python训练训练——简单股票数据分析
简单股票数据分析
本程序仅为个人学习测试使用,不做商业用途,据此操作,后果自负
本程序仅为个人学习测试使用,不做商业用途,据此操作,后果自负
主要的策略就是通过计算涨幅和平均值来判断买入与卖出的时机。
因为我自己本身对股票了解不多,所以我写的东西要为其他策略可能还是会有点困难的。
框架解释
框架解释
获取数据
用爬虫等相关操作获取到数据,并保存到本地,以避免重复爬取浪费时间与性能
将本地的数据导入我们的程序
通过保存的数据计算涨幅,并获取涨幅最大的股票
计算某段时间内的平均价格
实行买卖的判断
买操作
卖操作
画图,实现数据可视化
代码实现
代码实现
做最开始的初始化
做最开始的初始化
1. 输入参数的初始化
输入参数的初始化
codes
传入所需要分析的代码
列表格式,建议在定义对象之前就写好这个列表
默认是空,也就是 “[]”
in_date
数据分析最开始的日期
默认是2014-01-01
这个日期在后续的计算中会一直后推,直到等于time
time
数据分析的截止日期
默认是系统现在的日期,而且要格式化为“年-月-日”
time_span_inc
用于分析涨幅
默认13,即求13天内的涨幅
time_span_avg
用于分析平均价格
默认13,即求13天内的平均价格
funds
是你手上现有的资金
默认为10w
path
传入保存地址
2. 全局变量的初始化
全局变量的初始化
self.df = None
保存从本地文件中获取的数据
self.the_code = {“code”: None, “price”: None}
保存你手上持有的股票和买入的价格
在后续中可以改为列表,然后再添加一个字典属性:持有量
self.change = {“funds”: [], “date”: []}
获取所持有资金的变化数据,为后面 数据可视化做准备
3.示例示例
def __init__(self, codes=[], in_date="2014-01-01", time=time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime(time.time())),
time_span_inc=13, time_span_avg=13, funds=100000, path="D:/"):
self.codes = codes # 所需要获取的股票
self.in_date = in_date # 数据处理开始日期
self.time = time # 数据处理结束日期
self.time_span_inc = time_span_inc # 涨幅跨度
self.time_span_avg = time_span_avg # 平均值跨度
self.funds = funds # 现有资金
self.path = path # 获取股票数据保存的地址
self.df = None
self.the_code = {"code": None, "price": None}
self.change = {"funds": [], "date": []}
在互联网上获取数据
在互联网上获取数据
因为爬取的方法很多很多,我只用了最简单的方法
主要是通过循环获取传入的股票代码的相关信息,并格式化保存到本地
这个方法是只需要运行一次,把数据保存下来以后可以重复使用,方便改数据调整方案。
示例示例
获取的初步结果,所有相关数据都有,但是我们只要收盘的数据
�
筛选并保存数据
首先将“Close”这一列的标签索引重命名,然后只把这一列保存下来
这个就是保存的格式
在个别电脑上会出现只保留后面的数据,而不保存表头的情况,建议在保存到本地之后检查一下格式是否和下面是否相同
相关代码
# 获取相关数据
def get_all_data(self):
# 获取数据的时间段-结束时间
end = datetime.date.today()
for code in self.codes:
# 这个方法是pandas_datareader.data里面自带的,通过传入股票代码可以在相关网站获取对应数据
stock = web.DataReader(code, "yahoo", self.in_date, end)
# 将“Close”重命名为对应的code
stock.rename(columns={"Close": code}, inplace=True)
stock[code].to_csv(self.path + code + ".csv") # 保存到本地
获取本地的数据
获取本地的数据
将本地的数据获取到目前的程序里面来
# 获取Excel中数据,并存到data列表中
def get_data(self):
# 直接将self.df初始化为第一支股票对应的数据,后面的数据只需要在这个基础上列相加就好了
self.df = pd.read_csv(self.path + self.codes[0] + ".csv")
# 通过循环获取所有的数据
for code in self.codes[1:]:
# 获取csv文件
df = pd.read_csv(self.path + code + ".csv")
# 数据合并
self.df = pd.merge(self.df, df, left_on="Date", right_on="Date", how="outer")
# 将索引设置为date
self.df.set_index('Date', inplace=True)
获取某一天之前n天前的数据
获取某一天之前
天前的数据
这里的n是前面初始化的时候定义的time_span_inc与time_span_avg中更大的那个,为了在后续的处理中可以有充足的数据
获取的方法最好用切片,效率高也看起来方便,但是我的返回值时用的numpy,后面的操作基本上是根据numpy来的,所以懒得改了
# 获取那n天的数据,格式是numpy
def get_n_day(self, in_data):
try:
# 获取输入那天的位置索引
position_index = self.df.index.get_loc(in_data)
# 如果位置索引小于计算所需要的数字,那么说明数据量不够,
if position_index>=max(self.time_span_avg, self.time_span_inc):
# 用于保存每支股票的数据
code_list = [] for code in range(len(self.codes)):
# 用于保存当前股票的数据
i_list = [] for i in range(max(self.time_span_avg, self.time_span_inc)):
# 获取数据
i_list.append(self.df.iloc[position_index - i - 1, code])
code_list.append(i_list)
# 这个地方应该要用切片来获取数据的,这么改虽然麻烦但是看得懂啊(其实就是懒得改了)
return np.array(code_list)
# 数据量不够,不能带入进行计算
else:
return np.array([0])
except Exception as e:
print("获取"+in_data+"的近日数据失败,估计这天没开盘,没有数据")
return np.array([0])
获取涨幅与平均价格
获取涨幅与平均价格
在获取涨幅的时候,还顺便获取了涨幅最大的股票代码号的序列号
# 计算涨幅
def get_increase(self, result):
inc = [] for code in range(len(self.codes)):
# 今天的价格/time_span_inc天前的价格 - 1
increase = (result[code][0] / result[code][self.time_span_inc - 1]) - 1
inc.append(increase)
# 不仅仅获取了对应的涨幅,还获取了涨幅最大的股票代码号的序列号
return inc, inc.index(max(inc))
# 计算平均价格
def get_avg(self, result):
avg_result = result[:, :self.time_span_avg].mean(axis=1)
return avg_result
模拟买卖
模拟买卖
买的条件是判断现在的价格大于平均价格,涨幅最大而且要大于0
卖的条件是现在持有的股票不再是涨幅第一,或者现价小于近些天的平均价格
买卖的过程基本上就是重置手上持有的股票和持有的资金来完成的
1. 判断是买还是卖
判断是买还是卖
# 判断实行买卖
def buy_sell(self, increase, avg, result):
# 参考数据
# ([0.05955, 0.02632, 0.058093], 0) 最后一个是涨幅最大的代码号
# [1.68161 3.96707 5.50792] 这段时间的平均价格
# [1.70799 4.01599 5.62799] 当前天的价格
�
# 获取现在涨幅最大股票的价格和平均价格
new_price = result[increase[1]] avg_price = avg[increase[1]]
# 如果没有持有的股票则考虑买入
if self.the_code["code"] is None:
# 满足条件:现在的价格大于平均价格,涨幅最大而且要大于0
if new_price > avg_price:
self.buy(self.codes[increase[1]], new_price)
# 如果现在持有的股票不再是涨幅第一,或者现价小于近些天的平均价,或者到了最后一天更新时间
elif (self.the_code["code"] != self.codes[increase[1]]) | (new_price avg_price) & (increase[0][increase[1]] > 0):
self.buy(self.codes[increase[1]], new_price)
else:
print(self.in_date + "继续持有:", self.the_code["code"])
2. 卖卖
def sell(self, result):
# 因为卖出了,更新现有资金,并将现在持有的股票清空,用现在的价格/先前的价格再*现有的资金
print("卖" + "*" * 30)
print("在" + self.in_date + "卖出")
print("全部卖出:", self.the_code["code"])
# 卖出价格是持有股票(self.the_code["code"])的现价
sell_price = result[self.codes.index(str(self.the_code["code"]))] print("卖出价格", sell_price)
# 更新价格
self.funds = self.funds * (sell_price / self.the_code["price"])
self.change["funds"].append(self.funds)
self.change["date"].append(self.in_date)
self.the_code["code"] = None
self.the_code["price"] = None
print("资金持有变为:", self.funds)
print("*" * 30)
3. 买买
def buy(self, code, new_price):
# 更新持有股票和对应买入价格
self.the_code["code"] = code
self.the_code["price"] = new_price
self.change["funds"].append(self.funds)
self.change["date"].append(self.in_date)
print("在" + self.in_date + "买入")
print("将资金全部买入", self.the_code["code"])
print("买入价格:", self.the_code["price"])
print("资金持有变为:", self.funds)
print("*" * 30)
后续辅助功能
后续辅助功能
将时间后推
tim就是后推的天数
没有返回值,直接操作in_date
# 输入某天获取到第二天的str
def get_next_day(self, tim=1):
timeArray = time.strptime(self.in_date, "%Y-%m-%d")
timeStamp = int(time.mktime(timeArray))
timeStamp = timeStamp + 86400 * tim
timeArray = time.localtime(timeStamp)
self.in_date = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", timeArray)
画一个能看的图
# 画图
def draw(self):
x = self.change["date"] y = self.change["funds"] # 设置图片大小
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), dpi=80)
# 绘图(折线)
plt.plot(x, y, color="red", linewidth=2, alpha=0.6)
# 设置轴的刻度
plt.xticks(list(x)[::20], x[::20], rotation=45) # rotation 为旋转角度
# 展示图片
plt.show()
最后的执行框架
最后的执行框架
获取本地数据
从第一天开始循环,将in_date后推
获取涨幅与平均价格
判断买卖,并实行
在循环结束之后输出现有的资金,和最大持有资金
画一个折线图反映变化
# 主函数
def the_main(self):
self.get_data()
while self.in_date != self.time:
# 获取涨幅以及平均价格
np_result = self.get_n_day(self.in_date)
# 得确定获取的数据是非为空
if np_result.any():
increase = self.get_increase(np_result)
# 再次确定获取的数据是非为空
if increase != 0:
avg = self.get_avg(np_result)
# 进行买卖等操作
self.buy_sell(increase, avg, np_result[:, 0])
# 进入下一天
self.get_next_day()
print("现在持有", self.funds)
print(max(self.change["funds"]))
�
self.draw()
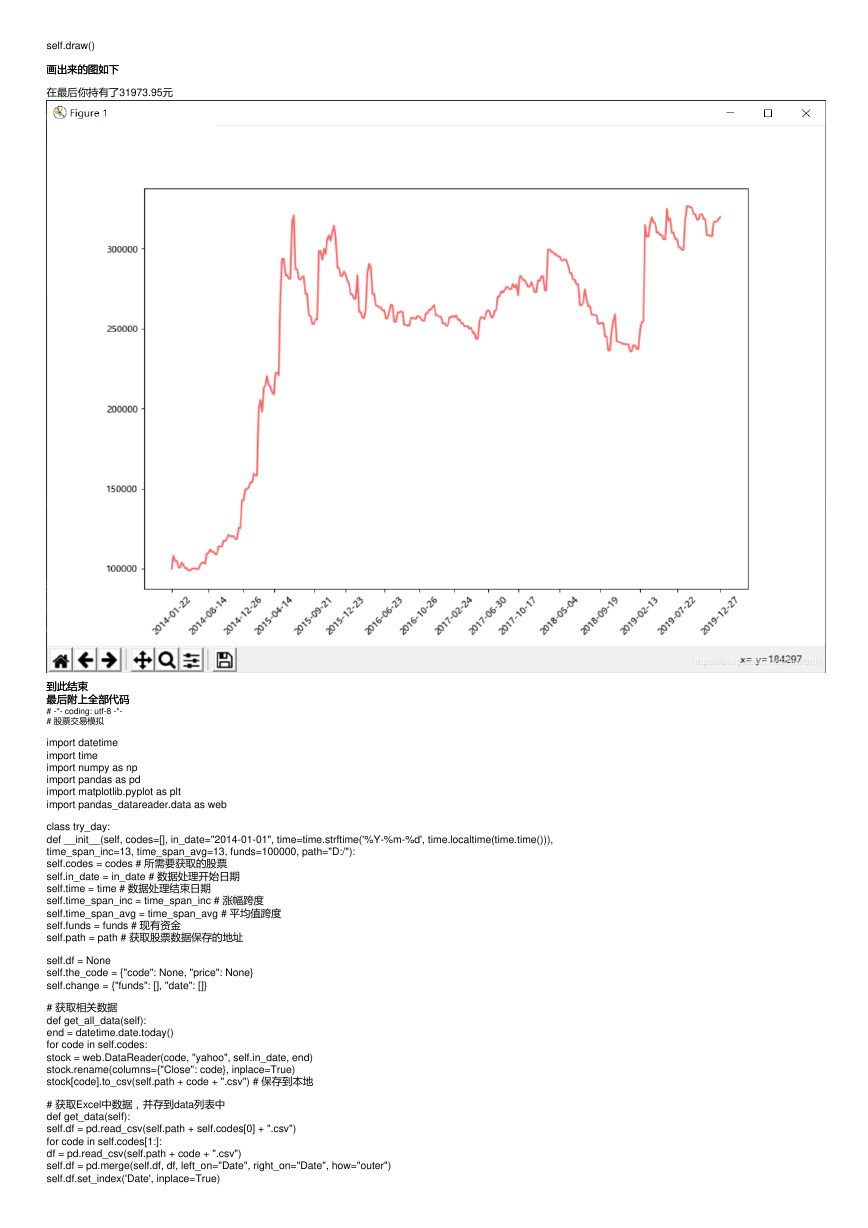
画出来的图如下
画出来的图如下
在最后你持有了31973.95元
到此结束
到此结束
最后附上全部代码
最后附上全部代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 股票交易模拟
import datetime
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas_datareader.data as web
class try_day:
def __init__(self, codes=[], in_date="2014-01-01", time=time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime(time.time())),
time_span_inc=13, time_span_avg=13, funds=100000, path="D:/"):
self.codes = codes # 所需要获取的股票
self.in_date = in_date # 数据处理开始日期
self.time = time # 数据处理结束日期
self.time_span_inc = time_span_inc # 涨幅跨度
self.time_span_avg = time_span_avg # 平均值跨度
self.funds = funds # 现有资金
self.path = path # 获取股票数据保存的地址
self.df = None
self.the_code = {"code": None, "price": None}
self.change = {"funds": [], "date": []}
# 获取相关数据
def get_all_data(self):
end = datetime.date.today()
for code in self.codes:
stock = web.DataReader(code, "yahoo", self.in_date, end)
stock.rename(columns={"Close": code}, inplace=True)
stock[code].to_csv(self.path + code + ".csv") # 保存到本地
# 获取Excel中数据,并存到data列表中
def get_data(self):
self.df = pd.read_csv(self.path + self.codes[0] + ".csv")
for code in self.codes[1:]:
df = pd.read_csv(self.path + code + ".csv")
self.df = pd.merge(self.df, df, left_on="Date", right_on="Date", how="outer")
self.df.set_index('Date', inplace=True)
�
# 获取那n天的数据,格式是numpy
def get_n_day(self, in_data):
try:
position_index = self.df.index.get_loc(in_data)
if position_index >= max(self.time_span_avg, self.time_span_inc):
code_list = [] for code in range(len(self.codes)):
i_list = [] for i in range(max(self.time_span_avg, self.time_span_inc)):
i_list.append(self.df.iloc[position_index - i - 1, code])
code_list.append(i_list)
return np.array(code_list)
else:
return np.array([0])
except Exception as e:
return np.array([0])
# 计算涨幅
def get_increase(self, result):
inc = [] for code in range(len(self.codes)):
increase = (result[code][0] / result[code][self.time_span_inc - 1]) - 1
inc.append(increase)
return inc, inc.index(max(inc))
# 计算平均价格
def get_avg(self, result):
avg_result = result[:, :self.time_span_avg].mean(axis=1)
return avg_result
# 判断实行买卖
def buy_sell(self, increase, avg, result):
new_price = result[increase[1]] avg_price = avg[increase[1]] if self.the_code["code"] is None:
if new_price > avg_price:
self.buy(self.codes[increase[1]], new_price)
elif (self.the_code["code"] != self.codes[increase[1]]) | (new_price avg_price) & (increase[0][increase[1]] > 0):
self.buy(self.codes[increase[1]], new_price)
else:
print(self.in_date + "继续持有:", self.the_code["code"])
def sell(self, result):
print("卖" + "*" * 30)
print("在" + self.in_date + "卖出")
print("全部卖出:", self.the_code["code"])
sell_price = result[self.codes.index(str(self.the_code["code"]))] print("卖出价格", sell_price)
self.funds = self.funds * (sell_price / self.the_code["price"])
self.change["funds"].append(self.funds)
self.change["date"].append(self.in_date)
self.the_code["code"] = None
self.the_code["price"] = None
print("资金持有变为:", self.funds)
print("*" * 30)
def buy(self, code, new_price):
self.the_code["code"] = code
self.the_code["price"] = new_price
self.change["funds"].append(self.funds)
self.change["date"].append(self.in_date)
print("在" + self.in_date + "买入")
print("将资金全部买入", self.the_code["code"])
print("买入价格:", self.the_code["price"])
print("资金持有变为:", self.funds)
print("*" * 30)
# 画图
def draw(self):
x = self.change["date"] y = self.change["funds"] plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), dpi=80)
plt.plot(x, y, color="red", linewidth=2, alpha=0.6)
plt.xticks(list(x)[::20], x[::20], rotation=45) # rotation 为旋转角度
plt.show()
# 主函数
def the_main(self):
self.get_data()
while self.in_date != self.time:
np_result = self.get_n_day(self.in_date)
if np_result.any():
increase = self.get_increase(np_result)
if increase != 0:
avg = self.get_avg(np_result)
self.buy_sell(increase, avg, np_result[:, 0])
# 进入下一天
self.get_next_day()
print("现在持有", self.funds)
print(max(self.change["funds"]))
self.draw()
# 输入某天获取到第二天的str
def get_next_day(self, tim=1):
timeArray = time.strptime(self.in_date, "%Y-%m-%d")
timeStamp = int(time.mktime(timeArray))
timeStamp = timeStamp + 84600 * tim
timeArray = time.localtime(timeStamp)
self.in_date = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", timeArray)
�
if __name__ == '__main__':
codes = ['159915.SZ', '510300.SS', '510500.SS'] p = try_day(path="D:/", codes=codes, time='2019-12-31')
# p.get_all_data()
p.the_main()
作者:Alivorth
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc