Omni
ision ®
General Description
The OV2640 CAMERACHIPTM is a low voltage CMOS image
sensor that provides the full functionality of a single-chip
UXGA (1632x1232) camera and image processor in a small
footprint package. The OV2640 provides
full-frame,
sub-sampled, scaled or windowed 8-bit/10-bit images in a
wide range of formats, controlled through the Serial Camera
Control Bus (SCCB) interface.
This product has an image array capable of operating at up
to 15 frames per second (fps) in UXGA resolution with
complete user control over image quality, formatting and
output data transfer. All required image processing functions,
including exposure control, gamma, white balance, color
saturation, hue control, white pixel canceling, noise
canceling, and more, are also programmable through the
SCCB interface. The OV2640 also includes a compression
engine
In addition,
OmniVision CAMERACHIPS use proprietary sensor technology
to improve image quality by reducing or eliminating common
lighting/electrical sources of image contamination, such as
fixed pattern noise, smearing, etc., to produce a clean, fully
stable color image.
increased processing power.
for
Pb
Note: The OV2640 uses a lead-free
package.
Features
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
High sensitivity for low-light operation
Low operating voltage for embedded portable apps
Standard SCCB interface
Output support for Raw RGB, RGB (RGB565/555),
GRB422, YUV (422/420) and YCbCr (4:2:2) formats
Supports image sizes: UXGA, SXGA, SVGA, and any
size scaling down from SXGA to 40x30
VarioPixel® method for sub-sampling
Automatic image control functions including Automatic
Exposure Control (AEC), Automatic Gain Control
(AGC), Automatic White Balance (AWB), Automatic
Band Filter (ABF), and Automatic Black-Level
Calibration (ABLC)
Image quality controls including color saturation,
gamma, sharpness (edge enhancement), lens
correction, white pixel canceling, noise canceling, and
50/60 Hz luminance detection
Line optical black level output capability
Video or snapshot operation
Zooming, panning, and windowing functions
Internal/external frame synchronization
Variable frame rate control
Supports LED and flash strobe mode
Supports scaling
Supports compression
Embedded microcontroller
Ordering Information
Product
Package
OV02640-VL9A (Color, lead-free)
38-pin CSP2
Advanced Information
Preliminary Datasheet
OV2640 Color CMOS UXGA (2.0 MegaPixel) CAMERACHIPTM
with OmniPixel2TM Technology
Applications
•
•
•
•
Cellular and Camera Phones
Toys
PC Multimedia
Digital Still Cameras
Key Specifications
Array Size
Power Supply
Power
Requirements
Temperature
Range
UXGA 1600 x 1200
Core 1.2VDC + 5%
Analog 2.5 ~ 3.0VDC
I/O 1.7V to 3.3V
Active
125 mW (for 15 fps, UXGA
YUV mode)
140 mW (for 15 fps, UXGA
compressed mode)
Standby 600 µA
Operation -30°C to 70°C
Stable Image 0°C to 50°C
Output Formats (8-bit)
• YUV(422/420)/YCbCr422
• RGB565/555
• 8-bit compressed data
• 8-/10-bit Raw RGB data
Lens Size 1/4"
Chief Ray Angle 25° non-linear
Maximum
Image
Transfer Rate
UXGA/SXGA 15 fps
SVGA 30 fps
CIF 60 fps
Sensitivity 0.6 V/Lux-sec
S/N Ratio 40 dB
Dynamic Range 50 dB
Scan Mode Progressive
Maximum Exposure Interval 1247 x tROW
Gamma Correction Programmable
Pixel Size 2.2 µm x 2.2 µm
Dark Current 15 mV/s at 60°C
Well Capacity 12 Ke
Fixed Pattern Noise <1% of VPEAK-TO-PEAK
Image Area 3590 µm x 2684 µm
Package Dimensions 5725 µm x 6285 µm
Figure 1 OV2640 Pin Diagram (Top View)
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
DOGND EXPST_B
AGND SGND VREFN STROBE
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
DOVDD FREX
AVDD SVDD SVDD PWDN
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
SIO_D SIO_C
D2
VSYNC
HREF XVCLK VREFH RESETB
OV2640
D6
NC
E1
Y1
F1
E2
Y0
F2
EVDD DVDD
G1
G2
EVDD DGND
E3
E4
PCLK EGND
F3
Y2
G3
Y3
F4
Y4
G4
Y5
E5
Y6
F5
Y8
G5
Y7
E6
DGND
F6
DVDD
G6
Y9
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
1
�
OV2640
Color CMOS UXGA (2.0 MegaPixel) OmniPixel2™ CAMERACHIP™
Omni
ision
Functional Description
Image Sensor Array (1632 x 1232 total image array)
Analog Signal Processor
10-Bit A/D Converters
Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
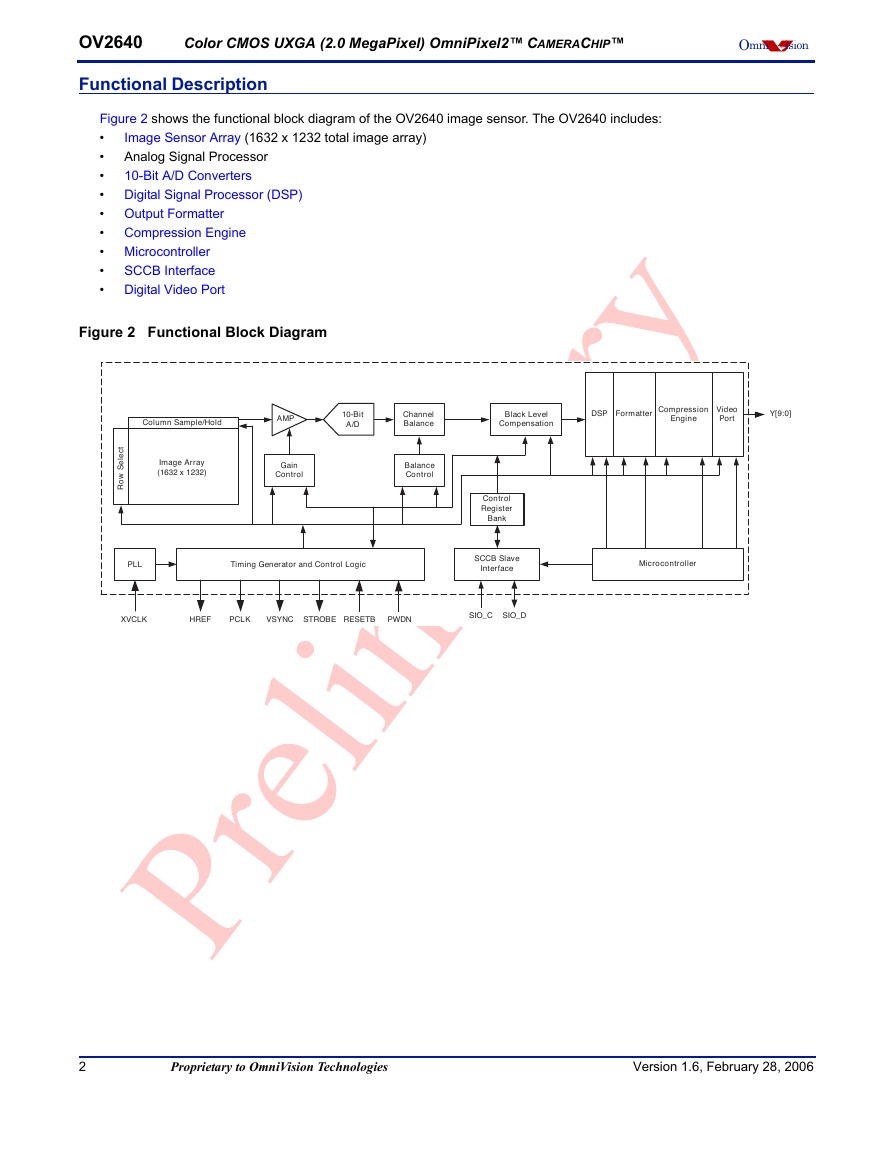
Figure 2 shows the functional block diagram of the OV2640 image sensor. The OV2640 includes:
•
•
•
•
• Output Formatter
•
• Microcontroller
•
SCCB Interface
Digital Video Port
•
Compression Engine
Figure 2 Functional Block Diagram
Column Sample/Hold
AMP
10-Bit
A/D
Channel
Balance
Black Level
Compensation
DSP Formatter
Compression
Engine
Video
Port
Y[9:0]
t
c
e
l
e
S
w
o
R
Image Array
(1632 x 1232)
Gain
Control
Balance
Control
PLL
Timing Generator and Control Logic
Control
Register
Bank
SCCB Slave
Interface
Microcontroller
XVCLK
HREF
PCLK
VSYNC STROBE
RESETB
PWDN
SIO_C SIO_D
2
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
�
Omni
ision
Functional Description
Image Sensor Array
10-Bit A/D Converters
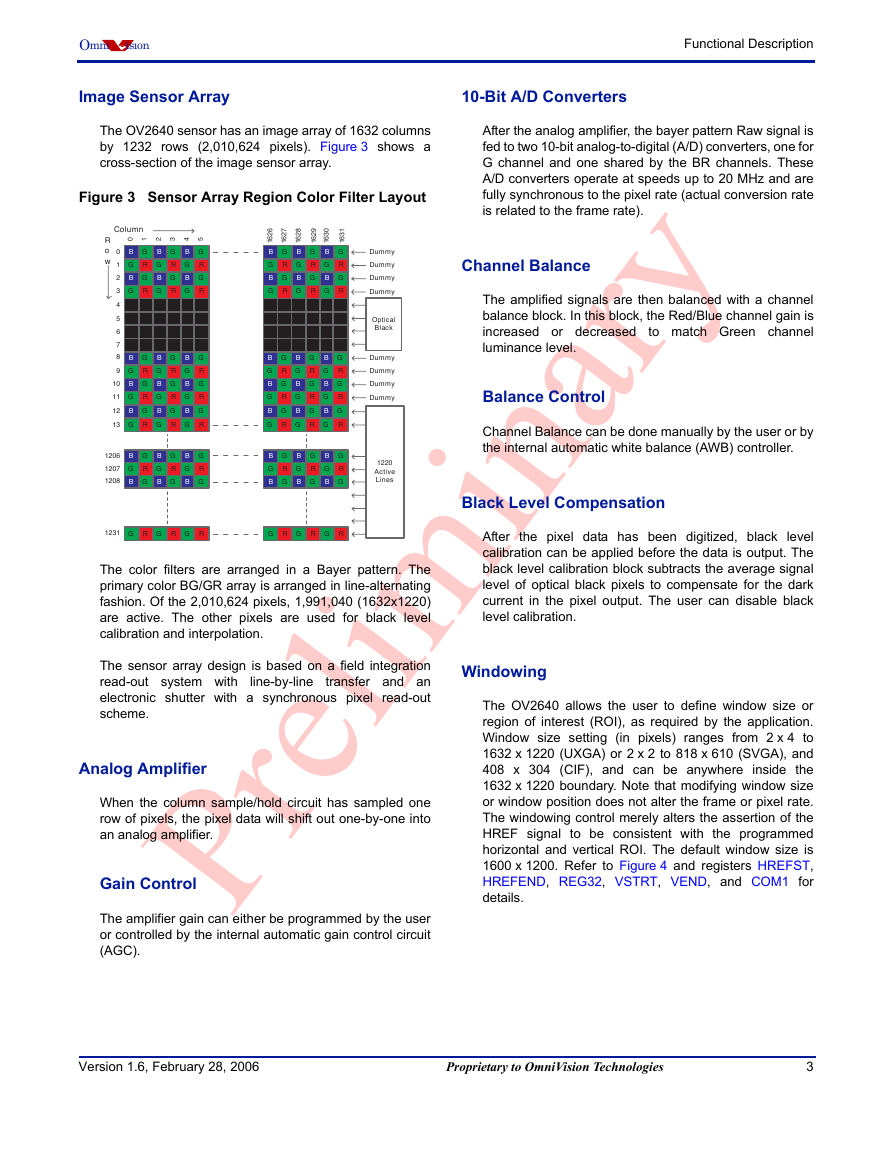
The OV2640 sensor has an image array of 1632 columns
by 1232 rows (2,010,624 pixels). Figure 3 shows a
cross-section of the image sensor array.
Figure 3 Sensor Array Region Color Filter Layout
After the analog amplifier, the bayer pattern Raw signal is
fed to two 10-bit analog-to-digital (A/D) converters, one for
G channel and one shared by the BR channels. These
A/D converters operate at speeds up to 20 MHz and are
fully synchronous to the pixel rate (actual conversion rate
is related to the frame rate).
Column
R
o
w
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
0 1 2 3 4 5
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
13
RG
RG
RG
6
2
6
1
7
2
6
1
8
2
6
1
9
2
6
1
0
3
6
1
1
3
6
1
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
Dummy
Dummy
Dummy
Dummy
Optical
Black
Dummy
Dummy
Dummy
Dummy
1206
1207
1208
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
RG
RG
RG
GB
GB
GB
1220
Active
Lines
1231
RG
RG
RG
RG
RG
RG
The color filters are arranged in a Bayer pattern. The
primary color BG/GR array is arranged in line-alternating
fashion. Of the 2,010,624 pixels, 1,991,040 (1632x1220)
are active. The other pixels are used for black level
calibration and interpolation.
The sensor array design is based on a field integration
read-out system with
transfer and an
electronic shutter with a synchronous pixel read-out
scheme.
line-by-line
Analog Amplifier
When the column sample/hold circuit has sampled one
row of pixels, the pixel data will shift out one-by-one into
an analog amplifier.
Gain Control
The amplifier gain can either be programmed by the user
or controlled by the internal automatic gain control circuit
(AGC).
Channel Balance
The amplified signals are then balanced with a channel
balance block. In this block, the Red/Blue channel gain is
increased or decreased
to match Green channel
luminance level.
Balance Control
Channel Balance can be done manually by the user or by
the internal automatic white balance (AWB) controller.
Black Level Compensation
After the pixel data has been digitized, black level
calibration can be applied before the data is output. The
black level calibration block subtracts the average signal
level of optical black pixels to compensate for the dark
current in the pixel output. The user can disable black
level calibration.
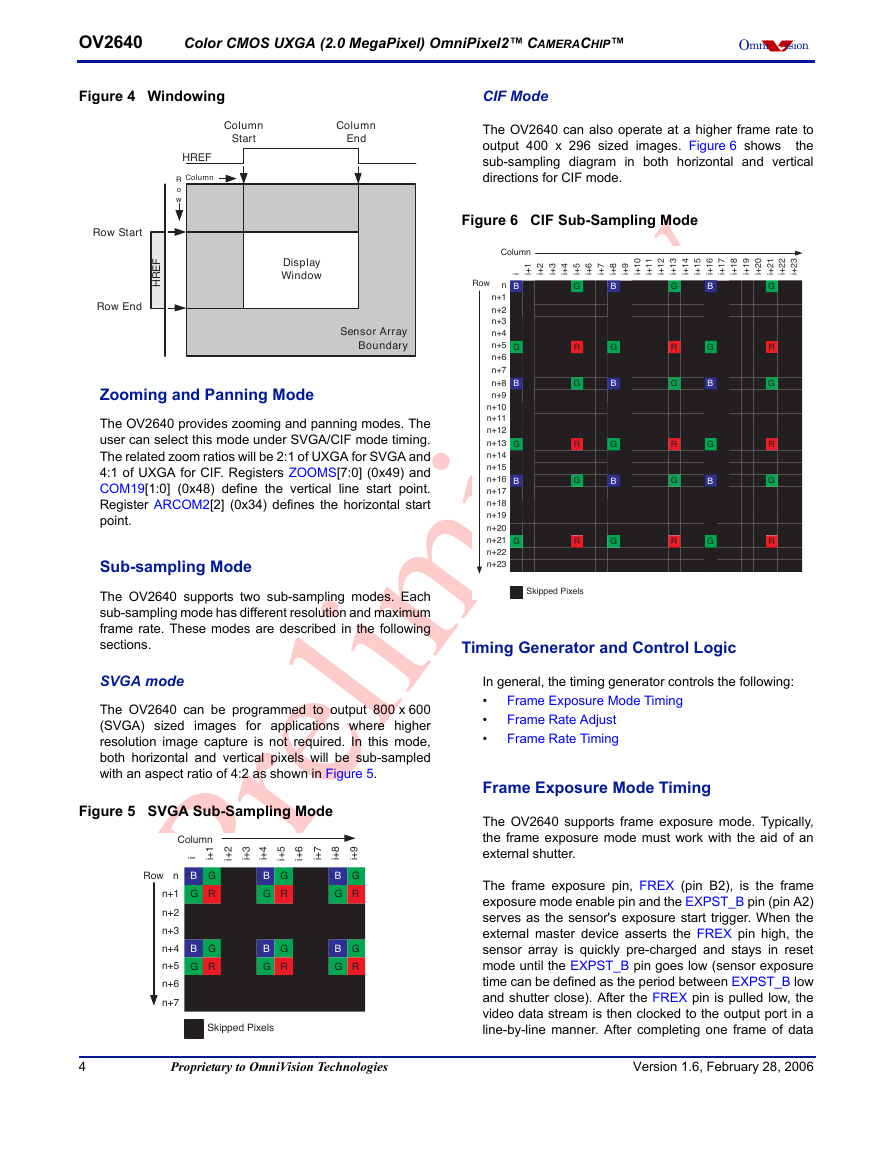
Windowing
The OV2640 allows the user to define window size or
region of interest (ROI), as required by the application.
Window size setting (in pixels) ranges from 2 x 4 to
1632 x 1220 (UXGA) or 2 x 2 to 818 x 610 (SVGA), and
408 x 304 (CIF), and can be anywhere inside the
1632 x 1220 boundary. Note that modifying window size
or window position does not alter the frame or pixel rate.
The windowing control merely alters the assertion of the
HREF signal to be consistent with the programmed
horizontal and vertical ROI. The default window size is
1600 x 1200. Refer to Figure 4 and registers HREFST,
HREFEND, REG32, VSTRT, VEND, and COM1 for
details.
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
3
�
OV2640
Color CMOS UXGA (2.0 MegaPixel) OmniPixel2™ CAMERACHIP™
Omni
ision
Figure 4 Windowing
CIF Mode
Column
Start
Column
End
HREF
Column
R
o
w
Row Start
F
E
R
H
Row End
Display
Window
Sensor Array
Boundary
Zooming and Panning Mode
The OV2640 provides zooming and panning modes. The
user can select this mode under SVGA/CIF mode timing.
The related zoom ratios will be 2:1 of UXGA for SVGA and
4:1 of UXGA for CIF. Registers ZOOMS[7:0] (0x49) and
COM19[1:0] (0x48) define the vertical line start point.
Register ARCOM2[2] (0x34) defines the horizontal start
point.
Sub-sampling Mode
The OV2640 supports two sub-sampling modes. Each
sub-sampling mode has different resolution and maximum
frame rate. These modes are described in the following
sections.
SVGA mode
The OV2640 can be programmed to output 800 x 600
(SVGA) sized images for applications where higher
resolution image capture is not required. In this mode,
both horizontal and vertical pixels will be sub-sampled
with an aspect ratio of 4:2 as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 SVGA Sub-Sampling Mode
Column
1
+
i i
2
+
i
3
+
i
4
+
i
5
+
i
6
+
i
7
+
i
8
+
i
9
+
i
B
G
G
R
B
G
G
R
Row
n
n+1
n+2
n+3
n+4
n+5
n+6
n+7
B
G
G
R
B
G
G
R
B
G
G
R
B
G
G
R
Skipped Pixels
The OV2640 can also operate at a higher frame rate to
output 400 x 296 sized images. Figure 6 shows the
sub-sampling diagram in both horizontal and vertical
directions for CIF mode.
Figure 6 CIF Sub-Sampling Mode
Column
1
+
i
2
+
i
3
+
i
4
+
i
5
+
i
6
+
i
7
+
i
8
+
i
9
+
i
0
1
+
i
1
1
+
i
2
1
+
i
3
1
+
i
4
1
+
i
5
1
+
i
6
1
+
i
7
1
+
i
8
1
+
i
9
1
+
i
0
2
+
i
1
2
+
i
2
2
+
i
3
2
+
i
G
B
G
B
R
G
R
G
G
B
G
B
R
G
R
G
G
B
G
B
R
G
R
G
G
R
G
R
G
R
i
B
G
B
G
B
G
Row
n
n+1
n+2
n+3
n+4
n+5
n+6
n+7
n+8
n+9
n+10
n+11
n+12
n+13
n+14
n+15
n+16
n+17
n+18
n+19
n+20
n+21
n+22
n+23
Skipped Pixels
Timing Generator and Control Logic
In general, the timing generator controls the following:
•
•
•
Frame Exposure Mode Timing
Frame Rate Adjust
Frame Rate Timing
Frame Exposure Mode Timing
The OV2640 supports frame exposure mode. Typically,
the frame exposure mode must work with the aid of an
external shutter.
The frame exposure pin, FREX (pin B2), is the frame
exposure mode enable pin and the EXPST_B pin (pin A2)
serves as the sensor's exposure start trigger. When the
external master device asserts the FREX pin high, the
sensor array is quickly pre-charged and stays in reset
mode until the EXPST_B pin goes low (sensor exposure
time can be defined as the period between EXPST_B low
and shutter close). After the FREX pin is pulled low, the
video data stream is then clocked to the output port in a
line-by-line manner. After completing one frame of data
4
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
�
Omni
ision
Functional Description
output, the OV2640 will output continuous live video data
unless in single frame transfer mode. Figure 18 and
Figure 19 show the detailed timing and Table 11 shows
the timing specifications for this mode.
Frame Rate Adjust
The OV2640 offers three methods for frame rate
adjustment:
•
Clock prescaler: (see “CLKRC” on page 23)
By changing the system clock divide ratio and PLL,
the frame rate and pixel rate will change together.
This method can be used for dividing the frame/pixel
rate by: 1/2, 1/3, 1/4 … 1/64 of the input clock rate.
Line adjustment: (see “REG2A” on page 26 and
“FRARL” on page 26)
By adding a dummy pixel timing in each line
(between HSYNC and pixel data out), the frame rate
can be changed while leaving the pixel rate as is.
Vertical sync adjustment:
By adding dummy line periods to the vertical sync
period (see “ADDVSL” on page 26 and “ADDVSH”
on page 26 or see “FLL” on page 27 and “FLH” on
page 27), the frame rate can be altered while the
pixel rate remains the same.
•
•
Frame Rate Timing
Default frame timing is illustrated in Figure 15, Figure 16,
and Figure 17. Refer to Table 1 for the actual pixel rate at
different frame rates.
Table 1
Frame/Pixel Rates in UXGA Mode
Frame Rate (fps)
PCLK (MHz)
15
36
7.5
18
2.5
6
1.25
3
Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
•
This block controls the interpolation from Raw data to
RGB and some image quality control.
•
Edge enhancement (a two-dimensional high pass
filter)
Color space converter (can change Raw data to RGB
or YUV/YCbCr)
RGB matrix to eliminate color cross talk
Hue and saturation control
Programmable gamma control
Transfer 10-bit data to 8-bit
•
•
•
•
• White pixel canceling
•
De-noise
Output Formatter
This block controls all output and data formatting required
prior to sending the image out.
Scaling Image Output
The OV2640 is capable of scaling down the image size
from CIF to 40x30. By using SCCB registers, the user can
output the desired image size. At certain image sizes,
HREF is not consistent in a frame.
Compression Engine
As shown in Figure 7, the Compression Engine consists
of three major blocks:
•
• QZ
•
Entropy Encoder
DCT
Figure 7 Compression Engine Block Diagram
Compression Engine
Video Data
DCT
QZ
Entropy Encoder
Compressed
Stream
Scale Factor
Q-Table
H-Table
Marker
Microcontroller
The OV2640 embeds an 8-bit microcontroller with
512-byte data memory and 4 KB program memory. It
provides the flexibility of decoding protocol commands
from the host for controlling the system, as well as the
ability to fine tune image quality.
SCCB Interface
The Serial Camera Control Bus (SCCB) interface controls
the CAMERACHIP operation. Refer
to OmniVision
Technologies Serial Camera Control Bus
(SCCB)
Specification for detailed usage of the serial control port.
Slave Operation Mode
The OV2640 can be programmed to operate in slave
mode (default is master mode).
When used as a slave device, COM7[3] (0x12), CLKRC[6]
(0x11), and COM2[2] (0x09) register bits should be set to
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
5
�
OV2640
Color CMOS UXGA (2.0 MegaPixel) OmniPixel2™ CAMERACHIP™
Omni
ision
"1" and the OV2640 will use PWDN and RESETB pins as
vertical and horizontal synchronization triggers supplied
by a master device. The master device must provide the
following signals:
1.
2.
3.
System clock MCLK to XVCLK pin
Horizontal sync MHSYNC to RESETB pin
Vertical frame sync MVSYNC to PWDN pin
See Figure 8 for slave mode connections and Figure 9 for
detailed timing considerations.
Figure 8 Slave Mode Connection
Y[9:0]
RESETB
PWDN
XVCLK
OV2640
MHSYNC
MVSYNC
MCLK
Master
Device
Figure 9 Slave Mode Timing
MVSYNC
MHSYNC
Tframe
TVS
Tline
THS
Tclk
MCLK
NOTE:
1) THS > 6 Tclk, Tvs > Tline
2) Tline = 1922 x Tclk (UXGA); Tline = 1190 x Tclk (SVGA);
Tline = 595 x Tclk (CIF)
3) Tframe = 1248 x Tline (UXGA); Tframe = 672 x Tline (SVGA);
Tframe = 336 x Tline (CIF)
Strobe Mode
The OV2640 has a Strobe mode that allows it to work with
an external flash and LED.
Reset
The OV2640 includes a RESETB pin (pin C6) that forces
a complete hardware reset when it is pulled low (GND).
The OV2640 clears all registers and resets them to their
default values when a hardware reset occurs. A reset can
also be initiated through the SCCB interface.
Power Down Mode
Two methods are available to place the OV2640 into
power-down mode: hardware power-down and SCCB
software power-down.
To initiate hardware power-down, the PWDN pin (pin B6)
must be tied to high. When this occurs, the OV2640
internal device clock is halted and all internal counters are
reset. The current draw is less than 15 µA in this standby
mode.
Executing a software power-down through the SCCB
interface suspends internal circuit activity but does not
halt the device clock. The current requirements drop to
less than 1 mA in this mode. All register content is
maintained in standby mode.
Digital Video Port
MSB/LSB Swap
The OV2640 has a 10-bit digital video port. The MSB and
LSB can be swapped with the control registers. Figure 10
shows some examples of connections with external
devices.
Figure 10 Connection Examples
MSB Y9
Y8
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
LSB Y0
OV2640
Y9
Y8
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
Y0
External
Device
LSB Y9
Y8
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
MSB Y0
OV2640
Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
Y9
External
Device
Default 10-bit Connection
Swap 10-bit Connection
MSB Y9
Y8
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
Y0
LSB Y9
Y8
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
LSB Y0
OV2640
MSB Y0
OV2640
External
Device
Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
External
Device
Default 8-bit Connection
Swap 8-bit Connection
6
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
�
Omni
ision
Functional Description
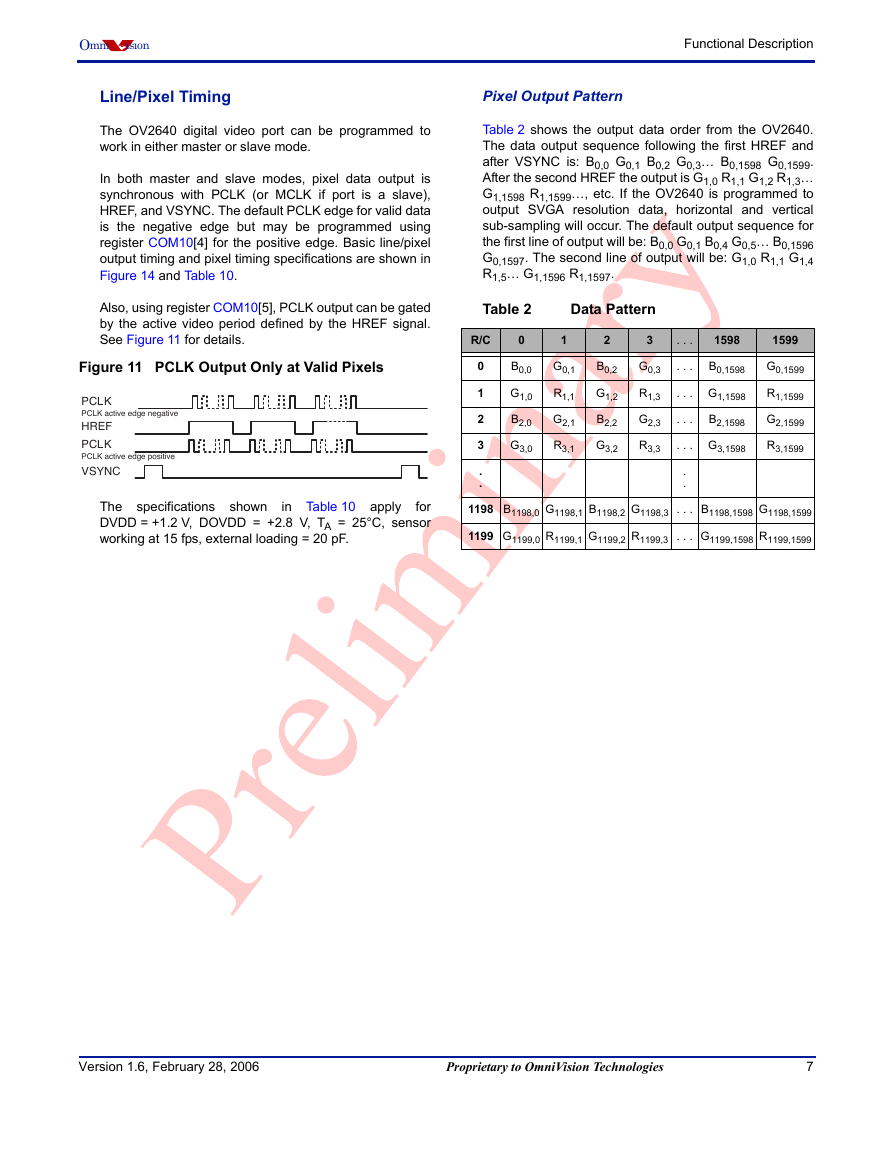
Line/Pixel Timing
Pixel Output Pattern
The OV2640 digital video port can be programmed to
work in either master or slave mode.
In both master and slave modes, pixel data output is
synchronous with PCLK (or MCLK if port is a slave),
HREF, and VSYNC. The default PCLK edge for valid data
is the negative edge but may be programmed using
register COM10[4] for the positive edge. Basic line/pixel
output timing and pixel timing specifications are shown in
Figure 14 and Table 10.
Also, using register COM10[5], PCLK output can be gated
by the active video period defined by the HREF signal.
See Figure 11 for details.
Figure 11 PCLK Output Only at Valid Pixels
PCLK
PCLK active edge negative
HREF
PCLK
PCLK active edge positive
VSYNC
Table 2 shows the output data order from the OV2640.
The data output sequence following the first HREF and
after VSYNC is: B0,0 G0,1 B0,2 G0,3… B0,1598 G0,1599.
After the second HREF the output is G1,0 R1,1 G1,2 R1,3…
G1,1598 R1,1599…, etc. If the OV2640 is programmed to
output SVGA resolution data, horizontal and vertical
sub-sampling will occur. The default output sequence for
the first line of output will be: B0,0 G0,1 B0,4 G0,5… B0,1596
G0,1597. The second line of output will be: G1,0 R1,1 G1,4
R1,5… G1,1596 R1,1597.
Table 2
Data Pattern
1
G0,1
R1,1
G2,1
R3,1
2
B0,2
G1,2
B2,2
G3,2
R/C
0
B0,0
G1,0
B2,0
G3,0
0
1
2
3
.
.
3
. . .
1598
1599
G0,3
R1,3
G2,3
R3,3
. . .
B0,1598
. . . G1,1598
B2,1598
. . .
. . . G3,1598
.
.
G0,1599
R1,1599
G2,1599
R3,1599
The specifications shown
for
DVDD = +1.2 V, DOVDD = +2.8 V, TA = 25°C, sensor
working at 15 fps, external loading = 20 pF.
in Table 10 apply
1198 B1198,0 G1198,1 B1198,2 G1198,3 . . . B1198,1598 G1198,1599
1199 G1199,0 R1199,1 G1199,2 R1199,3 . . . G1199,1598 R1199,1599
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
7
�
OV2640
Color CMOS UXGA (2.0 MegaPixel) OmniPixel2™ CAMERACHIP™
Omni
ision
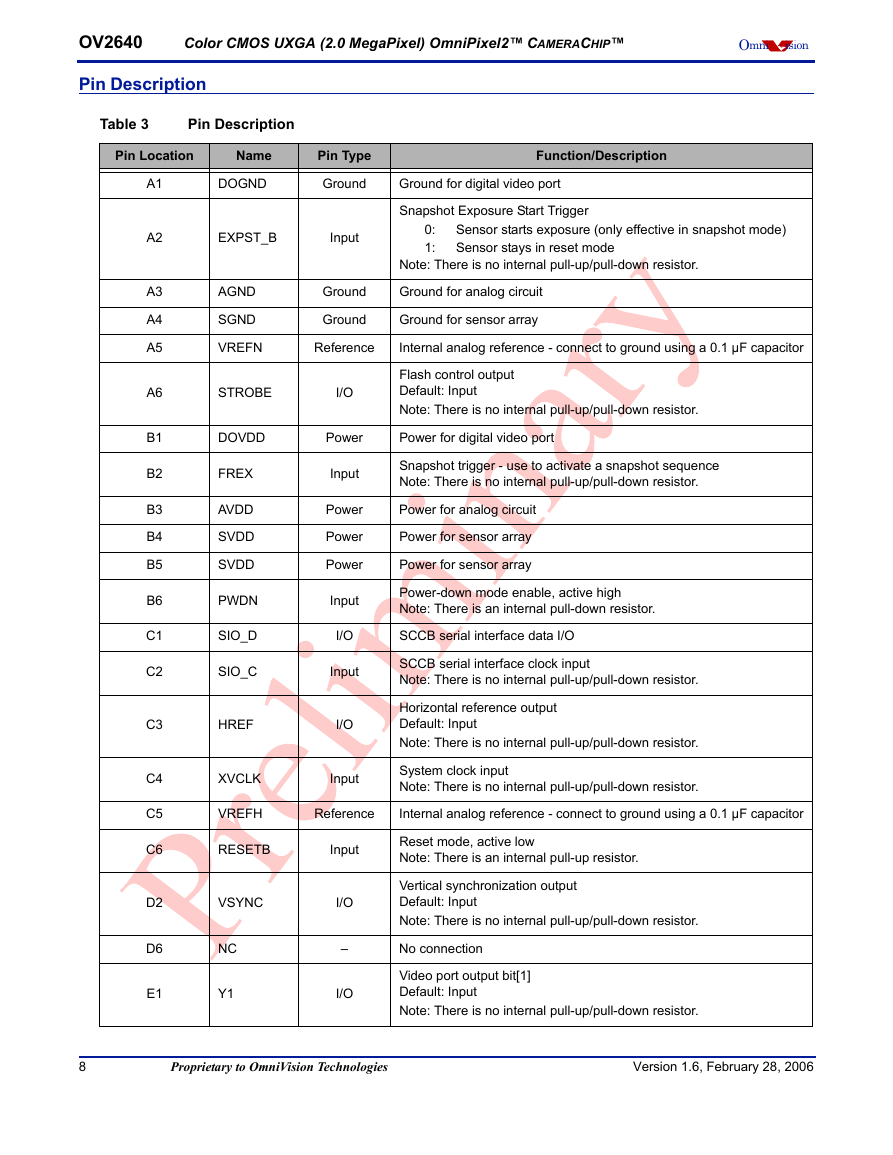
Pin Description
Table 3
Pin Description
Pin Location
Name
Pin Type
Function/Description
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
D2
D6
E1
DOGND
Ground
Ground for digital video port
Snapshot Exposure Start Trigger
EXPST_B
Input
0:
1:
Sensor starts exposure (only effective in snapshot mode)
Sensor stays in reset mode
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
AGND
SGND
VREFN
Ground
Ground
Ground for analog circuit
Ground for sensor array
Reference
Internal analog reference - connect to ground using a 0.1 µF capacitor
STROBE
I/O
Flash control output
Default: Input
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
DOVDD
Power
Power for digital video port
FREX
AVDD
SVDD
SVDD
PWDN
SIO_D
SIO_C
HREF
XVCLK
VREFH
Input
Power
Power
Power
Input
I/O
Input
I/O
Input
Snapshot trigger - use to activate a snapshot sequence
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
Power for analog circuit
Power for sensor array
Power for sensor array
Power-down mode enable, active high
Note: There is an internal pull-down resistor.
SCCB serial interface data I/O
SCCB serial interface clock input
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
Horizontal reference output
Default: Input
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
System clock input
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
Reference
Internal analog reference - connect to ground using a 0.1 µF capacitor
RESETB
Input
Reset mode, active low
Note: There is an internal pull-up resistor.
VSYNC
NC
Y1
I/O
–
I/O
Vertical synchronization output
Default: Input
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
No connection
Video port output bit[1]
Default: Input
Note: There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor.
8
Proprietary to OmniVision Technologies
Version 1.6, February 28, 2006
�