SiS964/SiS180 SATA w/ RAID
User’s Manual
Quick User’s Guide
Version 0.3
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
Edition
December 2003
Copyright
© 2003 Silicon Integrated Systems Corp.
Trademarks
SiS is a registered trademark of Silicon Integrated Systems Corp.
All brand or product names mentioned are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
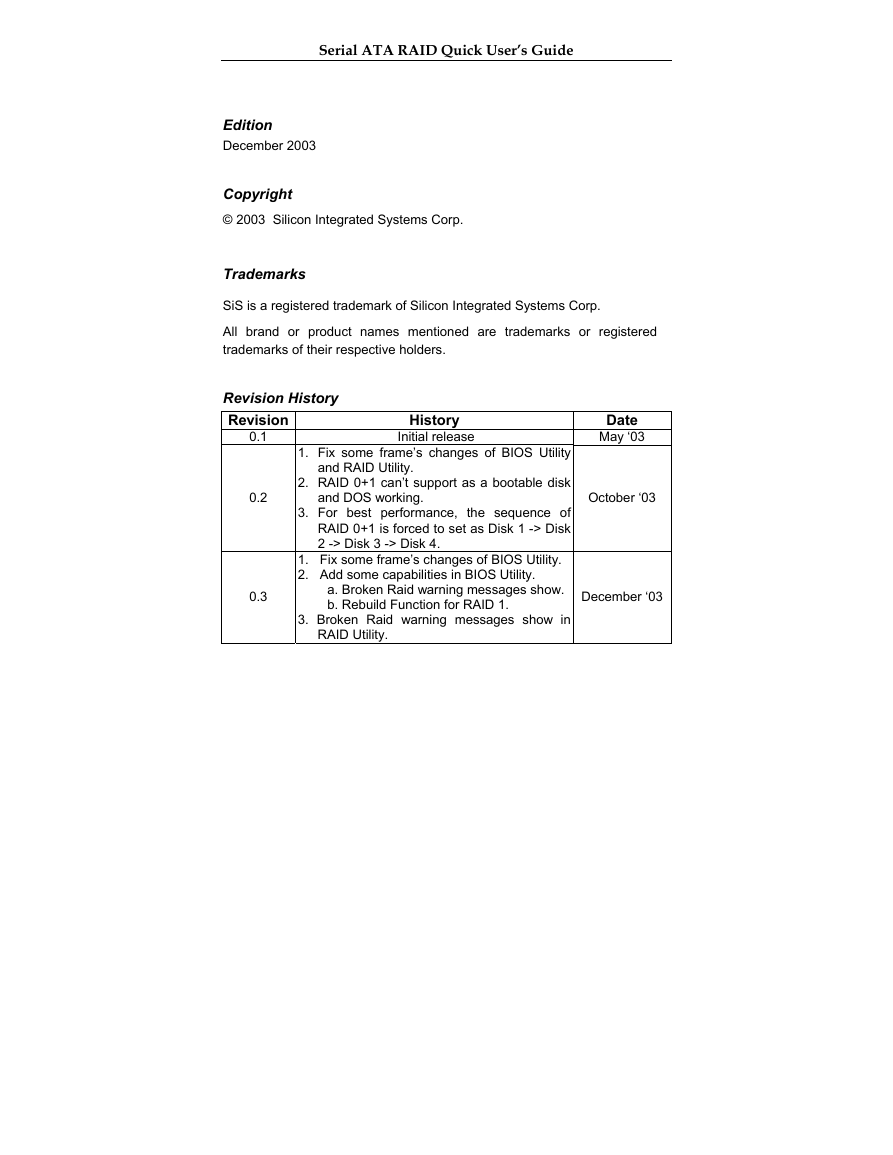
Revision History
Revision
History
Initial release
1. Fix some frame’s changes of BIOS Utility
0.1
0.2
0.3
2. RAID 0+1 can’t support as a bootable disk
and RAID Utility.
and DOS working.
3. For best performance, the sequence of
RAID 0+1 is forced to set as Disk 1 -> Disk
2 -> Disk 3 -> Disk 4.
1. Fix some frame’s changes of BIOS Utility.
2. Add some capabilities in BIOS Utility.
a. Broken Raid warning messages show.
b. Rebuild Function for RAID 1.
3. Broken Raid warning messages show in
RAID Utility.
Date
May ‘03
October ‘03
December ‘03
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
CONTENTS
Introduction ................................................................................................1
Features .......................................................................................................2
Support operating Systems........................................................................2
KNOW HOW..........................................................................................4
PERFORMANCE HINTS AND RECOMMEND SETTING.............4
Step 1. Hardware Setup .............................................................................6
HARD DRIVES SETUP ........................................................................6
FOR RAID 0 (STRIPING ARRAY) ............................................................... 6
FOR RAID 1 (MIRROR ARRAY).................................................................. 7
FOR RAID 0+1 (STRIPE-MIRROR ARRAY)............................................... 7
FOR JBOD (SPANNING ARRAY) ................................................................ 8
Step 2. Installing Software Drivers ...........................................................9
WINDOWS XP/2000/ME/98SE.............................................................9
NEW WINDOWS XP/2000 INSTALLATION................................................ 9
EXISTING WINDOWS XP/2000/ME/98SE INSTALLATION.................... 10
CONFIRMING WINDOWS XP/2000 DRIVER INSTALLATION .............. 10
CONFIRMING WINDOWS ME/98SE DRIVER INSTALLATION............. 10
Step 3. BIOS Utility Operation................................................................11
STARTING BIOS UTILITY...............................................................11
CREATE RAID ....................................................................................14
CREATING A RAID 0 (STRIPE) ARRAY FOR PERFORMANCE ............ 14
CREATING A RAID 1 (MIRROR) ARRAY................................................. 19
CREATING A JBOD ARRAY ...................................................................... 23
CREATING A RAID 0+1 (STRIPE-MIRROR) ARRAY.............................. 26
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
DELETE RAID.....................................................................................28
STARTING TO DELETE A RAID ARRAY................................................. 28
Step 4. SiS964/SiS180 RAID Utility ........................................................31
STARTING TO USE SIS964/SIS180 RAID UTILITY.....................31
ABOUT CREATE RAID ....................................................................34
VIEWING THE “CREATE RAID” ............................................................... 34
CREATE A RAID SET.................................................................................. 37
ABOUT DELETE RAID.....................................................................46
VIEWING THE RAIDTYPE MEANING...................................................... 47
DELETE A RAID SET .................................................................................. 49
ABOUT RAID RECOVERY..............................................................52
RAID RECOVERY OPERATION................................................................. 52
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
Introduction
The SiS180 SATA controller is a hybrid solution that combines two
independent SATA ports and one Ultra ATA port for support of up to two
Serial ATA (Serial ATA RAID) and two Ultra ATA (Ultra ATA RAID) drives.
However the South Bridge SiS964 SATA controller only support two Serial
ATA on two independent ports. Specifications are as follows:
Serial ATA Interface
Serial ATA (SATA) is the latest generation of the ATA interface. SATA hard
drives deliver blistering transfer speeds of up to 150MB/sec. Serial ATA uses
long, thin cables, making it easier to connect your drive and improving the
airflow inside your PC.
♦ Supports 150 MB/s transfers with CRC error checking
♦ Large LBA support for drives over 137 GB
♦ Data handling optimizations including tagged command queuing, elevator seek
and packet chain command
Ultra ATA Interface
♦ Standard ATA/IDE interface
♦ Supports Ultra ATA/133, Ultra ATA/100, and Ultra ATA/66 drives
♦ Supports CRC error checking for Ultra ATA drives
♦ Separate timing control for two devices attached to one ATA channel
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID Interfaces
The Serial/Ultra ATA RAID is designed to provide a cost-effective, high
performance RAID solution that adds performance and/or reliability to PC
desktops and/or servers using Serial ATA/150, Ultra ATA/133, Ultra ATA/100,
Ultra ATA/66 hard disks.
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID function supports striping (RAID 0), mirroring (RAID
1), striping + mirroring (RAID 0+1) and span (JBOD). Please note that the
function supports hard disk drives only and the South Bridge SiS964
SATA controller don’t support Striping + mirroring (Raid 0+1).
With striping, identical drives can read and write data in parallel to increase
performance. Mirroring increases read performance through load balancing
and elevator sorting while creating a complete backup of your files. Span
would increase the logic hard disk space.
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID striped arrays can double the sustained data transfer
rate of Serial ATA/150 and Ultra ATA/133 drives. Serial/Ultra ATA RAID fully
1
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
supports Serial ATA/150 and Ultra ATA/133 specification of up to 150MB/sec
per drive, depending on individual drive specifications.
The technology also offers fault tolerant, data redundancy for entry-level
network file servers or simply for desktop PC users wanting to continually
protect valuable data on their PC. The Serial/Ultra ATA RAID offers RAID 1
mirroring (for two drives) to protect data. Should a drive that is part of a
mirrored array fail, Serial/Ultra ATA RAID technology uses the mirrored drive
(which contains identical data) to assume all data handling. When a new
replacement drive is later installed, Serial/Ultra ATA RAID rebuilds data to
the new drive from the mirrored drive to restore fault tolerance.
Features
The SiS180 controller support two Serial ATA (Serial ATA RAID)
and two Ultra ATA (Ultra ATA RAID) drives. The South Bridge SiS964
SATA controller only support two Serial ATA (Serial ATA RAID) drivers.
Support RAID function: RAID 0, RAID 1, JBOD and RAID 0+1.
(RAID 0+1 function can be used by SiS180 controller with all
hard drivers on it.)
Support bootable disk except for RAID 0+1.
Windows-based SiS RAID Utility software tool (only support
Windows XP and 2000).
BIOS RAID Setting Utility
Support operating Systems
Microsoft Windows 98 Second Edition
2
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
Microsoft Windows Me
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional and Server
Microsoft Windows XP
3
�
Serial ATA RAID Quick User’s Guide
Step 0. What is RAID
Know How
This section will give you an overview about the RAID system and introduce
the basic background and glossary which you need to know before using
“SiS RAID Controller Application”.
1. RAID: (Redundant Array of Independent Disk Drives) use jointly several
hard drives to increase data transfer rates and data security. It depends
on the number of drives present and RAID function you select to fulfill
the security or performance purposes or both.
2. RAID 0: Also known as “Stripping”. All of the data are distributed evenly
to all of the existing drives. You gain benefits on performance because
the data transfer rate is multiplied by the number of drives. However,
RAID 0 has high risks of data security. All of the stored data will be lost if
even any one drive in the RAID set crashes.
3. RAID 1: Also known as “Mirroring”. Two hard drives are required. The
goal of RAID 0 is to ensure data security. Data is written to two or more
drives synchronously. That is, 100% duplication of data from one drive
to another.
4. RAID 0+1: Also known as “StripeMirror”. At least four hard drivers are
required. RAID 0+1 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. Data is
striped into two drives then mirrored. It provides high performance and
high data protection. This is a costly solution as RAID 1 because the two
mirrored drives represent an expensive insurance
5. JBOD: (Just a Bunch of Drives). Also known as “Spanning”. Two or
more hard drives are required. Several hard disk types configured as a
single hard disk. The hard drives are simply hooked up in series. This
expands the capacity of your drive and results in a useable total capacity.
However, JBOD will not increase any performance or data security.
Performance hints and recommend setting
For
the best performance and reliability, please read
suggestions.
1.
In Serial ATA port, use Native Serial ATA drives. Parallel ATA to Serial
ATA converter board is NOT suggested.
In Parallel ATA port, use ATA 66/100/133 hard drives
the
following
2.
3. Use the same model hard drives.
4.
If you have only two Serial ATA drives, the auto-configure function will
assign each on a different channel as a master drive. Using only two
Parallel ATA drives to create a RAID array is NOT suggested. It might
decrease performance.
4
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc