包含激活函数的多层神经元网络及 matlab 实现
1. 两层神经网络结构
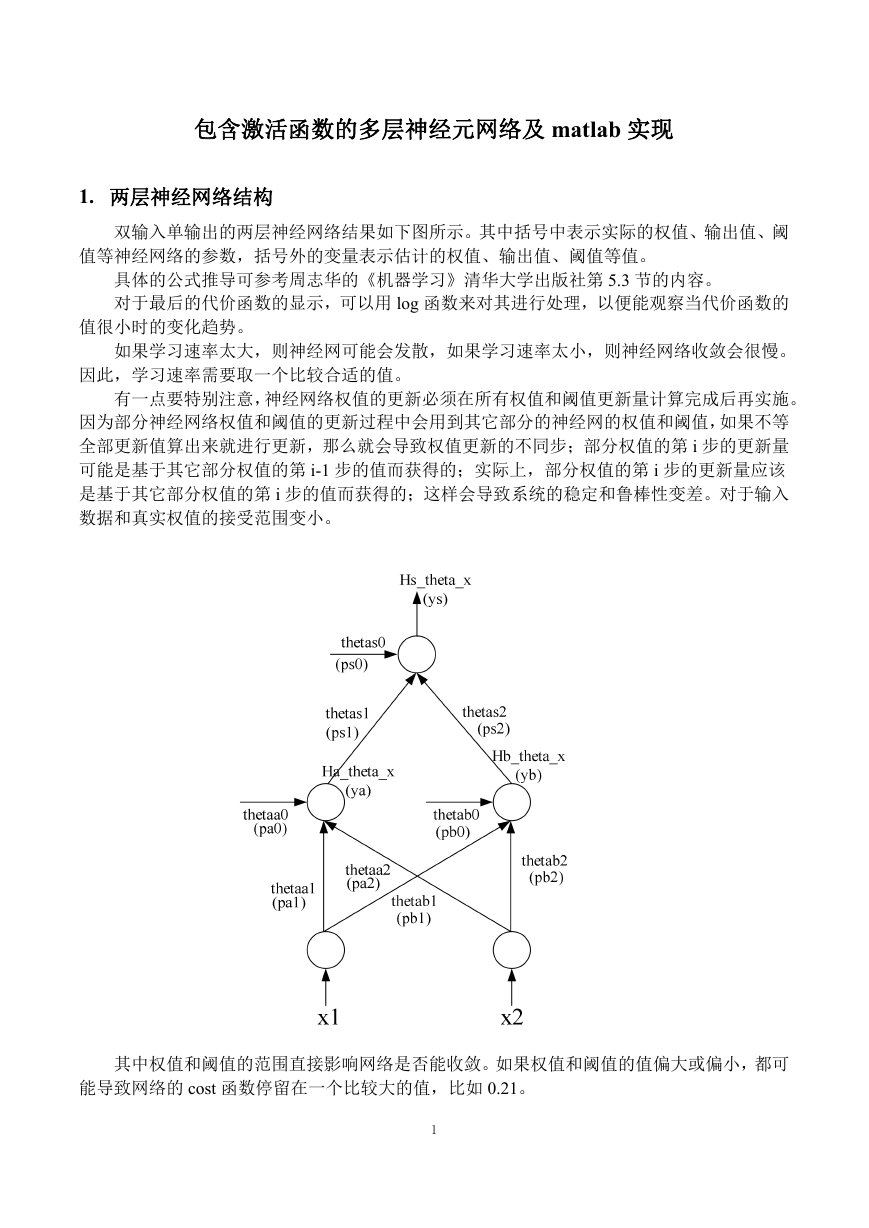
双输入单输出的两层神经网络结果如下图所示。其中括号中表示实际的权值、输出值、阈
值等神经网络的参数,括号外的变量表示估计的权值、输出值、阈值等值。
具体的公式推导可参考周志华的《机器学习》清华大学出版社第 5.3 节的内容。
对于最后的代价函数的显示,可以用 log 函数来对其进行处理,以便能观察当代价函数的
值很小时的变化趋势。
如果学习速率太大,则神经网可能会发散,如果学习速率太小,则神经网络收敛会很慢。
因此,学习速率需要取一个比较合适的值。
有一点要特别注意,神经网络权值的更新必须在所有权值和阈值更新量计算完成后再实施。
因为部分神经网络权值和阈值的更新过程中会用到其它部分的神经网的权值和阈值,如果不等
全部更新值算出来就进行更新,那么就会导致权值更新的不同步;部分权值的第 i 步的更新量
可能是基于其它部分权值的第 i-1 步的值而获得的;实际上,部分权值的第 i 步的更新量应该
是基于其它部分权值的第 i 步的值而获得的;这样会导致系统的稳定和鲁棒性变差。对于输入
数据和真实权值的接受范围变小。
其中权值和阈值的范围直接影响网络是否能收敛。如果权值和阈值的值偏大或偏小,都可
能导致网络的 cost 函数停留在一个比较大的值,比如 0.21。
1
�
2. 两层神经网络梯度下降公式推导
两层神经网络的输出层包含一个神经元,这个神经元不包含激活函数。隐层包含两个神经
元,这两个神经元包含 sigmoid 激活函数。
(1). 前向计算过程
隐层第二个神经元的输出
隐层第一个神经元的输出
x1=ℎa =(0+11+22)
其中=0+11+22
x2=ℎ =(0+11+22)
其中b=0+11+22
输出层神经元的输出ℎs1,2 =0+11+22
上式中,表示各种权值;a 表示隐层第一个神经元的编号;b 表示隐层第二个神经元的
编号;s 表示这个神经元是输出神经元。其偏置值对应θs0。1表示隐层第一个神经元的输出,
也是输出层神经元的第一个输入;2表示隐层第二个神经元的输出,也是输出层神经元的第
二个输入。
(1)
(2)
(3)
(2). 反向误差传播过程
(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(xi,yi),…(xt,yt)是真实的输入输出数据。反向误差传播的主要目标是,当神经网
络的输入值是 x1,x2,xi,…xt 时,使得神经网络的输出值无线逼近输出数据 y1,y2,yi,…yt。因此,
定义损失函数如下。
损失函数的(cost Function)的内部构造如下面公式所述:
(0,1,2)=1 =1 (ℎ() 1,2 −())2
�
其中:
(4)
表示向量 x 中的第 i 个元素;
表示向量 y 中的第 i 个元素;
表示已知的假设函数;
m 为训练集的数量。
误差反向传播主要用于减少权值和阈值的误差,将它们调整至期望的范围。调整方法主要
是在原权值和阈值的基础上减去一个调整量。这个调整量就是根据梯度下降算法计算所获得的
损失函数对于权值和阈值的偏导数与学习速率的乘积。
即
为 s0,s1,s2,对应0,1,2。
2
=− ()
(5)
上式中 r 代表所有阈值或权值的下标,r 可以包含多个值,比如对于输出层而言,r 的值
�
输出层的神经元的阈值和权值的偏导数如下所示:
(6)
ℎ0=1
ℎ1=1()
ℎ2=2()
0()= 12 =1 2×(ℎ()−())×ℎ0
=1 =1 (ℎ()−())
�
1()= 12 =1 2× ℎ()− ×ℎ1
ℎ()− ×
=1 =1
�
1
2()
=1 =1 (ℎ()−())×
2()= 12 =1 2×(ℎ()−())×ℎ2
�
隐层的第一个神经元(a)的阈值和权值的偏导数如下所示:
(7)
(8)
(12)
(13)
�
�
�
0=1
1=1()
2=2()
()
0=()x1∙x1∙0=()
=(ℎ()−())∙1∙x1∙ 1−x1
1=x1∙x1∙1=ℎ
=(ℎ()−())∙1∙x1∙ 1−x1 ∙1()
2=x1∙x1∙2=ℎ
=(ℎ()−())∙1∙x1∙ 1−x1 ∙2()
0=1
1=1()
(19)
3
(15)
ℎ()∙ℎ()x1∙x1∙ 1−x1 ∙1
∙ℎx1∙x1∙ 1−x1 ∙1
∙ℎx1∙x1∙ 1−x1 ∙2
(9)
(10)
(11)
(14)
(16)
(17)
(18)
隐层的第二个神经元(b)的阈值和权值的偏导数如下所示:
�
2=2()
()
0=()x2∙x2∙0=()
=(ℎ()−())∙2∙x2∙ 1−x2
1=x2∙x2∙1=ℎ
=(ℎ()−())∙2∙x2∙ 1−x2 ∙1()
2=x2∙x2∙2=ℎ
=(ℎ()−())∙2∙x2∙ 1−x2 ∙2()
ℎ()∙ℎ()x2∙x2∙ 1−x2 ∙1
∙ℎx2∙x2∙ 1−x2 ∙1
∙ℎx2∙x2∙ 1−x2 ∙2
(23)
(21)
(20)
(22)
3. Matlab 实现不带激活函数的两层神经元网络功能
clear all
clc
close all
pa0=6; pa1=6.7; pa2=0.2;
pb0=13; pb1=0.5; pb2=1.1;
s0=1.2; s1=1.6; s2=0.7;
5];
x1=[7 9 12 5 4 9 23
x2=[1 8 21 3 5 8 3 31];
x1_mean=mean(x1)
x1_max=max(x1)
x1_min=min(x1)
x2_mean=mean(x2)
x2_max=max(x2)
x2_min=min(x2)
x1=(x1-x1_mean)/(x1_max-x1_min)
x2=(x2-x2_mean)/(x2_max-x2_min)
ya=pa0+pa1*x1+pa2*x2;
yb=pb0+pb1*x1+pb2*x2;
4
�
ys=s0+s1*ya+s2*yb;
num_sample=size(ys,2);
% gradient descending process
% initial values of parameters
thetaa0=9/100; thetaa1=3/100; thetaa2=9/100;
thetab0=4/100; thetab1=2/100; thetab2=1/100;
thetas0=1/100; thetas1=3/100; thetas2=2/1000;
%learning rate
alpha=0.0001; % good for the system
epoch=8200;
for k=1:epoch
%
v_k=k
if k<=3000
alpha=0.01;
elseif k<=6000
alpha=0.01;
else
end
alpha=0.001;
ha_theta_x=thetaa0+thetaa1*x1+thetaa2*x2; % hypothesis function
hb_theta_x=thetab0+thetab1*x1+thetab2*x2; % hypothesis function
hs_theta_x=thetas0+thetas1*ha_theta_x+thetas2*hb_theta_x; % hypothesis function
Jcosts(k)=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).^2)/num_sample;
rs0=sum(hs_theta_x-ys);
rs1=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).*ha_theta_x);
rs2=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).*hb_theta_x);
thetas0=thetas0-alpha*rs0/num_sample;
thetas1=thetas1-alpha*rs1/num_sample;
thetas2=thetas2-alpha*rs2/num_sample;
ra0=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas1);
thetaa0=thetaa0-alpha*ra0/num_sample;
ra1=sum(((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas1).*x1); thetaa1=thetaa1-alpha*ra1/num_sample;
ra2=sum(((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas1).*x2); thetaa2=thetaa2-alpha*ra2/num_sample;
rb0=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas2);
thetab0=thetab0-alpha*rb0/num_sample;
rb1=sum(((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas2).*x1); thetab1=thetab1-alpha*rb1/num_sample;
rb2=sum(((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas2).*x2); thetab2=thetab2-alpha*rb2/num_sample;
end
yst=thetas0+thetas1*ha_theta_x+thetas2*hb_theta_x;
v_yst=yst
5
�
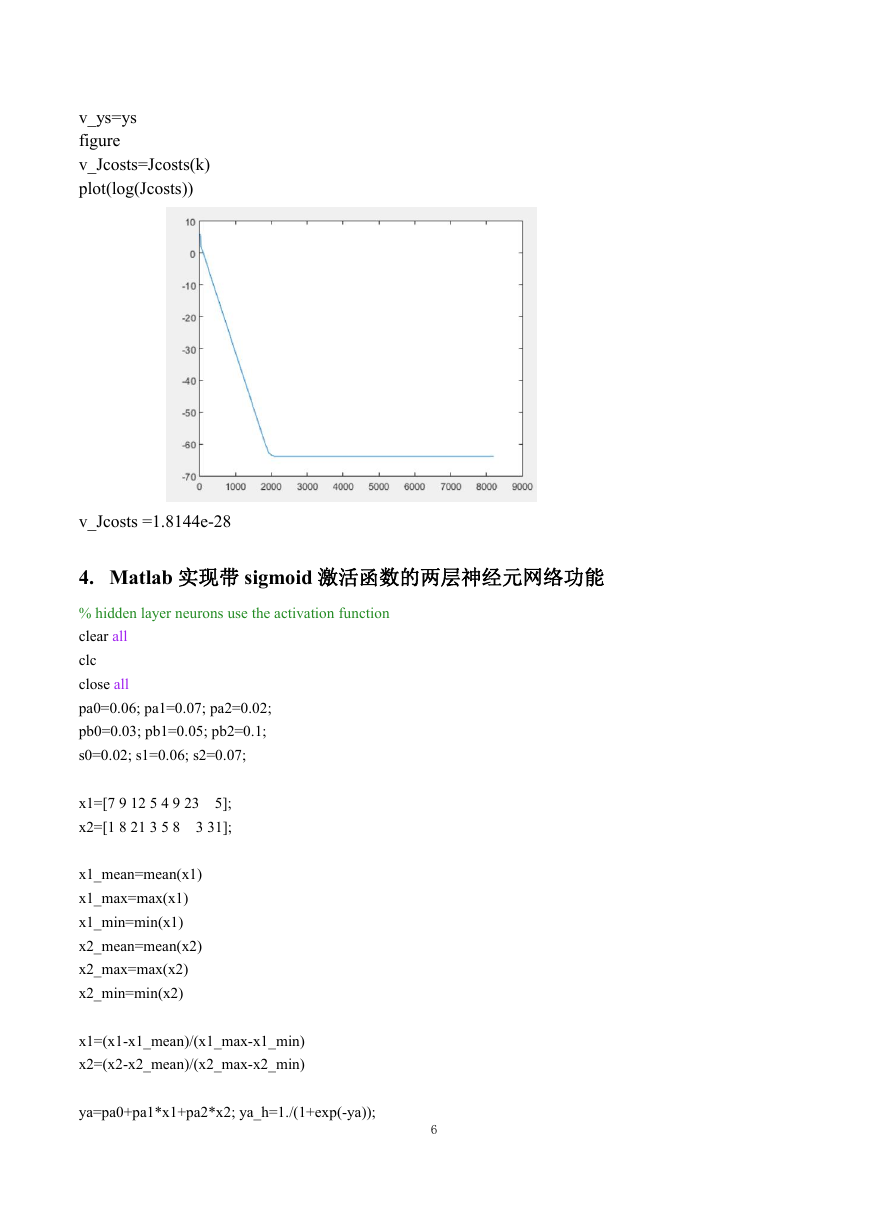
v_ys=ys
figure
v_Jcosts=Jcosts(k)
plot(log(Jcosts))
v_Jcosts =1.8144e-28
4. Matlab 实现带 sigmoid 激活函数的两层神经元网络功能
% hidden layer neurons use the activation function
clear all
clc
close all
pa0=0.06; pa1=0.07; pa2=0.02;
pb0=0.03; pb1=0.05; pb2=0.1;
s0=0.02; s1=0.06; s2=0.07;
x1=[7 9 12 5 4 9 23
x2=[1 8 21 3 5 8
5];
3 31];
x1_mean=mean(x1)
x1_max=max(x1)
x1_min=min(x1)
x2_mean=mean(x2)
x2_max=max(x2)
x2_min=min(x2)
x1=(x1-x1_mean)/(x1_max-x1_min)
x2=(x2-x2_mean)/(x2_max-x2_min)
ya=pa0+pa1*x1+pa2*x2; ya_h=1./(1+exp(-ya));
6
�
yb=pb0+pb1*x1+pb2*x2; yb_h=1./(1+exp(-yb));
ys=s0+s1*ya_h+s2*yb_h;
num_sample=size(ys,2);
% gradient descending process
% initial values of parameters
thetaa0=9/100; thetaa1=3/100; thetaa2=9/100;
thetab0=4/100; thetab1=2/100; thetab2=1/100;
thetas0=1/100; thetas1=3/100; thetas2=2/1000;
%learning rate
alpha=0.001; % good for the system
epoch=7900;
for k=1:epoch
v_k=k
%
if k<=3000
alpha=0.001;
elseif k<=4000
alpha=0.0001;
else
end
alpha=0.0001;
ha_theta_x=thetaa0+thetaa1*x1+thetaa2*x2; ha_out=1./(1+exp(-ha_theta_x));
hb_theta_x=thetab0+thetab1*x1+thetab2*x2; hb_out=1./(1+exp(-hb_theta_x));
hs_theta_x=thetas0+thetas1*ha_out+thetas2*hb_out; % hypothesis function
Jcosts(k)=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).^2)/num_sample;
rs0=sum(hs_theta_x-ys);
rs1=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).*ha_theta_x);
rs2=sum((hs_theta_x-ys).*hb_theta_x);
dha_out=ha_out.*(1-ha_out);
ra0=sum(((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas1).*dha_out);
ra1=sum((((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas1).*dha_out).*x1);
ra2=sum((((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas1).*dha_out).*x2);
dhb_out=hb_out.*(1-hb_out);
rb0=sum(((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas2).*dhb_out);
rb1=sum((((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas2).*dhb_out).*x1);
rb2=sum((((hs_theta_x-ys).*thetas2).*dhb_out).*x2);
7
�
thetas0=thetas0-alpha*rs0/num_sample;
thetas1=thetas1-alpha*rs1/num_sample;
thetas2=thetas2-alpha*rs2/num_sample;
thetaa0=thetaa0-alpha*ra0/num_sample;
thetaa1=thetaa1-alpha*ra1/num_sample;
thetaa2=thetaa2-alpha*ra2/num_sample;
thetab0=thetab0-alpha*rb0/num_sample;
thetab1=thetab1-alpha*rb1/num_sample;
thetab2=thetab2-alpha*rb2/num_sample;
end
yst=thetas0+thetas1*ha_out+thetas2*hb_out;
v_yst=yst
v_ys=ys
figure
v_Jcosts=Jcosts(k)
plot(log(Jcosts))
v_Jcosts =2.3851e-06
5. Matlab 实现带 sigmoid 激活函数的两层神经元网络功能 2
v_Jcosts =7.2385877e-28
% hidden layer neurons use the activation function
% update action is performed after all update values are obtained.
% the above item is very important. because if the update action is
% performed before all update values are obtained, the update action may
% use the new update values to update former weights or biases. the newwork
% may be unstable.
clear all
clc
8
�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc