Revit IFC manual
Detailed instructions for handling IFC files
02
2
0
1
8
�
2 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
S
T
N
E
T
N
O
C
1.
2.
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
3
4
4.1
4.2
5
5.1
5.2
5.3
6
6.1
6.2
6.3
6.4
6.5
6.6
7
INTRODUCTION .......................................................................
THE BASICS ..............................................................................
IFC file formats
IFC versions (schema)
Model view definition (MVD)
IFC structure
2.4.1 IFC classes and types
2.4.2 Geometric representation of IFC items
2.4.3 Default attributes
2.4.4 Reference structure within an IFC file
LOD
Open-source IFCs
IFC viewers
LINKING IFC FILES IN REVIT................................................
OPENING IFC FILES.................................................................
Mapping table
Import options
EXPORTING IFC FILES.............................................................
Mapping tables
Revit IFC exporter settings
5.2.1 General settings
5.2.2 Additional content
5.2.3 Property sets
5.2.4 Level of detail
5.2.5 Advanced settings
Other settings
EXAMPLES OF APPLICATIONS ..............................................
Floor slab construction
Aperture planning
Assigning assemblies
Assigning default attributes
Structuring the IFC data model
Usage groups in the IFC data model
SUMMARY .................................................................................
3
5
5
5
6
8
9
10
11
14
14
15
16
17
18
18
19
22
22
25
26
31
32
37
38
40
44
44
45
47
48
50
51
52
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�
3 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
1. INTRODUCTION
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is an intelligent 3D model-based process that gives
architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals the insight and tools to more
efficiently plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure. At the heart of BIM is
a smart building data model that incorporates not only 3D geometry but also all the relevant data
relating to the building and its components. This kind of building data model can only be created
using complex, BIM-enabled software such as Autodesk Revit®.
Provided that all of those involved in the
planning are working with the same software,
data exchange is loss-free. The native BIM
format also facilitates the coordination of all
planning stages and stakeholders.
In building projects, it can happen that
those involved in the planning process are
using different BIM software from different
providers. The buildingSMART initiative (www.
buildingSMART.org), in which Autodesk has
been actively involved from the very outset,
has developed the IFC format to support such
openBIM workflows. IFC allows the exchange
of a specific subset of the native model.
Since the IFC4 release, the IFC format has met
a recognized ISO standard (ISO 16739:2013). In
its current version, buildingSMART maintains a
list of all applications with certified IFC support:
www.buildingsmart.org/compliance/certified-
software/
IFC as the standard for exchanging BIM information
The Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) are an open standard for the exchange of building data models
used in building design and construction across different software. They are used to exchange
information within a project team and between software applications used in design, construction,
procurement, maintenance, and operation. Current IFC Model View Definitions primarily support 3D
geometry and property data. If exchange of 2D information, such as plan views and annotations,
is important, Revit and coordination tools such as Autodesk BIM 360 which support the native file
format should be preferred.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�
4 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
With IFC, the standard workflow is as per this model:
Native format
IFC
Coordination/
No editing
Find out more on the buildingSMART website:
https://www.buildingsmart.org/users/international-user-group-faqs/
Using IFC in practice
In an ideal scenario, the IFC file should be used
for coordination purposes in an IFC viewer or
as a reference within the editor software. For
instance, the architect would receive an IFC file
from the building equipment engineer, allowing
them to see where the installation is placed.
This workflow is referred to as the coordination
workflow and is covered with the Coordination
Model Views in IFC.
The Revit IFC manual
This document is intended to serve as a guide
for Revit users handling IFC data and providing
a better understanding of the settings available
in Revit, discussing the way they can influence
the quality and the content of the IFC file. The
In some cases they may be the need for a design
transfer workflow, for example if the architect
had created the design in another software, but
needs to carry on planning the building in Revit.
This is the more difficult workflow and often
requires manual adjustments to deal with the
differences in software.
Revit IFC manual therefore sets out the basics
of IFC and explains in detail how to export, link
and open IFC files in Revit.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�
5 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
2. THE BASICS
The key considerations when using an IFC file are the file format, IFC version, model view definitions,
and file structure. We explain all these on the following pages.
2.1 IFC file formats
.ifc
.ifcZIP
Standard format, based on STEP (STEP: Standard for the Exchange of
Product Model Data).
Compressed IFC files with much smaller file size; can be read by most
software applications that support IFC. It can be unpacked to make the
uncompressed IFC file visible.
.ifcXML
XML-based representation of IFC data, required by certain calculation
software.
2.2 IFC versions (schema)
The IFC definitions are regularly updated and developed by buildingSMART. It is recommended that
you use the latest versions wherever possible. Among other things, the IFC4 format allows better
representation of complex geometries.
Current versions:
•
IFC4 (still in beta, certification process in progress, offers certain advanced possibilities but is
not widely supported yet);
IFC2x3 (currently the most supported and stable format, certified in Revit and recommended for
production);
IFC2x2 (recommended if the recipient of the file does not have software with IFC2x3 or IFC4
support).
•
•
Revit no longer supports the following older versions: IFC2.0 (import still supported), IFC1.5.1,
IFC1.5, and IFC1.0
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�
6 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
2.3 Model view definition (MVD)
In addition to the file format and versions, the
model view definition determines how you use
an IFC file, because it enables a specific data
exchange scenario.
MVDs are used for the targeted exchange
of specialized models, taking account of the
graphic and content-related information that
the planner needs.
For
instance, thermal simulations require
information about lighting areas in a wall and a
room. Conversely, specialized IFC models require
only the basic geometric information to be
transferred to an FM system, and focus instead
on spatial information and specific component
features (such as system information, fire
protection features, and usable areas) in relation
to the MVDs. Moreover, a specialized model for
structure planning requires specific information
about the supporting building elements and
apertures.
The official, buildingSMART-defined MVDs available in Revit are listed below.
IFC4: Model Reference View
The model reference view was designed for
the standard delivery of a reference model for
specialist planners in IFC4. In the first instance,
it provides an IFC model for coordination
and model-based quantity determination, as
referred to in the modeling software. A model
exported as a Model Reference View is not
suitable for importing with the intention of
conducting further work on the geometry, as
it contains only the most essential geometric
definitions.
The model is not necessarily heavily simplified
in graphic terms; it serves merely as a reference
that may be quite detailed but cannot be edited.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�
7 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
IFC4: Design Transfer View (beta)
Introduced for the first time with IFC4, this is
used to transfer IFC models for the purpose
of importing and editing them in BIM-enabled
software. As previously mentioned, the ability
to transmit parametric design and complex
contexts is restricted in the IFC format, so some
manual adjustments will be needed to deal with
differences in software, and the data should
always be manually verified.
IFC2x3 Coordination View Version 2.0
Optimized for the coordinated exchange of BIM
models between the main disciplines in the
building industry. Coordination View 2.0—also
known as CV 2.0—is currently the most widely
used and supported Model View Definition. CV 2.0
supports the rudimentary parametric derivation
of building components when importing into
planning tools.
IFC2x3 COBie 2.4 Design Deliverable
IFC format equivalent to the COBie (Construction
Operations Building Information Exchange)
output required by the UK government for their
2016 Level 2 BIM mandate for collaboration on
public-sector work.
For exporting in COBie format, the relevant add-
on from http://www.biminteroperabilitytools.com
can also be installed.
IFC2x2 Coordination View
Used only in isolated cases, such as when
exporting MVDs for software that does not
support IFC2x3.
Each of these model view definitions (MVDs)
can naturally be adapted to the needs of the
workflows—more information on this can be
found in the following chapter, “Exporting IFC
files.”
This MVD is primarily used for exchanging
architectural,
and
construction engineering models.
technology,
building
To identify which MVD is used by an existing IFC file, you can open the file in a text editor of your
choice. The header contains all the information about the MVD, the exact IFC exporter version and
the software that it has been exported from:
FILE_DESCRIPTION((‘ViewDefinition [ReferenceView_V1.0]’),‘2;1’);
FILE_NAME(‘Project Number’,‘2016-12-14T17:37:10’,(‚‘),(‚‘),‘The EXPRESS Data Manager Version 5.02.0100.07:
28 Aug 2013’,‘20161006_0315(x64) - Exporter 17.2.0.0 - Alternate UI 17.2.0.0’,’’);
FILE_SCHEMA((‘IFC4’));
ENDSEC;
DATA;
#1= IFCORGANIZATION($,‘Autodesk Revit 2017 (ENU)’,$,$,$);
#5= IFCAPPLICATION(#1,‘2017’,‘Autodesk Revit 2017 (ENU)’,‘Revit’);
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�
8 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
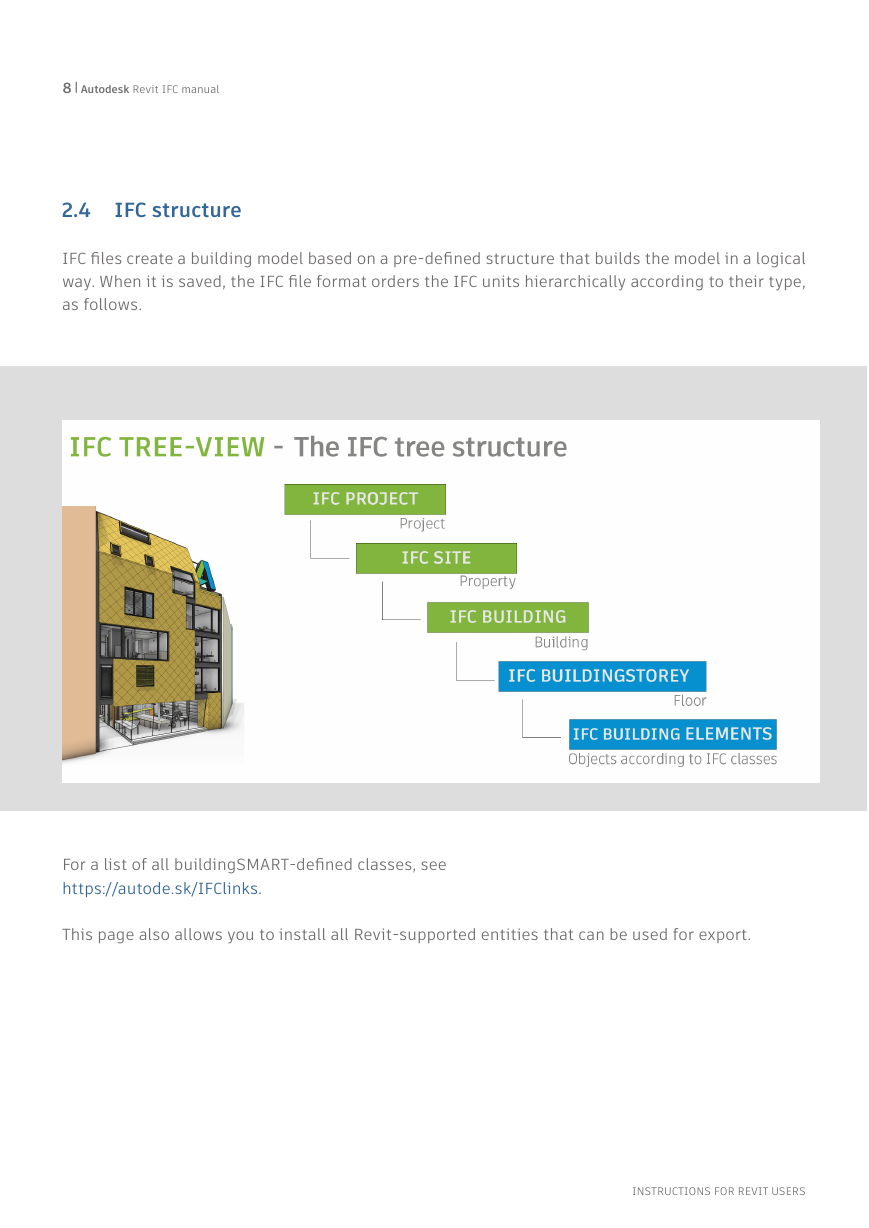
2.4 IFC structure
IFC files create a building model based on a pre-defined structure that builds the model in a logical
way. When it is saved, the IFC file format orders the IFC units hierarchically according to their type,
as follows.
For a list of all buildingSMART-defined classes, see
https://autode.sk/IFClinks.
This page also allows you to install all Revit-supported entities that can be used for export.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc