JanusGraph
底层数据库基于HBase,检索服务基于Elasticserach。
系统运行服务大致如下:
[root@xnode208 ~] jps
21584 GremlinServer
27857 DataNode
23218 Jps
3251 HMaster
27283 NameNode
21707 Console
17131 Elasticsearch
29503 SecondaryNameNode
下载janusgraph0.22安装包并解压
wget https://github.com/JanusGraph/janusgraph/releases/download/v0.2.2/janusgraph-0.
2.2-hadoop2.zip
unzip janusgraph-0.2.2-hadoop2.zip
cd janusgraph-0.2.2-hadoop2
gremlin-server
在这里我们采用的是启动gremlin-server服务时,加载指定配置文件的方法创建图表
创建gremlin-server端配置文件janusgraph-0.2.2-hadoop2/conf/gremlin-server/socket-
gremlin-server.yaml,这里我们复制gremlin服务默认的配置文件,在此基础上进行修改
cp conf/gremlin-server/gremlin-server.yaml conf/gremlin-server/socket-gremlin-serve
r.yaml
修改socket-gremlin-server.yaml:在配置文件中添加graphManager;并在graphs项中添加
graph键及其值,一个键值代表一个图表,值表示对图表的设置(可添加多个图表,每一个图
JanusGraph单机搭建及简单使用(1).md
1 / 6
搭
建
及
简
单
使
用
基
本
环
境
安
装
配
置
设
置
端
以
及
图
表
的
配
置
文
件
�
表都有自己的配置文件),如:
graphManager: org.janusgraph.graphdb.management.JanusGraphManager
graphs: {
blablabla,
graph: conf/gremlin-server/socket-jg-hbase_fyk-server-configraph.properties
}
准备上述socket-gremlin-server.yaml中对图表进行设置的properties文件,conf/gremlin-
server/socket-jg-hbase_fyk-server-configraph.properties文件内容如下:
gremlin.graph=org.janusgraph.core.JanusGraphFactory
graph.graphname=graph
storage.backend=hbase # 设置我们本地启动的hbase作为底层数据库
storage.hostname=127.0.0.1
index.search.backend=elasticsearch # 设置Janus graph自带的es作为我们的检索服务
index.search.hostname=127.0.0.1
cache.db-cache = true
cache.db-cache-clean-wait = 20
cache.db-cache-time = 180000
cache.db-cache-size = 0.5
(
gremlin.sh
hbase,elasticsearch
gremlin-server
)
hbase
[root@xnode208 ~] start-hbase.sh
elasticsearch.(注:Janusgraph自带的elastic search服务启动时为确保安全被禁止使用root用
户)
[zkr@xnode208 ~] cd /usr/local/janusgraph-0.2.2-hadoop2
[zkr@xnode208 elasticsearch] ./bin/elasticsearch
gremlin-server(启动成功后,会创建我们在配置文件中设计的图表)
JanusGraph单机搭建及简单使用(1).md
2 / 6
基
本
用
法
依
次
启
动
以
及
,
最
后
进
入
客
户
端
对
图
表
进
行
操
作
�
[zkr@xnode208 janusgraph0.2] ./bin/gremlin-server.sh ./conf/gremlin-server/socket-gr
emlin-server.yaml
gremlin.sh(进入gremlin交互式客户端)
[root@xnode208 janusgraph0.2] ./bin/gremlin.sh
gremlin>
# 连接gremlin server
gremlin> :remote connect tinkerpop.server conf/remote.yaml session
==>Configured localhost/127.0.0.1:8182-[f6db862e-752c-48db-839b-1b5b16f1786a]
gremlin> :remote console
==>All scripts will now be sent to Gremlin Server - [localhost/127.0.0.1:8182]-[f6db
862e-752c-48db-839b-1b5b16f1786a] - type ':remote console' to return to local mode
# 加载诸神图到我们创建的空图表中
gremlin> GraphOfTheGodsFactory.load(graph)
==>null
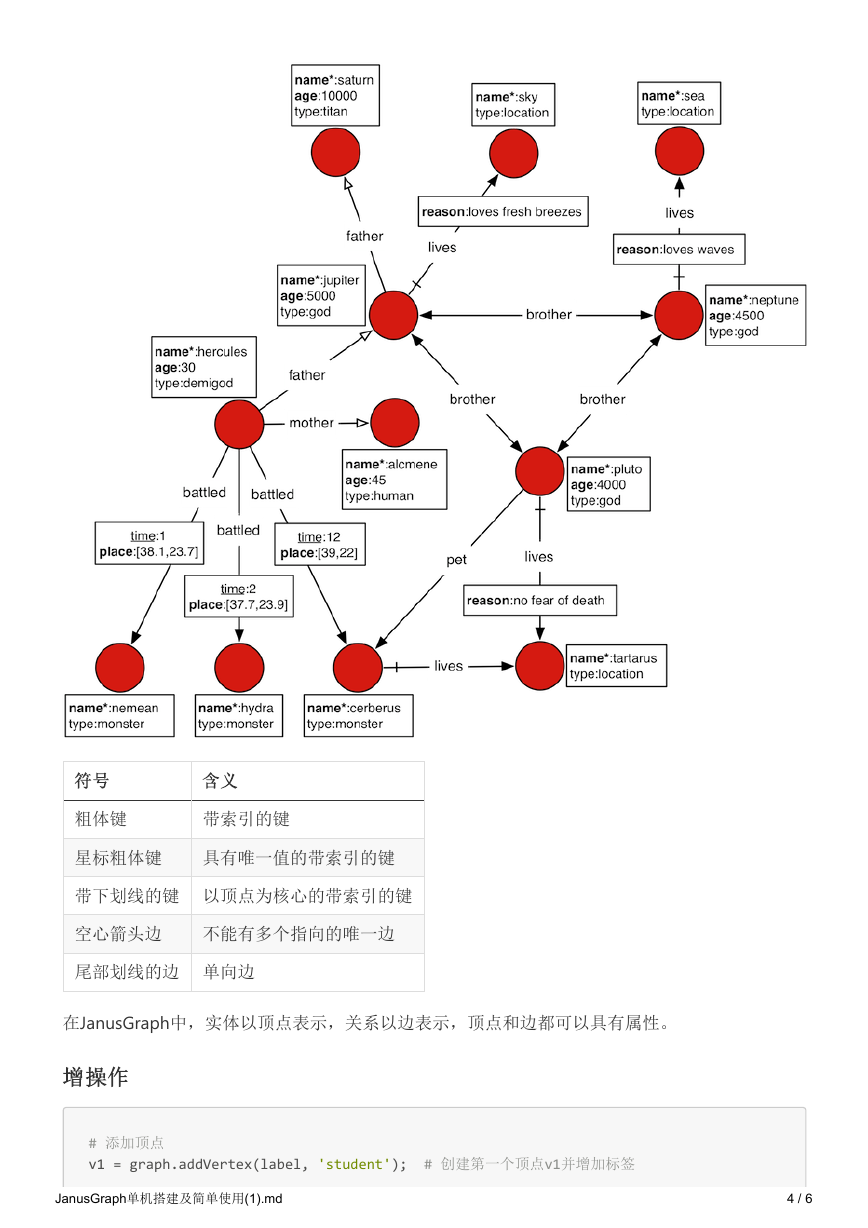
示例数据描述了一部分希腊诸神以及他们居住的诸神殿的相关关系。
JanusGraph单机搭建及简单使用(1).md
3 / 6
加
载
诸
神
图
一
些
基
本
操
作
示
例
数
据
:
诸
神
图
�
粗体键
带索引的键
星标粗体键
具有唯一值的带索引的键
带下划线的键 以顶点为核心的带索引的键
空心箭头边
不能有多个指向的唯一边
尾部划线的边 单向边
在JanusGraph中,实体以顶点表示,关系以边表示,顶点和边都可以具有属性。
# 添加顶点
v1 = graph.addVertex(label, 'student'); # 创建第一个顶点v1并增加标签
JanusGraph单机搭建及简单使用(1).md
4 / 6
符
号
含
义
增
操
作
�
v2 = graph.addVertex(); # 创建第二个顶点没有标签
# 为顶点添加属性
v1.property('id', '1'); # 为顶点v1添加id属性,值为1
v3 = graph.addVertex(label,'girl','name','huahua'); # 创建第三个顶点并且增加标签,属性
以及属性值
v4 = graph.addVertex(label,'boy','name','wuyanzu','age',18) # 创建第四个顶点添加标签
以及多个属性属性值
# 添加边
t1 = v1.addEdge('friends', v2); # 为v1添加关系到v2,并定义这个关系为t1
t2 = v1.addEdge('boyfriend', v2); # 两个顶点之间可以增加多种关系
# 为边增加属性
t1.property('reason','cool'); # 为t1增加属性
v3.addEdge('boyfriend',v4,'reason','because the reason'); # v3添加关系到v4并且增加关
系属性及属性值
# 提交修改
graph.tx().commit();
# 清空
g.V().drop(); # 删除所有点/图
g.E().drop(); # 删除所有边
graph1.close();
JanusGraphFactory.drop(graph1); # 清空图中的所有数据
# 删除顶点
pluto = g.V().has('name','pluto').next();g.V(pluto).drop().iterate(); # 删除name属性
为"pluto"的顶点
g.V().has('keys','ll').drop().iterate(); # 删除keys属性为"ll"的顶点
g.V().hasLabel('student').has('name','ll').drop().iterate(); # 删除标签为student,并
且顶点属性name的值为"ll"的顶点
# 删除边
g.E().has('uuu','because the reason').drop().iterate(); # 删除边属性uuu的属性值为beca
use the reason的边
g.E().hasLabel('boyfriend').has('event','the reason').drop().iterate(); # 删除边标签
为boyfriend并且边属性event的值为the reason的边
# 删除顶点标签以及顶点属性
g.V().hasLabel('girl').drop(); # 删除标签girl以及标签为girl的所有顶点
g.V().properties('name').drop(); # 删除顶点属性name
# 删除边标签、边属性以及属性值
g.E().hasLabel('boyfriend').drop(); # 删除边标签boyfriend
g.E().properties('uuu').drop(); # 删除边属性uuu
g.E().hasLabel("friend").properties().drop(); # 删除边标签为friend的所有属性以及属性值
g.E().values('because the reason').drop(); # 删除边属性值为because the reason以及对应
JanusGraph单机搭建及简单使用(1).md
5 / 6
删
操
作
�
的属性
graph.tx().commit(); # 提交
# 设置g=graph.traversal(),方便查询
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[standardjanusgraph[hbase:[127.0.0.1]], standard]
# 顶点标签查询
g.V(); # 查看所有顶点id
g.V().label(); # 查看所有顶点标签
g.V().hasLabel("god"); # 查看所有标签为god的顶点id
g.V().filter(label().is('god')); # 用filter查看所有标签为god的顶点id
g.V().has('name','hercules'); # 查看属性为name,值为hercules的顶点
# 顶点属性及属性值查询
g.V().valueMap(); # 遍历每个顶点的属性及属性值(若没有展示空集)
g.V().properties(); # 查看所有顶点的属性及属性值(不展示空)
g.V().hasLabel("god").values(); # 查看所有顶点标签为god的属性值
g.V().hasLabel("god").properties(); # 查看顶点标签为god的所有顶点属性以及属性值
g.V().values('id'); # 查看顶点属性为id的属性值
g.V().properties('id') # 查看顶点属性为id的属性及属性值
# 边标签查询
g.E(); # 查看所有顶点之间的边 顶点id--->边--->顶点id
g.E().label(); # 查看所有边的标签(关系)
g.E().hasLabel("battled") # 查看标签为battled的所有边
g.E().filter(label().is('battled')); # 用filter查看标签为battled的所有边
g.E().has('time',12); # 查看属性time的值为12的所有边
# 边属性及属性值查询
g.E().valueMap(); # 遍历所有边属性及属性值
g.E().properties(); # 查看所有边属性及属性值
g.E().hasLabel("battled").values(); # 查看所有标签为battled的边属性值
g.E().hasLabel("battled").properties(); # 查看所有标签为battled的边属性以及属性值
g.E().values('reason'); # 查看边属性为reason的属性值
g.E().properties('reason'); # 查看边属性为reason的属性及属性值
JanusGraph单机搭建及简单使用(1).md
6 / 6
查
询
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc