Polar Encoder/Decoder
v1.0
LogiCORE IP Product Guide
Vivado Design Suite
PG280 June 6, 2018
�
Table of Contents
IP Facts
Chapter 1: Overview
Feature Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Licensing and Ordering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Chapter 2: Product Specification
Port Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Data Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Register Space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Chapter 3: Designing with the Core
Clocking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Polar Code Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Chapter 4: Design Flow Steps
Customizing and Generating the Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Constraining the Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Simulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Synthesis and Implementation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Chapter 5: C Model
Unpacking and Model Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
C Model Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
MATLAB Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
2
Send Feedback�
Chapter 6: Example Design
Simulation-Only Example Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Processor-Based Example Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Appendix A: Upgrading
Appendix B: Debugging
Finding Help on Xilinx.com . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Debug Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Simulation Debug. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Hardware Debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Interface Debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Appendix C: Polar Encoder/Decoder Bare-Metal Driver
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Data Structures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
User API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Interrupt Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Appendix D: Additional Resources and Legal Notices
Xilinx Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Documentation Navigator and Design Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Please Read: Important Legal Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
3
Send Feedback�
IP Facts
LogiCORE™ IP Facts Table
Core Specifics
Supported
Device Family(1)
Supported User
Interfaces
Resources
Design Files
Example Design
Test Bench
Constraints File
Simulation
Model
Supported
S/W Driver
Design Entry
Simulation
Synthesis
UltraScale™, UltraScale+™
7 Series
AXI4-Lite, AXI4-Stream
Performance and Resource Utilization web page
Provided with Core
N/A
IP Integrator Block Diagram
Verilog
Xilinx Design Constraints (XDC)
System Verilog Secure model
Bit-accurate C model
MEX file for use with MATLAB
Standalone
Tested Design Flows(2)
Vivado® Design Suite
For supported simulators, see the
Xilinx Design Tools: Release Notes Guide.
Vivado
Support
Provided by Xilinx at the Xilinx Support web page
Notes:
1. For a complete list of supported devices, see the Vivado IP
catalog.
2. For the supported versions of the tools, see the Xilinx Design
Tools: Release Notes Guide.
Introduction
The Polar Encoder/Decoder soft IP core
supports Polar encoding and decoding. The
Polar codes are configurable and can be used
on a block-by-block basis.
In this document, a block is the general term
Note:
for an atomic unit of data processed by an encoder
or decoder. A codeword is the specific form of an
encoded block and is used when discussing the
code parameters used to generate it.
Features
•
Supports 3GPP TS 38.212 V15.1.1 3rd
Generation Partnership Project; Technical
Specification Group Radio Access Network;
NR; Multiplexing and channel coding
(Release 15) [Ref 10]
Polar encode or decode
Throughput(1) up to:
° >80 Mb/s for decoder (N=1024, K=200)
° >700 Mb/s for encoder (N=1024, K=200)
•
•
• High bandwidth AXI4-Stream interfaces
1. See Performance. Figures are for a clock frequency of
400 MHz and should be scaled for achieved clock
frequency. Throughput is a function of many factors
including code size, code mix, clock frequency and
augmentation parameters.
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
4
Product Specification
Send Feedback�
Chapter 1
Overview
Forward Error Correction (FEC) codes such as Polar codes provide a means to detect and
correct errors in data transmissions over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The
Polar Encoder/Decoder core provides an optimized block for encoding and soft-decision
decoding of these codes. Codes can be specified through an AXI4-Lite bus.
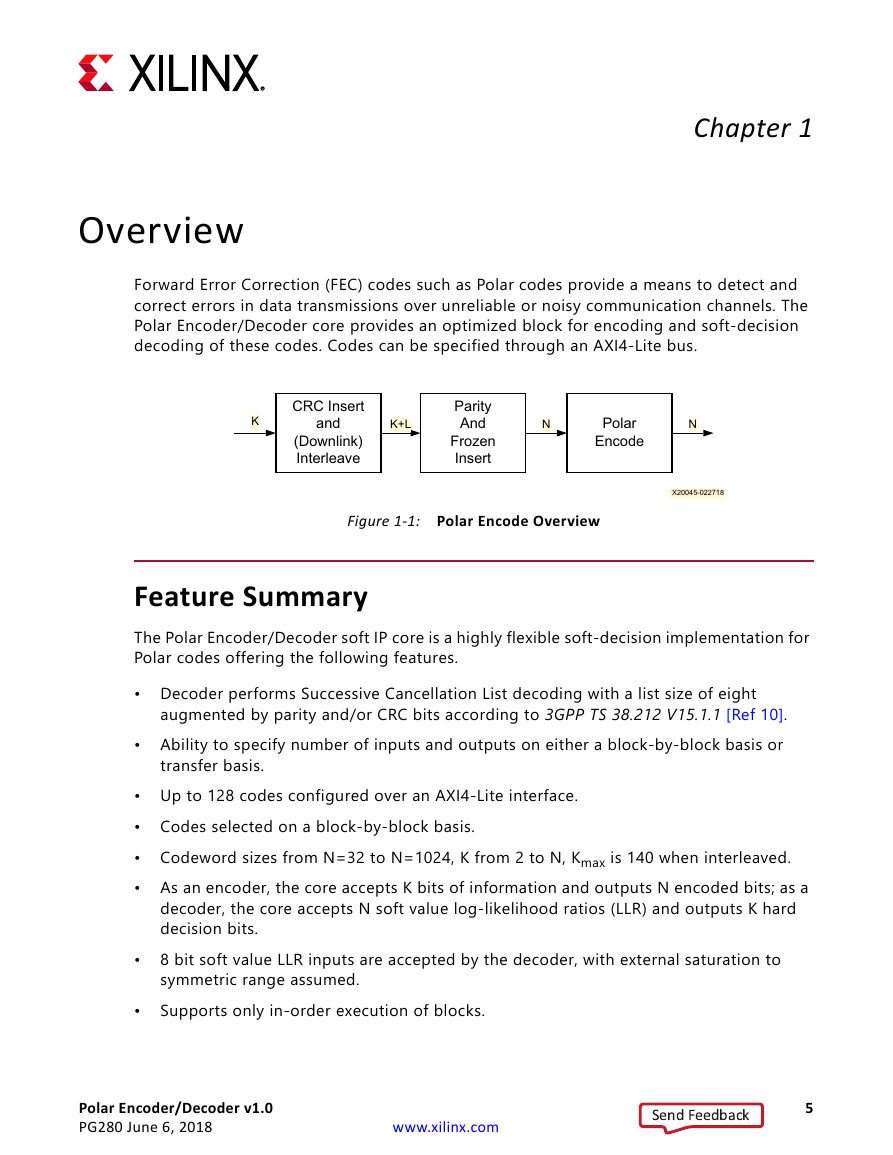
X-Ref Target - Figure 1-1
K
CRC Insert
and
(Downlink)
Interleave
K+L
Parity
And
Frozen
Insert
N
Polar
Encode
N
Figure 1-1: Polar Encode Overview
X20045-022718
Feature Summary
The Polar Encoder/Decoder soft IP core is a highly flexible soft-decision implementation for
Polar codes offering the following features.
• Decoder performs Successive Cancellation List decoding with a list size of eight
augmented by parity and/or CRC bits according to 3GPP TS 38.212 V15.1.1 [Ref 10].
• Ability to specify number of inputs and outputs on either a block-by-block basis or
transfer basis.
• Up to 128 codes configured over an AXI4-Lite interface.
• Codes selected on a block-by-block basis.
• Codeword sizes from N=32 to N=1024, K from 2 to N, Kmax is 140 when interleaved.
• As an encoder, the core accepts K bits of information and outputs N encoded bits; as a
decoder, the core accepts N soft value log-likelihood ratios (LLR) and outputs K hard
decision bits.
8 bit soft value LLR inputs are accepted by the decoder, with external saturation to
symmetric range assumed.
Supports only in-order execution of blocks.
•
•
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
5
Send Feedback�
• Wide data interfaces on input and output.
•
Separate input and output streams allow control parameters and status to be provided
on a block-by-block basis.
Chapter 1: Overview
Applications
The Polar Encoder/Decoder core is intended for, but not limited to, use in applications
requiring Polar encode/decode, such as 5G wireless (3GPP TS 38.212 V15.1.1 Multiplexing
and channel coding (Release 15) [Ref 10]). Table 1-1 describes the settings required for each
of the Polar use modes described in 3GPP TS 38.212 V15.1.1 [Ref 10].
Table 1-1: Polar Use Mode Settings
Augment
BOTH or CRC
CRC
CRC
CRC_SEL
CRC6 or CRC11
CRC24C
CRC24C
ITLV(1)
CRC_INIT
N, K
0
1
1
0
0
1
As required
Use Mode
UCI
BCH
DCI
Notes:
1.
Interleaving enable/disable flag.
Licensing and Ordering
This Xilinx LogiCORE™ IP module is provided under the terms of the Xilinx Core License
Agreement. The module is shipped as part of the Vivado® Design Suite. For full access to
all core functionalities in simulation and in hardware, you must purchase a license for the
core. To generate a full license, visit the product licensing web page. Evaluation licenses and
hardware timeout licenses might be available for this core or subsystem. Contact your local
Xilinx sales representative for information about pricing and availability.
For more information, visit the Polar Encoder/Decoder product web page.
Information about other Xilinx LogiCORE IP modules is available at the Xilinx Intellectual
Property page. For information on pricing and availability of other Xilinx LogiCORE IP
modules and tools, contact your local Xilinx sales representative.
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
6
Send Feedback�
Chapter 2
Product Specification
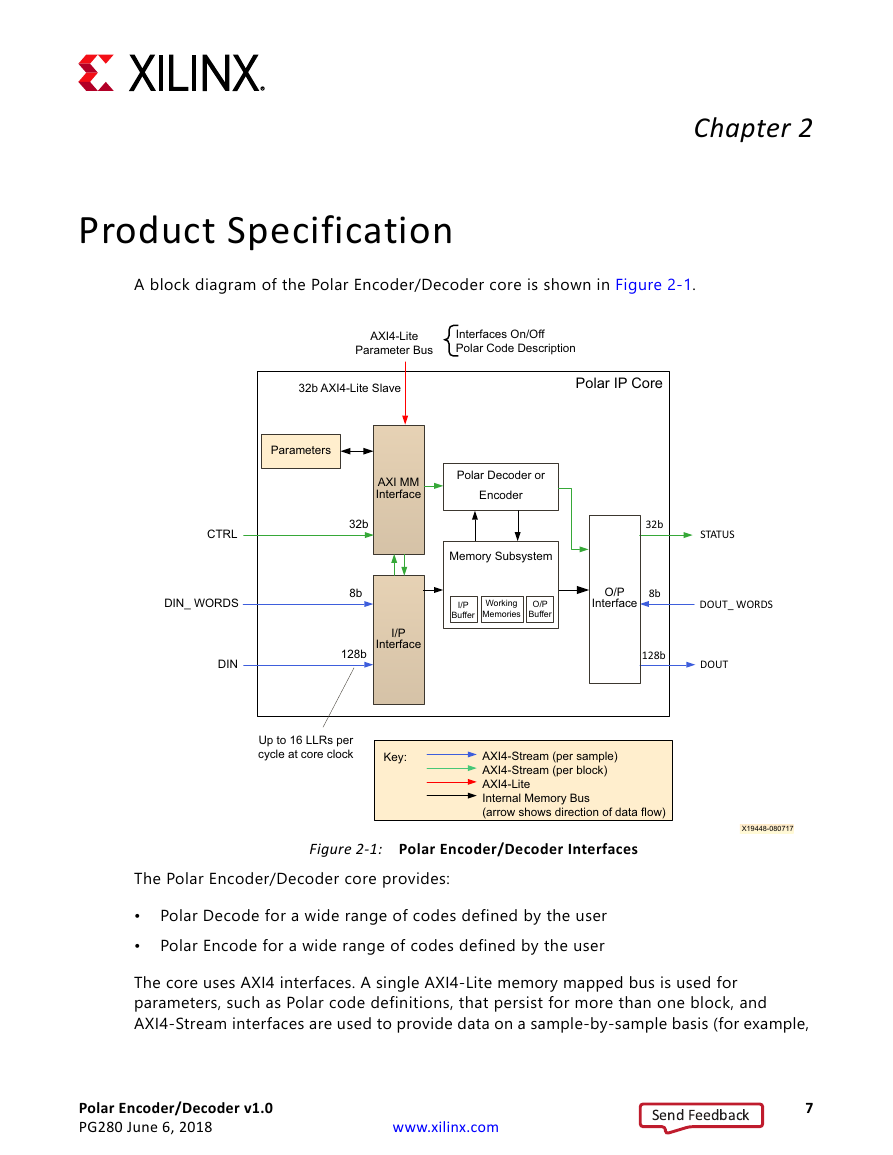
A block diagram of the Polar Encoder/Decoder core is shown in Figure 2-1.
X-Ref Target - Figure 2-1
AXI4-Lite
Parameter Bus
Interfaces On/Off
Polar Code Description
32b AXI4-Lite Slave
Polar IP Core
Parameters
AXI MM
Interface
Polar Decoder or
Encoder
CTRL
DIN_ WORDS
DIN
32b
8b
I/P
Interface
128b
Memory Subsystem
I/P
Buffer
Working
Memories
O/P
Buffer
32b
STATUS
O/P
Interface
8b
DOUT_ WORDS
128b
DOUT
Up to 16 LLRs per
cycle at core clock
Key:
AXI4-Stream (per sample)
AXI4-Stream (per block)
AXI4-Lite
Internal Memory Bus
(arrow shows direction of data flow)
Figure 2-1: Polar Encoder/Decoder Interfaces
X19448-080717
Polar Decode for a wide range of codes defined by the user
Polar Encode for a wide range of codes defined by the user
The Polar Encoder/Decoder core provides:
•
•
The core uses AXI4 interfaces. A single AXI4-Lite memory mapped bus is used for
parameters, such as Polar code definitions, that persist for more than one block, and
AXI4-Stream interfaces are used to provide data on a sample-by-sample basis (for example,
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
7
Send Feedback�
Chapter 2: Product Specification
DIN), or block-by-block basis (for example, CTRL). These interfaces provide handshake
signals in addition to data. Further details are given in AXI4-Stream Interface. Data input
and output buffers provide some scope to overlap input and output with encoder/decoder
operation.
Each block is input through the data input interface (DIN) over a number of cycles. The
amount of data transferred on each cycle is set by a separate data stream (DIN_WORDS)
where a value is given per transaction on DIN. The output is generated in a similar way on
the DOUT output stream, and similarly, the amount of data transferred is specified on the
input data stream, DOUT_WORDS.
For each block, a single input is required on the control (CTRL) input stream, specifying the
code to use and a user supplied ID field. One control word (transaction) is required for each
data block, and data input stalls until the relevant control word is available. When decoded
(or encoded), the output data is provided on DOUT along with a status word on the status
(STATUS) output interface.
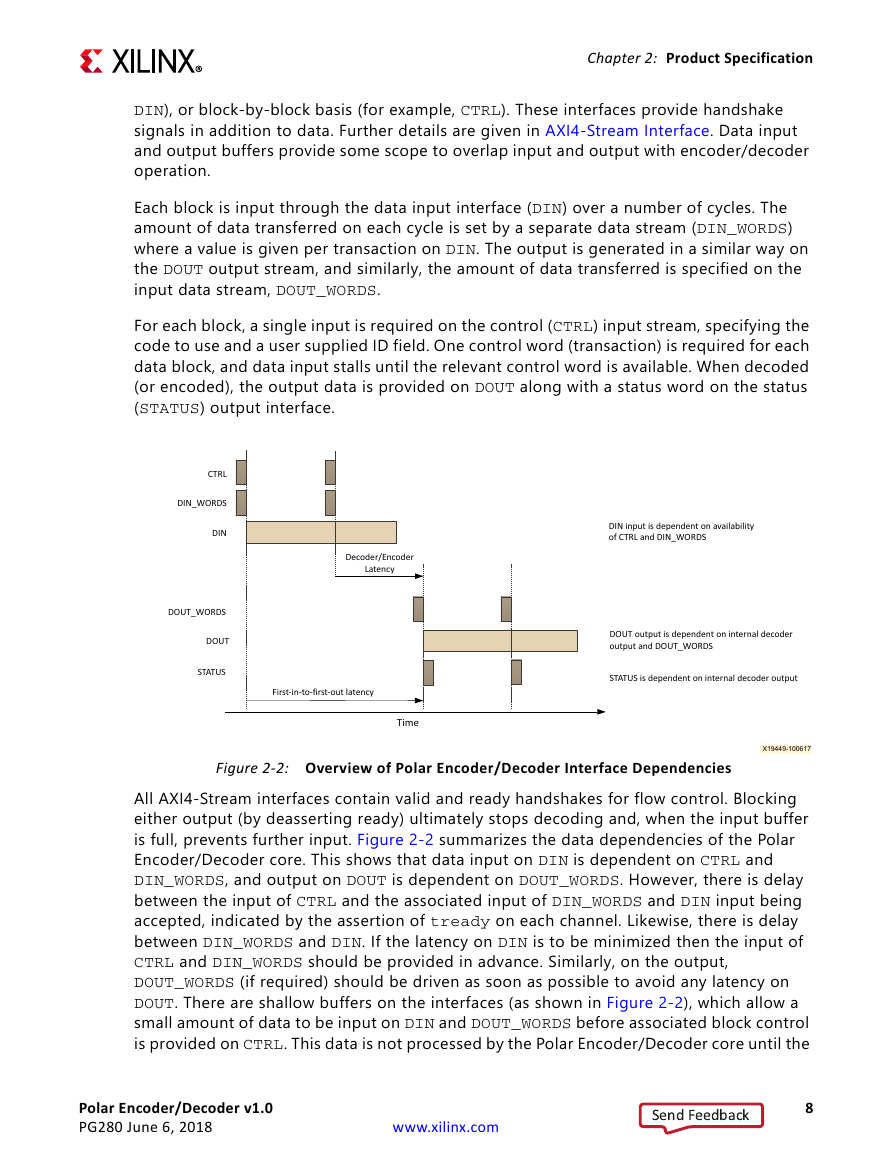
X-Ref Target - Figure 2-2
CTRL
DIN_WORDS
DIN
DOUT_WORDS
DOUT
STATUS
Decoder/Encoder
Latency
First-in-to-first-out latency
Time
DIN input is dependent on availability
of CTRL and DIN_WORDS
DOUT output is dependent on internal decoder
output and DOUT_WORDS
STATUS is dependent on internal decoder output
X19449-100617
Figure 2-2: Overview of Polar Encoder/Decoder Interface Dependencies
All AXI4-Stream interfaces contain valid and ready handshakes for flow control. Blocking
either output (by deasserting ready) ultimately stops decoding and, when the input buffer
is full, prevents further input. Figure 2-2 summarizes the data dependencies of the Polar
Encoder/Decoder core. This shows that data input on DIN is dependent on CTRL and
DIN_WORDS, and output on DOUT is dependent on DOUT_WORDS. However, there is delay
between the input of CTRL and the associated input of DIN_WORDS and DIN input being
accepted, indicated by the assertion of tready on each channel. Likewise, there is delay
between DIN_WORDS and DIN. If the latency on DIN is to be minimized then the input of
CTRL and DIN_WORDS should be provided in advance. Similarly, on the output,
DOUT_WORDS (if required) should be driven as soon as possible to avoid any latency on
DOUT. There are shallow buffers on the interfaces (as shown in Figure 2-2), which allow a
small amount of data to be input on DIN and DOUT_WORDS before associated block control
is provided on CTRL. This data is not processed by the Polar Encoder/Decoder core until the
Polar Encoder/Decoder v1.0
PG280 June 6, 2018
www.xilinx.com
8
Send Feedback�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc