IEEE Std 802.3ab-1999
(Supplement to IEEE Std 802.3, 1998 Edition)
Information technology—
Telecommunications and information exchange between systems—
Local and metropolitan area networks—Specific requirements—
Supplement to Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Access Method and
Physical Layer Specifications—
Physical Layer Parameters and Specifications for
1000 Mb/s Operation Over 4-Pair of Category 5
Balanced Copper Cabling, Type 1000BASE-T
Sponsor
LAN MAN Standards Committee
of the
IEEE Computer Society
Approved 26 June 1999
IEEE-SA Standards Board
Abstract:
Type 1000BASE-T PCS, type 1000BASE-T PMA sublayer, and type 1000BASE-T Me-
dium Dependent Interface (MDI) are defined. This supplement provides fully functional, electrical
and mechanical specifications for the type 1000BASE-T PCS, PMA, and MDI. This supplement also
specifies the baseband medium used with 1000BASE-T.
Keywords:
dependent interface, physical coding sublayer, Physical Layer, physical medium attachment
Auto-Negotiation, Category 5, copper, Ethernet, gigabit, MASTER-SLAVE, medium
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
345 East 47th Street, New York, NY 10017-2394, USA
Copyright © 1999 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
All rights reserved. Published 26 July 1999. Printed in the United States of America.
Print:
PDF:
ISBN 0-7381-1741-2 SH94754
SS94754
ISBN 0-7381-1742-0
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form, in an electronic retrieval system or otherwise, without the prior
written permission of the publisher.
�
IEEE Standards
documents are developed within the IEEE Societies and the Standards Coordinat-
ing Committees of the IEEE Standards Association (IEEE-SA) Standards Board. Members of the
committees serve voluntarily and without compensation. They are not necessarily members of the
Institute. The standards developed within IEEE represent a consensus of the broad expertise on the
subject within the Institute as well as those activities outside of IEEE that have expressed an inter-
est in participating in the development of the standard.
Use of an IEEE Standard is wholly voluntary. The existence of an IEEE Standard does not imply
that there are no other ways to produce, test, measure, purchase, market, or provide other goods and
services related to the scope of the IEEE Standard. Furthermore, the viewpoint expressed at the
time a standard is approved and issued is subject to change brought about through developments in
the state of the art and comments received from users of the standard. Every IEEE Standard is sub-
jected to review at least every five years for revision or reaffirmation. When a document is more
than five years old and has not been reaffirmed, it is reasonable to conclude that its contents,
although still of some value, do not wholly reflect the present state of the art. Users are cautioned to
check to determine that they have the latest edition of any IEEE Standard.
Comments for revision of IEEE Standards are welcome from any interested party, regardless of
membership affiliation with IEEE. Suggestions for changes in documents should be in the form of a
proposed change of text, together with appropriate supporting comments.
Interpretations: Occasionally questions may arise regarding the meaning of portions of standards as
they relate to specific applications. When the need for interpretations is brought to the attention of
IEEE, the Institute will initiate action to prepare appropriate responses. Since IEEE Standards rep-
resent a consensus of all concerned interests, it is important to ensure that any interpretation has
also received the concurrence of a balance of interests. For this reason, IEEE and the members of its
societies and Standards Coordinating Committees are not able to provide an instant response to
interpretation requests except in those cases where the matter has previously received formal
consideration.
Comments on standards and requests for interpretations should be addressed to:
Secretary, IEEE-SA Standards Board
445 Hoes Lane
P.O. Box 1331
Piscataway, NJ 08855-1331
USA
Note: Attention is called to the possibility that implementation of this standard may
require use of subject matter covered by patent rights. By publication of this standard,
no position is taken with respect to the existence or validity of any patent rights in
connection therewith. The IEEE shall not be responsible for identifying patents for
which a license may be required by an IEEE standard or for conducting inquiries into
the legal validity or scope of those patents that are brought to its attention.
Authorization to photocopy portions of any individual standard for internal or personal use is
granted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., provided that the appropriate
fee is paid to Copyright Clearance Center. To arrange for payment of licensing fee, please contact
Copyright Clearance Center, Customer Service, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923 USA;
(978) 750-8400. Permission to photocopy portions of any individual standard for educational class-
room use can also be obtained through the Copyright Clearance Center.
�
Introduction to IEEE Std 802.3ab-1999
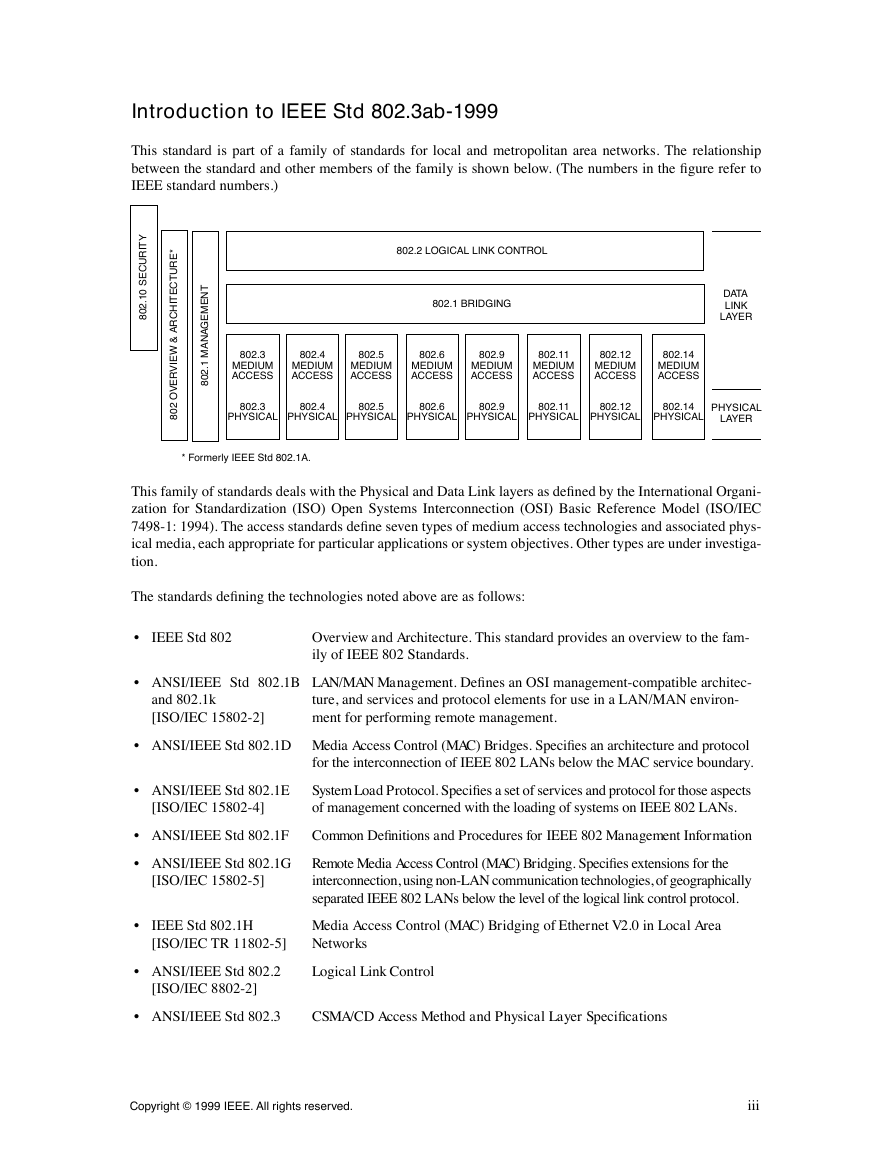
This standard is part of a family of standards for local and metropolitan area networks. The relationship
between the standard and other members of the family is shown below. (The numbers in the figure refer to
IEEE standard numbers.)
I
Y
T
R
U
C
E
S
0
1
2
0
8
.
I
*
E
R
U
T
C
E
T
H
C
R
A
&
W
E
V
R
E
V
O
2
0
8
I
T
N
E
M
E
G
A
N
A
M
1
2
0
8
.
802.2 LOGICAL LINK CONTROL
802.1 BRIDGING
DATA
LINK
LAYER
802.3
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.4
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.5
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.6
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.9
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.11
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.12
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.14
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.3
PHYSICAL
802.4
PHYSICAL
802.5
PHYSICAL
802.6
PHYSICAL
802.9
PHYSICAL
802.11
PHYSICAL
802.12
PHYSICAL
802.14
PHYSICAL
PHYSICAL
LAYER
* Formerly IEEE Std 802.1A.
This family of standards deals with the Physical and Data Link layers as defined by the International Organi-
zation for Standardization (ISO) Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Basic Reference Model (ISO/IEC
7498-1: 1994). The access standards define seven types of medium access technologies and associated phys-
ical media, each appropriate for particular applications or system objectives. Other types are under investiga-
tion.
The standards defining the technologies noted above are as follows:
•
IEEE Std 802
Overview and Architecture.
ily of IEEE 802 Standards.
This standard provides an overview to the fam-
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1B
and 802.1k
[ISO/IEC 15802-2]
LAN/MAN Management.
ture, and services and protocol elements for use in a LAN/MAN environ-
ment for performing remote management.
Defines an OSI management-compatible architec-
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1D
Specifies an architecture and protocol
Media Access Control
(MAC) Bridges.
for the interconnection of IEEE 802 LANs below the MAC service boundary.
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1E
[ISO/IEC 15802-4]
System Load Protocol.
of management concerned with the loading of systems on IEEE 802 LANs.
Specifies a set of services and protocol for those aspects
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1F
Common Definitions and Procedures for IEEE 802 Management Information
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1G
[ISO/IEC 15802-5]
Remote Media Access Control
(MAC) Bridging
interconnection, using non-LAN communication technologies, of geographically
separated IEEE 802 LANs below the level of the logical link control protocol.
. Specifies extensions for the
•
IEEE Std 802.1H
[ISO/IEC TR 11802-5]
Media Access Control (MAC) Bridging of Ethernet V2.0 in Local Area
Networks
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.2
Logical Link Control
[ISO/IEC 8802-2]
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.3
CSMA/CD Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications
Copyright © 1999 IEEE. All rights reserved.
iii
�
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.4
Token Passing Bus Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications
[ISO/IEC 8802-4]
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.5
Token Ring Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications
[ISO/IEC 8802-5]
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.6
[ISO/IEC 8802-6]
Distributed Queue Dual Bus Access Method and Physical Layer
Specifications
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.9
[ISO/IEC 8802-9]
Integrated Services (IS) LAN Interface at the Medium Access Control
(MAC) and Physical (PHY) Layers
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.10
Interoperable LAN/MAN Security
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.11
[ISO/IEC DIS 8802-11]
Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer
Specifications
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.12
[ISO/IEC 8802-12]
Demand Priority Access Method, Physical Layer and Repeater
Specifications
In addition to the family of standards, the following is a recommended practice for a common Physical
Layer technology:
•
IEEE Std 802.7
IEEE Recommended Practice for Broadband Local Area Networks
The following additional working group has authorized standards projects under development:
• IEEE 802.14
Standard Protocol for Cable-TV Based Broadband Communication Network
Conformance test methodology
An additional standards series, identified by the number 1802, has been established to identify the conform-
ance test methodology documents for the 802 family of standards. Thus the conformance test documents for
802.3 are numbered 1802.3.
IEEE Std 802.3ab-1999
This standard contains state-of-the-art material. The area covered by this standard is undergoing evolution.
Revisions are anticipated to this standard within the next few years to clarify existing material, to correct
possible errors, and to incorporate new related material. Details on the contents of this standard are provided
on the following pages.
The IEEE 802.3 Working Group acknowledges and appreciates that many concepts embodied in this stan-
dard are based largely upon the CSMA/CD access method earlier described in
specification as
written jointly by individuals from Xerox Corporation, Digital Equipment Corporation, and Intel Corpora-
tion. Appreciation is also expressed to Robert M. Metcalfe and David R. Boggs for their pioneering work in
establishing the original concepts.
The Ethernet
iv
Copyright © 1999 IEEE. All rights reserved.
�
Participants
The following is a list of participants in the IEEE 802.3 Working Group when this standard was balloted:
David J. Law,
Vice Chair
Geoffrey O. Thompson,
Chair
Robert M. Grow,
Secretary
George Eisler,
Colin K. Mick,
Chair, 802.3ab Task Force
Editor, 802.3ab Task Force
Oscar Agazzi
Paul Ahrens
Alan Albrecht
Don Alderrou
Abe Ali
Brad Allen
Ralph Andersson
Khaled Amer
Steve Augusta
Kameran Azadet
Guna Bala
Denis Beaudoin
April Bergstrom
John L. Bestel
Michel Bohbot
Brad J. Booth
Kirk Bovill
Steve Brewer
Benjamin J. Brown
Daniel J. Brown
Bill Bunch
Ed Cady
John Cagle
Richard Cam
Bob Campbell
Andrew Castellano
Edward Chang
Linda Cheng
Hon Wah Chin
Henry Choy
Chris Christ
George Chu
Terry Cobb
Ian Crayford
John Creigh
David Cunningham
Simon Cushin
Robert Dahlgren
Kevin Daines
Subrata Datta
Tom Debiec
Chris DiMinico
Thomas Dineen
Dan Dove
Steve Dreyer
Michael Elswick
Nick Esser
Daniel Essig
Mark Feuerstraeter
Dave Fifield
John Fitzgerald
Alan Flatman
Howard M. Frazier
Ken Friedenbach
Scott Fritz
Richard Froke
Judy Fuess
Darrell Furlong
Robin Gangopadhya
Joel Goergen
Tom Grasmehr
Bryan Gregory
Richard Grenier
Edward Grivna
Stephen Haddock
G. Y. Hanna
Del Hanson
Lloyd Hasley
Mehdi Hatamian
Kirk Hayden
Claude Hayek
Gaby Hecht
Ariel Hendel
John Hill
Henry Hinrichs
Charlie Hochstedler
Henry Hsiaw
Jacob Hsu
Todd Hudson
Ajit Jadeja
Robert Jin
Clarence Joh
Howard Johnson
Scott Johnson
Thomas K. Jørgensen
Juan Jover
Shinkyo Kaku
Mohan Kalkunte
Amrit Kalla
Jamie Kardontchik
Allen Kasey
Sumesh Kaul
Tuan Khuu
Yongbum Kim
Richard Knight
Paul Kolesar
Kishan Rao Konda
Josef Kosilek
Daniel Krent
Richard LaCerte
Hans Lackner
Gadi Lahat
Bruce LaVigne
Fu-Ho Lee
Tommy Leung
Chan-De Lin
George Lin
Larry Lomelino
Andy J. Luque
Jeffrey Lynch
Brian MacLeod
Kenneth MacLeod
Rabih Makarem
Jim Mangin
Arlen Martin
Jeff Martin
Thomas Mathey
Bob Mayer
Joseph Mazor
Kelly McClellan
John McCool
Grahame Measor
Vince Melendy
Steve Metzger
Tremont Miao
Larry D. Miller
Mart L. Molle
Octavio Morales
Shimon Muller
Carrie Munson
Denis Murphy
Samba Murthy
Robert Musk
Ken Naganuma
Hari Naidu
Kristian Nelson
Paul Nikolich
David Nim
Mark Nowell
Satoshi Obara
Mitsuji Okada
Paul Pace
Jim F. Parker
Jerry Pate
John Payne
Petar Pepeljugoski
John Proffitt
Steve Pryor
William Quackenbush
Sreen Raghavan
Sailesh K. Rao
Peter Rautenberg
John Ritger
Ramz Rizk
Carlos Rodriguez
Floyd Ross
Tam Ross
Tony Rowell
Larry Rubin
Khosrow Sadeghi
Dalit Sagi
Mark Sankey
Arindam Sarkar
Rich Seifert
Koichiro Seto
Cheng-Chung Shih
David Smith
Michael A. Smith
Walter Sotelo
David N. Stacy
Stephen Strong
Steve Swanson
Andre Szczepanek
Tad Szostak
Rich Taborek
Wen-Tsung Tang
Jim Tatum
Ken Taylor
Pat Thaler
R. Jonathan Thatcher
Walter Thirion
Douglas Thomson
Carlos Tomaszewski
Hiep Tran
Zbigniew Turlej
Jacob Twersky
Todd Vafiades
Schelto van Doorn
David J. Van Goor
Bill Verheggen
Greg Wang
Yun-Che Wang
Jeff Warren
Jim Welch
Willem Wery
Mike Witkowski
John Wolcott
David Wong
Don Wong
Robert Wu
Stefan M. Wurster
Michael Yam
Mark Yu
Igor Zhovnirovsky
Copyright © 1999 IEEE. All rights reserved.
v
�
The following members of the balloting committee voted on this standard:
Don Alderrou
Jack S. Andresen
J. Paul Benson, Jr.
Brad J. Booth
Steve Brewer
Benjamin J. Brown
James T. Carlo
David E. Carlson
Robert S. Crowder
Thomas J. Dineen
George Eisler
John W. Fendrich
Howard M. Frazier
Ken J. Friedenbach
Patrick S. Gonia
Robert M. Grow
Chris G. Guy
Allen W. Hathaway
Donald N. Heirman
Richard J. Iliff
Raj Jain
Howard Johnson
David J. Law
Randolph S. Little
Robert D. Love
John L. Messenger
Bennett Meyer
Colin K. Mick
Gene E. Milligan
David S. Millman
John E. Montague
Shimon Muller
Paul Nikolich
Robert O'Hara
Charles Oestereicher
Sai leh Rao
Edouard Y. Rocher
Floyd E. Ross
Rich Seifert
John A. Siemon
Michael A. Smith
Patricia Thaler
Geoffrey O. Thompson
Emmanuel Van Lil
Paul A. Willis
Oren Yuen
Jonathan M. Zweig
When the IEEE-SA Standards Board approved this standard on 26 June 1999, it had the following
membership:
Richard J. Holleman,
Chair
Donald N. Heirman,
Vice Chair
Judith Gorman,
Secretary
Satish K. Aggarwal
Dennis Bodson
Mark D. Bowman
James T. Carlo
Gary R. Engmann
Harold E. Epstein
Jay Forster*
Ruben D. Garzon
*Member Emeritus
James H. Gurney
Lowell G. Johnson
Robert J. Kennelly
E. G. “Al” Kiener
Joseph L. Koepfinger*
L. Bruce McClung
Daleep C. Mohla
Robert F. Munzner
Louis-François Pau
Ronald C. Petersen
Gerald H. Peterson
John B. Posey
Gary S. Robinson
Akio Tojo
Hans E. Weinrich
Donald W. Zipse
Also included is the following nonvoting IEEE-SA Standards Board liaison:
Robert E. Hebner
Catherine K.N. Berger
IEEE Standards Project Editor
This standard is dedicated to the memory of our friend and colleague
Valerie E. Zelenty
IEEE Standards Editor 1993–1999
vi
Copyright © 1999 IEEE. All rights reserved.
�
Contents
REVISIONS TO IEEE Std 802.3, 1998 Edition AS SUPPLEMENTED BY IEEE 802.3ac-1998
1.
(Changes to) Introduction .................................................................................................................... 1
1.3(Changes to) Normative references ................................................................................................ 1
1.4 (Changes to) Definitions ................................................................................................................ 2
1.5 (Changes to) Abbreviations ........................................................................................................... 4
(Changes to) Reconciliation Sublayer (RS) and Media Independent Interface (MII) ......................... 4
(Changes to) Physical Layer link signaling for 10 Mb/s and 100 Mb/s Auto-Negotiation
on twisted pair...................................................................................................................................... 5
(Changes to) 10 Mb/s, 100 Mb/s, and 1000 Mb/s Management.......................................................... 8
(Changes to) Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS), Physical Medium Attachment (PMA) sublayer
and baseband medium, type 100BASE-T2.......................................................................................... 8
(Changes to) Introduction to 1000 Mb/s baseband network................................................................ 9
(Changes to) System considerations for multisegment 1000 Mb/s networks...................................... 9
22.
28.
30.
32.
34.
42.
ANNEXES
(Changes to) Annex A (informative) Additional reference material ............................................................. 10
(Changes to) Annex 28B (normative) IEEE 802.3 Selector Base Page definition........................................ 10
(Changes to) Annex 28C (normative) Next Page Message Code Field definitions ...................................... 13
(Changes to) Annex 28D (normative) Description of extensions to Clause 28 and associated annexes....... 14
(Changes to) Annex 30B (normative) GDMO and ASN.1 definitions for management............................... 14
40.
Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS), Physical Medium Attachment (PMA) sublayer and baseband
medium, type 1000BASE-T............................................................................................................... 15
40.1 Overview .................................................................................................................................. 15
40.1.1 Objectives ........................................................................................................................... 15
40.1.2 Relationship of 1000BASE-T to other standards ................................................................ 16
40.1.3 Operation of 1000BASE-T .................................................................................................. 16
40.1.4 Signaling ............................................................................................................................. 20
40.1.5 Inter-sublayer interfaces....................................................................................................... 20
40.1.6 Conventions in this clause .................................................................................................. 20
40.2 1000BASE-T Service Primitives and Interfaces ...................................................................... 21
40.2.1 Technology-Dependent Interface...................................................................................... 21
40.2.2 PMA Service Interface...................................................................................................... 22
40.2.3 PMA_TXMODE.indicate ................................................................................................. 23
40.2.4 PMA_CONFIG.indicate ................................................................................................... 24
40.2.5 PMA_UNITDATA.request............................................................................................... 24
40.2.6 PMA_UNITDATA.indicate ............................................................................................. 25
40.2.7 PMA_SCRSTATUS.request ............................................................................................ 26
40.2.8 PMA_RXSTATUS.indicate.............................................................................................. 26
40.2.9 PMA_REMRXSTATUS.request ...................................................................................... 27
40.2.10 PMA_RESET.indicate ..................................................................................................... 27
Copyright © 1999 IEEE. All rights reserved.
vii
�
40.3 Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) ............................................................................................. 27
40.3.1 PCS functions ..................................................................................................................... 28
40.3.2 Stream structure .................................................................................................................. 43
40.3.3 State variables ..................................................................................................................... 43
40.3.4 State diagrams ..................................................................................................................... 48
40.4 Physical Medium Attachment (PMA) sublayer ....................................................................... 53
40.4.1 PMA functional specifications ............................................................................................ 53
40.4.2 PMA functions .................................................................................................................... 54
40.4.3 MDI ..................................................................................................................................... 56
40.4.4 Automatic MDI/MDI-X Configuration .............................................................................. 57
40.4.5 State variables ..................................................................................................................... 57
40.4.6 State Diagrams .................................................................................................................... 60
40.5 Management interface .............................................................................................................. 62
40.5.1 Support for Auto-Negotiation .............................................................................................. 62
40.5.2 MASTER-SLAVE configuration resolution........................................................................ 66
40.6 PMA electrical specifications................................................................................................... 68
40.6.1 PMA-to-MDI interface tests ................................................................................................ 68
40.7 Link segment characteristics .................................................................................................... 89
40.7.1 Cabling system characteristics ............................................................................................ 89
40.7.2 Link transmission parameters ............................................................................................. 89
40.7.3 Coupling parameters ........................................................................................................... 90
40.7.4 Delay ................................................................................................................................... 91
40.7.5 Noise environment .............................................................................................................. 91
40.8 MDI specification..................................................................................................................... 92
40.8.1 MDI connectors ................................................................................................................... 92
40.8.2 Crossover function .............................................................................................................. 93
40.8.3 MDI electrical specifications .............................................................................................. 94
40.9 Environmental specifications ................................................................................................... 96
40.9.1 General safety ...................................................................................................................... 96
40.9.2 Network safety .................................................................................................................... 96
40.9.3 Environment ........................................................................................................................ 97
40.10 PHY labeling............................................................................................................................ 97
40.11 Delay constraints...................................................................................................................... 97
40.11.1 MDI to GMII delay constraints ...................................................................................... 98
40.11.2 DTE delay constraints (half duplex only)........................................................................ 99
40.11.3 Carrier de-assertion/assertion constraint (half duplex mode).......................................... 99
viii
Copyright © 1999 IEEE. All rights reserved.
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc