender about the contents.
d. A certified mail is actually the same as the regular mail with delivery confirma-
tion and the recipient signature.
e. A mail can be insured. However, this is not security in the sense we are talking
in this chapter. Secured mail can only provide compensation if the mail is lost.
f. A registered mail is different from all of the previous delivery methods. A reg-
istered mail is carried by the post office under the tight security. This means that
the confidentiality and integrity of the mail is guaranteed. Since a registered
mail normally includes the signed receipt, the nonrepudiation is also guaran-
teed. However, nonrepudiation is only at the mail level, not the content level.
The recipient of the registered mail cannot deny that the mail has been deliv-
ered, but it can deny that it contained a special message or an item of some
value.
7.
8.
9.
a. This is snooping (attack to the confidentiality of stored data). Although the con-
tents of the test is not confidential on the day of the test, it is confidential before
the test day.
b. This is modification (attack to the integrity of data). The value of the check is
changed (from $10 to $100).
c. This is denial of service (attack to availability). Sending so many e-mails may
crash the server and the service may be interrupted.
a. This provides access control mechanism. The process is to prove that the stu-
dent has right to access the school resources.
b. This can provide routing control. The school may be doing this to prevent a stu-
dent from eavesdropping on a particular route.
c. This can be authentication exchange mechanism. The professor needs to
authenticate the student before sending the grade. The preassigned identifica-
tion is a secret between the student and the professor.
d. The mechanism is similar to digital signature. It can be used for two purposes.
If the signature of the customer is checked against a signature on the file, it can
provide authentication. The signature on the withdrawal document definitely is
served as the nonrepudiation. The customer cannot later denies that she has not
received the cash.
khdaw.com
a. This is steganography. The answers to the test has not been changed; they have
been only hidden.
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com 课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn 若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知! 课后答案网 www.hackshp.cn �
b. This is cryptography. The characters in the message are not hidden; they are
replaced by another characters.
4
c. This is steganography. The special ink hides the actual writing on the check.
d. This is steganography. The water marks hides the actual contents of the thesis.
10. A signature on a document is like a digital signature on a message. It protects the
integrity of the document, it provides authentication, and it protects non-repudia-
tion.
khdaw.com
khdaw.com
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com 课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn 若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知! 课后答案网 www.hackshp.cn �
Mathematics of Cryptography
Part I
CHAPTER 2
khdaw.com
(Solution to Practice Set)
Review Questions
1. The set of integers is Z. It contains all integral numbers from negative infinity to
positive infinity. The set of residues modulo n is Zn. It contains integers from 0 to
n − 1. The set Z has non-negative (positive and zero) and negative integers; the set
Zn has only non-negative integers. To map a nonnegative integer from Z to Zn, we
need to divide the integer by n and use the remainder; to map a negative integer
from Z to Zn, we need to repeatedly add n to the integer to move it to the range 0 to
n − 1.
2. We mentioned four properties:
Property 1: if a | 1, then a = ±1.
Property 2: if a | b and b | a, then a = ±b.
Property 3: if a | b and b | c, then a | c.
Property 4: if a | b and a | c, then a | (m × b + n × c), where m and n are arbi-
trary integers.
3. The number 1 is an integer with only one divisor, itself. A prime has only two divi-
sors: 1 and itself. For example, the prime 7 has only two divisor 7 and 1. A com-
posite has more than two divisors. For example, the composite 42 has several
divisors: 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, and 42.
4. The greatest common divisor of two positive integers, gcd (a, b), is the largest pos-
itive integer that divides both a and b. The Euclidean algorithm can find the great-
est common divisor of two positive integers.
5. A linear Diophantine equation of two variables is of the form ax + by = c. We need
to find integer values for x and y that satisfy the equation. This type of equation has
either no solution or an infinite number of solutions. Let d = gcd (a, b). If d does
not divide c then the equation have no solitons. If d divides c, then we have an infi-
nite number of solutions. One of them is called the particular solution; the rest, are
/.
called the general solutions.
khdaw.com
1
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com 课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn 若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知! 课后答案网 www.hackshp.cn �
2
khdaw.com
6. The modulo operator takes an integer a from the set Z and a positive modulus n.
The operator creates a nonnegative residue, which is the remainder of dividing a
by n. We mentioned three properties for the modulo operator:
First: (a + b) mod n = [(a mod n) + (b mod n)] mod n
Second: (a − b) mod n = [(a mod n) − (b mod n)] mod n
Third: (a × b) mod n = [(a mod n) × (b mod n)] mod n
7. A residue class [a] is the set of integers congruent modulo n. It is the set of all inte-
gers such that x = a (mod n). In each set, there is one element called the least (non-
negative) residue. The set of all of these least residues is Zn.
8. The set Zn is the set of all positive integer between 0 and n − 1. The set Zn∗ is the
set of all integers between 0 and n − 1 that are relatively prime to n. Each element
in Zn has an additive inverse; each element in Zn∗ has a multiplicative inverse. The
extended Euclidean algorithm is used to find the multiplicative inverses in Zn∗.
9. A matrix is a rectangular array of l × m elements, in which l is the number of rows
and m is the number of columns. If a matrix has only one row (l = 1), it is called a
row matrix; if it has only one column (m = 1), it is called a column matrix. A
square matrix is a matrix with the same number of rows and columns (l = m). The
determinant of a square matrix A is a scalar defined in linear algebra. The multipli-
cative inverse of a square matrix exists only if its determinant has a multiplicative
inverse in the corresponding set.
10. A linear equation is an equation in which the power of each variable is 1. A linear
congruence equation is a linear equation in which calculations are done modulo n.
An equation of type ax = b (mod n) can be solved by finding the multiplicative
inverse of a. A set of linear equations can be solved by finding the multiplicative
inverse of a matrix.
Exercises
11.
a. It is false because 26 = 2 × 13.
b. It is true because 123 = 3 × 41.
c. It is true because 127 is a prime.
d. It is true because 21 = 3 × 7.
e. It is false because 96 = 25 × 3.
f. It is false because 8 is greater than 5.
12.
khdaw.com
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com 课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn 若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知! 课后答案网 www.hackshp.cn �
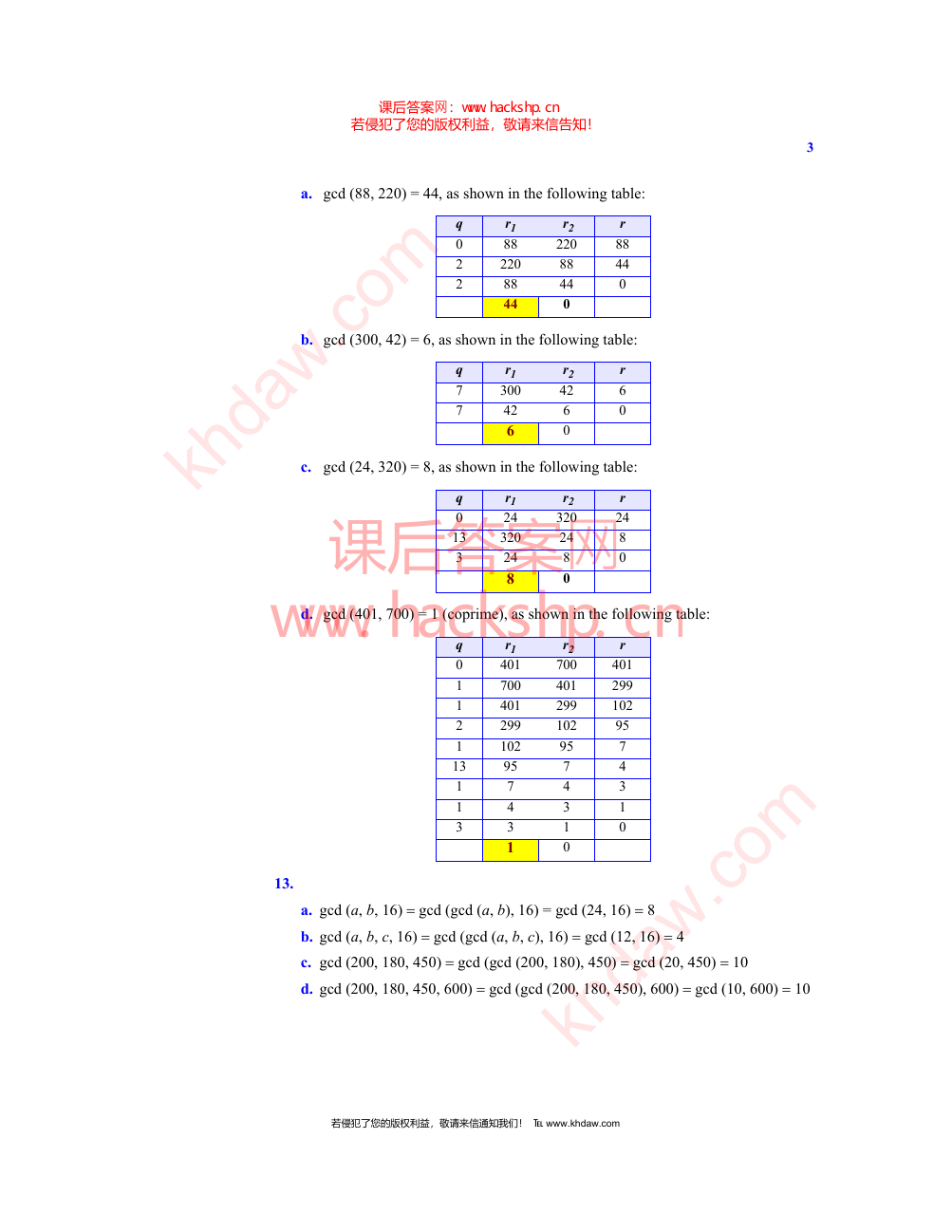
a. gcd (88, 220) = 44, as shown in the following table:
3
b. gcd (300, 42) = 6, as shown in the following table:
gcd (24, 320) = 8, as shown in the following table:
khdaw.com
c.
q
0
2
2
r1
88
220
88
44
r2
220
88
44
0
r
88
44
0
q
7
7
r1
300
42
6
r2
42
6
0
r
6
0
q
0
13
3
r1
24
320
24
8
r2
320
24
8
0
r
24
8
0
d. gcd (401, 700) = 1 (coprime), as shown in the following table:
q
0
1
1
2
1
13
1
1
3
r1
401
700
401
299
102
95
7
4
3
1
13.
r2
700
401
299
102
95
7
4
3
1
0
r
401
299
102
95
7
4
3
1
0
khdaw.com
a. gcd (a, b, 16) = gcd (gcd (a, b), 16) = gcd (24, 16) = 8
b. gcd (a, b, c, 16) = gcd (gcd (a, b, c), 16) = gcd (12, 16) = 4
c. gcd (200, 180, 450) = gcd (gcd (200, 180), 450) = gcd (20, 450) = 10
d. gcd (200, 180, 450, 600) = gcd (gcd (200, 180, 450), 600) = gcd (10, 600) = 10
若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信通知我们! ℡ www.khdaw.com 课后答案网:www.hackshp.cn 若侵犯了您的版权利益,敬请来信告知! 课后答案网 www.hackshp.cn �















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc