中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
行程时间可靠度综述#
涂辉招*
(同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室,上海 201804)
5 摘要:行程时间可靠度是评价交通路网性能的重要指标之一。本文综述行程时间可靠度的研
究现状,展望了行程时间可靠度的发展趋势和研究方向:现有可靠度指标侧重量化了不确定
性,忽略了考虑交通状态突变引起的不稳定性,导致了在面向行程时间可靠度的路网性能分
析评价中存在不符合逻辑的高流量高可靠性现象,由此提出行程时间可靠度的内涵应包括交
通供需随机波动等外部环境因素导致的不确定性和交通流内部因素产生交通状态突变
(traffic breakdown)引起的不稳定性。
关键词:行程时间可靠度; 行程时间分布; 不确定性; 不稳定性
中图分类号:U 491
10
15
20
25
A Review on Travel Time Reliability
TU Huizhao
(Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering of the Ministry of Education, Tongji University,
Shanghai 201804, China)
Abstract: Travel time reliability is considered to be one of the key indicators of transport network
performances and measured in various ways. This paper summarizes distributions of travel times,
definition and measures of travel time reliability, mechanism of travel time reliability. It concludes
that travel time reliability of a trip does not just depend on the uncertainty of travel times, but also
on the instability of travel times, or more concisely, on the instability of the prevailing traffic
conditions. The consequence of neglecting travel time unreliability caused by traffic instability is
the misinterpretation of reliability performance under high traffic volumes. Therefore, a more
comprehensive measurement of reliability is eagerly needed to capture the unreliability caused by
traffic breakdown, to make logical and reasonable evaluations of network reliability performances.
Key words: travel time reliability; distributions of travel time; travel time uncertainty; travel
time instability
30
0 引言
35
40
畅通、可靠的城市交通系统既是城市交通管理者期望达到的交通运行目标,也是出行者
实现出行目的的基础[1]。随着社会和经济的迅速发展和城市化水平不断提高,交通需求与供
给在总量和结构上的不均衡造成了目前大中城市的交通,尤其在高峰时段,始终处于饱和、
拥堵的状态。在面对交通拥堵时,交通管理、规划、设计、分析评价中越来越关注可靠的行
程时间,期望能减少行程时间的波动。行程时间可靠度是交通管理和决策者评价道路路网性
能[2, 3]和衡量道路交通状态是否可靠[4]的重要指标。例如,荷兰政府 2005 年就向荷兰议会提
交了一份议案[5]:在交通运输方面的政策目标就是“面向可靠的、可预测的交通出行”。我
国《国家中长期科学和技术发展规划纲要(2006--2020 年)》中提出的交通领域发展思路:
“以提供顺畅、便捷的人性化交通运输服务为核心”,而顺畅、便捷的交通需要可靠的路网
做支撑。国内外专家、学者由此对行程时间可靠度的定义和量化指标等方面开展了大量的、
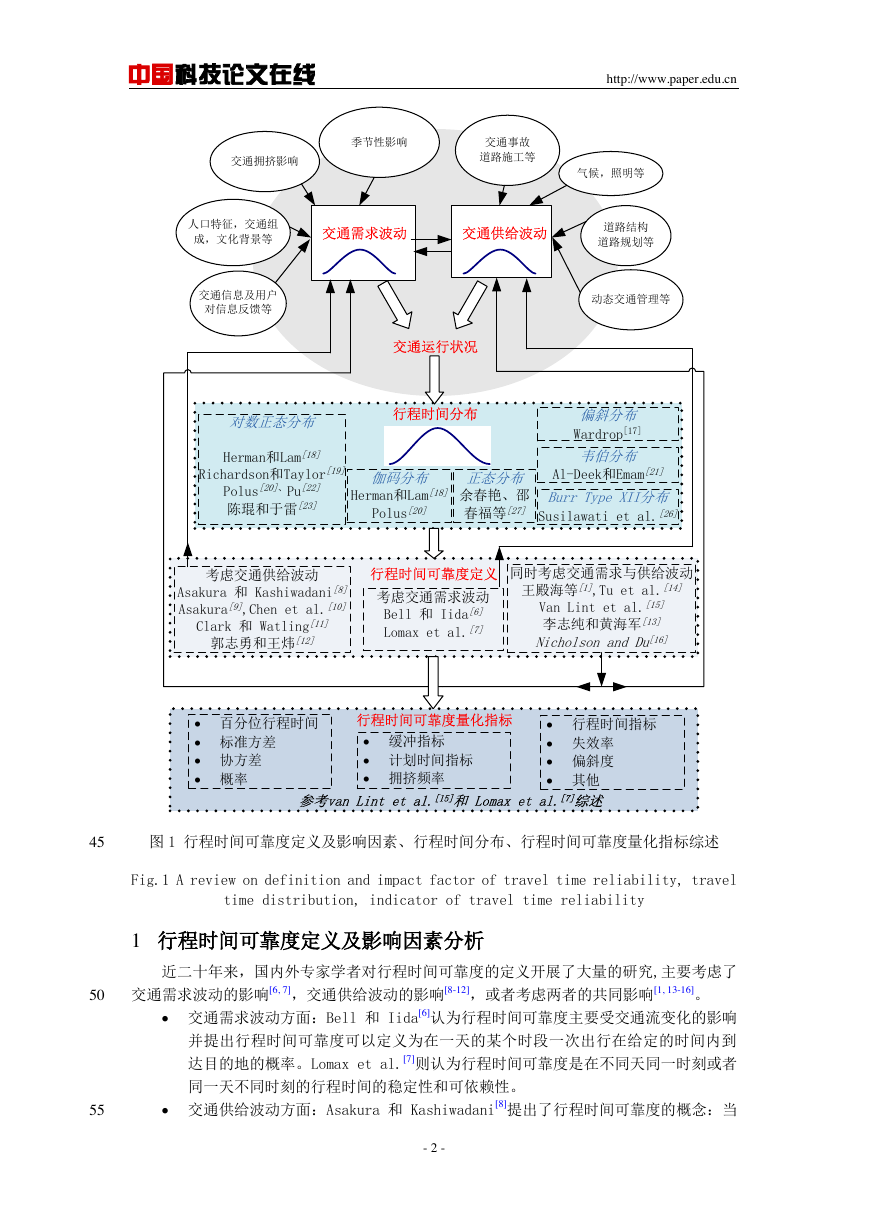
卓有成效的研究。行程时间可靠度定义及其影响因素、行程时间分布、行程时间可靠度量化
指标及行程时间可靠度机理等几方面的综述如图 1 所示。
基金项目:教育部博士点基金新教师类(20120072120023)
作者简介:涂辉招(1977—),男,副教授,博士生导师,研究方向:路网可靠度,交通风险评估,应急交通
管理. E-mail: huizhaotu@tongji.edu.cn
- 1 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
45
图 1 行程时间可靠度定义及影响因素、行程时间分布、行程时间可靠度量化指标综述
Fig.1 A review on definition and impact factor of travel time reliability, travel
time distribution, indicator of travel time reliability
1 行程时间可靠度定义及影响因素分析
近二十年来,国内外专家学者对行程时间可靠度的定义开展了大量的研究,主要考虑了
50
交通需求波动的影响[6, 7],交通供给波动的影响[8-12],或者考虑两者的共同影响[1, 13-16]。
· 交通需求波动方面:Bell 和 Iida[6]认为行程时间可靠度主要受交通流变化的影响
并提出行程时间可靠度可以定义为在一天的某个时段一次出行在给定的时间内到
达目的地的概率。Lomax et al.[7]则认为行程时间可靠度是在不同天同一时刻或者
同一天不同时刻的行程时间的稳定性和可依赖性。
55
· 交通供给波动方面:Asakura 和 Kashiwadani[8]提出了行程时间可靠度的概念:当
- 2 -
交通运行状况 交通拥挤影响季节性影响交通事故道路施工等气候,照明等道路结构道路规划等动态交通管理等人口特征,交通组成,文化背景等交通信息及用户对信息反馈等交通需求波动 交通供给波动行程时间分布对数正态分布Herman和Lam[18]Richardson和Taylor[19]Polus[20]、Pu[22]陈琨和于雷[23]韦伯分布Al-Deek和Emam[21]伽码分布Herman和Lam[18]Polus[20]偏斜分布Wardrop[17]考虑交通需求波动Bell 和 Iida[6]Lomax et al.[7]行程时间可靠度定义考虑交通供给波动Asakura 和 Kashiwadani[8]Asakura[9],Chen et al.[10]Clark 和 Watling[11]郭志勇和王炜[12] 同时考虑交通需求与供给波动王殿海等[1],Tu et al.[14]Van Lint et al.[15]李志纯和黄海军[13]Nicholson and Du[16]行程时间可靠度量化指标· 百分位行程时间· 标准方差· 协方差· 概率· 缓冲指标· 计划时间指标· 拥挤频率· 行程时间指标· 失效率· 偏斜度· 其他参考van Lint et al.[15]和 Lomax et al.[7]综述Burr Type XII分布Susilawati et al.[26]正态分布余春艳、邵春福等[27]�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
路段通行能力随机变化时,给定 OD 的一次出行在规定的时间内完成的概率。
Asakura[9]定义的行程时间可靠度考虑到道路交通条件恶化和通行能力的下降,考虑
的是行程时间的变异性:将现状的行程时间与正常情况下的行程时间相比较。Chen
et al.[10]从路网服务水平的角度出发,考虑通行能力由于天气、事故等随机因素影
响而退化进而影响行程时间可靠度,定义行程时间可靠度为路网服务水平在一定阈
值范围内的概率,并用蒙特卡罗方法测试了一个小型路网,分析了行程时间可靠度
在路段通行能力的波动下的敏感性,结果表明行程时间可靠度随着交通需求的增加
而降低。Clark and Watling[11]利用解析法测试了一个小型路网,得出了与 Chen et
al.[10]类似的结论。郭志勇和王炜[12]将行程时间引入到城市区域交通控制系统,并
在武汉市进行测试,结果表明区域控制系统能够显著的提高路行程时间可靠度。
· 交通需求与交通供给波动方面:王殿海等[1]认为路网不可靠的的原因可以归结为:
路段通行能力的波动、交通需求的波动、出行者路径选择的感知误差和路段行程时
间的波动。Tu et al.[14]将行程时间的变异性定义为百分位行程时间,认为百分位
行程时间能很好的同时表征行程时间的平均值和行程时间的变异性,并利用实际交
通数据分析了交通流量的变异性和通行能力的变异性对行程时间变异性的影响。结
果表明在高快速路上,通行能力的变异性对行程时间变异性的影响要比交通流量的
变异性所造成的影响大。van Lint et al.[15] 基于行程时间的分布特征提出了同时
量化行程时间偏斜和方差的可靠度方法,并用此方法鉴别了不同的交通状态(自由
流、拥堵产生、拥堵消散等状态)。李志纯和黄海军[13]提出了时变行程时间可靠
度和停车可靠度概念,即在某一时刻,出行者能在预期时间内完成出行和搜索到停
车泊位的概率。Nicholson and Du[16]根据静态交通分配模型的结果,表明行程时间
变异性随通行能力和交通需求变异性改变而变化。同时也提出行程时间变异性是两
种因素共同作用的结果,难以区分单个因素对可靠度的影响。
由此分析可以得出:①行程时间可靠度的定义侧重关注了由于交通供需随机波动等外部
因素导致的不确定性,但对于交通流微观行为内部因素导致的不稳定性未予以考虑;②在对
行程时间可靠度的影响因素时也主要是定性的分析为主,缺乏一个行程时间可靠度与主要影
响因素的函数关系,难以直接分析评价面向可靠度的路网性能。
2 行程时间分布曲线及可靠度量化指标
行程时间可靠度描述的定义不同,造成了量化指标的差异。已有研究主要通过统计方法
(来源于大量的历史数据和经验估计)、模拟方法(采用蒙特卡罗和敏感度分析求解等)和
仿真方法(利用交通仿真模型)等得到的行程时间数据来拟合行程时间分布线[17-27],进而提
出相应的量化指标。例如, Wardrop[17]认为行程时间是一个偏斜分布。Herman 和 Lam[18]建
议用伽码(Gamma)分布或对数正态分布来表征行程时间分布。Richardson 和 Taylor[19]发
现观测的行程时间服从对数正态分布。Polus[20]认为伽码分布比对数正态分布更适合于拟合
行程时间分布。Al-Deek 和 Emam[21] 建议用韦伯(Weibull)分布来拟合。Pu[22]、陈琨和于
雷[23]认为对数正态分布适合于行程时间分布。Susilawati et al.[26]基于 GPS 浮动车采集的
城市道路行程时间数据,认为 Burr Type XII 分布曲线较好的拟合了城市道路行程时间分布。
余春艳和邵春福等[27]分析处理道路实时交通数据,统计行程时间分布,得出路段行程时间
服从正态分布。基于这些行程时间分布,研究人员提出了一系列的行程时间可靠度量化指标
[7, 8, 15, 28-34]。典型的量化措施可以归纳为:百分位行程时间(如 95 分位行程时间)、标准方
差、协方差、偏斜度、缓冲指标、计划时间指标、拥挤频率、失效率和行程时间指标等(参
考 van Lint et al.[15]和 Lomax et al.[7]综述)。
行程时间可靠度量化指标的共同点是:①和行程时间分布有着密切的联系,尤其是和分
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
- 3 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
布形状相关;②基于行程时间分布曲线,侧重量化行程时间的不确定性(通常以行程时间的
100
变异性为量化指标)。
3 行程时间可靠度机理
目前已有的行程时间可靠度定义和量化指标在交通路网设计、交通控制方法、交通性能
评价、应急交通疏散仿真等方面得到了广泛的应用[12, 14, 15, 35-41],但行程时间可靠度的量化指
标存在多样化的现象。van Lint et al.[15]通过对实际采集的交通数据来分析标准方差等 8
中不同的行程时间可靠度量化指标,结果表明不同的指标或定义之间存在很大差异,各个指
标反映的结果也不一致。造成这种现象的原因之一可能是对行程时间可靠度机理的认识及其
量化上存在偏差[15]。
一方面,行程时间的不可靠包括由于交通供给和交通需求的随机波动造成的行程时间不
确定性[14]:交通流状态可能处于自由流状态也可能处于拥挤堵塞状态。另一方面,随机动态
是城市交通系统交通流的基本特性之一[42],而交通状态突变[43-49]在随机动态饱和交通流状
态下发生的概率高[44, 50]:当前处于自由流状态的交通流可能在短时间内由于干扰或事故等
随机因素导致交通流迅速变为拥挤堵塞状态。交通状态突变可能在流量低于通行能力时发
生,并且其发生具有一种概率特征[44, 49, 50]:饱和交通下交通状态突变发生的概率高,此时
的交通流处于极其不稳定状态;低流量交通状态下交通状态突变发生的概率低,此时的交通
流状态处于较为稳定的状态。由此可见,从机理分析来看,两个方面对行程时间可靠度产生
了重要的影响:交通供给与需求波动造成的不确定性和交通状态突变造成的不稳定性。从逻
辑上来说,不确定性和不稳定性并不是相互独立。交通状态突变发生前的行程时间不确定性
小,而交通状态突变发生后的不确定性高。然而现有的可靠度量化指标研究并没有完整地表
征行程时间可靠度的机理:相关研究重点量化了不确定性,鲜有成果详细考虑交通状态突变
导致的不稳定性影响[42]。
105
110
115
120
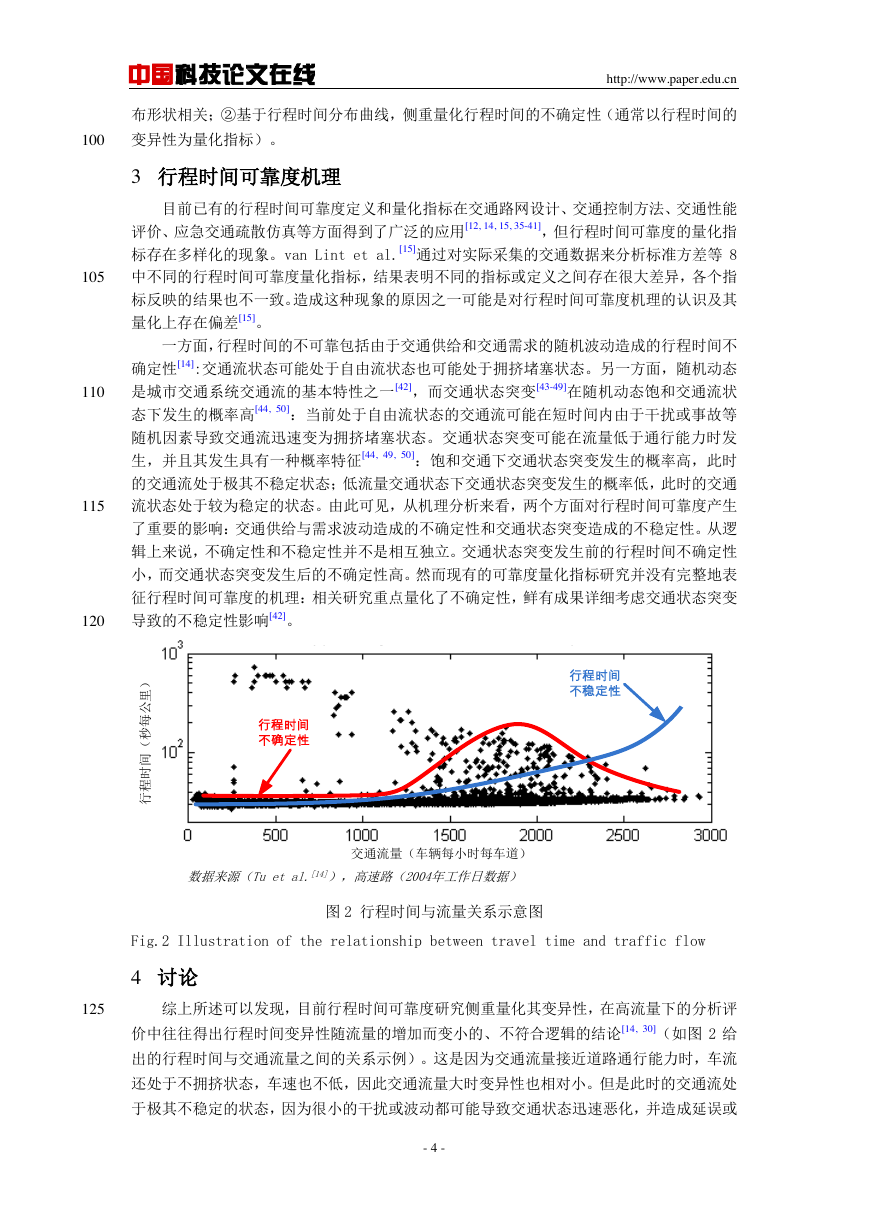
Fig.2 Illustration of the relationship between travel time and traffic flow
图 2 行程时间与流量关系示意图
4 讨论
125
综上所述可以发现,目前行程时间可靠度研究侧重量化其变异性,在高流量下的分析评
价中往往得出行程时间变异性随流量的增加而变小的、不符合逻辑的结论[14, 30](如图 2 给
出的行程时间与交通流量之间的关系示例)。这是因为交通流量接近道路通行能力时,车流
还处于不拥挤状态,车速也不低,因此交通流量大时变异性也相对小。但是此时的交通流处
于极其不稳定的状态,因为很小的干扰或波动都可能导致交通状态迅速恶化,并造成延误或
- 4 -
数据来源(Tu et al.[14]),高速路(2004年工作日数据)交通流量(车辆每小时每车道)行程时间(秒每公里)行程时间不确定性行程时间不稳定性�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
130
排队等后果,通常将这种现象的发生定义为交通状态突变(traffic breakdown)[43-49],尤
其是饱和交通流容易受由交通事件、交通事故和伴随着高流量的频繁干扰的交通状态突变影
响[43, 47]。行程时间作为表征交通流运行状态的重要指标必然受到交通状态突变的影响[51],
从而导致了高流量下的行程时间具有不稳定性特征[42]。由此可见,在交通流量大时,虽然
行程时间的不确定性(变异性)小,但由于此时发生交通状态突变的概率大,因此不稳定性
135
在交通流低密度下表现不明显,但在高密度下概率明显提高。而现有的行程时间可靠度定义
及其量化指标恰恰鲜有刻画高流量条件下交通状态突变对行程时间造成的不稳定性影响,导
致了行程时间可靠度在分析评价方面存在不符合逻辑的高流量高可靠性现象[14, 30]。此外,
由于影响行车时间可靠度的因素众多[15],因此难以建立一个基于多(影响)因素的、面向
可靠度路网性能评价的模型。
140
5 结论与展望
行程时间可靠度作为评价路网性能的重要指标,在定义、量化措施和应用等方面都得到
了广泛的关注与研究。然而目前行程时间可靠度研究以量化不确定性为主,在分析评价中往
往存在高流量高可靠性的、不符合逻辑的现象。造成这种现象的主要原因是忽略了考虑交通
状态突变引起的行程时间不稳定性。因此,行程时间可靠度的研究需要从揭示行程时间可靠
145
度的机理入手,在考虑交通状态突变的基础上提炼行程时间可靠度的基本元素,鉴别行程时
间的不确定性和不稳定性,建立交通状态突变(发生)概率随机模型和构建融合交通状态突
变的行程时间可靠度模型,为合理分析评价行程时间可靠度提供理论基础。行程时间可靠度
也需要从单纯考虑不确定性扩展到兼顾不稳定性,从而拓展行程时间可靠度的理论研究领
域,对于展示和量化行程时间可靠度机理有重要的意义,同时也为面向行程时间可靠度的路
150
网性能分析评价提供理论依据。
[参考文献] (References)
155
160
165
170
175
[1] 王殿海,祁宏生,徐程, 交通可靠性研究综述[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010. 10(5): p. 12-21.
[2] Ferrari, P., The Reliability of the Motorway Transport System[J]. Transportation Research Part B:
Methodological, 1988. 228(4): p. 291-310.
[3] 贺方会(导师金键), 基于浮动车数据的路段行程时间可靠性研究. 2010, 西南交通大学. p. 1-61.
[4] Bell, M.G.H., C. Cassir, Y. Iida, and W.H.K. Lam. A sensitivity-based approach to network reliability
assessment[C]. in Proceedings 14th International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory. 1999.
Jerusalem. p. 283-300.
[5] V&W, Mobility Paper (Dutch: Nota Mobiliteit), in 2005, Dutch Ministry of Transport, Public Works and
Water Management, http://www.notamobiliteit.nl: The Hague, The Netherlands.
[6] Bell, M., G.H. and Y. Iida, Transportation Network Analysis, Chapter 8: Network Reliability[J]. , ed. J.
Wiley and W.S. Sons. 1997. 179-192.
[7] Lomax, T., D. Schrank, S. Tyrmer, and R. Margiotta, Report of Selecting Travel Reliability Measures[M], in
2003, Texas Transportation Institute: Texas, USA.
[8] Asakura, Y. and M. Kashiwadani. Road Network Reliability Caused by Daily Fluctuation of Traffic Flow[C].
in Proceedings of the 19th PTRC Summer Annual Meeting. 1991. Brighton. p. 73-84.
[9] Asakura, Y. Reliability Measures of an Origin and Destination Pair in a Deteriorated Road Network with
Variable Flows[C]. in In: Proceedings of the 4th Meeting of the EURO Working Group in Transportation. 1996.
[10] Chen, A., H. Yang, H.K. Lo, and W.H. Tang, Capacity reliability of a road network: an assessment
methodology and numerical results[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2002. 36(3): p. 225-252.
[11] Clark, S. and D. Watling, Modelling network travel time reliability under stochastic demand[J].
Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2005. 39(2): p. 119.
[12] 郭志勇,王炜, 基于行程时间可靠度的区域交通控制系统评价方法[J]. 东南大学学报, 2010. 40(4): p.
848-851.
[13] 李志纯,黄海军. 拟动态随机停车行为模型及可靠度分析[C]. in 2005 年全国博士生学术论坛---交通
运输工程学科. 2005. p. 218-228.
- 5 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
[14] Tu, H., J.W.C. van Lint, and H.J. van Zuylen, The Impact of Traffic Flow on Travel Time Variability of
Freeway Corridors[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2007. 1993:
p. 59-66.
[14] Tu, H., J.W.C. van Lint, and H.J. van Zuylen, The Impact of Traffic Flow on Travel Time Variability of
Freeway Corridors[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2007. 1993:
p. 59-66.
[15] van Lint, J.W.C., H.J. van Zuylen, and H. Tu, Travel time unreliability on freeways: Why measures based on
variance tell only half the story [J]. Journal of Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2008. 42: p.
258-277.
[16] Nicholson, A. and Z.-P. Du, Degradable transportation systems: An integrated equilibrium model[J].
Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 1997. 31(3): p. 209.
[17] Wardrop, J.G. Some Theoretical Aspects of Road Traffic Research[C]. in Proceedings of the Institute of
Civil Engineers. 1952. p. 325-378.
[18] Herman, R. and T. Lam, Trip Time Characteristics of Journeys to and from Work.[M], in Transportation
and Traffic Theory, D.J. Buckley, Editor. 1974: Sydney. p. 57-85.
[19] Richardson, A.J. and M.A.P. Taylor, Travel Time Variability on Commuter Journeys[J]. High Speed
Ground Transportation Journal, 1978. 6: p. 77-79.
[20] Polus, A., A Study of Travel Time and Reliability on Arterial Routes[J]. Transportation, 1979. 8: p. 141-151.
[21] Al-Deek, H. and E.B. Emam, New Methodology for Estimating Reliability in Transportation Networks with
Degraded Link Capacities[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2006. 10: p. 117-129.
[22] Pu, W. Analytic Relationships between Travel Time Reliability Measures[C]. in www.trb.org Compendium of
papers TRB 90th Annual Meeting. 2010. Washington D.C., USA.
[23] 陈琨,于雷, 基于对数正态和分布的路径行程时间可靠性模型[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2009. 33(3): p.
35-39.
[24] 聂庆慧,夏井新,张韦华, 基于多源 ITS 数据的行程时间预测体系框架及核心技术[J]. 东南大学 学报
(自然科学版), 2011. 41(1): p. 199-204.
[25] 况爱武,黄中祥,况群, 随机需求道路网络出行时间可靠性评估方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2011. 46(5):
p. 861-867.
[26] Susilawati, S., M.A.P. Taylor, and S.V.C. Somenahalli, Distributions of Travel Time Variability on Urban
Roads[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2012. DOI: 10.1002/atr.192.
[27] 余艳春,邵春福,郭钰愫,熊志华, 基于实时数据的路网行程时间可靠度模型研究[J]. 现代交通技术,
2006. 2: p. 70-73.
[28] Fosgereau, M. and A. Karlstrom, The Value of Reliability[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological,
2010. 44(1): p. 38-49.
[29] Bates, J., J. Polak, P. Jones, and A. Cook, The Valuation of Reliability for Personal Travel[J]. Transportation
Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2001. 37: p. 191-229.
[30] Peer, S., C.C. Koopmans, and E.T. Verhoef, Prediction of travel time variability for cost-benefit analysis[J].
Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2012. 46(1): p. 79-90.
[31] 陈小鸿,冯均佳,杨超, 基于浮动车数据的行程时间可靠度特征研究[J]. 城市交通, 2007. 5(5): p. 42-45.
[32] 刘海旭,卜雷,蒲云, 随机路网的行程时间可靠性[J]. 土木工程学报, 2004. 37(8): p. 102-105.
[33] 李先,温慧敏,高永,陈琨, 北京市路网单位距离行程时间可靠性评价[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,
2007. 7(2): p. 72-76.
[34] Li, R., G. Rose, and M. Sarvi, Using Automatic Vehicle Identification Data to Gain Insight into Travel Time
Variability and its Causes[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 206.
1945: p. 24-32.
[35] 侯立文,蒋馥, 基于路网可靠性的路网服务水平[J]. 系统工程理论方法应用, 2002. 12(3): p. 248-252.
[36] 许良,高自友, 基于出行时间可靠性的城市交通路网设计[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2008. 20(2): p. 494-498.
[37] Li, H., M.C.J. Bliemer, and P.H.L. Bovy, Modeling Departure Time Choice with Stochastic Networks
Involved in Network Design[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board,
2009. 2091: p. 61-69.
[38] 张勇,王世明,杨晓光, 信号控制道路行程时间可靠度计算与实证[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2009.
37(6): p. 772-776.
[39] Tu, H., A.J. Pel, H. Li, and L. Sun, Travel Time Reliability During Evacuaiton: The Impact of Heterogeneous
Driving Behavior[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board (in press),
2012: p. 1-14.
[40] 陈艳艳,梁颖,杜华兵, 可靠度在路网运营状态评价中的应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2003. 36(1): p. 36-40.
[41] 罗霞,吴宗奇, 可靠性理论在路网规划中的应用[J]. 中国交通工程, 1993. 3: p. 22-24.
[42] 马寿峰,贺正冰,张思伟, 基于风险的交通网络可靠性分析方法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2010. 30(3): p.
550-556.
[43] 邓卫,李峻利, 高速公路常发性与偶发性交通拥挤的判别[J]. 东南大学学报, 1994. 24(2): p. 60-65.
[44] Elefteriadou, L., R.P. Roess, and W.R. Mcshane, Probabilistic Nature of Breakdown at Freeway Merge
Junctions[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1995. 1484: p.
80-89.
[45] Daganzo, C.F., M.J. Cassidy, and R.L. Bertini, Possible Explanations of Phase Transitions in Highway
Traffic[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 1999. 33(5): p. 365-379.
180
185
190
195
200
205
210
215
220
225
230
235
240
- 6 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
245
250
255
[46] Lorenz, M. and L. Elefteriadou. A probabilistic approach to defining freeway capacity and breakdown[C]. in
Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Highway Capacity. 2000. Transportation Research Board,
Washington, D. C. USA. p. 84-95
[47] Polus, A. and M.A. Pollatschek, Stochastic nature of freeway capacity and its estimation[J]. Canadian
Journal of Civil Engineering, 2002. 29: p. 842-852.
[48] 王欣,王炜,李文权,程琳, 用密度-流量关系模型解释交通流量陡降现象[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2009.
44(1): p. 141-146.
[49] Dong, J. and H.S. Mahmassani, Flow Breakdown and Travel Time Reliability[J]. Transportation Research
Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2009. 2124: p. 203-212.
[50] Kühne, R., R. Mahnke, I. Lubashevsky, and J. Kaupužs, Probabilistic Description of Traffic Breakdowns[J].
Physical Review E, 2002. 65(6): p. 6125.
[51] 杨超,涂颖菲,陈小鸿, 交通网络需求脆弱性分析及应用[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2012. 40(9):
p. 1329-1332.
- 7 -
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc