python+opencv车道线检测(简易实现)
车道线检测(简易实现)
python+opencv车道线检测(简易实现)
车道线检测(简易实现)
技术栈:python+opencv
技术栈:
实现思路:
实现思路:
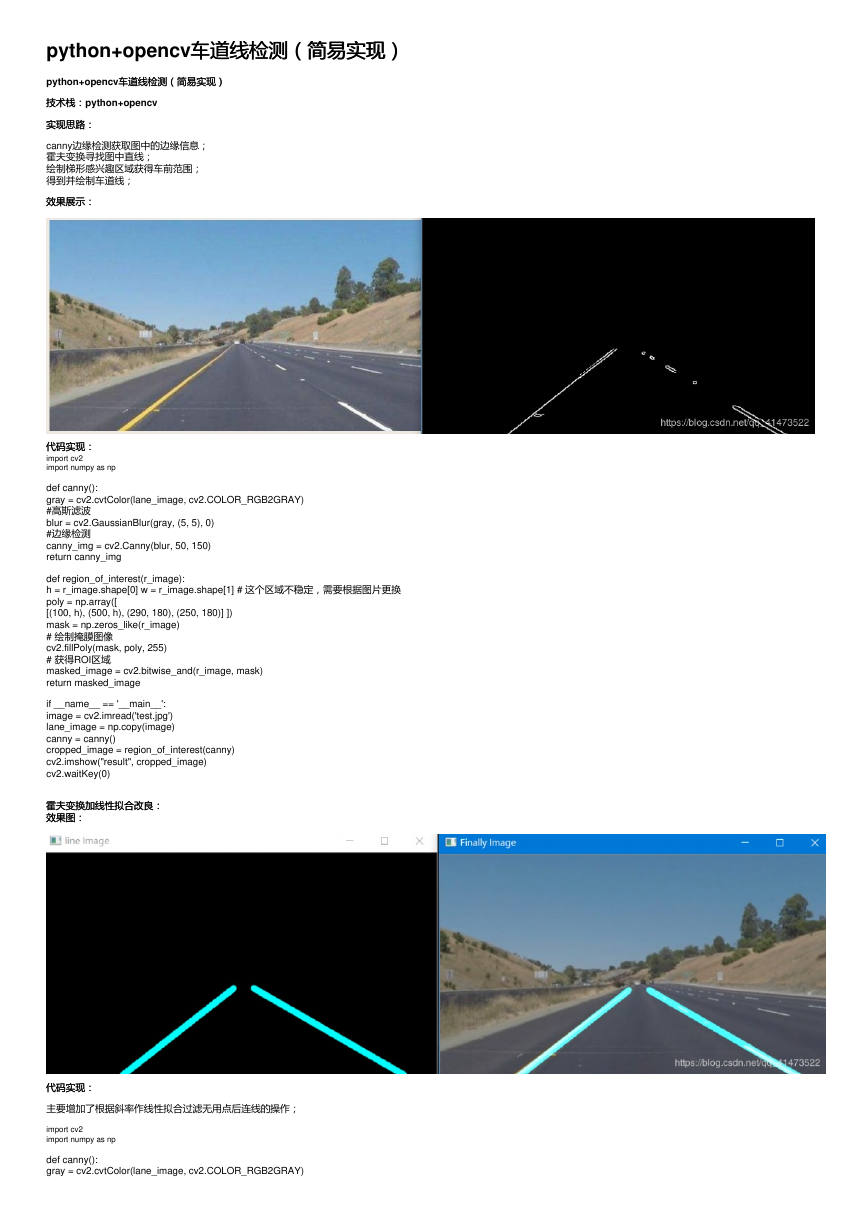
canny边缘检测获取图中的边缘信息;
霍夫变换寻找图中直线;
绘制梯形感兴趣区域获得车前范围;
得到并绘制车道线;
效果展示:
效果展示:
代码实现:
代码实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
def canny():
gray = cv2.cvtColor(lane_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
#高斯滤波
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
#边缘检测
canny_img = cv2.Canny(blur, 50, 150)
return canny_img
def region_of_interest(r_image):
h = r_image.shape[0] w = r_image.shape[1] # 这个区域不稳定,需要根据图片更换
poly = np.array([
[(100, h), (500, h), (290, 180), (250, 180)] ])
mask = np.zeros_like(r_image)
# 绘制掩膜图像
cv2.fillPoly(mask, poly, 255)
# 获得ROI区域
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(r_image, mask)
return masked_image
if __name__ == '__main__':
image = cv2.imread('test.jpg')
lane_image = np.copy(image)
canny = canny()
cropped_image = region_of_interest(canny)
cv2.imshow("result", cropped_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
霍夫变换加线性拟合改良:
霍夫变换加线性拟合改良:
效果图:
效果图:
代码实现:
代码实现:
主要增加了根据斜率作线性拟合过滤无用点后连线的操作;
import cv2
import numpy as np
def canny():
gray = cv2.cvtColor(lane_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
�
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
canny_img = cv2.Canny(blur, 50, 150)
return canny_img
def region_of_interest(r_image):
h = r_image.shape[0] w = r_image.shape[1]
poly = np.array([
[(100, h), (500, h), (280, 180), (250, 180)] ])
mask = np.zeros_like(r_image)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, poly, 255)
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(r_image, mask)
return masked_image
def get_lines(img_lines):
if img_lines is not None:
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
# 分左右车道
k = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
if k 0:
mean = np.mean(slope) # 计算平均斜率
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slope] # 每条线斜率与平均斜率的差距
idx = np.argmax(diff) # 找到最大斜率的索引
if diff[idx] > slo_th: # 大于预设的阈值选取
slope.pop(idx)
after_lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
return after_lines
def clac_edgepoints(points, y_min, y_max):
x = [p[0] for p in points] y = [p[1] for p in points]
k = np.polyfit(y, x, 1) # 曲线拟合的函数,找到xy的拟合关系斜率
func = np.poly1d(k) # 斜率代入可以得到一个y=kx的函数
x_min = int(func(y_min)) # y_min = 325其实是近似找了一个
x_max = int(func(y_max))
return [(x_min, y_min), (x_max, y_max)]
if __name__ == '__main__':
image = cv2.imread('F:\\A_javaPro\\test.jpg')
lane_image = np.copy(image)
canny_img = canny()
cropped_image = region_of_interest(canny_img)
lefts = [] rights = [] lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(cropped_image, 1, np.pi / 180, 15, np.array([]), minLineLength=40, maxLineGap=20)
get_lines(lines) # 分别得到左右车道线的图片
good_leftlines = choose_lines(lefts, 0.1) # 处理后的点
good_rightlines = choose_lines(rights, 0.1)
leftpoints = [(x1, y1) for left in good_leftlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in left] leftpoints = leftpoints + [(x2, y2) for left in good_leftlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in left]
rightpoints = [(x1, y1) for right in good_rightlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in right] rightpoints = rightpoints + [(x2, y2) for right in good_rightlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in right]
lefttop = clac_edgepoints(leftpoints, 180, image.shape[0]) # 要画左右车道线的端点
righttop = clac_edgepoints(rightpoints, 180, image.shape[0])
src = np.zeros_like(image)
cv2.line(src, lefttop[0], lefttop[1], (255, 255, 0), 7)
cv2.line(src, righttop[0], righttop[1], (255, 255, 0), 7)
cv2.imshow('line Image', src)
src_2 = cv2.addWeighted(image, 0.8, src, 1, 0)
cv2.imshow('Finally Image', src_2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
待改进:
待改进:
代码实用性差,几乎不能用于实际,但是可以作为初学者的练手项目;
斑马线检测思路
斑马线检测思路:获取车前感兴趣区域,判断白色像素点比例即可实现;
行人检测思路:opencv有内置行人检测函数,基于内置的训练好的数据集;
行人检测思路
作者:毛钱儿
�



 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc