Data Sheet, Rev. 2.0, June 2008
BTN7971B
High Current PN Half Bridge
NovalithIC™
Automotive Power
�
High Current PN Half Bridge
BTN7971B
Table of Contents
1
2
2.1
2.2
3
3.1
3.2
4
4.1
4.2
4.3
5
5.1
5.2
5.2.1
5.2.2
5.2.3
5.3
5.3.1
5.3.2
5.3.3
5.3.4
5.3.5
5.3.6
5.4
5.4.1
5.4.2
5.4.3
5.4.4
5.4.5
5.4.6
6
6.1
6.2
6.3
7
8
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Pin Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Pin Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Pin Definitions and Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
General Product Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Functional Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Thermal Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Block Description and Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Supply Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Power Stages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Power Stages - Static Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Switching Times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Power Stages - Dynamic Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Protection Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Overvoltage Lock Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Undervoltage Shut Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Overtemperature Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Current Limitation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Short Circuit Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Electrical Characteristics - Protection Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Control and Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Input Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Dead Time Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Adjustable Slew Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Status Flag Diagnosis With Current Sense Capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Truth Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Electrical Characteristics - Control and Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Application Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Layout Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Half-bridge Configuration Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Package Outlines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Data Sheet
2
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�
High Current PN Half Bridge
NovalithIC™
1
Overview
Features
• Path resistance of max. 30.5 mΩ @ 150 °C (typ. 16 mΩ @ 25 °C)
High Side: max. 12.8 mΩ @ 150 °C (typ. 7 mΩ @ 25 °C)
Low Side: max. 17.7 mΩ @ 150 °C (typ. 9 mΩ @ 25 °C)
Low quiescent current of typ. 7 μA @ 25 °C
•
• PWM capability of up to 25 kHz combined with active freewheeling
• Enhanced switching speed for reduced switching losses
• Switched mode current limitation for reduced power dissipation
in overcurrent
• Current limitation level of 50 A min. / 70 A typ. (low side)
• Status flag diagnosis with current sense capability
• Overtemperature shut down with latch behavior
• Overvoltage lock out
• Undervoltage shut down
• Driver circuit with logic level inputs
• Adjustable slew rates for optimized EMI
• Green Product (RoHS compliant)
• AEC Qualified
BTN7971B
PG-TO263-7-1
Description
The BTN7971B is a integrated high current half bridge for motor drive applications. It is part of the NovalithIC™
family containing one p-channel highside MOSFET and one n-channel lowside MOSFET with an integrated driver
IC in one package. Due to the p-channel highside switch the need for a charge pump is eliminated thus minimizing
EMI. Interfacing to a microcontroller is made easy by the integrated driver IC which features logic level inputs,
diagnosis with current sense, slew rate adjustment, dead time generation and protection against overtemperature,
overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent and short circuit.
The BTN7971B provides a cost optimized solution for protected high current PWM motor drives with very low
board space consumption.
Type
BTN7971B
Data Sheet
Package
PG-TO263-7-1
3
Marking
BTN7971B
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�
High Current PN Half Bridge
BTN7971B
Block Diagram
Block Diagram
2
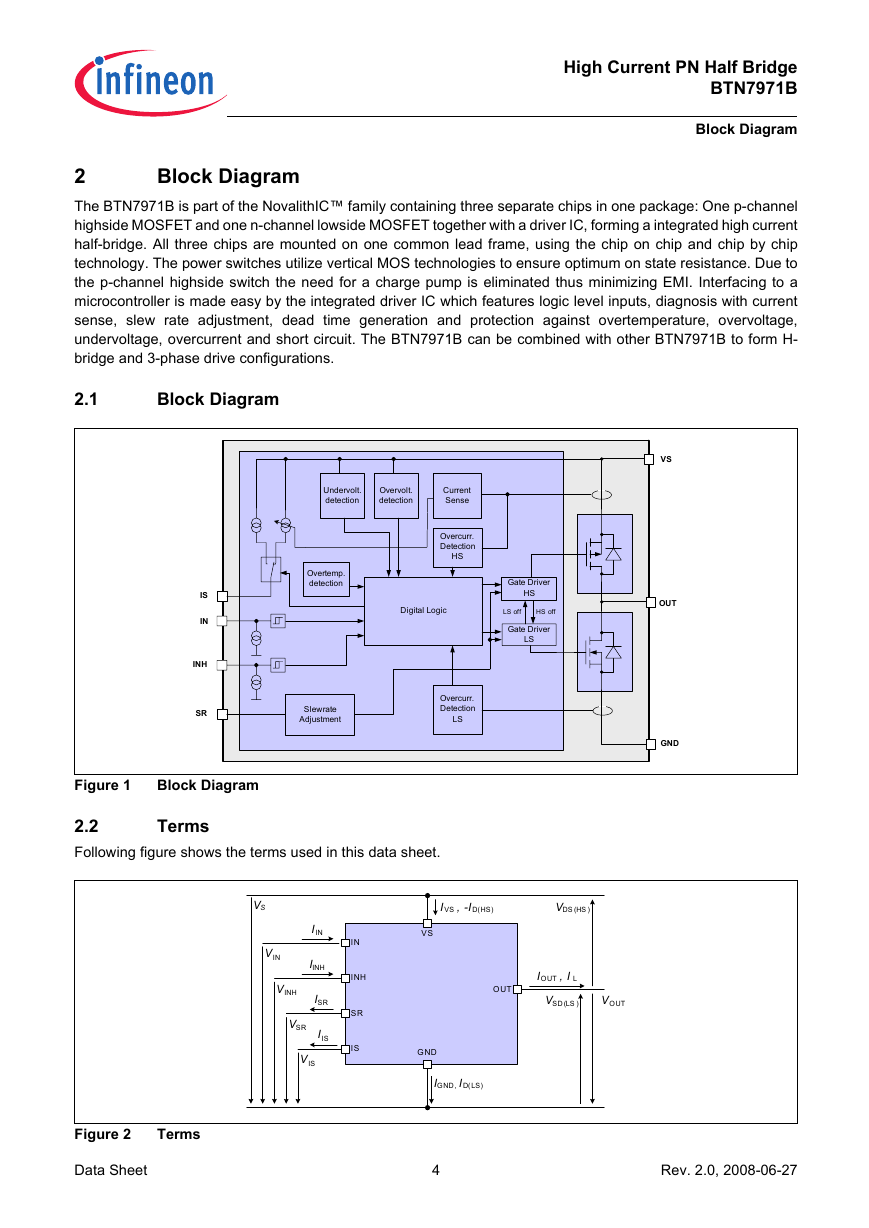
The BTN7971B is part of the NovalithIC™ family containing three separate chips in one package: One p-channel
highside MOSFET and one n-channel lowside MOSFET together with a driver IC, forming a integrated high current
half-bridge. All three chips are mounted on one common lead frame, using the chip on chip and chip by chip
technology. The power switches utilize vertical MOS technologies to ensure optimum on state resistance. Due to
the p-channel highside switch the need for a charge pump is eliminated thus minimizing EMI. Interfacing to a
microcontroller is made easy by the integrated driver IC which features logic level inputs, diagnosis with current
sense, slew rate adjustment, dead time generation and protection against overtemperature, overvoltage,
undervoltage, overcurrent and short circuit. The BTN7971B can be combined with other BTN7971B to form H-
bridge and 3-phase drive configurations.
2.1
Block Diagram
Undervolt.
detection
Overvolt.
detection
Current
Sense
Overtemp.
detection
Overcurr.
Detection
HS
Digital Logic
Gate Driver
HS
LS off
HS off
Gate Driver
LS
Slewrate
Adjustment
Overcurr.
Detection
LS
IS
IN
INH
SR
VS
OUT
GND
Figure 1
Block Diagram
2.2
Following figure shows the terms used in this data sheet.
Terms
VS
VIN
VINH
VSR
I IN
IINH
ISR
I IS
VIS
IN
INH
SR
IS
I VS , -I D(HS)
VDS (HS )
VS
OUT
I OUT , I L
VSD (LS )
VOUT
GND
IGND , I D(LS)
Figure 2
Terms
Data Sheet
4
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�
3
3.1
Pin Configuration
Pin Assignment
High Current PN Half Bridge
BTN7971B
Pin Configuration
8
1 2 3 5 6 7
4
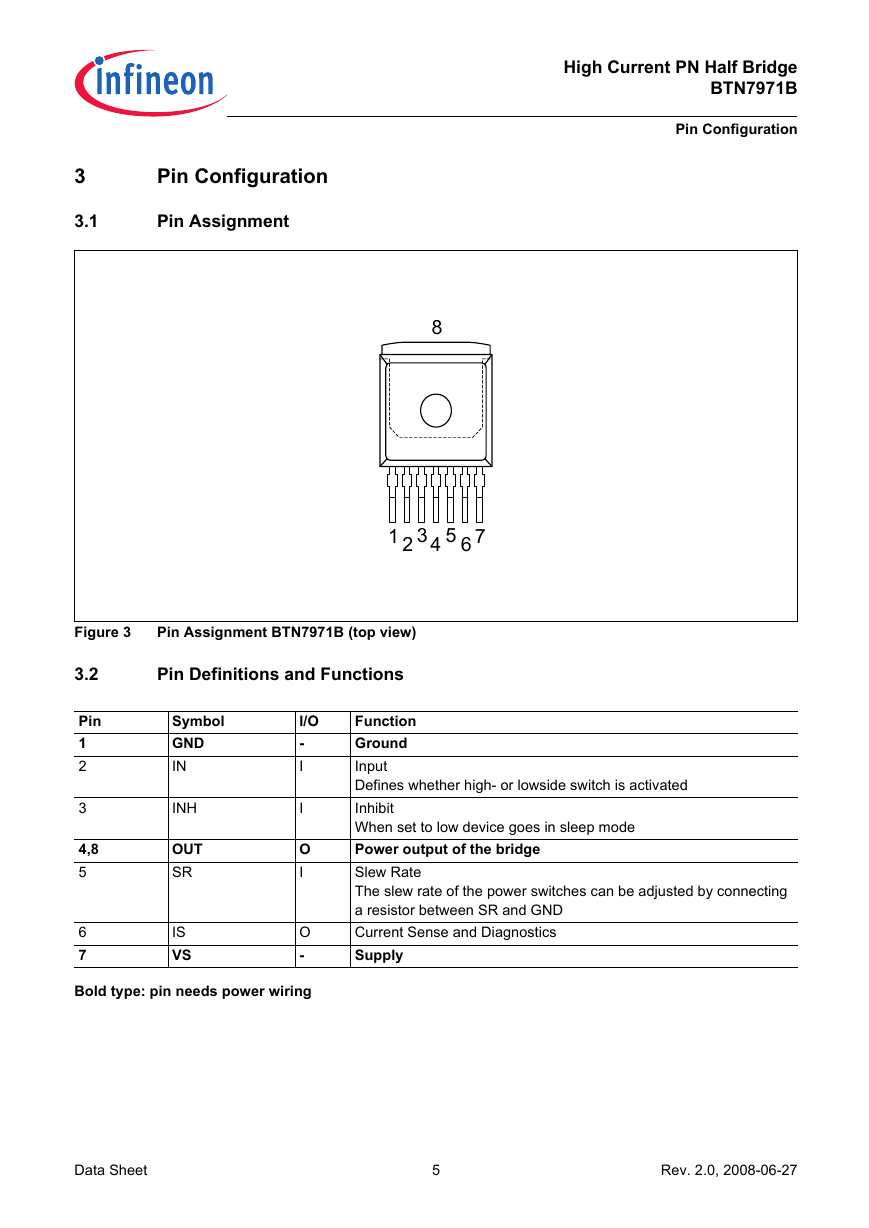
Figure 3
Pin Assignment BTN7971B (top view)
3.2
Pin Definitions and Functions
Pin
1
2
3
4,8
5
6
7
Symbol
GND
IN
INH
OUT
SR
IS
VS
I/O
-
I
I
O
I
O
-
Function
Ground
Input
Defines whether high- or lowside switch is activated
Inhibit
When set to low device goes in sleep mode
Power output of the bridge
Slew Rate
The slew rate of the power switches can be adjusted by connecting
a resistor between SR and GND
Current Sense and Diagnostics
Supply
Bold type: pin needs power wiring
Data Sheet
5
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�
4
4.1
General Product Characteristics
Absolute Maximum Ratings
High Current PN Half Bridge
BTN7971B
General Product Characteristics
Absolute Maximum Ratings 1)
Tj = -40 °C to +150 °C; all voltages with respect to ground, positive current flowing into pin
(unless otherwise specified)
Pos.
Parameter
Symbol
Unit
Limit Values
Max.
Conditions
–
–
–
–
–
TC < 85°C
switch active
TC < 125°C
switch active
TC < 85°C
tpulse = 10ms
single pulse
TC < 125°C
tpulse = 10ms
single pulse
TC < 85°C
f = 1kHz, DC = 50%
TC < 125°C
f = 1kHz, DC = 50%
TC < 85°C
f = 20kHz, DC = 50%
TC < 125°C
f = 20kHz, DC = 50%
V
V
V
V
V
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
°C
°C
kV
–
–
HBM3)
Voltages
4.1.1
4.1.2
4.1.3
4.1.4
4.1.5
Currents
4.1.6
Supply Voltage
Logic Input Voltage
Voltage at SR Pin
Voltage between VS and IS Pin
Voltage at IS Pin
HS/LS Continuous Drain Current2)
4.1.7
HS/LS Pulsed Drain Current2)
4.1.8
HS/LS PWM Current2)
Junction Temperature
Storage Temperature
Temperatures
4.1.9
4.1.10
ESD Susceptibility
4.1.11
ESD Susceptibility HBM
IN, INH, SR, IS
OUT, GND, VS
VS
VIN
VINH
VSR
VS -VIS
VIS
ID(HS)
ID(LS)
ID(HS)
ID(LS)
ID(HS)
ID(LS)
Tj
Tstg
VESD
Min.
-0.3
-0.3
-0.3
-0.3
-20
-44
-40
-90
-85
-55
-50
-60
-54
-40
-55
-2
-6
45
5.3
1.0
45
45
44
40
90
85
55
50
60
54
150
150
2
6
1) Not subject to production test, specified by design
2) Maximum reachable current may be smaller depending on current limitation level
3) ESD susceptibility, HBM according to EIA/JESD22-A114-B (1.5 kΩ, 100 pF)
Data Sheet
6
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�
High Current PN Half Bridge
BTN7971B
General Product Characteristics
Note: Stresses above the ones listed here may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Note: Integrated protection functions are designed to prevent IC destruction under fault conditions described in the
data sheet. Fault conditions are considered as “outside” normal operating range. Protection functions are
not designed for continuous repetitive operation.
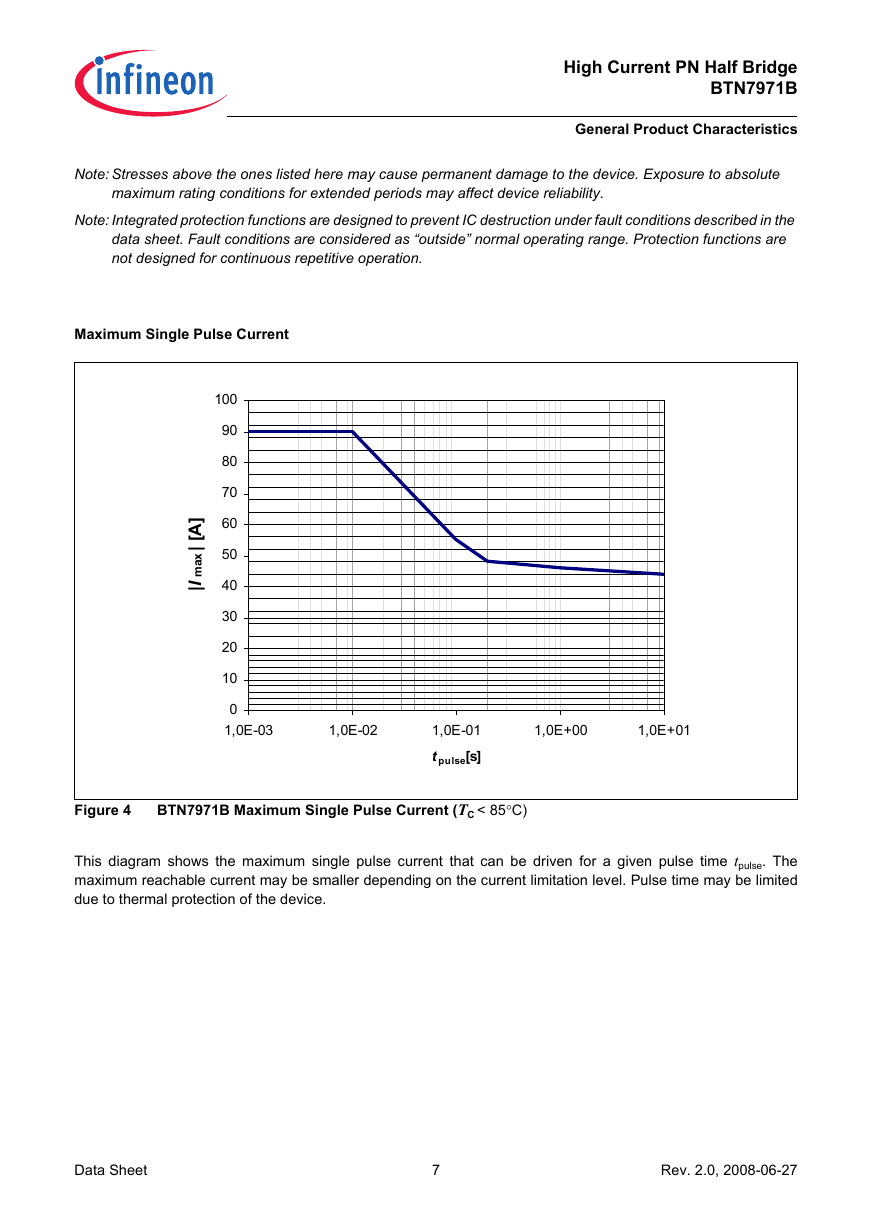
Maximum Single Pulse Current
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
]
A
[
|
x
a
m
I
|
0
1,0E-03
1,0E-02
1,0E-01
t pulse[s]
1,0E+00
1,0E+01
Figure 4
BTN7971B Maximum Single Pulse Current (TC < 85°C)
This diagram shows the maximum single pulse current that can be driven for a given pulse time tpulse. The
maximum reachable current may be smaller depending on the current limitation level. Pulse time may be limited
due to thermal protection of the device.
Data Sheet
7
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�
High Current PN Half Bridge
BTN7971B
General Product Characteristics
Symbol
VS(nom)
Limit Values
Max.
18
Min.
8
VS(ext)
VUV(OFF)max 28
Tj
-40
150
Unit
Conditions
V
V
°C
–
Parameter
Deviations possible
–
4.2
Functional Range
Pos.
Parameter
4.2.1
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3
Supply Voltage Range for
Nominal Operation
Extended Supply Voltage Range for
Operation
Junction Temperature
Thermal Resistance
Pos.
Parameter
Symbol
Limit Values
Unit
Conditions
4.3.1
4.3.2
4.3.3
4.3.4
Thermal Resistance
Junction-Case, Low Side Switch1)
Rthjc(LS) = ΔTj(LS)/ Pv(LS)
Thermal Resistance
Junction-Case, High Side Switch1)
Rthjc(HS) = ΔTj(HS)/ Pv(HS)
Thermal Resistance
Junction-Case, both Switches1)
Rthjc = max[ΔTj(HS), ΔTj(LS)] /
(Pv(HS) + Pv(LS))
Thermal Resistance
Junction-Ambient1)
Min.
RthJC(LS) –
Typ.
1.3
Max.
1.8
K/W –
RthJC(HS) –
0.6
0.9
K/W –
RthJC
–
0.7
1.0
K/W –
RthJA
–
20
–
K/W 2)
1) Not subject to production test, specified by design
2) Specified RthJA value is according to Jedec JESD51-2,-5,-7 at natural convection on FR4 2s2p board; The Product
(chip+package) was simulated on a 76.2 x 114.3 x 1.5 mm board with 2 inner copper layers (2 x 70 µm Cu, 2 x 35 µm Cu).
Data Sheet
8
Rev. 2.0, 2008-06-27
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc