慢 SQL 优化 In PostgreSQL
目录
1、Create Index Directly..................................................................................................................................................................1
2、Change Conditions to Use Index............................................................................................................................................2
3、尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段进行运算,导致查询规划器放弃使用 index..................................................... 4
4、尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段类型进行强制转换,导致查询规划器放弃使用 index...................................4
5、少用 outer join,减少不必要的 sub-query 层级数【在不影响得到正确结果的前提下】................................5
6、坚决避免 select * 和 redundant columns【多余字段】.............................................................................................. 6
7、Index on Expressions..................................................................................................................................................................7
8、Partial Indexes...............................................................................................................................................................................8
9、Decompose DDL【分解 DDL】..............................................................................................................................................9
10、Comprehensive optimization【综合优化】..................................................................................................................10
11、索引的创建............................................................................................................................................................................... 10
12、查找需要删除的索引.............................................................................................................................................................11
13、查找重复的索引......................................................................................................................................................................12
14、查找需要维护的索引,并自定创建索引维护 SQL......................................................................................................12
15、一个 index size 影响 query plan 的例子......................................................................................................................... 13
1、Create Index Directly
总结:需要注意数据选择比的问题,如果 where 条件时 update_flag=false,效果就不会有这么明显,因为 update_flag
�
字段值几乎都是 false,尽管有 index,其效果和 Seq Scan 时间没什么差别。
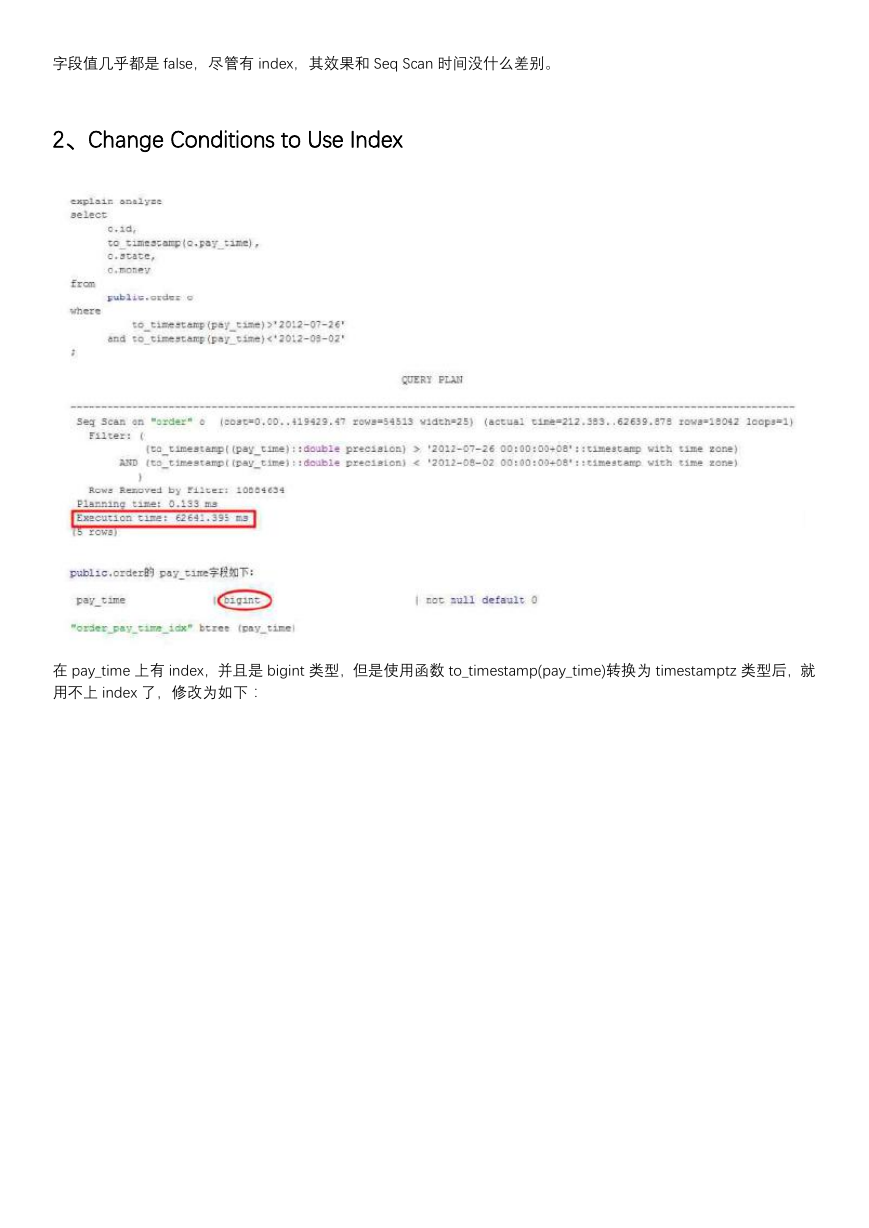
2、Change Conditions to Use Index
在 pay_time 上有 index,并且是 bigint 类型,但是使用函数 to_timestamp(pay_time)转换为 timestamptz 类型后,就
用不上 index 了,修改为如下:
�
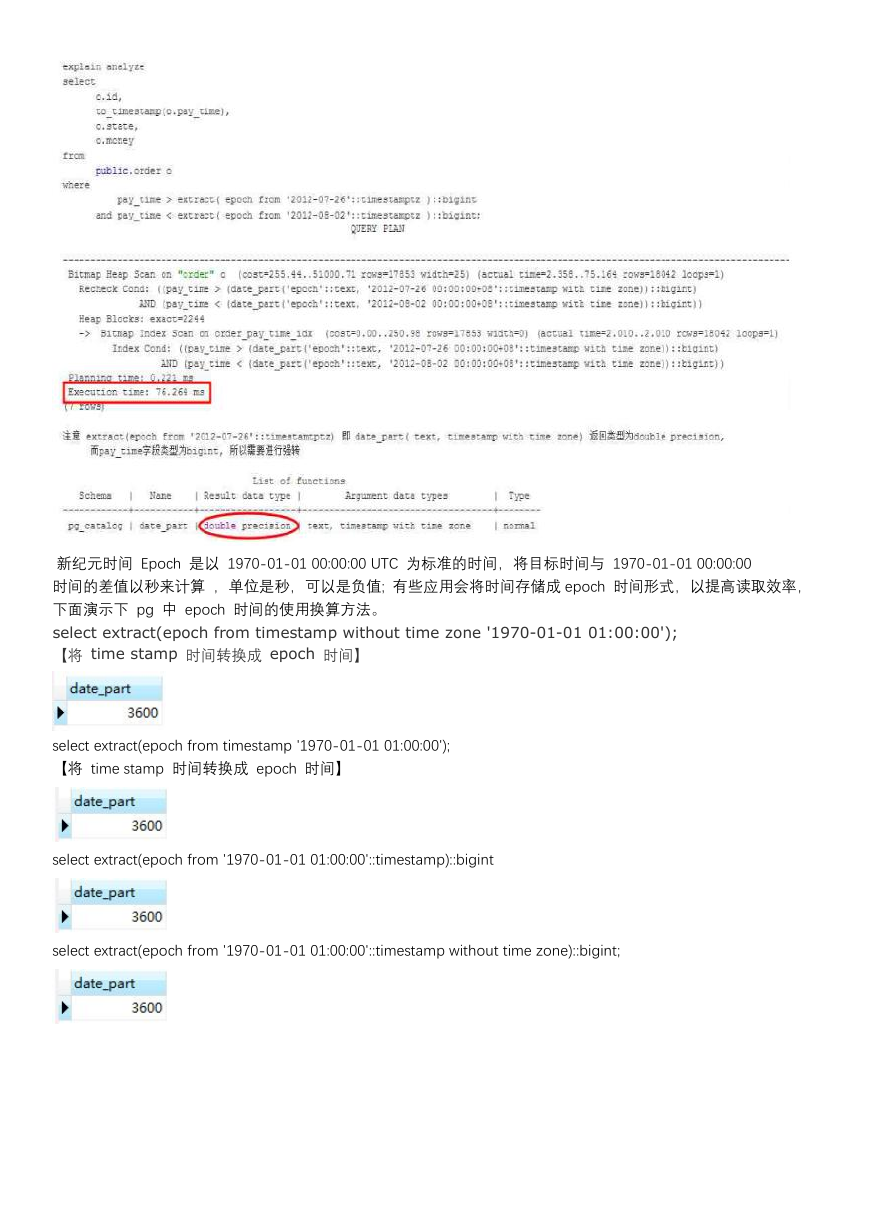
新纪元时间 Epoch 是以 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 为标准的时间,将目标时间与 1970-01-01 00:00:00
时间的差值以秒来计算 ,单位是秒,可以是负值; 有些应用会将时间存储成 epoch 时间形式,以提高读取效率,
下面演示下 pg 中 epoch 时间的使用换算方法。
select extract(epoch from timestamp without time zone '1970-01-01 01:00:00');
【将 time stamp 时间转换成 epoch 时间】
select extract(epoch from timestamp '1970-01-01 01:00:00');
【将 time stamp 时间转换成 epoch 时间】
select extract(epoch from '1970-01-01 01:00:00'::timestamp)::bigint
select extract(epoch from '1970-01-01 01:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)::bigint;
�
3、尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段进行运算,导致查询规划器放弃使用 index
4、尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段类型进行强制转换,导致查询规划器放
弃使用 index
�
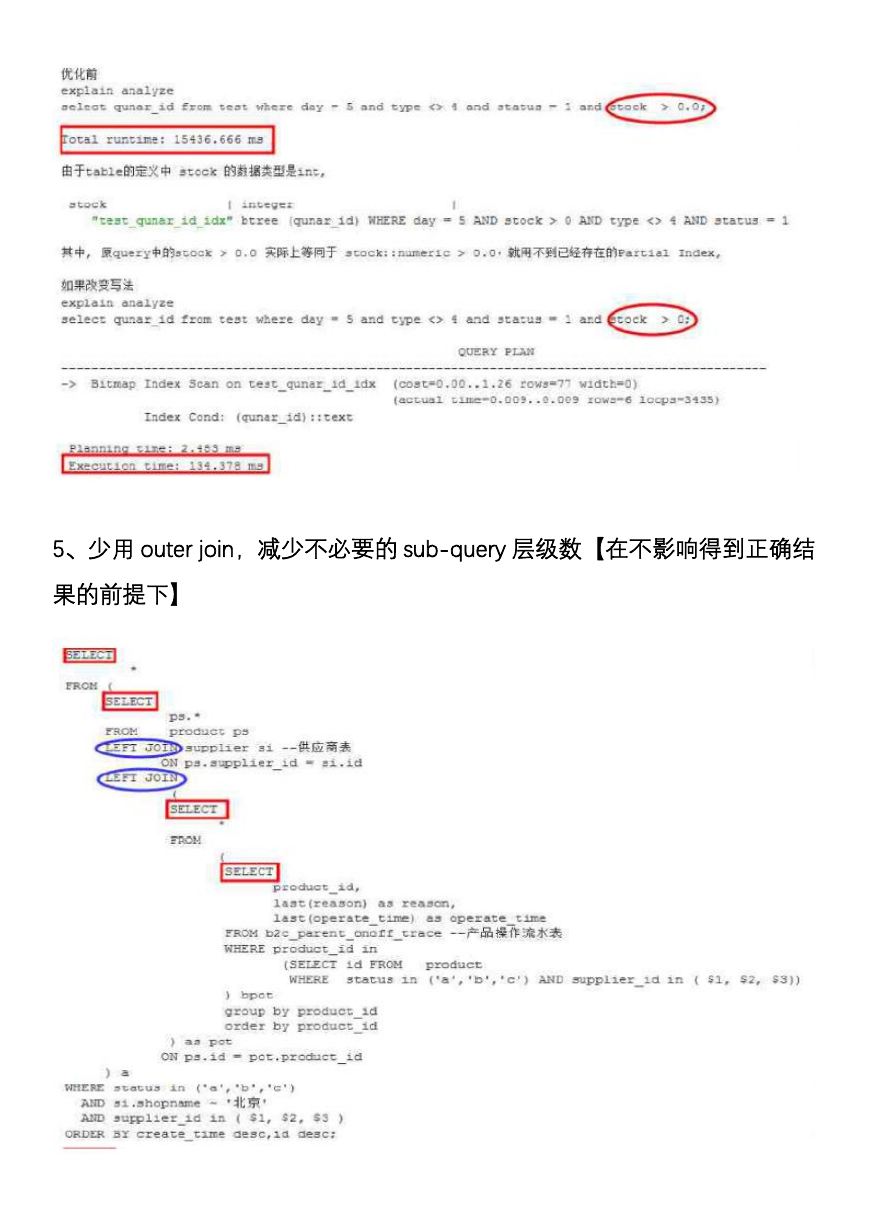
5、少用 outer join,减少不必要的 sub-query 层级数【在不影响得到正确结
果的前提下】
�
6、坚决避免 select * 和 redundant columns【多余字段】
�
7、Index on Expressions
�
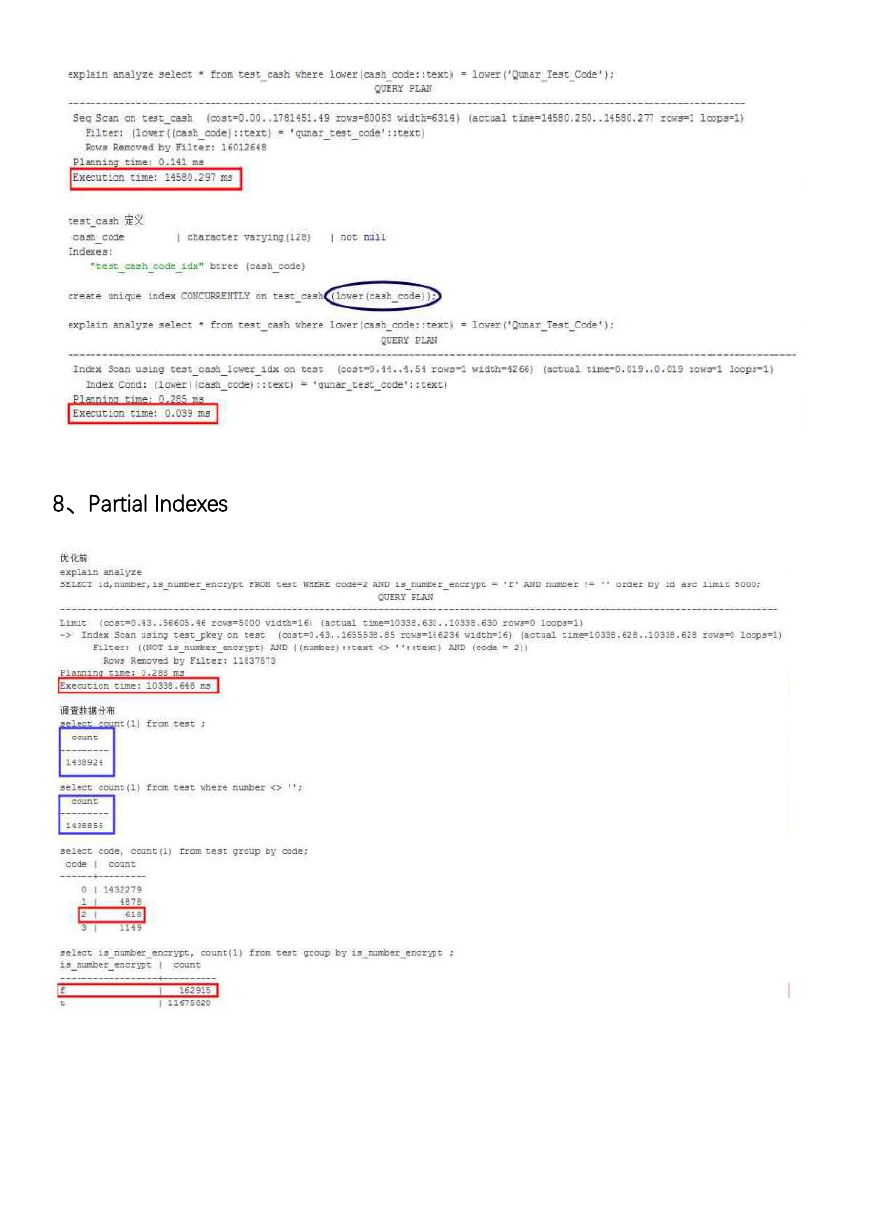
8、Partial Indexes
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc