To the Shareholders of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.:
Our gain in net worth during 1986 was $492.5 million, or
26.1%. Over the last 22 years (that is, since present management
took over), our per-share book value has grown from $19.46 to
$2,073.06, or 23.3% compounded annually. Both the numerator and
denominator are important in the per-share book value
calculation: during the 22-year period our corporate net worth
has increased 10,600% while shares outstanding have increased
less than 1%.
In past reports I have noted that book value at most
companies differs widely from intrinsic business value - the
number that really counts for owners. In our own case, however,
book value has served for more than a decade as a reasonable if
somewhat conservative proxy for business value. That is, our
business value has moderately exceeded our book value, with the
ratio between the two remaining fairly steady.
The good news is that in 1986 our percentage gain in
business value probably exceeded the book value gain. I say
"probably" because business value is a soft number: in our own
case, two equally well-informed observers might make judgments
more than 10% apart.
A large measure of our improvement in business value
relative to book value reflects the outstanding performance of
key managers at our major operating businesses. These managers -
the Blumkins, Mike Goldberg, the Heldmans, Chuck Huggins, Stan
Lipsey, and Ralph Schey - have over the years improved the
earnings of their businesses dramatically while, except in the
case of insurance, utilizing little additional capital. This
accomplishment builds economic value, or "Goodwill," that does
not show up in the net worth figure on our balance sheet, nor in
our per-share book value. In 1986 this unrecorded gain was
substantial.
So much for the good news. The bad news is that my
performance did not match that of our managers. While they were
doing a superb job in running our businesses, I was unable to
skillfully deploy much of the capital they generated.
Charlie Munger, our Vice Chairman, and I really have only
two jobs. One is to attract and keep outstanding managers to run
our various operations. This hasn’t been all that difficult.
Usually the managers came with the companies we bought, having
demonstrated their talents throughout careers that spanned a wide
variety of business circumstances. They were managerial stars
long before they knew us, and our main contribution has been to
not get in their way. This approach seems elementary: if my job
were to manage a golf team - and if Jack Nicklaus or Arnold
Palmer were willing to play for me - neither would get a lot of
directives from me about how to swing.
Some of our key managers are independently wealthy (we hope
they all become so), but that poses no threat to their continued
interest: they work because they love what they do and relish the
thrill of outstanding performance. They unfailingly think like
owners (the highest compliment we can pay a manager) and find all
aspects of their business absorbing.
(Our prototype for occupational fervor is the Catholic
tailor who used his small savings of many years to finance a
pilgrimage to the Vatican. When he returned, his parish held a
B
E
R
K
S
H
I
R
E
H
A
T
H
A
W
A
Y
I
N
C
.
�
special meeting to get his first-hand account of the Pope. "Tell
us," said the eager faithful, "just what sort of fellow is he?"
Our hero wasted no words: "He’s a forty-four, medium.")
Charlie and I know that the right players will make almost
any team manager look good. We subscribe to the philosophy of
Ogilvy & Mather’s founding genius, David Ogilvy: "If each of us
hires people who are smaller than we are, we shall become a
company of dwarfs. But, if each of us hires people who are
bigger than we are, we shall become a company of giants."
A by-product of our managerial style is the ability it gives
us to easily expand Berkshire’s activities. We’ve read
management treatises that specify exactly how many people should
report to any one executive, but they make little sense to us.
When you have able managers of high character running businesses
about which they are passionate, you can have a dozen or more
reporting to you and still have time for an afternoon nap.
Conversely, if you have even one person reporting to you who is
deceitful, inept or uninterested, you will find yourself with
more than you can handle. Charlie and I could work with double
the number of managers we now have, so long as they had the rare
qualities of the present ones.
We intend to continue our practice of working only with
people whom we like and admire. This policy not only maximizes
our chances for good results, it also ensures us an
extraordinarily good time. On the other hand, working with
people who cause your stomach to churn seems much like marrying
for money - probably a bad idea under any circumstances, but
absolute madness if you are already rich.
The second job Charlie and I must handle is the allocation
of capital, which at Berkshire is a considerably more important
challenge than at most companies. Three factors make that so: we
earn more money than average; we retain all that we earn; and, we
are fortunate to have operations that, for the most part, require
little incremental capital to remain competitive and to grow.
Obviously, the future results of a business earning 23% annually
and retaining it all are far more affected by today’s capital
allocations than are the results of a business earning 10% and
distributing half of that to shareholders. If our retained
earnings - and those of our major investees, GEICO and Capital
Cities/ABC, Inc. - are employed in an unproductive manner, the
economics of Berkshire will deteriorate very quickly. In a
company adding only, say, 5% to net worth annually, capital-
allocation decisions, though still important, will change the
company’s economics far more slowly.
Capital allocation at Berkshire was tough work in 1986. We
did make one business acquisition - The Fechheimer Bros.
Company, which we will discuss in a later section. Fechheimer is
a company with excellent economics, run by exactly the kind of
people with whom we enjoy being associated. But it is relatively
small, utilizing only about 2% of Berkshire’s net worth.
Meanwhile, we had no new ideas in the marketable equities
field, an area in which once, only a few years ago, we could
readily employ large sums in outstanding businesses at very
reasonable prices. So our main capital allocation moves in 1986
were to pay off debt and stockpile funds. Neither is a fate
worse than death, but they do not inspire us to do handsprings
either. If Charlie and I were to draw blanks for a few years in
our capital-allocation endeavors, Berkshire’s rate of growth
would slow significantly.
We will continue to look for operating businesses that meet
our tests and, with luck, will acquire such a business every
couple of years. But an acquisition will have to be large if it
�
is to help our performance materially. Under current stock
market conditions, we have little hope of finding equities to buy
for our insurance companies. Markets will change significantly -
you can be sure of that and some day we will again get our turn
at bat. However, we haven’t the faintest idea when that might
happen.
It can’t be said too often (although I’m sure you feel I’ve
tried) that, even under favorable conditions, our returns are
certain to drop substantially because of our enlarged size. We
have told you that we hope to average a return of 15% on equity
and we maintain that hope, despite some negative tax law changes
described in a later section of this report. If we are to
achieve this rate of return, our net worth must increase $7.2
billion in the next ten years. A gain of that magnitude will be
possible only if, before too long, we come up with a few very big
(and good) ideas. Charlie and I can’t promise results, but we do
promise you that we will keep our efforts focused on our goals.
Sources of Reported Earnings
The table on the next page shows the major sources of
Berkshire’s reported earnings. This table differs in several
ways from the one presented last year. We have added four new
lines of business because of the Scott Fetzer and Fechheimer
acquisitions. In the case of Scott Fetzer, the two major units
acquired were World Book and Kirby, and each is presented
separately. Fourteen other businesses of Scott Fetzer are
aggregated in Scott Fetzer - Diversified Manufacturing. SF
Financial Group, a credit company holding both World Book and
Kirby receivables, is included in "Other." This year, because
Berkshire is so much larger, we also have eliminated separate
reporting for several of our smaller businesses.
In the table, amortization of Goodwill is not charged
against the specific businesses but, for reasons outlined in the
Appendix to my letter in the 1983 Annual Report, is aggregated as
a separate item. (A Compendium of earlier letters, including the
Goodwill discussion, is available upon request.) Both the Scott
Fetzer and Fechheimer acquisitions created accounting Goodwill,
which is why the amortization charge for Goodwill increased in
1986.
Additionally, the Scott Fetzer acquisition required other
major purchase-price accounting adjustments, as prescribed by
generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The GAAP
figures, of course, are the ones used in our consolidated
financial statements. But, in our view, the GAAP figures are not
necessarily the most useful ones for investors or managers.
Therefore, the figures shown for specific operating units are
earnings before purchase-price adjustments are taken into
account. In effect, these are the earnings that would have been
reported by the businesses if we had not purchased them.
A discussion of our reasons for preferring this form of
presentation is in the Appendix to this letter. This Appendix
will never substitute for a steamy novel and definitely is not
required reading. However, I know that among our 6,000
shareholders there are those who are thrilled by my essays on
accounting - and I hope that both of you enjoy the Appendix.
In the Business Segment Data on pages 41-43 and in the
Management’s Discussion section on pages 45-49, you will find
much additional information about our businesses. I urge you to
read those sections, as well as Charlie Munger’s letter to Wesco
shareholders, describing the various businesses of that
subsidiary, which starts on page 50.
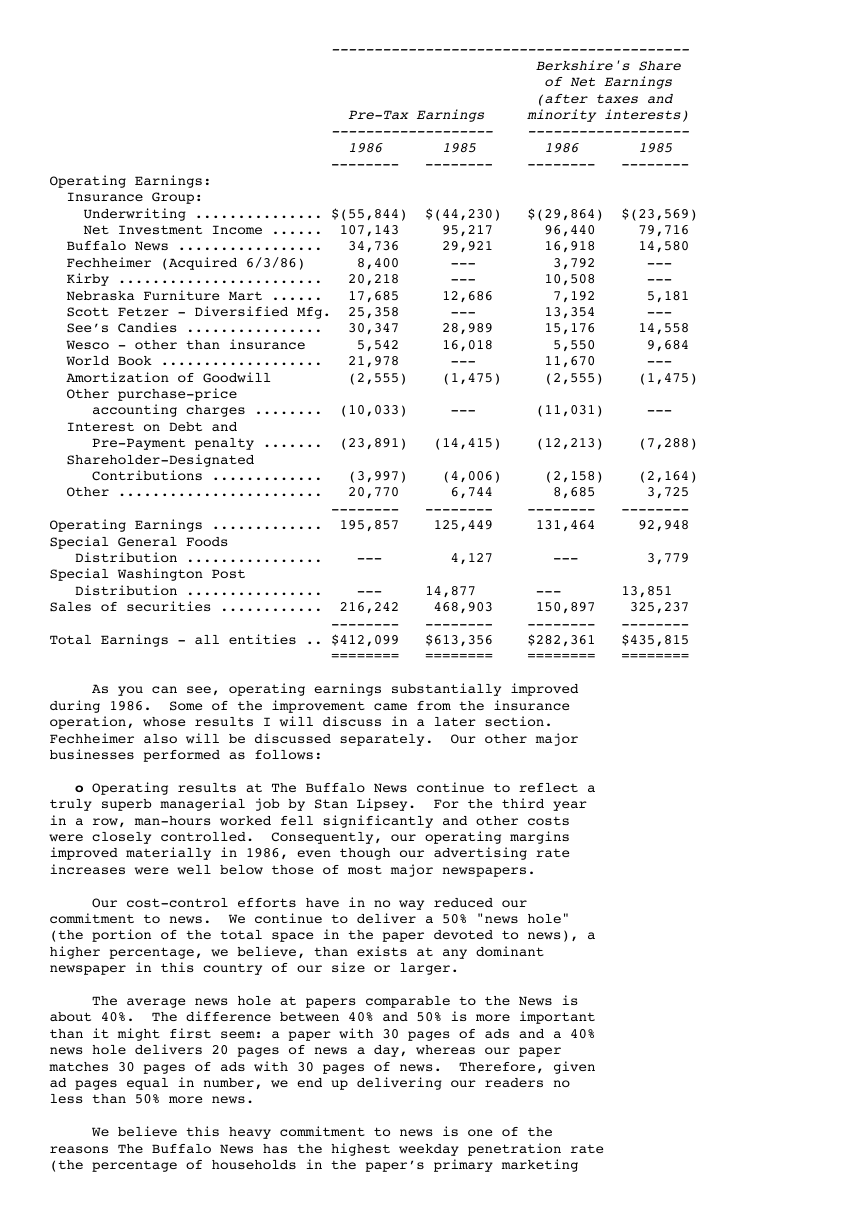
(000s omitted)
�
------------------------------------------
Berkshire's Share
of Net Earnings
(after taxes and
Pre-Tax Earnings minority interests)
------------------- -------------------
1986 1985 1986 1985
-------- -------- -------- --------
Operating Earnings:
Insurance Group:
Underwriting ............... $(55,844) $(44,230) $(29,864) $(23,569)
Net Investment Income ...... 107,143 95,217 96,440 79,716
Buffalo News ................. 34,736 29,921 16,918 14,580
Fechheimer (Acquired 6/3/86) 8,400 --- 3,792 ---
Kirby ........................ 20,218 --- 10,508 ---
Nebraska Furniture Mart ...... 17,685 12,686 7,192 5,181
Scott Fetzer - Diversified Mfg. 25,358 --- 13,354 ---
See’s Candies ................ 30,347 28,989 15,176 14,558
Wesco - other than insurance 5,542 16,018 5,550 9,684
World Book ................... 21,978 --- 11,670 ---
Amortization of Goodwill (2,555) (1,475) (2,555) (1,475)
Other purchase-price
accounting charges ........ (10,033) --- (11,031) ---
Interest on Debt and
Pre-Payment penalty ....... (23,891) (14,415) (12,213) (7,288)
Shareholder-Designated
Contributions ............. (3,997) (4,006) (2,158) (2,164)
Other ........................ 20,770 6,744 8,685 3,725
-------- -------- -------- --------
Operating Earnings ............. 195,857 125,449 131,464 92,948
Special General Foods
Distribution ................ --- 4,127 --- 3,779
Special Washington Post
Distribution ................ --- 14,877 --- 13,851
Sales of securities ............ 216,242 468,903 150,897 325,237
-------- -------- -------- --------
Total Earnings - all entities .. $412,099 $613,356 $282,361 $435,815
======== ======== ======== ========
As you can see, operating earnings substantially improved
during 1986. Some of the improvement came from the insurance
operation, whose results I will discuss in a later section.
Fechheimer also will be discussed separately. Our other major
businesses performed as follows:
o Operating results at The Buffalo News continue to reflect a
truly superb managerial job by Stan Lipsey. For the third year
in a row, man-hours worked fell significantly and other costs
were closely controlled. Consequently, our operating margins
improved materially in 1986, even though our advertising rate
increases were well below those of most major newspapers.
Our cost-control efforts have in no way reduced our
commitment to news. We continue to deliver a 50% "news hole"
(the portion of the total space in the paper devoted to news), a
higher percentage, we believe, than exists at any dominant
newspaper in this country of our size or larger.
The average news hole at papers comparable to the News is
about 40%. The difference between 40% and 50% is more important
than it might first seem: a paper with 30 pages of ads and a 40%
news hole delivers 20 pages of news a day, whereas our paper
matches 30 pages of ads with 30 pages of news. Therefore, given
ad pages equal in number, we end up delivering our readers no
less than 50% more news.
We believe this heavy commitment to news is one of the
reasons The Buffalo News has the highest weekday penetration rate
(the percentage of households in the paper’s primary marketing
�
area purchasing it each day) among any of the top 50 papers in
the country. Our Sunday penetration, where we are also number
one, is even more impressive. Ten years ago, the only Sunday
paper serving Buffalo (the Courier-Express) had circulation of
271,000 and a penetration ratio of about 63%. The Courier-
Express had served the area for many decades and its penetration
ratio - which was similar to those existing in many metropolitan
markets - was thought to be a "natural" one, accurately
reflecting the local citizenry’s appetite for a Sunday product.
Our Sunday paper was started in late 1977. It now has a
penetration ratio of 83% and sells about 100,000 copies more each
Sunday than did the Courier-Express ten years ago - even though
population in our market area has declined during the decade. In
recent history, no other city that has long had a local Sunday
paper has experienced a penetration gain anywhere close to
Buffalo’s.
Despite our exceptional market acceptance, our operating
margins almost certainly have peaked. A major newsprint price
increase took effect at the end of 1986, and our advertising rate
increases in 1987 will again be moderate compared to those of the
industry. However, even if margins should materially shrink, we
would not reduce our news-hole ratio.
As I write this, it has been exactly ten years since we
purchased The News. The financial rewards it has brought us have
far exceeded our expectations and so, too, have the non-financial
rewards. Our respect for the News - high when we bought it - has
grown consistently ever since the purchase, as has our respect
and admiration for Murray Light, the editor who turns out the
product that receives such extraordinary community acceptance.
The efforts of Murray and Stan, which were crucial to the News
during its dark days of financial reversals and litigation, have
not in the least been lessened by prosperity. Charlie and I are
grateful to them.
o The amazing Blumkins continue to perform business miracles
at Nebraska Furniture Mart. Competitors come and go (mostly go),
but Mrs. B. and her progeny roll on. In 1986 net sales increased
10.2% to $132 million. Ten years ago sales were $44 million and,
even then, NFM appeared to be doing just about all of the
business available in the Greater Omaha Area. Given NFM’s
remarkable dominance, Omaha’s slow growth in population and the
modest inflation rates that have applied to the goods NFM sells,
how can this operation continue to rack up such large sales
gains? The only logical explanation is that the marketing
territory of NFM’s one-and-only store continues to widen because
of its ever-growing reputation for rock-bottom everyday prices
and the broadest of selections. In preparation for further
gains, NFM is expanding the capacity of its warehouse, located a
few hundred yards from the store, by about one-third.
Mrs. B, Chairman of Nebraska Furniture Mart, continues at
age 93 to outsell and out-hustle any manager I’ve ever seen.
She’s at the store seven days a week, from opening to close.
Competing with her represents a triumph of courage over judgment.
It’s easy to overlook what I consider to be the critical
lesson of the Mrs. B saga: at 93, Omaha based Board Chairmen have
yet to reach their peak. Please file this fact away to consult
before you mark your ballot at the 2024 annual meeting of
Berkshire.
o At See’s, sales trends improved somewhat from those of
recent years. Total pounds sold rose about 2%. (For you
chocaholics who like to fantasize, one statistic: we sell over
12,000 tons annually.) Same-store sales, measured in pounds, were
virtually unchanged. In the previous six years, same store
�
poundage fell, and we gained or maintained poundage volume only
by adding stores. But a particularly strong Christmas season in
1986 stemmed the decline. By stabilizing same-store volume and
making a major effort to control costs, See’s was able to
maintain its excellent profit margin in 1986 though it put
through only minimal price increases. We have Chuck Huggins, our
long-time manager at See’s, to thank for this significant
achievement.
See’s has a one-of-a-kind product "personality" produced by
a combination of its candy’s delicious taste and moderate price,
the company’s total control of the distribution process, and the
exceptional service provided by store employees. Chuck
rightfully measures his success by the satisfaction of our
customers, and his attitude permeates the organization. Few
major retailing companies have been able to sustain such a
customer-oriented spirit, and we owe Chuck a great deal for
keeping it alive and well at See’s.
See’s profits should stay at about their present level. We
will continue to increase prices very modestly, merely matching
prospective cost increases.
o World Book is the largest of 17 Scott Fetzer operations
that joined Berkshire at the beginning of 1986. Last year I
reported to you enthusiastically about the businesses of Scott
Fetzer and about Ralph Schey, its manager. A year’s experience
has added to my enthusiasm for both. Ralph is a superb
businessman and a straight shooter. He also brings exceptional
versatility and energy to his job: despite the wide array of
businesses that he manages, he is on top of the operations,
opportunities and problems of each. And, like our other
managers, Ralph is a real pleasure to work with. Our good
fortune continues.
World Book’s unit volume increased for the fourth
consecutive year, with encyclopedia sales up 7% over 1985 and 45%
over 1982. Childcraft’s unit sales also grew significantly.
World Book continues to dominate the U.S. direct-sales
encyclopedia market - and for good reasons. Extraordinarily
well-edited and priced at under 5 cents per page, these books are
a bargain for youngster and adult alike. You may find one
editing technique interesting: World Book ranks over 44,000 words
by difficulty. Longer entries in the encyclopedia include only
the most easily comprehended words in the opening sections, with
the difficulty of the material gradually escalating as the
exposition proceeds. As a result, youngsters can easily and
profitably read to the point at which subject matter gets too
difficult, instead of immediately having to deal with a
discussion that mixes up words requiring college-level
comprehension with others of fourth-grade level.
Selling World Book is a calling. Over one-half of our
active salespeople are teachers or former teachers, and another
5% have had experience as librarians. They correctly think of
themselves as educators, and they do a terrific job. If you
don’t have a World Book set in your house, I recommend one.
o Kirby likewise recorded its fourth straight year of unit
volume gains. Worldwide, unit sales grew 4% from 1985 and 33%
from 1982. While the Kirby product is more expensive than most
cleaners, it performs in a manner that leaves cheaper units far
behind ("in the dust," so to speak). Many 30- and 40-year-old
Kirby cleaners are still in active duty. If you want the best,
you buy a Kirby.
Some companies that historically have had great success in
direct sales have stumbled in recent years. Certainly the era of
�
the working woman has created new challenges for direct sales
organizations. So far, the record shows that both Kirby and
World Book have responded most successfully.
The businesses described above, along with the insurance
operation and Fechheimer, constitute our major business units.
The brevity of our descriptions is in no way meant to diminish
the importance of these businesses to us. All have been
discussed in past annual reports and, because of the tendency of
Berkshire owners to stay in the fold (about 98% of the stock at
the end of each year is owned by people who were owners at the
start of the year), we want to avoid undue repetition of basic
facts. You can be sure that we will immediately report to you in
detail if the underlying economics or competitive position of any
of these businesses should materially change. In general, the
businesses described in this section can be characterized as
having very strong market positions, very high returns on capital
employed, and the best of operating managements.
The Fechheimer Bros. Co.
Every year in Berkshire’s annual report I include a
description of the kind of business that we would like to buy.
This "ad" paid off in 1986.
On January 15th of last year I received a letter from Bob
Heldman of Cincinnati, a shareholder for many years and also
Chairman of Fechheimer Bros. Until I read the letter, however, I
did not know of either Bob or Fechheimer. Bob wrote that he ran
a company that met our tests and suggested that we get together,
which we did in Omaha after their results for 1985 were compiled.
He filled me in on a little history: Fechheimer, a uniform
manufacturing and distribution business, began operations in
1842. Warren Heldman, Bob’s father, became involved in the
business in 1941 and his sons, Bob and George (now President),
along with their sons, subsequently joined the company. Under
the Heldmans’ management, the business was highly successful.
In 1981 Fechheimer was sold to a group of venture
capitalists in a leveraged buy out (an LBO), with management
retaining an equity interest. The new company, as is the case
with all LBOS, started with an exceptionally high debt/equity
ratio. After the buy out, however, operations continued to be
very successful. So by the start of last year debt had been paid
down substantially and the value of the equity had increased
dramatically. For a variety of reasons, the venture capitalists
wished to sell and Bob, having dutifully read Berkshire’s annual
reports, thought of us.
Fechheimer is exactly the sort of business we like to buy.
Its economic record is superb; its managers are talented, high-
grade, and love what they do; and the Heldman family wanted to
continue its financial interest in partnership with us.
Therefore, we quickly purchased about 84% of the stock for a
price that was based upon a $55 million valuation for the entire
business.
The circumstances of this acquisition were similar to those
prevailing in our purchase of Nebraska Furniture Mart: most of
the shares were held by people who wished to employ funds
elsewhere; family members who enjoyed running their business
wanted to continue both as owners and managers; several
generations of the family were active in the business, providing
management for as far as the eye can see; and the managing family
wanted a purchaser who would not re-sell, regardless of price,
and who would let the business be run in the future as it had
been in the past. Both Fechheimer and NFM were right for us, and
we were right for them.
�
You may be amused to know that neither Charlie nor I have
been to Cincinnati, headquarters for Fechheimer, to see their
operation. (And, incidentally, it works both ways: Chuck Huggins,
who has been running See’s for 15 years, has never been to
Omaha.) If our success were to depend upon insights we developed
through plant inspections, Berkshire would be in big trouble.
Rather, in considering an acquisition, we attempt to evaluate the
economic characteristics of the business - its competitive
strengths and weaknesses - and the quality of the people we will
be joining. Fechheimer was a standout in both respects. In
addition to Bob and George Heldman, who are in their mid-60s -
spring chickens by our standards - there are three members of the
next generation, Gary, Roger and Fred, to insure continuity.
As a prototype for acquisitions, Fechheimer has only one
drawback: size. We hope our next acquisition is at least several
times as large but a carbon copy in all other respects. Our
threshold for minimum annual after-tax earnings of potential
acquisitions has been moved up to $10 million from the $5 million
level that prevailed when Bob wrote to me.
Flushed with success, we repeat our ad. If you have a
business that fits, call me or, preferably, write.
Here’s what we’re looking for:
(1) large purchases (at least $10 million of after-tax
earnings),
(2) demonstrated consistent earning power (future
projections are of little interest to us, nor are
"turn-around" situations),
(3) businesses earning good returns on equity while
employing little or no debt.
(4) management in place (we can’t supply it),
(5) simple businesses (if there’s lots of technology, we
won’t understand it),
(6) an offering price (we don’t want to waste our time
or that of the seller by talking, even preliminarily,
about a transaction when price is unknown).
We will not engage in unfriendly takeovers. We can promise
complete confidentiality and a very fast answer - customarily
within five minutes - as to whether we’re interested. We prefer
to buy for cash, but will consider issuing stock when we receive
as much in intrinsic business value as we give. Indeed,
following recent advances in the price of Berkshire stock,
transactions involving stock issuance may be quite feasible. We
invite potential sellers to check us out by contacting people
with whom we have done business in the past. For the right
business - and the right people - we can provide a good home.
On the other hand, we frequently get approached about
acquisitions that don’t come close to meeting our tests: new
ventures, turnarounds, auction-like sales, and the ever-popular
(among brokers) "I’m-sure-something-will-work-out-if-you-people-
get-to-know-each-other." None of these attracts us in the least.
* * *
Besides being interested in the purchases of entire
businesses as described above, we are also interested in the
negotiated purchase of large, but not controlling, blocks of
stock, as in our Cap Cities purchase. Such purchases appeal to
us only when we are very comfortable with both the economics of
the business and the ability and integrity of the people running
the operation. We prefer large transactions: in the unusual case
we might do something as small as $50 million (or even smaller),
but our preference is for commitments many times that size.
�