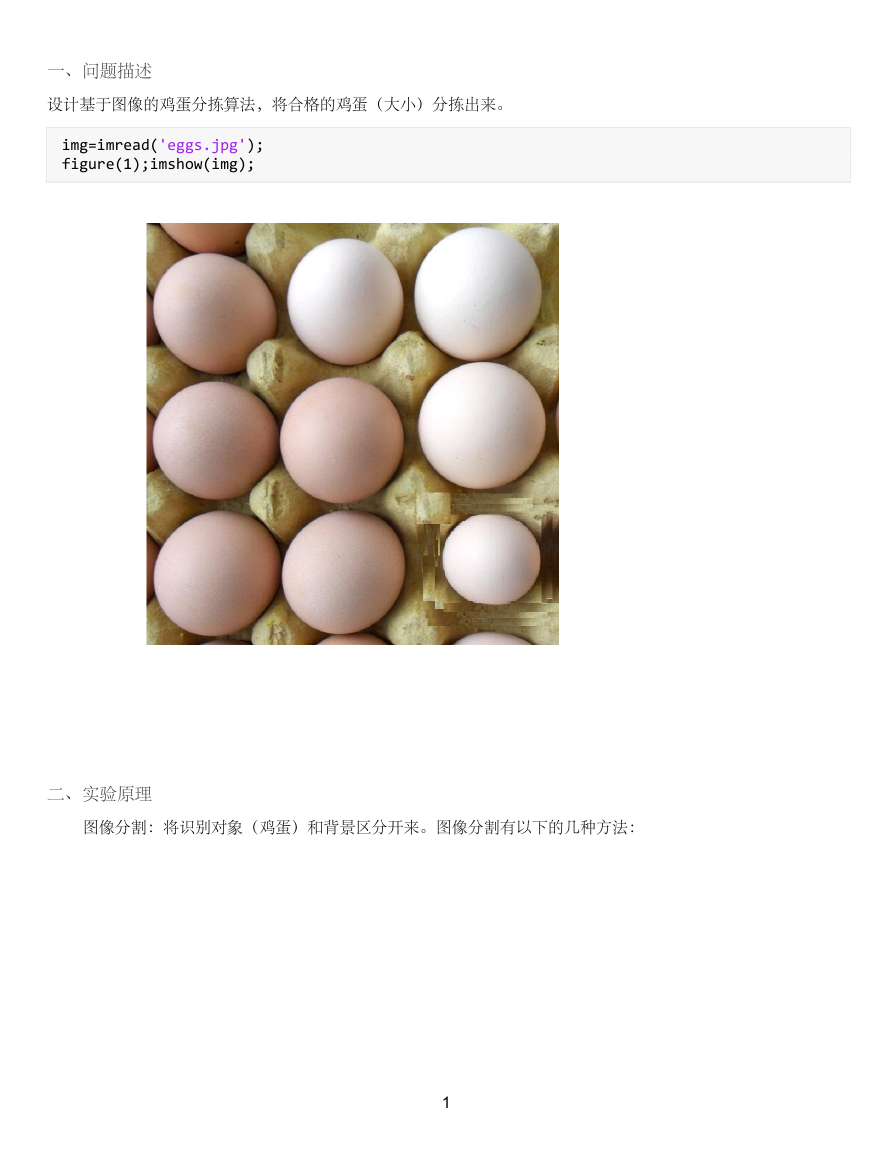
一、问题描述
设计基于图像的鸡蛋分拣算法,将合格的鸡蛋(大小)分拣出来。
img=imread('eggs.jpg');
figure(1);imshow(img);
二、实验原理
图像分割:将识别对象(鸡蛋)和背景区分开来。图像分割有以下的几种方法:
1
�
三、实验步骤及伪代码
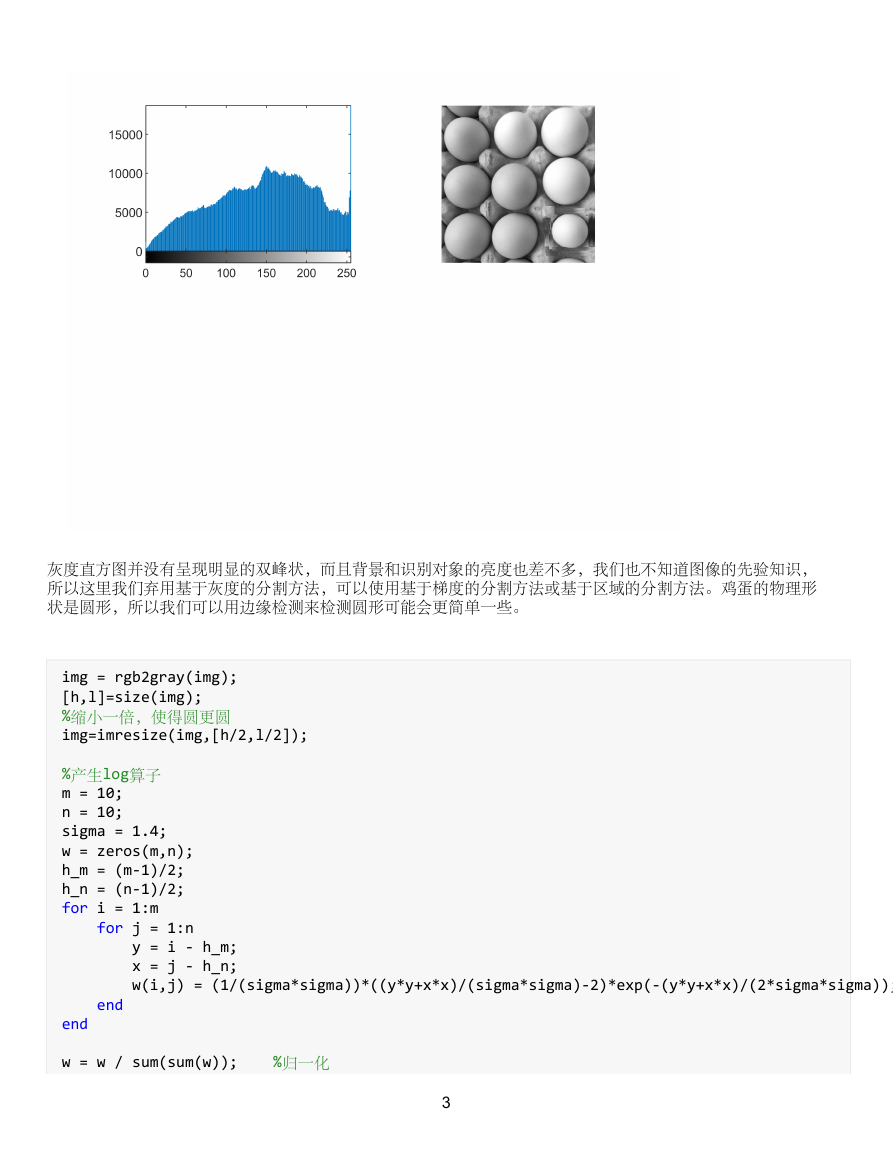
figure(2);
subplot(2,2,1);imhist(img);
I1=rgb2gray(img);
subplot(2,2,2);imshow(I1);
2
�
灰度直方图并没有呈现明显的双峰状,而且背景和识别对象的亮度也差不多,我们也不知道图像的先验知识,
所以这里我们弃用基于灰度的分割方法,可以使用基于梯度的分割方法或基于区域的分割方法。鸡蛋的物理形
状是圆形,所以我们可以用边缘检测来检测圆形可能会更简单一些。
img = rgb2gray(img);
[h,l]=size(img);
%缩小一倍,使得圆更圆
img=imresize(img,[h/2,l/2]);
%产生log算子
m = 10;
n = 10;
sigma = 1.4;
w = zeros(m,n);
h_m = (m-1)/2;
h_n = (n-1)/2;
for i = 1:m
for j = 1:n
y = i - h_m;
x = j - h_n;
w(i,j) = (1/(sigma*sigma))*((y*y+x*x)/(sigma*sigma)-2)*exp(-(y*y+x*x)/(2*sigma*sigma));
end
end
w = w / sum(sum(w)); %归一化
3
�
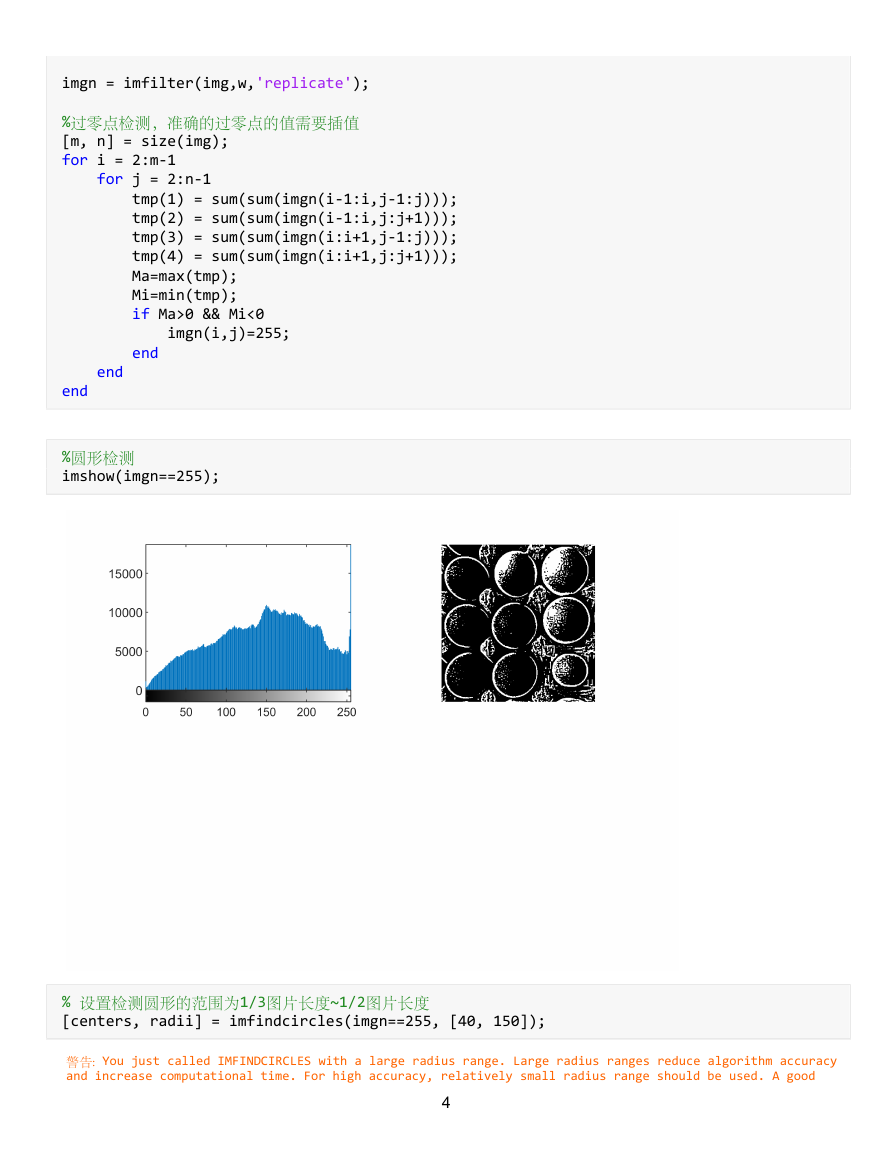
imgn = imfilter(img,w,'replicate');
%过零点检测,准确的过零点的值需要插值
[m, n] = size(img);
for i = 2:m-1
for j = 2:n-1
tmp(1) = sum(sum(imgn(i-1:i,j-1:j)));
tmp(2) = sum(sum(imgn(i-1:i,j:j+1)));
tmp(3) = sum(sum(imgn(i:i+1,j-1:j)));
tmp(4) = sum(sum(imgn(i:i+1,j:j+1)));
Ma=max(tmp);
Mi=min(tmp);
if Ma>0 && Mi<0
imgn(i,j)=255;
end
end
end
%圆形检测
imshow(imgn==255);
% 设置检测圆形的范围为1/3图片长度~1/2图片长度
[centers, radii] = imfindcircles(imgn==255, [40, 150]);
警告: You just called IMFINDCIRCLES with a large radius range. Large radius ranges reduce algorithm accuracy
and increase computational time. For high accuracy, relatively small radius range should be used. A good
4
�
rule of thumb is to choose the radius range such that Rmax < 3*Rmin and (Rmax - Rmin) < 100. If you have a
large radius range, say [20 100], consider breaking it up into multiple sets and call IMFINDCIRCLES for each
set separately, like this:
[CENTERS1, RADII1, METRIC1] = IMFINDCIRCLES(A, [20 60]);
[CENTERS2, RADII2, METRIC2] = IMFINDCIRCLES(A, [61 100]);
figure()
imshow(img);
%此处可以添加半径阈值,筛选出大小合格的鸡蛋。
viscircles(centers, radii, 'Edgecolor', 'b');
四、总结
鸡蛋由于其圆形的物理形状,我们可以用检测圆形来检测鸡蛋,检测圆形时,适当缩小图片后检测会使
得检测更加准确。
5
�






 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc