实验 2 进程状态转换及其 PCB 的变化
1.目的:
自行编制模拟程序,通过形象化的状态显示,使学生理解进程的概念、进程之间的状态
转换及其所带来的 PCB 内容 、组织的变化,理解进程与其 PCB 间的一一对应关系。
2. 内容及要求:
1)
2)
3)
4)
设计并实现一个模拟进程状态转换及其相应 PCB 内容、组织结构变化的程序。
独立编写、调试程序。进程的数目、进程的状态模型(三状态、五状态、七状
态或其它)以及 PCB 的组织形式可自行选择。
合理设计与进程 PCB 相对应的数据结构。PCB 的内容要涵盖进程的基本信息、控
制信息、资源需求及现场信息。
设计出可视性较好的界面,应能反映出进程状态的变化引起的对应 PCB 内容、
组织结构的变化。
代码书写要规范,要适当地加入注释。
鼓励在实验中加入新的观点或想法,并加以实现。
5)
6)
7) 认真进行预习,完成预习报告。
8) 实验完成后,要认真总结,完成实验报告。
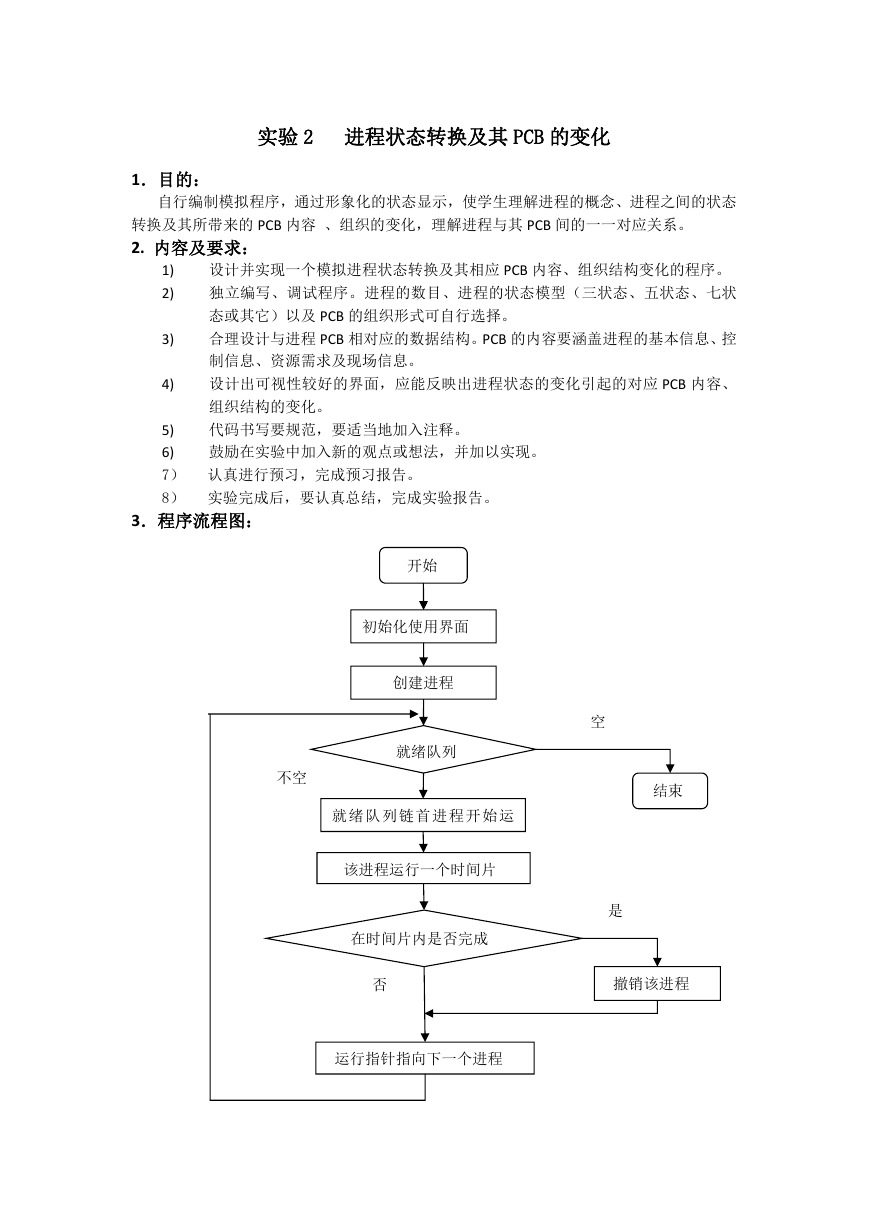
3.程序流程图:
开始
初始化使用界面
创建进程
就绪队列
不空
就绪 队列 链首 进程 开始 运
该进程运行一个时间片
在时间片内是否完成
结束
空
是
否
撤销该进程
运行指针指向下一个进程
�
4.使用的数据结构及说明:
在本实验中,主要用到的数据结构是 PCB 的结构,其中 PCB 的数据结构如下:
struct PCB
{
int P_Id;
char P_Name[10];
char P_State[10];
int P_Runtime;
int P_Requiry;
struct PCB * next ;
} ;
//PCB 的 ID 号
//PCB 的名称
//PCB 状态
//PCB 的所需要的运行时间
//PCB 所需要的资源要求
//PCB 块的下一个指针
其中,P_Id,和 P_Name 用来标示一个进程,而 P_State 用来标示进程的五种状态:
Create_state,Ready_state,Block_state,Run_state,Exit_state。P_Runtime 标示要完成一个进程所
需要的时间。P_Requiry 标示一个进程的执行所需要的其他条件,当其他的条件满足,则
P_Requiry 置 1,否则置 0。Struct PCB * next 用来指向同一队列中的下一个 PCB 块。
5.程序源代码,注释及说明文字:
#include"stdlib.h"
#include"stdio.h"
#include"string.h"
/********** globle structure and viable ******/
struct PCB
{
int P_Id;
char P_Name[10];
char P_State[10];
int P_Runtime;
int P_Requiry;
struct PCB * next ;
} ;
struct PCB * Create_state;
struct PCB * Run_state;
struct PCB * Ready_state;
struct PCB * Block_state;
struct PCB * Exit_state;
//PCB 的 ID 号
//PCB 的名称
//PCB 状态
//PCB 的所需要的运行时间
//PCB 所需要的资源要求
//PCB 块的下一个指针
//创建状态
//运行状态
//就绪状态
//阻塞状态
//退出状态
int signal4=0;
int signal5=0;
//标示进程 4 的完成状态
//标示进程 5 的完成状态
void InsertQueue(struct PCB **head,struct PCB *node)
{
/* insert node function */
struct PCB * p,*q;
node->next=NULL;
�
//如果队列为空
//队列不空
//找到最后的元素位置
if(*head==NULL)
{
*head=node;
}
Else
{
p=*head;
q=p->next;
while(q!=NULL)
{
p=q;
}
q=q->next;
p->next=node;
//将节点插入队列
}
}
void DeleteQueue(struct PCB **head,struct PCB *node)
{
//撤销进程,从队列中删除元素
//如果队列为空,返回
//如果要删除的元素是队首元素
//如果不是队列的首元素
struct PCB *p,*q;
q=*head;
if(*head==NULL||node==NULL)
return ;
if(*head==node)
*head=(*head)->next;
return;
{
}
Else
{
while(q->next!=p&&q->next!=NULL)
q=q->next;
q=p->next;
p->next=NULL;
}
}
void Display_Process(struct PCB * node)
{
//打印进程状态的元素函数
printf("\n\nthis process Id is
printf("this process name is
printf("this process state is
printf("this process Runtime is
: %d \n",node->P_Id);
: %s \n",node->P_Name);
: on %s \n ",node->P_State);
: %d \n",node->P_Runtime);
�
if(node->P_Requiry)
printf("this process resource is ready
\n");
else
printf("this process resource is not ready ! \n");
}
void DispatchToBlock(struct PCB *node)
{
// /* dispatch to block function*/
//调度到阻塞状态的函数
//struct PCB *p=(struct PCB *)malloc(sizeof(struct PCB));
if(!node->P_Requiry)
//如果所需要的资源没有满足则,调度到阻塞状态
{
strcpy(node->P_State,"block");
InsertQueue(&Block_state,node);
//插入到阻塞队列
Display_Process(node);
}
}
void DispatchToReady(struct PCB *node)
{
if(node->P_Requiry)
{
strcpy(node->P_State,"Ready");
InsertQueue(&Ready_state,node);
Display_Process(node);
}
}
// dispatch to ready state
//调度到就绪状态的函数
//如果所需的资源满足,则调度
void DispatchBlockToReady()
{
//dispatch the process to readyqueue
//从阻塞状态调度到就绪状态函数
struct PCB*p,*q;
q=Block_state;
while(q!=NULL)
{
p=q;
q=q->next;
if(signal4&&p->P_Id==4)
{
//如果阻塞状态队列不空
//如果所需要的资源满足
DeleteQueue(&Block_state,p);
strcpy(p->P_State,"ready");
InsertQueue(&Ready_state,p);
printf("process4 will be in the state of ready!\n");
Display_Process(p);
}
if(signal5&&p->P_Id==5)
�
DeleteQueue(&Block_state,p);
strcpy(p->P_State,"ready");
InsertQueue(&Ready_state,p);
printf("process5 will be in the state of ready!\n");
Display_Process(p);
{
}
}
}
void Create_Process()
{
int i;
struct PCB *p;
char name[10];
strcpy(name,"process");
for(i=1;i<3;i++)
{
p=(struct PCB *)malloc(sizeof(struct PCB));
p->P_Id=i;
name[7]=i+'0';
name[8]='\0';
strcpy(p->P_Name,name);
strcpy(p->P_State,"create");
p->P_Runtime=1;
p->P_Requiry=0;
//创建进程函数
//动态创建 2 个处于阻塞状态的进程
//所需要的时间片为 1
Display_Process(p);
sleep(4);
printf(" \n process%d will be in the state of Block, waiting the resource ready \n\n",i);
DispatchToBlock(p);
//同时调度到阻塞队列
//创建 4 个就绪状态的队列
}
for(i=3;i<7;i++)
{
p=(struct PCB *)malloc(sizeof(struct PCB));
p->P_Id=i;
name[7]=i+'0';
name[8]='\0';
strcpy(p->P_Name,name);
strcpy(p->P_State,"create");
p->P_Requiry=1;
if(i==6)
//在这里个进程 6 所需要的时间片为 2
�
p->P_Runtime=2;
else
p->P_Runtime=1;
Display_Process(p);
sleep(4);
printf(" \n process%d will be in the state of Ready, waiting to run \n\n",i);
DispatchToReady(p);
}
}
void display(struct PCB **head)
{
struct PCB *p,*q;
p=*head;
while(p!=NULL)
{
//打印各个状态队列里进程数目
sleep(2);
//printf("\n\n///////////////////////////////////\n");
printf("\n\nthis process Id is
printf("this process name is
printf("this process state is
printf("this process Runtime is
: %d \n",p->P_Id);
: %s \n",p->P_Name);
: on %s \n ",p->P_State);
: %d \n",p->P_Runtime);
if(p->P_Requiry)
printf("this process resource is ready
\n");
else
printf("this process resource is not ready ! \n");
p=p->next;
}
}
void Process_Run()
{
struct PCB *p,*q;
p=Ready_state;
q=p;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->P_Runtime<=0) break;
strcpy(p->P_State,"running");
Display_Process(p);
p->P_Runtime=p->P_Runtime-1;
sleep(4);
//进程运行函数
//就绪队列不空则继续执行
//如果时间片执行完了,则跳出循环
�
if(p->P_Runtime>0)
{
//没有完成,则进入就绪队列
printf("this process is not finished,will be dispatch to the ready queue!!\n");
DeleteQueue(&Ready_state,p);
strcpy(p->P_State,"ready");
InsertQueue(&Ready_state,p);
Display_Process(p);
}
Else
{
//执行完成,则跳出,并发送相应的信息
printf("\n\nProcess%d is finished and will be in the state of exit!\n\n",p->P_Id);
if(p->P_Id==4) signal4=1;
if(p->P_Id==5) signal5=1;
}
if(signal4||signal5)
DispatchBlockToReady();
//如果资源满足,则将进程调度到就绪队列
q=q->next;
p=q;
}
if(q==NULL)
printf("\nthere is no process ready!\n
}
STOP Machine!!!\n");
int main(int argc,char * argv[])
{
//主函数
//界面
int i;
char c='c';
printf("\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ \n");
printf("...................................Ding Hai bo\n");
printf("......Press s to start the process.......\n");
scanf("%c",&c);
while(1)
{
if(c=='s')break;
scanf("%c",&c);
}
Create_Process();
printf("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n");
printf("\n>>>>>>> Display the Ready queue
sleep(5);
display(&Ready_state);
printf("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n");
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n");
//调用创建进程函数
////////////////显示就绪队列里的进程
printf("\n>>>>>>>> Display the Block queue
>>>>>>>>>>>>\n");
�
sleep(5);
display(&Block_state);
printf("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n\n\n");
/////////////////////
//显示阻塞队列函数
printf("\n>>>>>>>> Now the process start to run
sleep(5);
Process_Run();
}
>>>>>>>>>>>\n");
//调用进程运行函数
6.运行结果及说明:
运行结果的截图:
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc