ASQatQccASRev1588173317223brQbuTSNCBQciQbvQcaQQchABQavTSNAVBEthernetTransportPlaybookTime-Sensitive Networking (TSN) PlaybookTest Cases & Methodologies�
Table of Contents
1. TSN Standards Overview ................................................................................................................................................................3
2. Conformance Testing ......................................................................................................................................................................4
2.1. Conformance Testing: TTsuite-AVB-AS ..............................................................................................................................5
2.1.1. Objective .....................................................................................................................................................................5
2.1.2. Test Topology .............................................................................................................................................................6
2.1.3. Expected Behavior .....................................................................................................................................................8
2.2. Conformance Testing: TTsuite-AVB-1722 ........................................................................................................................11
2.2.1. Objective ...................................................................................................................................................................11
2.2.2. Test Topology ...........................................................................................................................................................12
2.2.3. Expected Behavior ...................................................................................................................................................13
2.3. Conformance Testing: TTsuite-AVB-FQTSS .....................................................................................................................16
2.3.1. Objective ...................................................................................................................................................................16
2.3.2. Test Topology ...........................................................................................................................................................17
2.3.3. Expected Behavior ...................................................................................................................................................20
3. Timing and Synchronization .........................................................................................................................................................23
IEEE802.1AS Synchronization Testing .............................................................................................................................23
3.1.1. Test Case: Test DUT for Master Role ......................................................................................................................25
3.1.2. Test Case: Test DUT for Slave Role .........................................................................................................................27
3.1.3. Test Case: Test DUT for Slave Role in Automotive Profile ...................................................................................29
3.1.4. Test Case: Test DUT for Master Role in Automotive Profile ................................................................................31
IEEE802.1AS Scalability Testing .........................................................................................................................................33
3.2.1. Test Case: Test gPTP Scalability .............................................................................................................................36
IEEE802.1AS Grandmaster Selection Testing ..................................................................................................................43
3.3.1. Test Case: Test for Grandmaster Selection ...........................................................................................................47
IEEE802.1AS Bridge Performance Testing .......................................................................................................................50
3.4.1. Test Case: Test DUT for Time-Aware Bridge gPTP Timing Performance .........................................................50
4. Traffic Shaping and Prioritization .................................................................................................................................................58
4.1. Credit-Based Shaping and Bandwidth Reservation Testing .........................................................................................60
4.1.1. Test Case: Credit Shaping and Bandwidth Reservation Capabilities ..............................................................60
4.2. Pre-emption Testing .............................................................................................................................................................68
4.2.1. Test Case: Generation of Modified Preamble Packet Stream ...........................................................................69
4.2.2. Test Case: Creating Traffic Profiles to Cause Pre-emption Between Switch Egress Ports ..............................71
.....................................................................................................................................................................................76
5. Acronyms
3.1.
3.2.
3.3.
3.4.
www.spirent.comTime-Sensitive Networking (TSN) PlaybookTest Cases & Methodologies�
1.
TSN Standards Overview
While Ethernet is the most wide-spread networking technology employed, it inherently operates on a best effort basis
to deliver packets across a network. Ethernet Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) Standards enable Ethernet to become a
deterministic networking technology:
• Synchronization of network elements: end-points, switches and gateways
• Controlled and accountable delay (latency)
• Prioritization of traffic classes
• Guaranteed bandwidth reservation
• Redundancy
TSN is made up of many standards that have been and are being developed exclusively to tackle different issues and
functionalities. The following is the list of active and under development standards for TSN:
Standard
IEEE 802.1AS-2011
IEEE 802.1AS-Rev
IEEE 802.1Qav
IEEE 802.1Qbv
IEEE 802.1Qbu
IEEE 802.3br
IEEE 802.1Qat
IEEE 802.1Qca
IEEE 802.1Qcc
IEEE 802.1CB
IEEE 802.1Qci
IEEE 802.1Qch
IEEE 802.1CM
IEEE 802.1Qcr
IEEE 802.1CS
IEEE 1722-2011
IEEE 1722-Rev
IEEE 1733-2011
IEEE 1722.1-2013
Title
Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications in Bridged Local Area
Networks
Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications
Forwarding and Queuing Enhancements for Time-Sensitive Streams
Enhancements for Scheduled Traffic
Frame Pre-emption
Interspersing Express Traffic
Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP)
Path Control and Reservation
Enhancements and Performance Improvements
Seamless Redundancy
Per-Stream Filtering and Policing
Cyclic Queuing and Forwarding
Time-Sensitive Networking for Front-haul
Asynchronous Traffic Shaping
Local Registration Protocol
Layer 2 Transport Protocol for Time-Sensitive Applications in a Bridged Local Area
Network
Enhance the Stream Transport Protocol
Layer 3 Transport Protocol for Time-Sensitive Applications in Local Area Networks
Device Discovery, Enumeration, Connection Management and Control Protocol
This document provides an overview of the various Time-Sensitive Networking protocols and step-by-step instructions on how
to test different use cases using Spirent TestCenter.
3
�
2.
Conformance Testing
Spirent Automotive AVB Conformance Test Suite Pack is an Avnu Alliance accredited test solution. It consists of different
protocol conformance test suites for the Avnu Automotive AVB Profile running on Spirent C50 devices with BroadR-Reach
network interface cards. All test suites are prepared for full test automation and include frameworks for individual adaptation.
Users are able to customize test scenarios, for instance to modify or exclude test stub activities, or to add negative testing, etc.
Included Test Suites
• TTsuite-AVB-Startup
• TTsuite-AVB-Diagnostic
• TTsuite-AVB-Exceptions
• TTsuite-AVB-AS
• TTsuite-AVB-FQTSS
• TTsuite-AVB-1722
References
• IEEE 802.1AS-2011 IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Timing and Synchronization for Time-
Sensitive Applications in Bridged Local Area Networks
• IEEE 802.1Q-2014 IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks—Bridges and Bridged Networks
• IEEE 1722-2016 IEEE Standard for a Transport Protocol for Time-Sensitive Applications in Bridged Local Area Networks
• IEEE 1722.1-2013 IEEE Standard for Device Discovery, Connection Management, and Control Protocol for IEEE 1722
Based Devices
• Avnu Automotive Ethernet AVB Functional and Interoperability Specification, Revision 1.4 12 May 2015
Avnu Test Plans
• Automotive gPTP
• Automotive Bridge FQTSS and SR Classes
• Automotive EndStation Media Formats and SR Classes
• Automotive Exception Handling
• Automotive Diagnostic Counters
• Automotive Network Startup Requirements
• Spirent C50 with BroadR-Reach
For more information, visit: https://www.spirent.com/Products/TTworkbench/TTsuites/Automotive-AVB-Conformance
AVB Test Suites First Steps User’s Guide is available with any TT software and can be downloaded here.
www.spirent.comTime-Sensitive Networking (TSN) PlaybookTest Cases & Methodologies�
2.1. Conformance Testing: TTsuite-AVB-AS
2.1.1. Objective
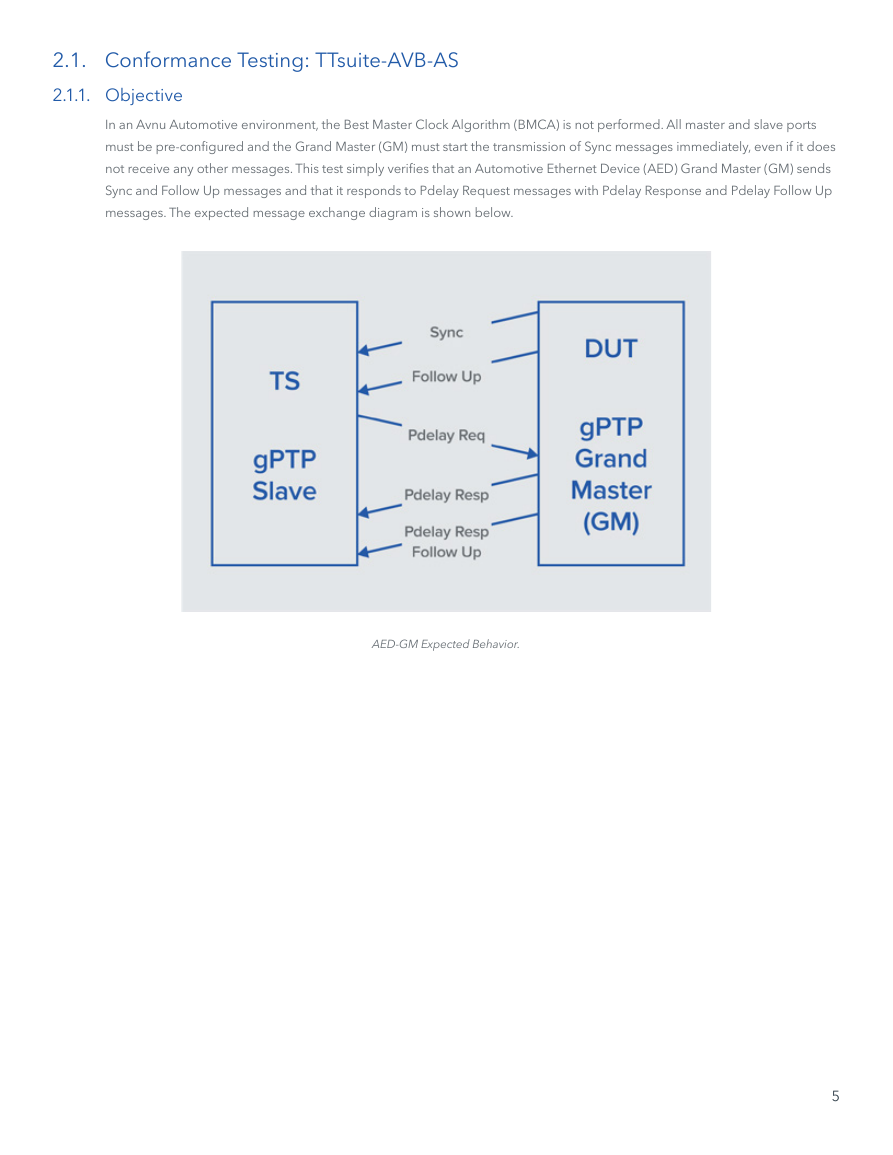
In an Avnu Automotive environment, the Best Master Clock Algorithm (BMCA) is not performed. All master and slave ports
must be pre-configured and the Grand Master (GM) must start the transmission of Sync messages immediately, even if it does
not receive any other messages. This test simply verifies that an Automotive Ethernet Device (AED) Grand Master (GM) sends
Sync and Follow Up messages and that it responds to Pdelay Request messages with Pdelay Response and Pdelay Follow Up
messages. The expected message exchange diagram is shown below.
AED-GM Expected Behavior.
5
�
2.1.2. Test Topology
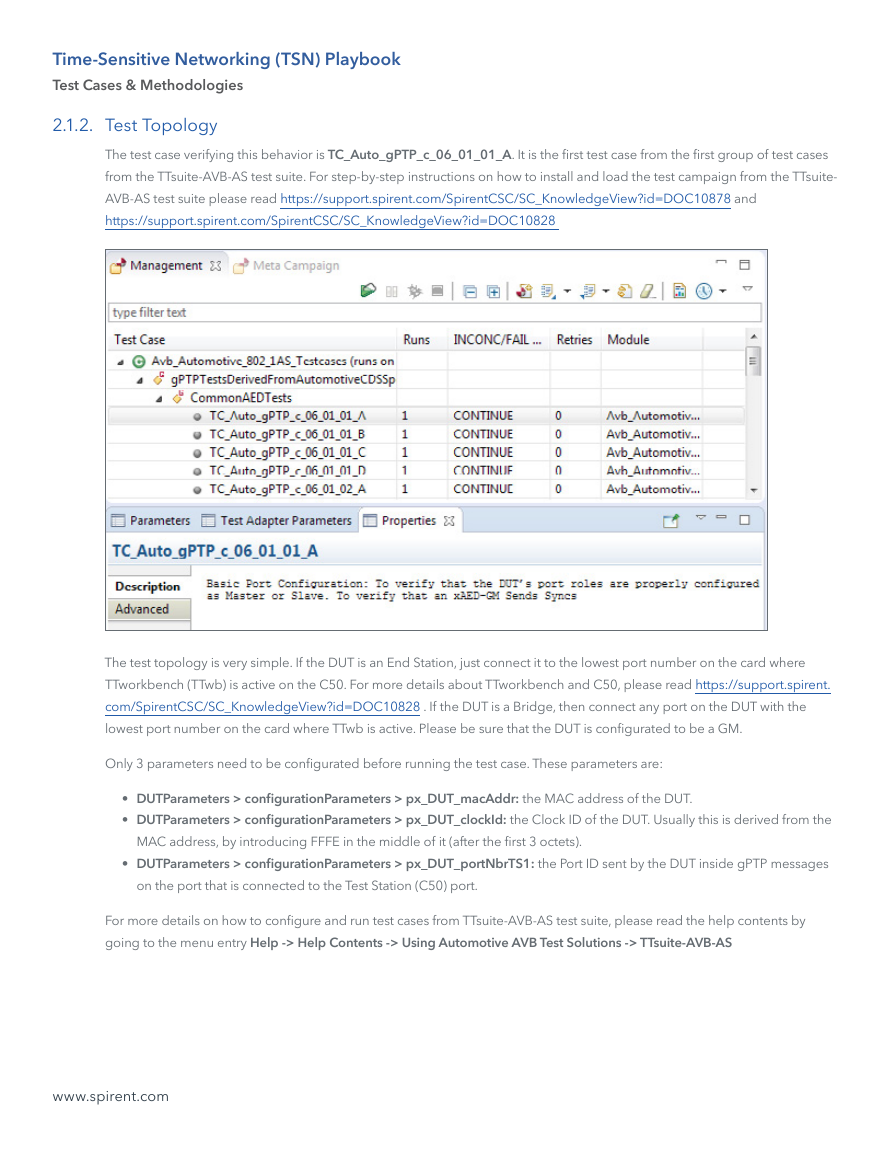
The test case verifying this behavior is TC_Auto_gPTP_c_06_01_01_A. It is the first test case from the first group of test cases
from the TTsuite-AVB-AS test suite. For step-by-step instructions on how to install and load the test campaign from the TTsuite-
AVB-AS test suite please read https://support.spirent.com/SpirentCSC/SC_KnowledgeView?id=DOC10878 and
https://support.spirent.com/SpirentCSC/SC_KnowledgeView?id=DOC10828
The test topology is very simple. If the DUT is an End Station, just connect it to the lowest port number on the card where
TTworkbench (TTwb) is active on the C50. For more details about TTworkbench and C50, please read https://support.spirent.
com/SpirentCSC/SC_KnowledgeView?id=DOC10828 . If the DUT is a Bridge, then connect any port on the DUT with the
lowest port number on the card where TTwb is active. Please be sure that the DUT is configurated to be a GM.
Only 3 parameters need to be configurated before running the test case. These parameters are:
• DUTParameters > configurationParameters > px_DUT_macAddr: the MAC address of the DUT.
• DUTParameters > configurationParameters > px_DUT_clockId: the Clock ID of the DUT. Usually this is derived from the
MAC address, by introducing FFFE in the middle of it (after the first 3 octets).
• DUTParameters > configurationParameters > px_DUT_portNbrTS1: the Port ID sent by the DUT inside gPTP messages
on the port that is connected to the Test Station (C50) port.
For more details on how to configure and run test cases from TTsuite-AVB-AS test suite, please read the help contents by
going to the menu entry Help -> Help Contents -> Using Automotive AVB Test Solutions -> TTsuite-AVB-AS
www.spirent.comTime-Sensitive Networking (TSN) PlaybookTest Cases & Methodologies�
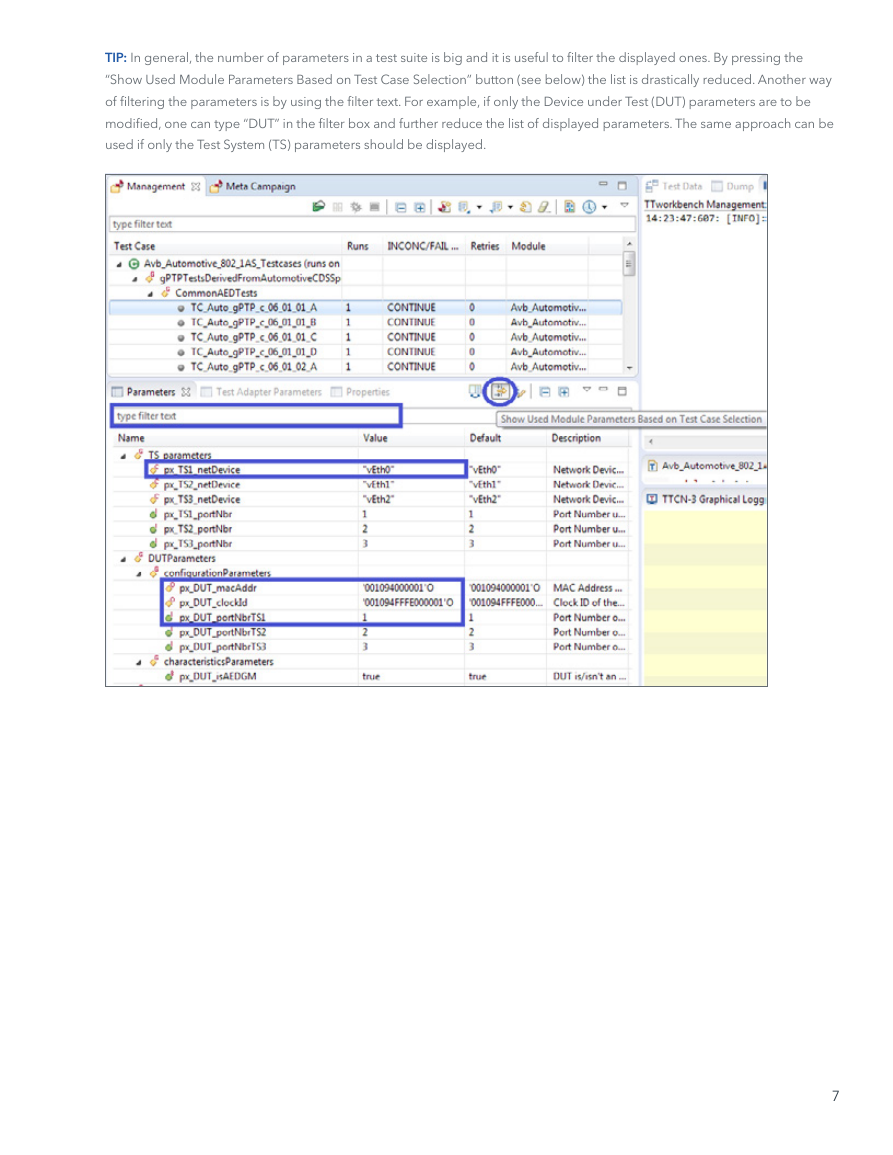
TIP: In general, the number of parameters in a test suite is big and it is useful to filter the displayed ones. By pressing the
“Show Used Module Parameters Based on Test Case Selection” button (see below) the list is drastically reduced. Another way
of filtering the parameters is by using the filter text. For example, if only the Device under Test (DUT) parameters are to be
modified, one can type “DUT” in the filter box and further reduce the list of displayed parameters. The same approach can be
used if only the Test System (TS) parameters should be displayed.
7
�
2.1.3. Expected Behavior
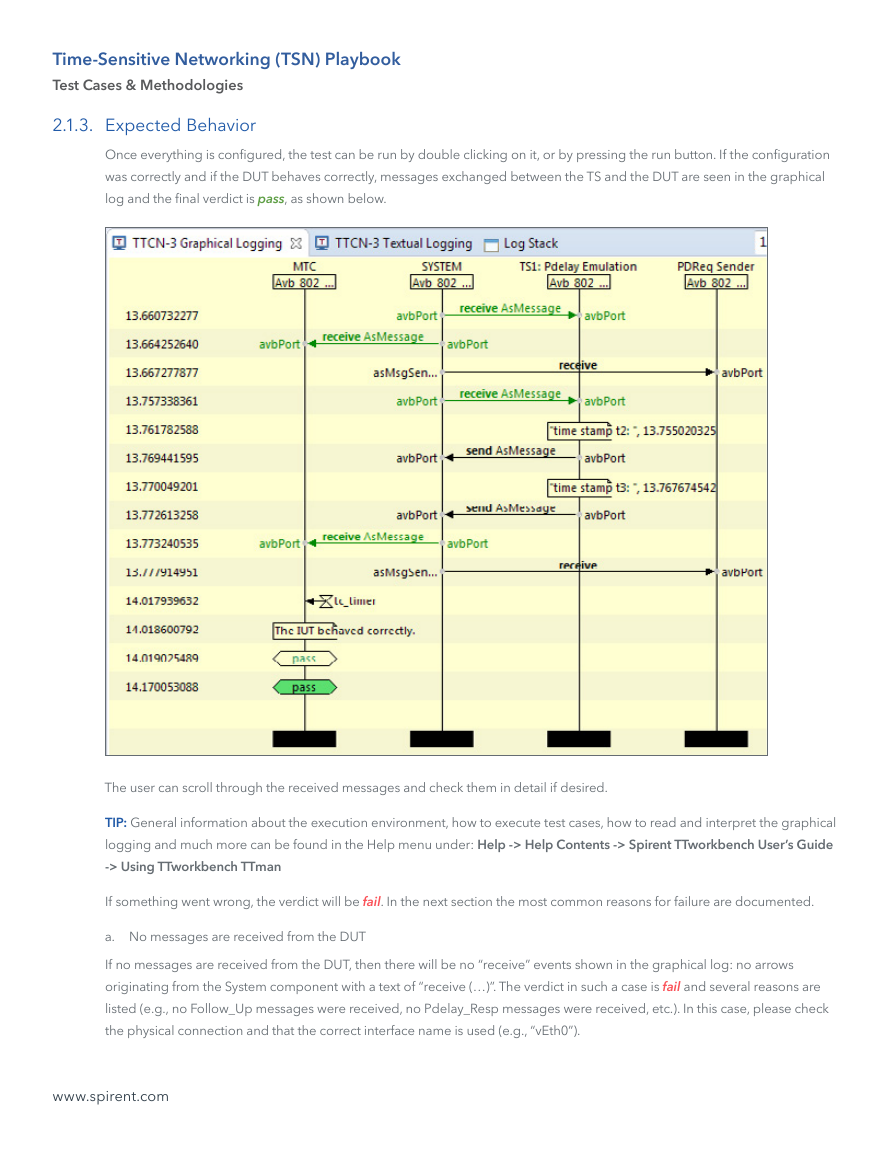
Once everything is configured, the test can be run by double clicking on it, or by pressing the run button. If the configuration
was correctly and if the DUT behaves correctly, messages exchanged between the TS and the DUT are seen in the graphical
log and the final verdict is pass, as shown below.
The user can scroll through the received messages and check them in detail if desired.
TIP: General information about the execution environment, how to execute test cases, how to read and interpret the graphical
logging and much more can be found in the Help menu under: Help -> Help Contents -> Spirent TTworkbench User’s Guide
-> Using TTworkbench TTman
If something went wrong, the verdict will be fail. In the next section the most common reasons for failure are documented.
a. No messages are received from the DUT
If no messages are received from the DUT, then there will be no “receive” events shown in the graphical log: no arrows
originating from the System component with a text of “receive (…)”. The verdict in such a case is fail and several reasons are
listed (e.g., no Follow_Up messages were received, no Pdelay_Resp messages were received, etc.). In this case, please check
the physical connection and that the correct interface name is used (e.g., “vEth0”).
www.spirent.comTime-Sensitive Networking (TSN) PlaybookTest Cases & Methodologies�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc