ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1B, 1995 edition
(Incorporating ANSI/IEEE Stds 802.1B-1992
and 802.1k-1993)
(Adopted by ISO/IEC and redesignated as
ISO/IEC 15802-2: 1995)
Information technology—
Telecommunications and information
exchange between systems—
Local and metropolitan area networks—
Common specifications—
Part 2: LAN/MAN management
Adopted by the ISO/IEC and redesignated as
ISO/IEC 15802-2: 1995
Sponsor
LAN/MAN Standards Committee
of the
IEEE Computer Society
�
Abstract:
Services and protocol elements that permit the exchange of management information
between stations attached to ISO/IEC standard local and metropolitan area networks are defined.
The standard includes the specification of managed objects that permit the operation of the protocol
elements to be remotely managed. In addition, an architecture for station discovery and the dynam-
ic control of event forwarding is defined. Services and protocols that support station discovery and
the dynamic control of event forwarding are defined.
Keywords:
management
event forwarding; local area networks, management; metropolitan area networks,
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
345 East 47th Street, New York, NY 10017-2394, USA
Copyright
All rights reserved. Published 1995. Printed in the United States of America.
1995 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
ISBN 1-55937-501-9
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form, in an electronic retrieval system or otherwise, without the prior
written permission of the publisher.
DATE TBD
SH94259
�
ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1B, 1995 Edition
IEEE Standards
documents are developed within the Technical Committees of the
IEEE Societies and the Standards Coordinating Committees of the IEEE Standards
Board. Members of the committees serve voluntarily and without compensation.
They are not necessarily members of the Institute. The standards developed within
IEEE represent a consensus of the broad expertise on the subject within the Institute
as well as those activities outside of IEEE that have expressed an interest in partici-
pating in the development of the standard.
Use of an IEEE Standard is wholly voluntary. The existence of an IEEE Standard
does not imply that there are no other ways to produce, test, measure, purchase, mar-
ket, or provide other goods and services related to the scope of the IEEE Standard.
Furthermore, the viewpoint expressed at the time a standard is approved and issued is
subject to change brought about through developments in the state of the art and
comments received from users of the standard. Every IEEE Standard is subjected to
review at least every five years for revision or reaffirmation. When a document is
more than five years old and has not been reaffirmed, it is reasonable to conclude that
its contents, although still of some value, do not wholly reflect the present state of the
art. Users are cautioned to check to determine that they have the latest edition of any
IEEE Standard.
Comments for revision of IEEE Standards are welcome from any interested party,
regardless of membership affiliation with IEEE. Suggestions for changes in docu-
ments should be in the form of a proposed change of text, together with appropriate
supporting comments.
Interpretations: Occasionally questions may arise regarding the meaning of portions
of standards as they relate to specific applications. When the need for interpretations
is brought to the attention of IEEE, the Institute will initiate action to prepare appro-
priate responses. Since IEEE Standards represent a consensus of all concerned inter-
ests, it is important to ensure that any interpretation has also received the concurrence
of a balance of interests. For this reason IEEE and the members of its technical com-
mittees are not able to provide an instant response to interpretation requests except in
those cases where the matter has previously received formal consideration.
Comments on standards and requests for interpretations should be addressed to:
Secretary, IEEE Standards Board
445 Hoes Lane
P.O. Box 1331
Piscataway, NJ 08855-1331
USA
IEEE Standards documents may involve the use of patented technology. Their
approval by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers does not mean that
using such technology for the purpose of conforming to such standards is authorized
by the patent owner. It is the obligation of the user of such technology to obtain all
necessary permissions.
iv
�
�
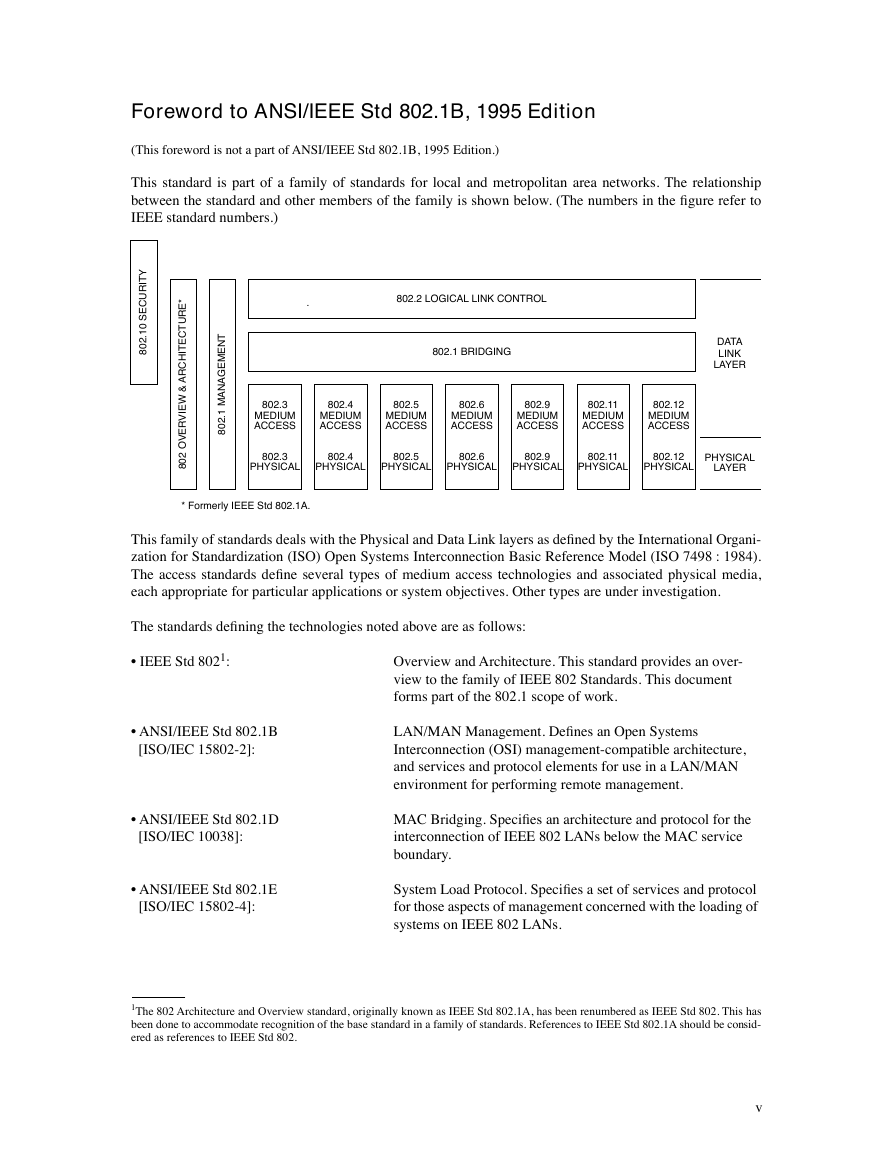
Foreword to ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1B, 1995 Edition
(This foreword is not a part of ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1B, 1995 Edition.)
This standard is part of a family of standards for local and metropolitan area networks. The relationship
between the standard and other members of the family is shown below. (The numbers in the figure refer to
IEEE standard numbers.)
I
Y
T
R
U
C
E
S
0
1
2
0
8
.
I
*
E
R
U
T
C
E
T
H
C
R
A
&
W
E
V
R
E
V
O
2
0
8
I
T
N
E
M
E
G
A
N
A
M
1
.
2
0
8
.
802.2 LOGICAL LINK CONTROL
802.1 BRIDGING
DATA
LINK
LAYER
802.3
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.4
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.5
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.6
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.9
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.11
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.12
MEDIUM
ACCESS
802.3
PHYSICAL
802.4
PHYSICAL
802.5
PHYSICAL
802.6
PHYSICAL
802.9
PHYSICAL
802.11
PHYSICAL
802.12
PHYSICAL
PHYSICAL
LAYER
* Formerly IEEE Std 802.1A.
This family of standards deals with the Physical and Data Link layers as defined by the International Organi-
zation for Standardization (ISO) Open Systems Interconnection Basic Reference Model (ISO 7498 : 1984).
The access standards define several types of medium access technologies and associated physical media,
each appropriate for particular applications or system objectives. Other types are under investigation.
The standards defining the technologies noted above are as follows:
1
• IEEE Std 802
:
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1B
[ISO/IEC 15802-2]:
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1D
[ISO/IEC 10038]:
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1E
[ISO/IEC 15802-4]:
Overview and Architecture. This standard provides an over-
view to the family of IEEE 802 Standards. This document
forms part of the 802.1 scope of work.
LAN/MAN Management. Defines an Open Systems
Interconnection (OSI) management-compatible architecture,
and services and protocol elements for use in a LAN/MAN
environment for performing remote management.
MAC Bridging. Specifies an architecture and protocol for the
interconnection of IEEE 802 LANs below the MAC service
boundary.
System Load Protocol. Specifies a set of services and protocol
for those aspects of management concerned with the loading of
systems on IEEE 802 LANs.
1
The 802 Architecture and Overview standard, originally known as IEEE Std 802.1A, has been renumbered as IEEE Std 802. This has
been done to accommodate recognition of the base standard in a family of standards. References to IEEE Std 802.1A should be consid-
ered as references to IEEE Std 802.
v
�
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.2 [ISO/IEC 8802-2]: Logical Link Control
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.3 [ISO/IEC 8802-3]: CSMA/CD Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.4 [ISO/IEC 8802-4]: Token Bus Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.5 [ISO/IEC 8802-5]: Token Ring Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications
• ANSI/IEEE Std 802.6 [ISO/IEC 8802-6]: Distributed Queue Dual Bus Access Method and Physical
Layer Specifications
• IEEE Std 802.9:
• IEEE Std 802.10:
Integrated Services (IS) LAN Interface at the Medium Access
Control (MAC) and Physical (PHY) Layers
Interoperable LAN/MAN Security,
Secure Data Exchange (SDE)
Currently approved:
In addition to the family of standards, the following is a recommended practice for a common Physical
Layer technology:
• IEEE Std 802.7:
IEEE Recommended Practice for Broadband Local Area
Networks
The following additional working groups have authorized standards projects under development:
• IEEE 802.11:
Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) Sublayer and
Physical Layer Specifications
• IEEE 802.12:
Demand Priority Access Method/Physical Layer Specifications
Conformance test methodology
An additional standards series, identified by the number 1802, has been established to identify the
conformance test methodology documents for the 802 family of standards. Thus the conformance test
documents for 802.3 are numbered 1802.3, the conformance test documents for 802.5 will be 1802.5, and so
on. Similarly, ISO will use 18802 to number conformance test standards for 8802 standards.
ANSI/IEEE Std 15802-2 : 1995 Edition
This document defines services and protocol elements that permit the exchange of management information
between stations attached to IEEE 802 local and metropolitan area networks. The standard includes the spec-
ification of managed objects that permit the operation of the protocol elements to be remotely managed.
The reader of this standard is urged to become familiar with the complete family of standards.
vi
�
This standard contains state-of-the-art material. The area covered by this standard is undergoing evolution.
Revisions are anticipated within the next few years to clarify existing material, to correct possible errors, and
to incorporate new related material. Information on the current revision state of this and other IEEE 802
standards may be obtained from
Secretary, IEEE Standards Board
445 Hoes Lane
P.O. Box 1331
Piscataway, NJ 08855-1331
USA
IEEE 802 committee working documents are available from
IEEE Document Distribution Service
AlphaGraphics #35
10201 N. 35th Avenue
Phoenix, AZ 85051
USA
Attn: P. Thrush
vii
�
Participants
The following is a list of participants in the Network Management effort of the IEEE Project 802 Working
Group at the time of 802.1B’s approval. Voting members at the time of publication are marked with an aster-
isk (*). Those who were participants at the time of 802.1k’s approval are marked with a dagger (†).
Tony Jeffree,
William P. Lidinsky,
Chair, Network Management Task Group*†
Chair*†
Fumio Akashi
Paul D. Amer
Charles Arnold
Naharaj Arunkumar
Floyd Backes*†
Ann Ballard
Richard Bantel
Robert Barrett*†
David Bartolini
Sy Bederman
Amatzia Ben-Artzi†
Anthony Berent†
Orna Berry*†
Robert Bledsoe
Kwame Boakye
Laura Bridge*†
Brian Brown†
Juan Bulnes
Fred Burg
Peter Carbone
Alan Chambers*†
Ken Chapman
Alice Chen
Michael Chernick
Jade Chien
Steve Cooper*†
Jim Corrigan
Paul Cowell*†
Mike Coy†
Andy Davis*†
Peter Dawe
Stan Degen
Frank Deignan
Desh Deshpande
Ron Dhondy
Mike Dickerson
Kurt Dobbins
Eiji Doi
Barbara J. Don Carlos
David Dyer-Bennet
Walter Eldon
Eldon D. Feist
Len Fishler*†
Kevin Flanagan
Bill Futral*†
Lionel Geretz*†
Richard Gilbert*†
Harry Gold†
Pat Gonia
Kathy de Graaf
Rich Graham
Michael A. Gravel
Andrew Green†
Sharam Hakimi*†
Jeanne Haney†
Mogens Hansen
Harold Harrington
John Hart*†
Mike Harvey†
Bob Herbst
Long Huang†
Jack R. Hung
Thomas Hytry
Jay Israel
Jan-Olof Jemnemo*†
Albert Juandy†
George Kajos†
Ram Kedlaya
Hal Keen*†
Alan Kirby
Kimberly Kirkpatrick
Steve Kleiman
Yoav Kluger†
James Kristof†
Hans Lackner*†
H. Eugene Latham
Choon Lee†
Chao-yu Liang
Bing Liao
George Lin*†
Mike Lumpkin
Andy Luque
Phil Magnuson
Joseph E. Massery†
Bruce McClure
Tom McGowan
Margaret A. Merrick
Jim Montrose
Jerry O’Keefe
Alan Oppenheimer*†
Richard Patti*†
Dave T. Perkins†
Roger Pfister
Thomas L. Phinney
Clive Philbrick
John Pickens*
David Piscitello
Daniel Pitt
Vencat Prasad*†
Ronald Presti†
Ron L. G. Prince
Maurice Qureshi†
Nigel Ramsden
Rich Rehberg
Jim Reinstedler
Trudy Reusser
Eduard Rocher
Paul Rosenblum*†
Paul Ruocchio*†
Tom Rutt*†
John Salter
Alan Sarsby
Susan Schanning
Mick Seaman*†
Gerry Segal*†
Rich Seifert*†
Steve Senum*†
Himanshu Shah*†
Howard Sherry
Wu-Shi Shung
W. Earl Smith*†
Mike Soha
Dan Stokesberry
Lennart Swartz
Kenta Takumi
Elysia Chiaw-Meng Tan
Robin Tasker*†
Angus Telfer
Dave Thompson
Geoff Thompson†
Nathan Tobol
Wendell Turner
Peter Videcrantz*†
Donald G. Vincent†
Paul Wainright
Trevor Warwick†
Scott Wasson
Bob Watson
Richard Watson*
Daniel Watts
Alan Weissberger
Deborah Wilbert
Bert Williams†
Jerry A. Wyatt†
Amnon Yacoby*†
Igor Zhovnirovsky
Carolyn Zimmer*†
Nick Zucchero
Additional participants in the development of 802.1k included the following:
Sai Boeker
Mike Dickerson
Bonnie B. Hromis
Brian J. Phillips
viii
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc