CFA® Society Boston Level III
2020 Practice Exam
Morning Session
CFA® is a licensed service mark owned by CFA Institute.
�
The following list contains the command words used on the Morning Session of the CFA
Society Boston Level III 2020 Practice Exam. Candidates may want to refer to this list as they
formulate their answers.
Calculate:
To find (the value of something) by using mathematics.
Classify:
To assign to categories or groups.
To note the similarities and differences of two or more things.
To state the differences between.
Compare:
Contrast:
Describe:
Determine: To decide; to ascertain.
Discuss:
To portray in words.
To examine critically and in detail.
To show to be valid or appropriate in a particular context.
To make clear the meaning of.
To recognize and correctly name.
Explain:
Identify:
Justify:
Recommend: To offer as being appropriate or good.
Select:
State:
To choose as being the best or most suitable.
Support:
To express in words the probability of an event in terms odds for or
against the event; to provide.
To provide corroboration for each response with one reason.
2
�
12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
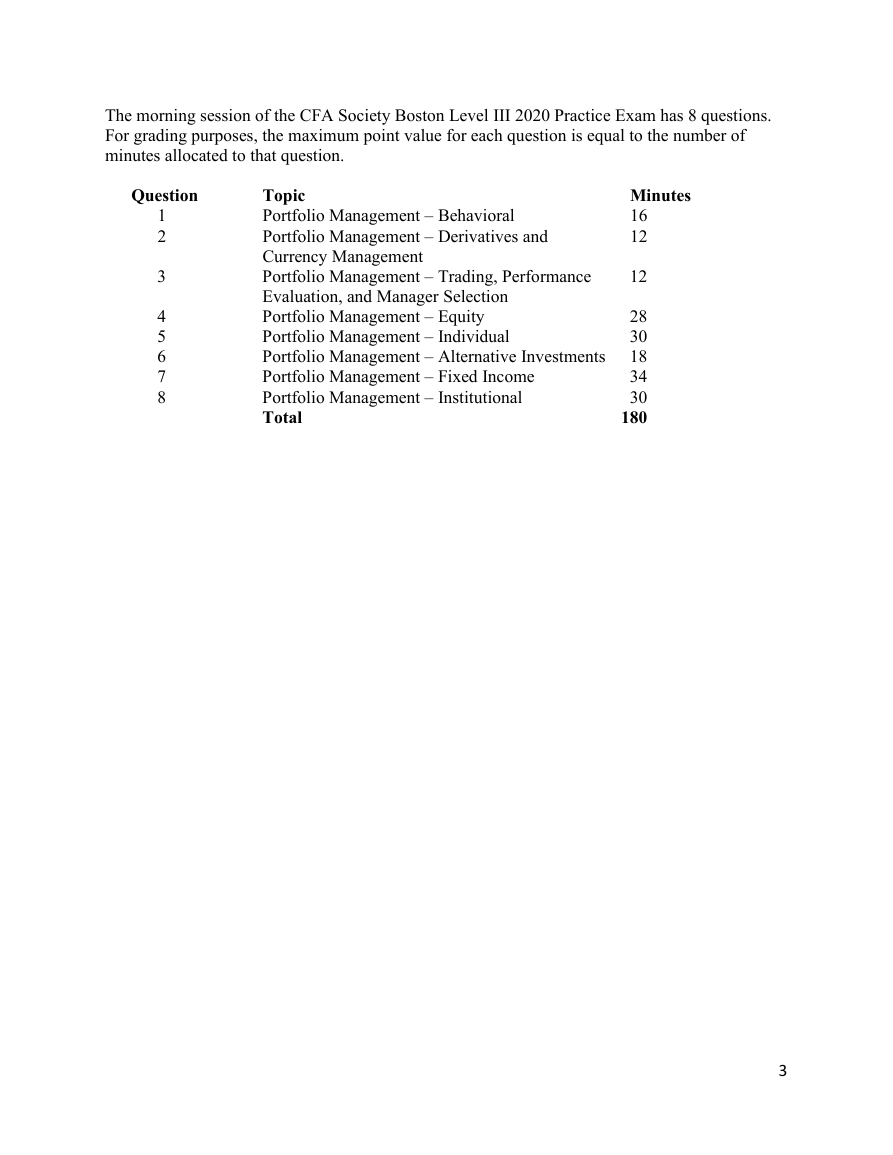
Minutes
16
12
28
30
18
34
30
180
Topic
Portfolio Management – Behavioral
Portfolio Management – Derivatives and
Currency Management
Portfolio Management – Trading, Performance
Evaluation, and Manager Selection
Portfolio Management – Equity
Portfolio Management – Individual
Portfolio Management – Alternative Investments
Portfolio Management – Fixed Income
Portfolio Management – Institutional
Total
The morning session of the CFA Society Boston Level III 2020 Practice Exam has 8 questions.
For grading purposes, the maximum point value for each question is equal to the number of
minutes allocated to that question.
Question
3
�
QUESTION 1 HAS A TOTAL OF FOUR PARTS (A, B, C, D) FOR A TOTAL OF 16
MINUTES.
Alexander James, CFA, is the head of asset management at AJ Investments, where he has
worked for eight years. James is meeting with Samuel and Nikita Erving and their son, Louis, to
discuss their personal investment strategies. All of the Erving family members have been clients
of AJ Investments for the last ten years.
Samuel Erving is 59 years of age and has been a manager at a blue-chip technology firm for 30
years. He has consistently invested in the company’s stock and employee stock options. Samuel
has accumulated a portfolio of $1.8 million, of which 80% is invested in his firm. Samuel
recognizes that he has no investment experience and considers himself to be a low to medium
risk taker. He relies on AJ Investments for advice and actively follows leads from research
reports and friends.
A.
Identify the behavioral investment type (BIT) that most likely describes Samuel.
3 minutes (Answer 1-A on page 6)
James recommends to Samuel that he reduce his exposure to his employer in the portfolio. The
current stock price of the employer’s stock is $98. Samuel is reluctant to sell and believes that
the share price will rebound towards its 52-week high of $160. After deciding to hold the stock,
Samuel observes that the quarterly sales of his firm have declined from the previous quarter. He
believes that this decline in sales is temporary because of the stock’s past success and reaffirms
his belief in his employer’s stock.
B.
Identify two behavioral biases exhibited by Samuel. State how he can overcome these
biases with one recommendation for each.
5 minutes (Answer 1-B on page 7)
Nikita Erving is a 49-year-old entrepreneur who attributes most of her success to the textile firm
she founded 15 years ago. Nikita recently sold the firm for $4 million, which is currently
invested in a diverse mix of stocks and bonds. Her total income is generated by the $4 million
portfolio. Nikita states that her objectives are 1) not losing capital, and 2) that her portfolio
generate enough income to cover all of her routine expenses. She also expresses an interest to
hold various buckets of investments, where each bucket is dedicated to generating monthly,
quarterly and annual income.
C.
Identify the behavioral bias exhibited by Nikita and describe briefly one consequence
of the bias.
3 minutes (Answer 1-C on page 8)
4
�
Louis Erving is 34 years old, single and a medical doctor. Louis indicates he has a low risk
tolerance on his existing $2.5 million portfolio composed exclusively of health care stocks, most
of which have realized a decline in value since their initial purchase. Because his earnings as a
physician cover his current expenses, he views the health care portfolio as providing the capital
for the purchase of a luxury home and a high-end vacation property. He also reiterates his
interest to preserve wealth without taking significant risk.
James makes the recommendation to sell the health care stocks and to diversify into a broader
market exposure. Louis declines this recommendation and states that he wants to hold on to the
health care positions for another year in anticipation of future price increases. He does not wish
to sell at a loss. Further, he would not want to miss out on any subsequent recovery if he were to
sell as James recommends.
Louis recently inherited real estate investments from his grandfather totaling $2 million. Louis
indicates his desire to sell the real estate properties and to redeploy his portfolio into stocks and
bonds for his retirement. Louis is determined to sell his properties above their current market
valuation of $2.5 million.
D.
Identify Louis’s behavioral investor type. Identify three emotional biases or cognitive
errors exhibited by him to support your choice.
5
5 minutes (Answer 1-D on page 9)
�
Answer Question 1-A on this page
Identify the behavioral investment type (BIT) that most likely describes Samuel.
6
�
Answer Question 1-B on this page
Recommendation
Identify two behavioral biases exhibited by Samuel. State how he can overcome these biases
with one recommendation for each.
Behavioral Bias
1.
2.
7
�
Answer Question 1-C on this page
Consequence
Identify the behavioral bias exhibited by Nikita and describe briefly one consequence of the
bias.
Behavioral Bias
8
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc