1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose and Scope
1.2 Intended audience
1.3 Glossary
1.4 References
1.5 General presentation of the PN532
2. Configuration Modes
2.1 Standard Mode
2.2 PN512 emulation mode
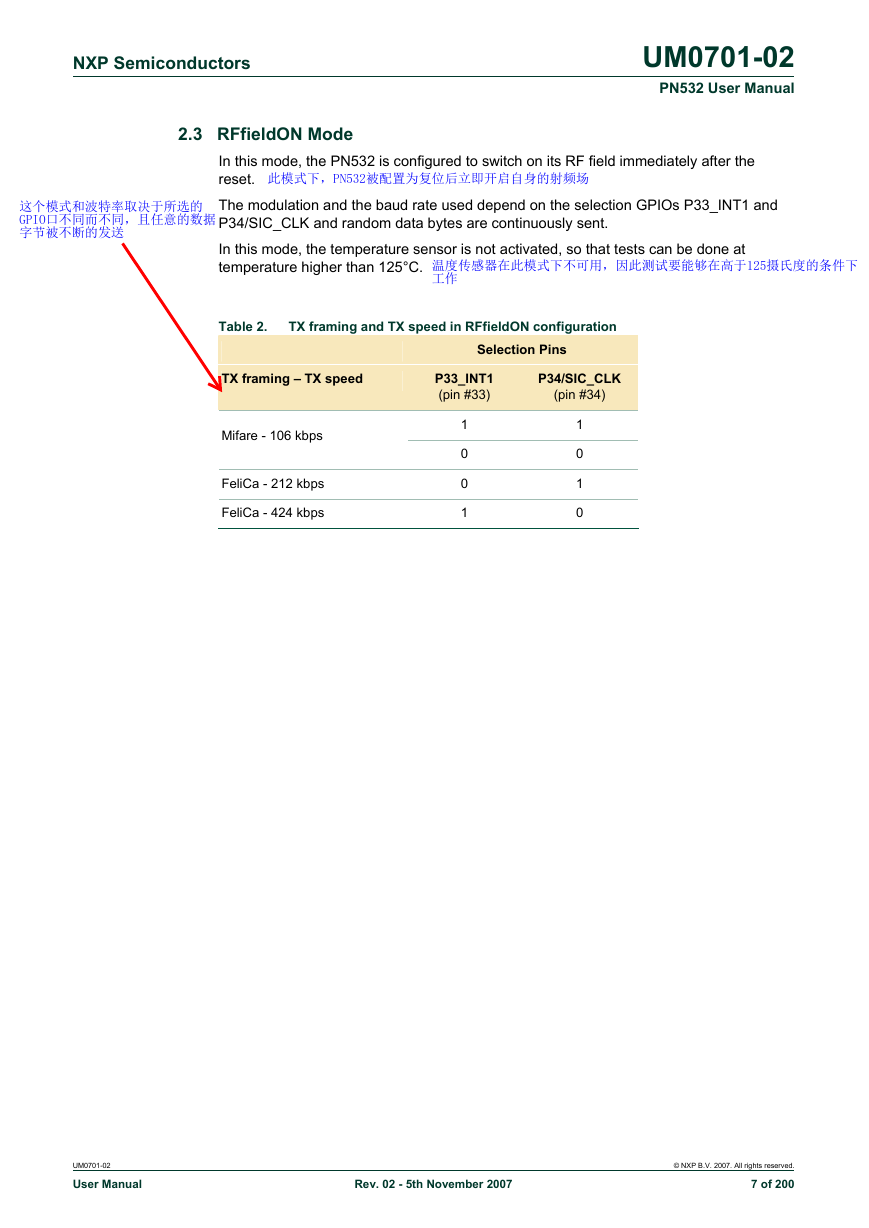
2.3 RFfieldON Mode
3. Power management
3.1.1 CPU frequency
3.1.2 Power modes of the PN532
3.1.2.1 Power modes for CPU
3.1.2.2 Power modes for Contact Less interface
3.1.3 Operating modes of the PN532
3.1.3.1 Mode dispatcher
3.1.3.2 Standby mode
3.1.3.3 LowVbat mode
3.1.3.4 Initiator / PCD mode
3.1.3.5 Target / PICC Mode
3.1.3.6 Virtual Card mode
3.1.3.7 Wired Card mode
3.1.3.8 Initialization sequence
3.1.3.9 Management of GPIO configuration
3.1.3.10 Management of RF field in the activation commands
4. ISO/IEC14443-4 PICC emulation concept
5. Over-current detection
6. Host controller Interfaces
6.1 General points
6.1.1 Possible links
6.1.1.1 SPI interface
6.1.1.2 HSU interface
6.1.1.3 I2C interface
6.1.2 P70_IRQ pin
6.2 Host controller communication protocol
6.2.1 Frames structure
6.2.1.1 Normal information frame
6.2.1.2 Extended information frame
6.2.1.3 ACK frame
6.2.1.4 NACK frame
6.2.1.5 Error frame
6.2.1.6 Preamble and Postamble
6.2.2 Dialog structure
6.2.2.1 Data link level
6.2.2.2 Application level
6.2.3 HSU communication details
6.2.4 I2C communication details
6.2.4.1 Classic I2C communication (without Handshake mechanism combination)
6.2.4.2 Advanced I2C communication (with Handshake mechanism combination)
6.2.5 SPI communication details
6.2.5.1 Classic SPI communication (without Handshake mechanism combination)
6.2.5.2 Advanced SPI communication (with Handshake mechanism combination)
6.3 Handshake mechanism
6.3.1 General presentation
6.3.2 Handshake mechanism in case of HSU link
6.3.2.1 Case of LowVbat
6.3.2.2 Normal case
6.3.2.3 Case of PN532 in Power Down mode
6.3.2.4 Case of the TgInitAsTarget command
6.3.2.5 Case of SAMConfiguration – Virtual Card
6.3.3 Handshake mechanism in case of I2C link
6.3.3.1 Case of LowVbat
6.3.3.2 Normal case
6.3.3.3 Case of PN532 in Power Down mode
6.3.3.4 Case of the TgInitAsTarget command
6.3.3.5 Case of SAMConfiguration – Virtual Card
6.3.4 Handshake mechanism in case of SPI link
6.3.4.1 Case of LowVbat
6.3.4.2 Normal case
6.3.4.3 Case of PN532 in Power Down mode
6.3.4.4 Case of the TgInitAsTarget Command
6.3.4.5 Case of SAMConfiguration – Virtual Card
7. Commands supported
7.1 Error handling
7.2 Miscellaneous commands
7.2.1 Diagnose
7.2.2 GetFirmwareVersion
7.2.3 GetGeneralStatus
7.2.4 ReadRegister
7.2.5 WriteRegister
7.2.6 ReadGPIO
7.2.7 WriteGPIO
7.2.8 SetSerialBaudRate
7.2.9 SetParameters
7.2.10 SAMConfiguration
7.2.11 PowerDown
7.3 RF Communication command
7.3.1 RFConfiguration
7.3.2 RFRegulationTest
7.3.3 InJumpForDEP
7.3.4 InJumpForPSL
7.3.5 InListPassiveTarget
7.3.6 InATR
7.3.7 InPSL
7.3.8 InDataExchange
7.3.9 InCommunicateThru
7.3.10 InDeselect
7.3.11 InRelease
7.3.12 InSelect
7.3.13 InAutoPoll
7.3.14 TgInitAsTarget
7.3.15 TgSetGeneralBytes
7.3.16 TgGetData
7.3.17 TgSetData
7.3.18 TgSetMetaData
7.3.19 TgGetInitiatorCommand
7.3.20 TgResponseToInitiator
7.3.21 TgGetTargetStatus
7.4 Commands summary
7.4.1 Commands for Initiator mode
7.4.2 Commands for Target mode
7.4.3 Commands for ISO/IEC14443-4 PICC mode
7.4.4 Target states summary
7.4.5 DEP chaining mechanism
7.4.6 ISO/IEC14443-4 PICC emulated chaining mechanism
7.4.7 Comparison of the length of Payload data field
7.5 Examples of use
7.5.1 PN532 acting as Mifare PCD
7.5.2 PN532 acting as FeliCa PCD
7.5.3 PN532 acting as 106 kbps target
7.5.4 PN532 acting as 212 kbps target
7.5.5 Peer to Peer example with two PN532 (passive mode)
7.5.6 Peer to Peer example with two PN532 (active mode)
8. Appendix
8.1 Command set
9. Legal information
9.1 Definitions
9.2 Disclaimers
9.3 Licenses
9.4 Patents
9.5 Trademarks
10. Tables
11. Figures
12. Contents














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc