INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
ISO/IEC
14496-1
Fourth edition
2010-06-01
Information technology — Coding of
audio-visual objects —
Part 1:
Systems
Technologies de l'information — Codage des objets audiovisuels —
Partie 1: Systèmes
Reference number
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
© ISO/IEC 2010
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
PDF disclaimer
This PDF file may contain embedded typefaces. In accordance with Adobe's licensing policy, this file may be printed or viewed but
shall not be edited unless the typefaces which are embedded are licensed to and installed on the computer performing the editing. In
downloading this file, parties accept therein the responsibility of not infringing Adobe's licensing policy. The ISO Central Secretariat
accepts no liability in this area.
Adobe is a trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Details of the software products used to create this PDF file can be found in the General Info relative to the file; the PDF-creation
parameters were optimized for printing. Every care has been taken to ensure that the file is suitable for use by ISO member bodies. In
the unlikely event that a problem relating to it is found, please inform the Central Secretariat at the address given below.
COPYRIGHT PROTECTED DOCUMENT
© ISO/IEC 2010
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from either ISO at the address below or
ISO's member body in the country of the requester.
ISO copyright office
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Geneva 20
Tel. + 41 22 749 01 11
Fax + 41 22 749 09 47
E-mail copyright@iso.org
Web www.iso.org
Published in Switzerland
ii
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
Contents
Page
Foreword ............................................................................................................................................................iv
Introduction...........................................................................................................................................vi
0
Scope......................................................................................................................................................1
1
2
Normative references............................................................................................................................1
Additional references............................................................................................................................2
3
Terms and definitions ...........................................................................................................................2
4
5
Abbreviated terms ...............................................................................................................................10
Conventions.........................................................................................................................................11
6
Streaming Framework.........................................................................................................................11
7
8
Syntactic Description Language........................................................................................................99
9
Profiles................................................................................................................................................110
Annex A (informative) Time Base Reconstruction ......................................................................................112
Annex B (informative) Registration procedure ............................................................................................115
Annex C (informative) The QoS Management Model for ISO/IEC 14496 Content.....................................119
Annex D (informative) Conversion Between Time and Date Conventions ...............................................120
Annex E (informative) Graphical Representation of Object Descriptor and Sync Layer Syntax...........122
Annex F (informative) Elementary Stream Interface....................................................................................130
Annex G (informative) Upstream Walkthrough............................................................................................132
Annex H (informative) Scene and Object Description Carrousel...............................................................137
Annex I (normative) Usage of ITU-T Recommendation H.264 | ISO/IEC 14496-10 AVC ..........................138
Annex J (informative) Patent statements .....................................................................................................141
Bibliography....................................................................................................................................................144
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
iii
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) and IEC (the International Electrotechnical
Commission) form the specialized system for worldwide standardization. National bodies that are members of
ISO or IEC participate in the development of International Standards through technical committees
established by the respective organization to deal with particular fields of technical activity. ISO and IEC
technical committees collaborate in fields of mutual interest. Other international organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO and IEC, also take part in the work. In the field of information
technology, ISO and IEC have established a joint technical committee, ISO/IEC JTC 1.
International Standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
The main task of the joint technical committee is to prepare International Standards. Draft International
Standards adopted by the joint technical committee are circulated to national bodies for voting. Publication as
an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the national bodies casting a vote.
ISO/IEC 14496-1 was prepared by Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1, Information technology,
Subcommittee SC 29, Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information.
This fourth edition cancels and replaces the third edition (ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004), which has been technically
revised.
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004/Amd.1:2005,
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004/Amd.2:2007,
Technical Corrigenda
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004/Amd.3:2007
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004/Cor.1:2006 and ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004/Cor.2:2007.
Amendments
also
and
It
incorporates
the
ISO/IEC 14496 consists of the following parts, under the general title Information technology — Coding of
audio-visual objects:
Part 1: Systems
Part 2: Visual
Part 3: Audio
Part 4: Conformance testing
Part 5: Reference software
Part 6: Delivery Multimedia Integration Framework (DMIF)
Part 7: Optimized reference software for coding of audio-visual objects
Part 8: Carriage of ISO/IEC 14496 contents over IP networks
Part 9: Reference hardware description
Part 10: Advanced Video Coding
Part 11: Scene description and application engine
Part 12: ISO base media file format
Part 13: Intellectual Property Management and Protection (IPMP) extensions
iv
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
Part 14: MP4 file format
Part 15: Advanced Video Coding (AVC) file format
Part 16: Animation Framework eXtension (AFX)
Part 17: Streaming text format
Part 18: Font compression and streaming
Part 19: Synthesized texture stream
Part 20: Lightweight Application Scene Representation (LASeR) and Simple Aggregation Format (SAF)
Part 21: MPEG-J Graphics Framework eXtensions (GFX)
Part 22: Open Font Format
Part 23: Symbolic Music Representation
Part 24: Audio and systems interaction
Part 25: 3D Graphics Compression Model
Part 26: Audio conformance
Part 27: 3D Graphics conformance
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
v
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
0
Introduction
0.1 Overview
ISO/IEC 14496 specifies a system for the communication of interactive audio-visual scenes. This specification
includes the following elements.
a) The coded representation of natural or synthetic, two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) objects
that can be manifested audibly and/or visually (audio-visual objects) (specified in Parts 2, 3, 10, 11, 16,
19, 20, 23 and 25 of ISO/IEC 14496).
b) The coded representation of the spatio-temporal positioning of audio-visual objects as well as their
behavior in response to interaction (scene description, specified in Parts 11 and 20 of ISO/IEC 14496).
c) The coded representation of information related to the management of data streams (synchronization,
identification, description and association of stream content, specified in this Part and in Part 24 of
ISO/IEC 14496).
d) A generic interface to the data stream delivery layer functionality (specified in Part 6 of ISO/IEC 14496).
e) An application engine for programmatic control of the player: format, delivery of downloadable Java byte
code as well as its execution lifecycle and behavior through APIs (specified in Parts 11 and 21 of
ISO/IEC 14496).
f) A file format to contain the media information of an ISO/IEC 14496 presentation in a flexible, extensible
format to facilitate interchange, management, editing, and presentation of the media specified in Part 12
(ISO File Format), Part 14 (MP4 File Format) and Part 15 (AVC File Format) of ISO/IEC 14496.
g) The coded representation of font data and of information related to the management of text streams and
font data streams (specified in Parts 17, 18 and 22 of ISO/IEC 14496).
The overall operation of a system communicating audio-visual scenes can be paraphrased as follows:
the sending
terminal,
the audio-visual scene
At
is compressed, supplemented with
synchronization information and passed to a delivery layer that multiplexes it into one or more coded binary
streams that are transmitted or stored. At the receiving terminal, these streams are demultiplexed and
decompressed. The audio-visual objects are composed according
the scene description and
synchronization information and presented to the end user. The end user may have the option to interact with
this presentation. Interaction information can be processed locally or transmitted back to the sending terminal.
ISO/IEC 14496 defines the syntax and semantics of the bitstreams that convey such scene information, as
well as the details of their decoding processes.
information
to
This part of ISO/IEC 14496 specifies the following tools.
A terminal model for time and buffer management.
A coded representation of metadata for the identification, description and logical dependencies of the
elementary streams (object descriptors and other descriptors).
A coded representation of descriptive audio-visual content information [object content information (OCI)].
An interface to intellectual property management and protection (IPMP) systems.
A coded representation of synchronization information (sync layer – SL).
A multiplexed representation of individual elementary streams in a single stream (M4Mux).
vi
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
⎯
�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
These various elements are described functionally in this clause and specified in the normative clauses that
follow.
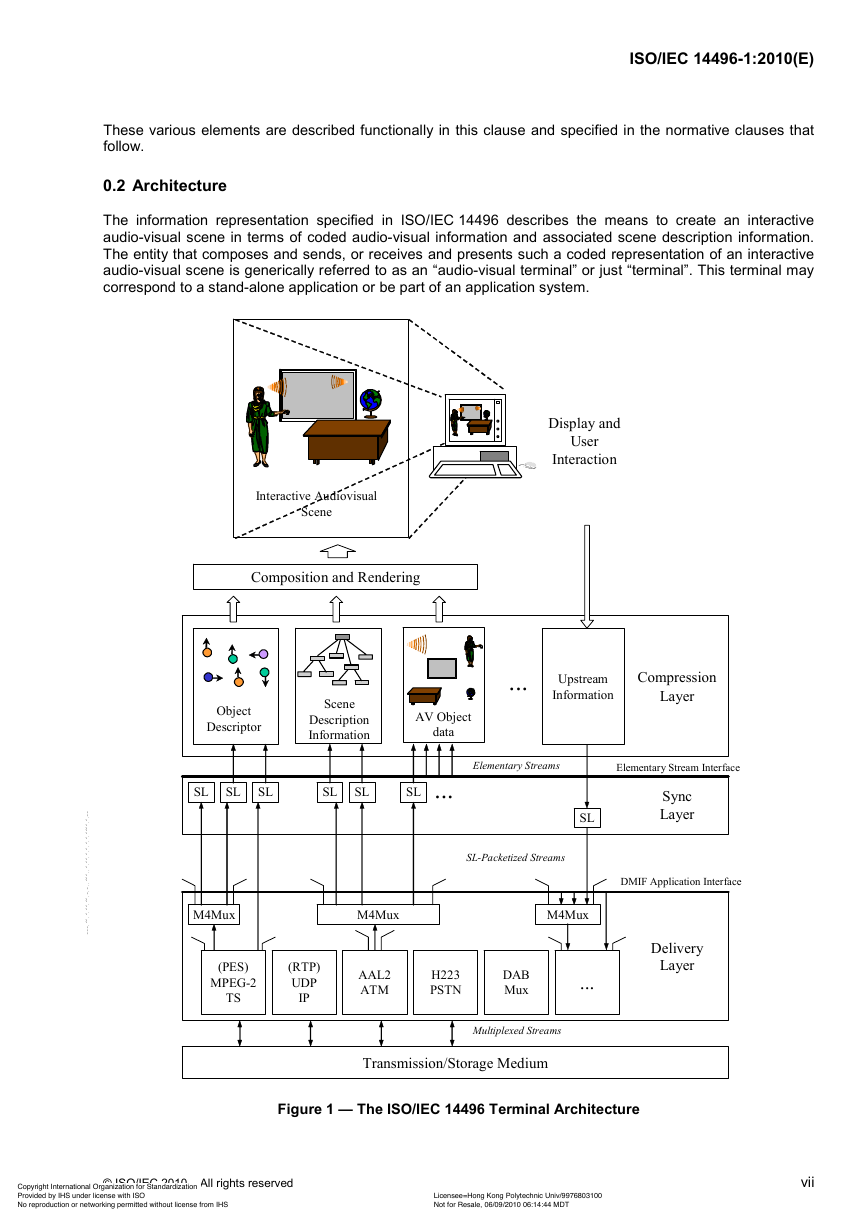
0.2 Architecture
The information representation specified in ISO/IEC 14496 describes the means to create an interactive
audio-visual scene in terms of coded audio-visual information and associated scene description information.
The entity that composes and sends, or receives and presents such a coded representation of an interactive
audio-visual scene is generically referred to as an “audio-visual terminal” or just “terminal”. This terminal may
correspond to a stand-alone application or be part of an application system.
Display and
User
Interaction
Interactive Audiovisual
Scene
Composition and Rendering
Object
Descriptor
Scene
Description
Information
AV Object
data
SL
SL
SL
SL
SL
SL
...
...
Upstream
Information
Compression
Layer
Elementary Streams
Elementary Stream Interface
SL
Sync
Layer
SL-Packetized Streams
DMIF Application Interface
M4Mux
M4Mux
M4Mux
(PES)
MPEG-2
TS
(RTP)
UDP
IP
AAL2
ATM
H223
PSTN
DAB
Mux
...
Delivery
Layer
Multiplexed Streams
Transmission/Storage Medium
Figure 1 — The ISO/IEC 14496 Terminal Architecture
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
vii
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---�
ISO/IEC 14496-1:2010(E)
The basic operations performed by such a receiver terminal are as follows. Information that allows access to
content complying with ISO/IEC 14496 is provided as initial session set up information to the terminal. Part 6
of ISO/IEC 14496 defines the procedures for establishing such session contexts as well as the interface to the
delivery layer that generically abstracts the storage or transport medium. The initial set up information allows,
in a recursive manner, to locate one or more elementary streams that are part of the coded content
representation. Some of these elementary streams may be grouped together using the multiplexing tool
described in ISO/IEC 14496-1.
Elementary streams contain the coded representation of either audio or visual data or scene description
information or user interaction data or text or font data. Elementary streams may as well themselves convey
information to identify streams, to describe logical dependencies between streams, or to describe information
related to the content of the streams. Each elementary stream contains only one type of data.
Elementary streams are decoded using their respective stream-specific decoders. The audio-visual objects
are composed according to the scene description information and presented by the terminal's presentation
device(s). All these processes are synchronized according to the systems decoder model (SDM) using the
synchronization information provided at the synchronization layer.
These basic operations are depicted in Figure 1, and are described in more detail below.
0.3 Terminal Model: Systems Decoder Model
The systems decoder model provides an abstract view of the behavior of a terminal complying with
ISO/IEC 14496-1. Its purpose is to enable a sending terminal to predict how the receiving terminal will behave
in terms of buffer management and synchronization when reconstructing the audio-visual information that
comprises the presentation. The systems decoder model includes a systems timing model and a systems
buffer model which are described briefly in the following Subclauses.
0.3.1 Timing Model
The timing model defines the mechanisms through which a receiving terminal establishes a notion of time that
enables it to process time-dependent events. This model also allows the receiving terminal to establish
mechanisms to maintain synchronization both across and within particular audio-visual objects as well as with
user interaction events. In order to facilitate these functions at the receiving terminal, the timing model
requires that the transmitted data streams contain implicit or explicit timing information. Two sets of timing
information are defined in ISO/IEC 14496-1: clock references and time stamps. The former convey the
sending terminal's time base to the receiving terminal, while the latter convey a notion of relative time for
specific events such as the desired decoding or composition time for portions of the encoded audio-visual
information.
0.3.2 Buffer Model
The buffer model enables the sending terminal to monitor and control the buffer resources that are needed to
decode each elementary stream in a presentation. The required buffer resources are conveyed to the
receiving terminal by means of descriptors at the beginning of the presentation. The terminal can then decide
whether or not it is capable of handling this particular presentation. The buffer model allows the sending
terminal to specify when information may be removed from these buffers and enables it to schedule data
transmission so that the appropriate buffers at the receiving terminal do not overflow or underflow.
0.4 Multiplexing of Streams: The Delivery Layer
The term delivery layer is used as a generic abstraction of any existing transport protocol stack that may be
used to transmit and/or store content complying with ISO/IEC 14496. The functionality of this layer is not
within the scope of ISO/IEC 14496-1, and only the interface to this layer is considered. This interface is the
DMIF Application Interface (DAI) specified in ISO/IEC 14496-6. The DAI defines not only an interface for the
delivery of streaming data, but also for signaling information required for session and channel set up as well
as tear down. A wide variety of delivery mechanisms exist below this interface, with some of them indicated in
Figure 1. These mechanisms serve for transmission as well as storage of streaming data, i.e., a file is
viii
© ISO/IEC 2010 – All rights reserved
Copyright International Organization for Standardization Provided by IHS under license with ISO Licensee=Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ/9976803100 Not for Resale, 06/09/2010 06:14:44 MDTNo reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS--`,`,,,,`,`,`,`,`,,`,``,,,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc